Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Ti-MWW/TS-1 Composite Zeolites
2010-09-05WANGLinglingDepartmentofEnvironmentalEngineeringShanghaiSecondPolytechnicUniversityShanghai201209
WANG Ling-ling(Department of Environmental Engineering, Shanghai Second Polytechnic University, Shanghai 201209, P.R.C)
Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Ti-MWW/TS-1 Composite Zeolites
WANG Ling-ling
(Department of Environmental Engineering, Shanghai Second Polytechnic University, Shanghai 201209, P.R.C)
The post-synthesis treatment of Ti-MWW having the three-dimensional (3D) MWW structure with TPAOH solutions has been transferred MWW phase into Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites. The composite zeolites obtained readily at 443 K at a TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio range of 0.03~0.04 within 16 h~24 h. The structure and morphology of obtained composite zeolites were characterized by XRD, UV and SEM. The structural change did not alter the coordination states of the Ti active sites. The crystals of the composite zeolite were formed with rectangular particles of 3~5 µm with the surface covered by a large amount of thin platelets. This kind of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolite exhibited superior catalytic activity to both TS-1 and Ti-MWW in the epoxidation of alkenes with H2O2oxidant.
Ti-MWW; TS-1; composite zeolite; epoxidation
0 Introduction
Composite zeolites, especially micro/microporous composites[1-8]and micro/mesoporous composites[9-12], have been paid much more attention due to their synergistic performances in catalytic reactions. Among them ZSM-5/ZSM-11 composite zeolite is a good example for industrial application, which exhibits high activity, good selectivity and excellent resistance to impurity for alkylation reaction of benzene with the dilute ethylene in FCC off-gas[1,13,14]. Composite zeolites with binary structure not only combine the advantages of the two distinct kinds of molecular sieve, but also induce the formation of special properties which can improve its catalytic performance. Thus exploration of new composite zeolite systems attracts more and more interest in scientific and industrial field.
It is well known that crystalline titanosilicates are highly active and selective catalysts for the production of oxygenated derivatives through the oxidation of hydrocarbons and alcohols, and the ammoximation of ketones with H2O2as an oxidant, in which water is the sole byproduct[15-18]. The representative titanosilicate is TS-1 with the MFI structure first reported two decades ago[15]. Up to date, only Ti-MWW with the MWW topology seems to be intrinsically more active than TS-1[19-21]. To the best of our knowledge, Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites have never been reported. Considered the unique catalytic activity of composite zeolites in this work, the exploration of synthesis conditions for Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites is focused, the characterizations and its catalytic properties in the oxidation of alkenes have been investigated to show its potential application as a green heterogeneous catalyst.
1 Experimental
1.1 Preparation of Materials
Ti-MWW was hydrothermally synthesized in the presence of boric acid using piperidine (PI) as a structure-directing agent (SDA). Following the procedures reported previously[20], the gels with the molar compositions of 1.0 SiO2: 0.05 TiO2:1.4 PI : 0.67 B2O3:19 H2O were crystallized under rotation (100 rat/min ) at 443 K for 7 days. The lamellar precursors were then refluxed with 2 M HNO3solution and further calcined at 823 K toobtain Ti-MWW which had the 3D MWW structure.
Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites were synthesized using 3D Ti-MWW as silicate source, the gels with the molar compositions of 1.0 3D Ti-MWW: (0.002~0.5) tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH): 19 H2O were crystallized under rotation (100 rpm) at 443 K for 2 hours~24 hours. The resultant solid was washed with deionized water, gathered by filtration and subsequently dried at 373 K overnight. The organic species occluded were burned off in air at 803 K for 6 h, which led to Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites.
1.2. Characterization
The samples were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns measured on Bruker D8 ADVANCE diffractometer using Cu-Kα radiation. UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu UV-2400PC spectrophotometer using BaSO4as a reference. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed on a Hitachi-4800 microscope after suspending the sample in ethanol.
