HYBRID MULTI-OBJECTIVE GRADIENT ALGORITHM FOR INVERSE PLANNING OF IMRT
2010-10-08LiGuoliShengDaningWangJunliangJingJiaWangChaoYanBing
Li Guoli,Sheng Daning,Wang Junliang,Jing Jia,Wang Chao,Yan Bing
(1.College of Information Engineering,Zhejiang University of Technology,Hangzhou,310034,P.R.China;2.School of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei,230009,P.R.China;3.School of Communication and Information Engineering,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu,611731,P.R.China)
INTRODUCTION
The optimization technology has made substantial progress with the rapid development of the computer.In addition to the traditional gradient method, the conjugate gradient(CG)method,and the Newton-method,etc.,a number of novel optimization algorithms,such as chaos, neural networks, genetic algorithms(GAs),simulated annealing,ant colony algorithm,are all proven to be good simulations of nature since the 1980′s.They provide a pathway for new ideas and directions to solve complex problems.
Most engineering and scientific problems are multi-objective optimization problems, which contain several conflicting objectives.How to obtain the optimal solution to these problems is always the research focus.In most cases,the performance improvement can cause the reduction of other targets.It is impossible to makeall of them achieve the best possible result.It is only possible to optimize the various trade-offs so as to make all the objective functions optimal.The optimal solution of theproblemis madeup of a large number,even infinite Pareto optimal solution.
Radiation therapy continues to explore ways to handle dose relationships between the tumor tissue and the surrounding normal tissue(NT).The goal is to maximize local control and irradiate only the tumor while minimizing radiation injury to the surrounding NT and critical organs[1-2].Therefore,the radiation therapy inverse planning process is actually a multi-objective optimization problem.
The early radiation treatment planning system often uses the gradient method CG[3]to inverse plans,and does not consider the multi-ob-jective characteristics of planning target volume(PTV),organ at risk(OAR)and NT.
In recent years,radiation therapy planning systems often use the algorithm,such as GA[4]and other multi-objective evolutionary algorithms.The randomness of the algorithms makes calculations more time-consuming. To address the multi-objective characteristics of radiotherapy inverse planning and time-consuming calculation,based on the prophase work of intensity modulated radiation treatment(IMRT)inverse planning of our group,a multi-objectivehybrid gradient algorithm is proposed in this paper to provide a high speed algorithm for the inverse planning of IMRT.
1 ALGORITHM
The algorithm uses the compatibility of GA and other heuristic algorithms[5].It combines the gradient algorithm with GA,by using the population characteristics of evolutionary algorithms and the search direction characteristic of the gradient algorithm.Each generation of the algorithm uses the gradient algorithm to obtain new populations for the next generation rather than the random search.At the same time,sinceit uses real numbers,the algorithm does not need to convert values between different descriptions,saving the computational time required for converting realform solutions to coding and vice versa.
The flow chart of the algorithm is shown in Fig.1.
2 TEST FUNCTIONS
Refs.[6-7]proposed the multi-objective optimization test functions with an expression in the form of


Fig.1 Flow chart of algorithm
In all the algorithms using test functions,the result in Ref.[8]is the latest one.Fig.2 shows the Pareto frontier distribution of themulti-objective hybrid gradient algorithm.Table 1 shows the convergence time of the algorithm (P4/2.66 GHz/DDR 512 MB).Results show that the algorithm can obtain good Pareto frontier distribution with less time-consuming calculation than the prophase work in Ref.[8].

Table 1 Convergence time of algorithm
3 EXAMPLE OFINVERSE PLANNING FOR IMRT

Fig.2 Distributions of Pareto frontier
The simulation involves anirregular field under the water phantom of 30× 30× 30[8].A slice of the irregular field is shown in Fig.3.The shadowed part is PTV,and the other is NT hypothetically. The average prescription percentage dose of PTV and NT are:DPTVref=89 and DNTref=1.26.
Objectivefunctions arebased on thedose distribution[9]as follows

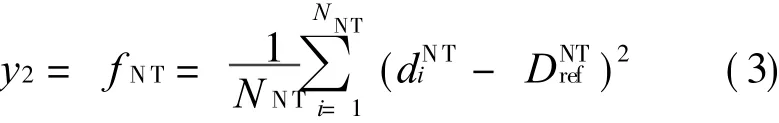
where dPiTVand dNiPTVare thecalculated dosevalues for PTV and NT,respectively;N PTV and N NT the corresponding numbers of sampling points.
The dose calculation method among inverse planning is an improved finite-size Pencil beam(fsPB)model,which comes from the prophase work of our group[10].
The fitness functions are as follows
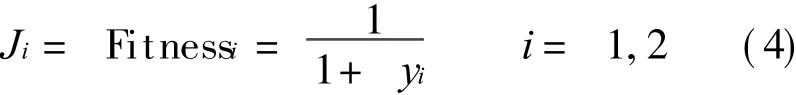
The sample points are in the middle of every sub-field.In Fig.3,NPTV=9,NNT=27.The inverse planning result is shown in Table 2.

