妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常患者子代甲状腺功能评估
2025-02-27李慧于晓晴刘作侠

[摘 要]目的 分析妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常孕妇其子代甲功及甲功五项变化,为临床应用提供依据。方法 选择2020年1月至2022年6月在我院收治的100例甲状腺功能异常孕妇作为研究对象,根据诊断结果进一步分为甲减组(n=50)和甲亢组(n=50),同期选择50例正常妊娠的健康孕妇作为对照组;所有孕妇在妊娠12周及妊娠24周孕检时采集空腹静脉血,检测受试者血中血清游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸(FT3)、血清游离甲状腺素(FT4)、促甲状腺激素(TSH)、三碘甲状原氨酸(T3)、甲状腺素(T4)水平;分娩后6周及12周时采集幼儿空腹静脉血,检测FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平;采用Spearman相关性分析母亲甲状腺功能状况与其子代甲功变化及甲功五项的相关性。结果 甲亢组、甲减组和对照组的孕妇在妊娠24周时FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与妊娠12周相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05);甲亢组在妊娠24周时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最高,TSH水平最低,甲减组在妊娠24周时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最低,TSH水平最高;甲减组孕妇其子代在出生后6周和12周时出现甲状腺功能减退的人数占比分别为34.0%、38.0%;甲亢组、甲减组的子代在产后12周FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与产后12周时对照组的子代相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05),甲亢组的子代在产后12周时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最高,TSH水平最低,甲减组的子代在产后12周时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最低,TSH水平最高;孕妇甲状腺功能状况与子代甲状腺功能状况呈显著正相关关系(r=0.703,Plt;0.05);孕妇甲状腺功能状况与其子代的FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平呈显著正相关关系(r值分别为0.765、0.694、0.685、0.727),与TSH水平呈显著负相关关系(r=-0.703),且差异均存在统计学意义(Plt;0.05)。结论 孕妇甲状腺功能状态与其子代甲功变化及甲功五项存在显著性相关关系,尤其是妊娠期甲减孕妇,应对其进行及时干预治疗并密切关注子代甲状腺功能状况,防止对婴儿发育和智力产生不良影响。
[关键词]甲亢;甲减;妊娠;婴儿;甲状腺功能;甲功五项
Doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5293.2025.01.011
[中图分类号]R172 [文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1673-5293(2025)01-0064-05
Evaluation of thyroid function of offspring in pregnant women with thyroid dysfunction
LI Hui1,YU Xiaoqing1,LIU Zuoxia2
(1.Department of Pediatrics;2.Department of Laboratory,Daxing District
People’s Hospital of Beijing,Beijing 102600,China)
[Abstract] Objective To observe and analyze changes in thyroid function status and five items of thyroid function of offspring of pregnant women with thyroid dysfunction,so as to provide a basis for clinical practice. Methods 100 pregnant women with abnormal thyroid function who admitted to our hospital from January 2020 to June 2022 were selected as research subjects,and all pregnant women were divided into hypothyroidism group and hyperthyroidism group according to thyroid function of the pregnant woman (n=50 in each group).Other 50 healthy pregnant women with normal thyroid function were as the control group.Fasting venous blood was collected for all pregnant women at 12 weeks and 24 weeks of gestation (G12 and G24),and serum levels of free triiodothyronine (FT3),free tetraidothyronine (FT4),thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH),triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraidothyronine (T4) of them were detected.At 6 months and 12 months after birth,the fasting venous blood of the infants was collected,and the serum levels of FT3,FT4,TSH,T3 and T4 were detected also.Spearman correlation was used to analyze correlations of maternal thyroid function statuses with changes in thyroid function status and five items of thyroid function of the offspring. Results At G24,the serum levels of FT3,FT4,TSH,T3 and T4 of the pregnant women in the hyperthyroidism group,the hypothyroidism group and the control group were all significantly different from those at G12,and the differences were statistically significant (all Plt;0.05).In the hyperthyroid group,the serum FT3,FT4,TSH,T3 and T4 