1.3. Catalytic Reactions
The epoxidation of 1-hexene with H2O2was also carried out bathwise. The mixture containing Ti-MWW catalyst or Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites, 10 mL MeCN, 10 mmol alkene, 10 mmol H2O2was stirred vigorously at 333 K for 2 h. After the catalysts powder was removed, the products for all reactions were analyzed on a gas chromatograph (Shimadzu 14B, FID detector) equipped with a 30 m DB-WAX or DB-1 capillary column. The amount of unconverted H2O2was quantified by standard titration method with a 0.1 M Ce(SO4)2solution. The products formed were determined using authentic chemicals on a GC-MS (Agilent 6890 series GC system, 5937 network mass selective detector).
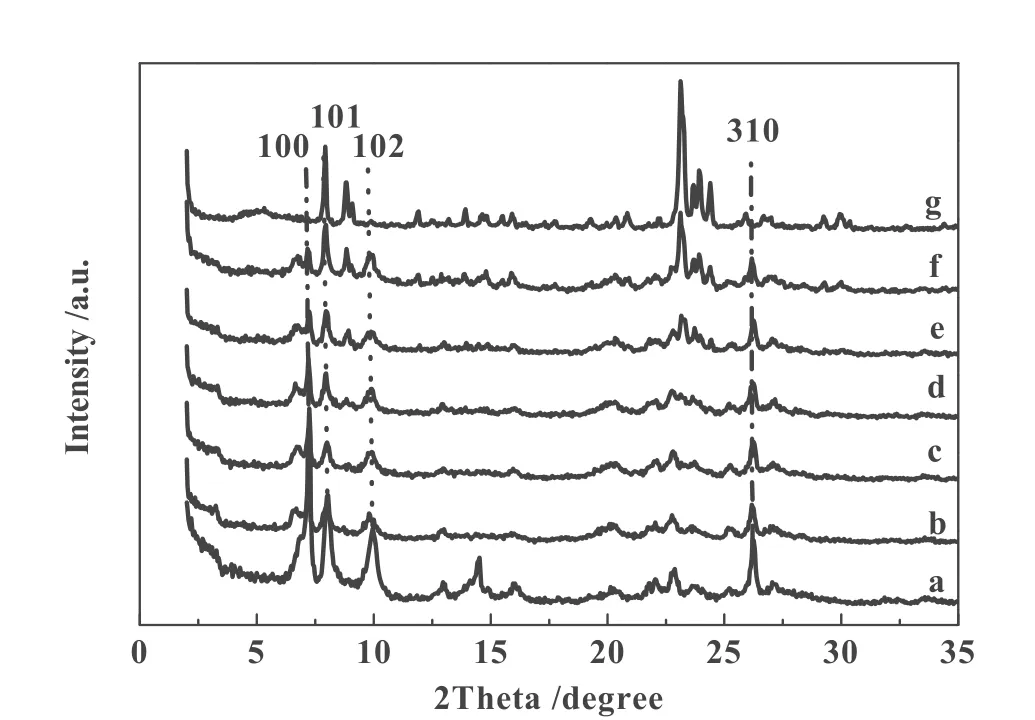
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of parent 3D Ti-MWW (a), and as-treated samples with TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio of 0.0025(b), 0.01(c), 0.02(d), 0.03(e), 0.04(f) and 0.05(g) at 443 K for 24 h
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Preparation of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites
Ti-MWW with the 3D MWW structure has been treated in the aqueous solution containing TPAOH. The parent 3D Ti-MWW sample with a Si/Ti molar ratio of 37 was prepared from a lamellar precursor (Si/Ti=20) by acid washing and calcination. Fig. 1 shows the XRD patterns of Ti-MWW before and after the TPAOH treatment at 443 K for different time but without calcination. The pattern of the parent sample showed the characteristic diffractions due to the 100, 101 and 102 planes of the MWW structure but with the absence of the 001 and 002 peaks due to the layered structure, which was fully consistent with that of well known 3D MWW structure.[19]
As shown in Fig.1, the 100, 101, 102, 310 peaks due to pure MWW phase were maintained by the TPAOH treatment in the TPAOH /SiO2molar ratio range of 0.002 5~0.02, showing lower amount of TPAOH can not transfer MWW to MFI phase. However, with the increase of TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio, diffractions of MWW phase were disappear gradually, while new diffractions were developed at 2θ =7.8°, 8.8°, 23.2°, 23.8° and 24.3° which are in agreement with the characteristic reflection peaks of the MFI structure[15]. Pure TS-1 was obtained at TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio of 0.05. The optimum TPAOH amount for synthesis Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites is in the TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio range of 0.03~0.04. The XRD patterns of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites are characteristic of presence of 100, 101, 102 and 310 peaks duo to MWW phase, concurrence of the peaks due to the MFI structure at 2θ =7.8°, 8.8°, 23.2°, 23.8° and 24.3°。