Fig.3 Simulation case

Table 2 Results of hybrid multi-objective gradient algor ithm
There are 37 non-dominance solutions in the Pareto frontier.One of them is shown in Fig.4.
The optimization result is compared with the prophase work of authors.For the same inverse planning example,the result of the hybrid multiobjective optimization algorithm based on the simulated annealing genetic algorithm(SAGA)is shown in Table 3,where randomseed and t0 are parameters,which must bedetermined before calculation.

Fig.4 Optimization results

Table 3 Results of SAGA
There are 96 non-dominance solutions in the Plato frontier.And one of them is shown in Fig.5.

Fig.5 Bar graph of SAGA results
The average dose calculation results of Figs.4,5 show that they both meet the requirements of the prescription percentage dose for PTV and NT.Compared with the hybrid multiobjective SA algorithm,the hybrid multi-objective gradient algorithm costs less computational time for the water phantom simulation case.Therefore,the preferred solution can meet the needs of practical applications.
4 CONCLUSION
The optimization algorithm is one of the key aspects in theinverse planning system of the radiation therapy,where the efficiency and thecalculation speed directly impact the quality of planning and the ultimate efficacy of radiation therapy.The simulation results under the water phantom show that the gradient-based algorithm for multi-objective optimization has the advantages of traditional algorithms and overcomes their shortcomings.A multiplier effect can be achieved by using the proposed algorithm.
[1] Li Guoli.Study on hybrid multi-objective optimization algorithm for inverse treatment planning of radiation therapy[J].Nuclear Techniques,2007,30(3):222-226.(in Chinese)
[2] Tang Mutao,Chen Chaomin,Zhou Linghong,et al.A preliminary study of beam weight optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy with genetic a lgorithm[J].Journal of First Military Medical U-niversity,2006,26(4):456-458.(in Chinese)
[3] Chen Baolin.Optimization theory and algorithms[M].Second Edition.Beijing: Tsinghua University Press,2005.(in Chinese)
[4] Holland JH.A dap tat ion in natural and artificial systems[M].New York:The University of Michigan Press,1975.
[5] Xing Wenxun,Xie Jinxing.Modern optimization method [M].Second Edition.Beijing: Tsinghua University Press,2005.(in Chinese)
[6] Zitzler E,Deb K,Thiele L.Comparison of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: empirical results[J].IEEE Trans Evol Computer,2000,8(2):173-195.
[7] Lohn J,Kraus W,Haith G.Comparing a coevolutionary genetic algorithm for multiobjectiveoptimization[C]//Proc 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation(CEC'02).Hawaii,USA: [s.n.],2002:1157-1162.
[8] Li Guoli,Wang Shifang,Wu Yican,et al.Study on hybrid multi-objective optimization algorithm of greedy genetic algorithm [J].Computer Science,2006,33(10):10-11.(in Chinese)
[9] Li Guoli,Wu Yican,Song Gang.Effect of objective function on multi-objective inverse planning of radiation therapy[J].Nuclear Physics Review,2006,23(2):233-236.
[10]Yang Zhu. Research on filtering techniques for Monte Carlo simulation and inhomogeneity correction algorithm for matrix model FSPB[D].Anhui:Hefei University of Technology,2009.(in Chinese)
杂志排行
Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics的其它文章
- FITTING CORRECTION METHOD OF RING ARTIFACTS FOR RECONSTRUCTING CONE-BEAM CT IMAGES
- IMAGING CHARACTERISTICSOF RAT MODELSOF PARKINSON DISEASE
- MOTOR CORTEX NETWORKSIN STROKE PATIENTS DURING RECOVERY WITH f MRI
- FLUORESCENCE SPECTRUM ANALYSISOF ETHER-WATER SOLUTION BASED ON GAUSSIAN DECOMPOSITION METHOD
- EFFECTIVE DETECTION DEPTH OF NEEDLE-LIKE OPTICAL PROBE
- PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF WATERSOLUBLE NEAR-INFRARED EMITTING PbSQUANTUM DOTS