Using the same Ti-MWW parent, we have further investigated in detail the effect of treatment time at TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio of 0.03. As shown in Fig. 2, the 100, 101, 102, 310 peaks due to pure MWW phase were maintained by the TPAOH treatment for 2 h to 9 h, and have notappeared new peaks. But the intensity of 100 peaks was decreased slightly with the duration of treatment time. The suitable treatment time for the formation of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites is in the range of 21 h to 24 h. When the TPAOH treatment time prolonged to 36 h, the TS-1 sample was obtained duo to characterization diffractions of MFI pure phase.
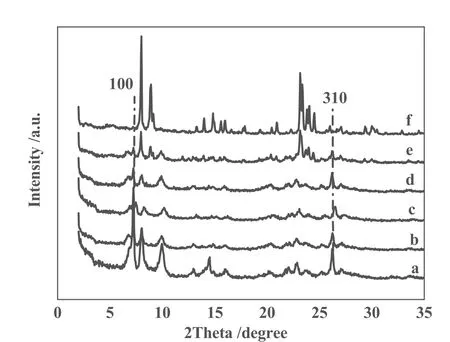
Fig.2 XRD patterns of parent 3D Ti-MWW (a), and as-treated samples at TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio of 0.03 for 1h(b), 6 h(c), 21h(d), 24 h(e) and 36 h(f) at 443 K
2.2 Characterization of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites
The UV-visible spectra of 3D Ti-MWW and TPAOH-treated samples are shown in Fig. 3. It should be first time noted that obvious band around 330 nm was observed for pure TS-1 samples (Fig. 3A,d), indicating that anatase-like phase was formed when the TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio is 0.05. The 220 nm band, resulting from the charge transfer from O2-to Ti4+, has been widely reported for the Ti-substituted zeolites and is characteristic of the tetrahedrally coordinated Ti highly dispersed in the framework[20]. After smaller amount of TPAOH treatment and further calcination, the Ti-MWW/TS-1composite zeolites still showed the similar band predominately at 220 nm (Fig. 3A, b and c), indicating the Ti active sites remained in the framework and had a tetrahedral coordination. All the Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites obtained from different time were characteristic of the tetrahedrally coordinated Ti highly dispersed in the framework, indicating different TPAOH treatment time had no obvious effect on the Ti active sites (Fig. 3B).
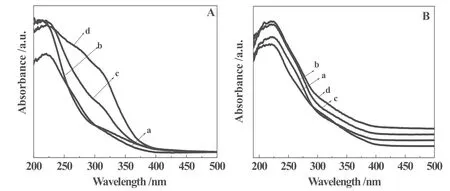
Fig. 3. UV-visible spectra of the calcined-samples treated by TPAOH at various TPAOH/Si ratios (A) and with different time (B); for Fig. 3A, the parent Ti-MWW (a) was treated at TPAOH/Si ratios ratio of 0.03(b), (c) 0.04, (d) 0.05 at 443 K for 24 h; for Fig. 3B, the parent 3D Ti-MWW(a) was treated at TPAOH/Si ratio of 0.03 at 443 K for 6 h (b), 21h days (c), 24 h (d).
The parent 3D Ti-MWW sample showed thin platelets, approximately 0.2 μm ~0.5 μm in length and 0.05μm ~0.1μm in thickness (Fig. 4a). From the SEM image of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites shown in Fig. 4, Ti-MWW was recrystallized into a TS-1-like sample with the aid of TPA cations that have a strong structure-directing effect for the formation of the MFI structure. The SEM image confirmed that the rectangular particles of 3 µm ~5 µm were formed with the surface covered by a large amount of thin platelets (Fig. 4b~4c). The rectangular particles became clearer gradually when the TPAOH treatment prolonged from 2 h to 24 h, with fewer and fewer MWW thin platelets. These larger particles showed the representative macroscopic morphology of the MFI phase, while the thin platelets adhering to the MFI-type crystals were those unconverted MWW phase during the TPAOH treatment at 443 K. When the treatment was prolonged to 36 h, a pure MFI phase with a higher crystallinity was obtained (Fig. 4d). These SEM results were accordance with XRD results.

Fig. 4 Scanning electron micrographes of parent 3D Ti-MWW (a), as-treated samples at TPAOH/SiO2molar ratio of 0.03 at 443 K for 21 h(b), 24 h(c), and 36 h(d)
2.3 Catalytic properties of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites
Both TS-1 and Ti-MWW have been reported to be a promising catalyst for the epoxidation of various alkenes with H2O2oxidant.[20,22]We thus have investigated the catalytic properties of Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites to check whether the composite zeolites are superior to TS-1 and Ti-MWW in the epoxidation of 1-hexene.
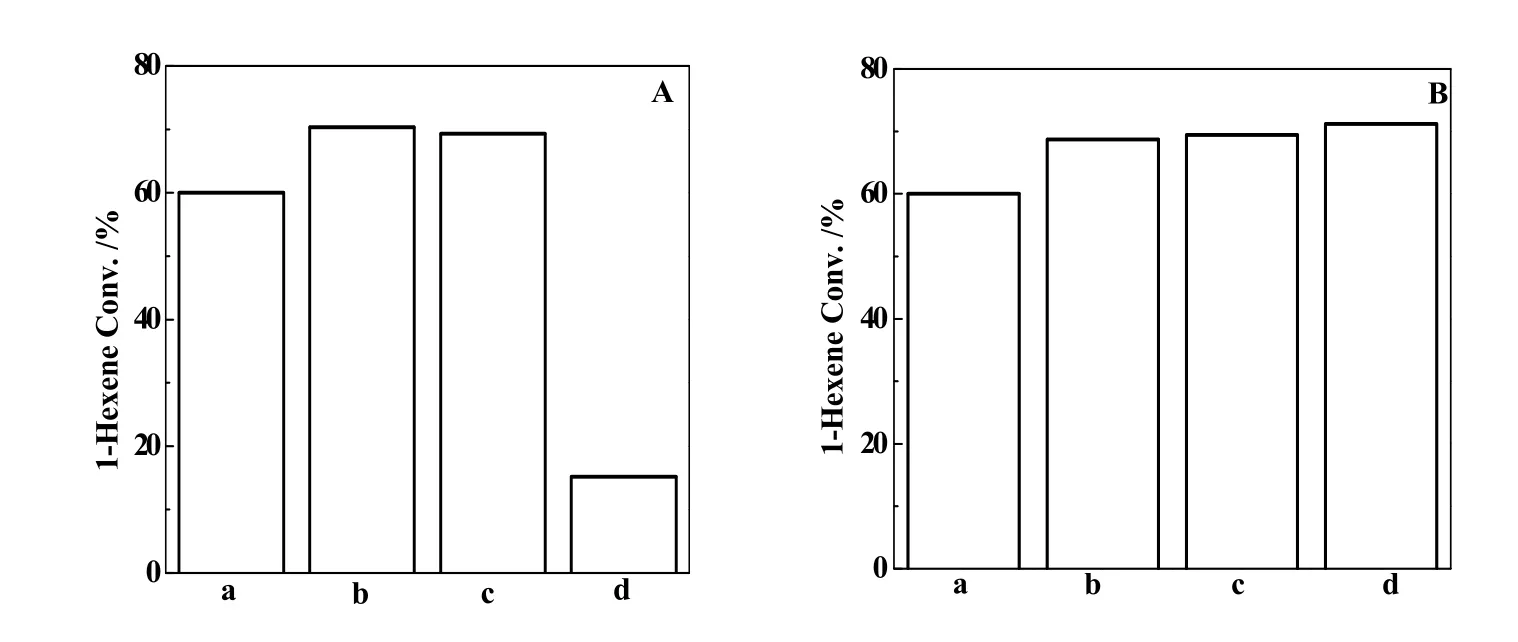
Fig. 5 A comparison of 1-hexene conversion of the calcined TPAOH-treated samples at various TPAOH/Si ratios (A) and for a different time (B); for Fig. 5A, the parent Ti-MWW (a) was treated at TPAOH/Si ratios ratio of 0.03(b), (c)0.04, (d) 0.05 at 443 K for 24h; for Fig. 5B, the parent 3D Ti-MWW(a) was treated at TPAOH/Si ratio of 0.03 at 443 K for 6 h (b), 21 h (c), 24 h (d); 1-Hexene epoxidation conditions: 0.05 g catalyst, 10 mmol 1-hexene, 10 mmol H2O2(ftaction of mass 30%), 10 mL MeCN solvent; 333 K, 2 h
As shown in Fig. 5, 1-hexene conversion for Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites obviously showed a higher conversion than the parent 3D Ti-MWW. The structural change enhanced the catalytic activity by 10 %~15 %. However, when TS-1 with MFI structure has been formed, the catalytic activity of 1-hexene would decrease obviously, due to the presence of anatase-like Ti species. With increase of treatment time at TPAOH/Si ratio of 0.03, the activity of 1-hexene for Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites increased gradually.
3 Conclusions
The post-synthesis treatment of 3D Ti-MWW zeolite with TPAOH leads to a Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites. Compared with conventional 3D Ti-MWW and TS-1, Ti-MWW/TS-1 composite zeolites shows improved catalytic activity in the liquid-phase epoxidation of a wide range of 1-hexene.
[1] WANG Q X, ZHANG S R, CAI G Y, et al. Alkylation catalyst and the application thereof: US, 6 093 866[P].2000-7-25.
[2] FRANCESCONI M S, LOPEZ Z E, UZCATEGUI D,et al. MFI/MEL intergrowth and its effect on n-decane cracking [J]. Catal. Today, 2005, 107:809-815.
[3] WANG P, SHEN B J, GAO J S. Synthesis of MAZ/ZSM-5 composite zeolite and its catalytic performance in FCC gasoline aromatization [J]. Catal. Commun, 2007, 8:1161-1166.
[4] FAN Y , LEI D, SHI G, et al. Synthesis of ZSM-5/SAPO-11 composite and its application in FCC gasoline hydro-upgrading catalyst [J]. Catal. Today, 2006, 114: 388-396.
[5] BOUIZI, Y, ROULEAU L, VALTCHEV V P. Bi-phase MOR/MFI-type zeolite core–shell composite [J]. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. , 2006, 91:70-77.
[6] GONZÁLEZ G, GONZÁLEZ C S, STRACKE W. New zeolite topologies based on intergrowths of FAU/EMT systems[J]. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. , 2007, 101:30-42.
[7] QI X L, LI B, LI S J, et al. Acidity and Catalytic Performance of BEA/MOR Intergrowth Zeolites [J]. Chin. J. Catal., 2006, 27:228-232.
[8] NIU X L, SONG Y Q , XIE S J , et al. Synthesis and Catalytic Reactivity of MCM-22/ZSM-35 Composites for Olefin Aromatization [J]. Catal. Lett., 2005, 103:211-218.
[9] KARLSSON A STKER M , SCHMIDT R. Composites of micro- and mesoporous materials: simultaneous syntheses of MFI/MCM-41 like phases by a mixed template approach [J]. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, 27:181-192.
[10] SOLBERG S M , KUMAR D , LANDRY C C. Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of a New Ti-Containing Microporous/Mesoporous Material [J]. J. Phys. Chem. B ,2005, 109:24331-24337.
[11] PROKEŠOV P, MINTOVA S , BEIN T. Catalytic activity of micro/mesoporous composites in toluene alkylation with propylene [J]. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. ,2005, 281:85-91.
[12] KOLLÁR M, MIHÁLYI R M , VALYON J. Micro/mesoporous aluminosilicate composites from zeolite MCM-22 precursor [J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2007, 99:37-46.
[13] WANG Q X , ZHANG S R, CAI G Y. Rare earth--ZSM-5/ZSM-11 cocrystalline zeolite:US, 5 869 021[P].1999-2-9.
[14] XU L Y, LIU J X, WANG Q X. Coking kinetics on the catalyst during alkylation of fcc off-gas with benzene to ethylbenzene [J]. Appl. Catal. A: Gen.,2004, 258:47-53.
[15] TARAMASSO T, PEREGO G, NOTARI B. Preparation of porous crystalline synthetic materials comprised of silicon and titanium oxides. US, 4 410 501[P]. 1983-10-18.
[16] CLERICI M G, BELLUSSI G, ROMANO U. Synthesis of propylene oxide from propylene and hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by titanium silicalite [J]. J. Catal., 1991, 129:159-167.
[17] CLERICI M G, INGALLINA P. Epoxidation of lower olefins with hydrogen peroxide and titanium silical [J]. J. Catal., 1993, 140:71-83.
[18] CORMA A , CAMBLOR M A , ESTEVE P. Activity of Ti-Beta Catalyst for the Selective Oxidation of Alkenes and Alkanes [J]. J. Catal., 1994, 145:151-158.
[19] WANG Q F , Mi Z T , WANG Y Q. Epoxidation of allyl choride with molecular oxygen and 2-ethyl-anthrahydroquinone catalyzed by TS-1 [J]. J. Mol. Catal. A, 2005, 229:71-75.
[20] WU P , TATSUMI T , KOMATSU T. A novel titanosilicate with MWW structure. I. hydrothermal synthesis, elimination of extraframework Titanium, and Characterizations [J]. J. Phys. Chem. B , 2001, 105:2897-2905.
[21] WU P, TATSUMI T. Preparation of B-free Ti-MWW through reversible structural conversion [J]. Chem. Commun., 2002, 10: 1026-1027.
[22] FAN W B, DUAN R G, YOKOI T. Synthesis, crystallization mechanism, and catalytic properties of Titanium-Rich TS-1 free of extraframework ,Titanium species [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130:10150-10164
Ti-MWW/TS-1复合分子筛的合成、表征及催化性能的研究
汪玲玲
(上海第二工业大学城市建设与环境工程学院,上海 201209)
TPAOH碱溶液处理三维Ti-MWW 能将三维结构转化为Ti-MWW和TS-1的复合分子筛。这些复合分子筛的合成条件为TPAOH/SiO2的摩尔比为0.03到0.04,在443K条件下晶化16小时~24小时。我们采用XRD,UV和SEM对复合分子筛的结构和形貌进行了详细的表征。在结构转换过程中,并没有改变复合分子筛中钛的配位状态。TPAOH处理后的样品形貌为长方形,晶体尺寸约为3 µm~5 µm,而且很明显这些大的晶粒上面还有大量小的薄片。在以双氧水为氧化剂烯烃的环氧化反应中,Ti-MWW/TS-1复合分子筛烯烃表现出比TS-1和Ti-MWW更优越的催化性能。
Ti-MWW; TS-1; 复合分子筛; 环氧化
TB383
A
1001-4543(2010)01-0030-06
2009-12-21;
2010-02-23
汪玲玲(1982-),女,博士研究生,主要研究方向为环境友好功能材料,电子邮件:llwang@eed.sspu.cn。
上海市教委项目(No.egd08017)