levels of the pregnant women were the highest and the TSH level was the lowest at G24,while in the hypothyroidism group,the serum FT3,FT4,T3 and T4 levels were the lowest and the TSH level was the highest at G24.And in the hypothyroidism group,the proportions of hypothyroidism in the offspring at 6 weeks and 12 months after birth were 34% and 38% respectively.At 12 weeks after birth,the serum levels of FT3,FT4,T3 and T4 of the infants in the hyperthyroidism group and the hypothyroidism group were different from those of the infants in the control group (all Plt;0.05).The serum levels of FT3,FT4,TSH,T3 and T4 of the offspring in the hyperthyroidism group and the hypothyroidism group were significantly different from those of the offspring in the control group at 12 weeks after birth (all Plt;0.05):the serum levels of FT3,FT4,T3 and T4 of the offspring in the hyperthyroidism group were the highest and the TSH level was the lowest at 12 weeks after birth,while in the hypothyroidism group,the serum levels of FT3,FT4,T3 and T4 of the offspring were the lowest and the TSH level was the highest at 12 weeks after birth.The maternal thyroid function status was significantly positively correlated with her offspring’s thyroid function status (r=0.703,Plt;0.05),and the thyroid function statuses of the pregnant women were significantly positively correlated with serum levels of FT3,FT4,T3 and T4 of their offspring (r=0.765,0.694,0.685 and 0.727 respectively),while the maternal serum TSH level was negatively correlated with that of their offspring (r=-0.703),and the differences were all statistically significant (all Plt;0.05). Conclusion There are significant correlations between the maternal thyroid function statuses and their offspring’s changes in thyroid function and the five items of thyroid function.Especially for those pregnant women with hypothyroidism,timely interventions and treatment should be given,and the thyroid function statuses of their offspring should be focused closely,in order to prevent from adverse effects of maternal hypothyroidism on physical development and intellectual development of their offspring.
[Key words] hyperthyroidism;hypothyroidism;pregnancy;infant;thyroid function;five items of thyroid function
妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常指孕期孕妇出现甲状腺功能异常,包括甲状腺功能亢进和甲状腺功能减退[1]。甲状腺功能亢进(甲亢)指甲状腺分泌过多的甲状腺激素,导致身体新陈代谢过快[2]。妊娠期发生甲亢可能会增加胎儿早产、低出生体重的风险,还可能增加孕妇患高血压、心血管疾病、产后出血等并发症的概率[3]。甲状腺功能减退(甲减)指甲状腺分泌的甲状腺激素不足,导致身体新陈代谢减慢[4]。妊娠期间发生甲抗可能会影响胎儿智力发育,增加早产、低出生体重、胎儿死亡的风险,还可能引发妊娠期高血压、贫血、子痫前期、胎盘剥离等并发症[4]。目前妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常患者其子代的甲功及甲功五项变化仍少有研究,因此,本研究旨在分析妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常产妇其子代甲功及甲功五项变化,为临床应用提供依据。
1资料与方法
1.1研究对象
选择2020年1月至2022年6月在我院收治的100例甲状腺功能异常孕妇作为研究对象,检测孕妇血中促甲状腺激素(TSH)、血清游离甲状腺素(FT4)、甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体(TPOAb)水平,并依据《妊娠和产后甲状腺疾病诊治指南(第2版)》[5]将上述研究对象根据甲状腺功能异常情况分为甲减组(n=50)和甲亢组(n=50),同期选择50例正常妊娠的健康孕妇作为对照组。
1.2纳排标准
纳入标准:①患者经检查确诊为甲状腺功能异常;②受试者在我院完成妊娠周期的随访和分娩;③孕前12周未服用胺碘酮;④所有研究对象的监护人均知情同意自愿参与研究。排除标准:①合并疑似甲状腺癌的甲状腺结节;②合并结缔组织病变;③合并其他自身免疫疾病;④临床资料缺失或主动申请退出本研究。本研究已经我院伦理委员会审议并批准。
1.3检测方法
所有受试孕妇在妊娠12周(G12)和24周(G24)孕检时采集空腹静脉血,检测受试者血中血清游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸(FT3)、FT4、TSH、三碘甲状原氨酸(T3)、甲状腺素(T4)水平,并对甲状腺功能异常孕妇依照指南标准[5]进行对症治疗和干预。对受试者进行随访,并在分娩后的6周和12周时采集幼儿的空腹静脉血,检测FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平,并分析幼儿的甲状腺功能,将幼儿依照标准[6]分为甲状腺功能减退者、健康查体者。
1.4统计学方法
应用SPSS 20.0统计分析,计量资料以x-±s表示,行t检验,计数资料以n(%)表示,行χ2分析。采用Spearman相关性分析母亲甲状腺功能状况与其子代甲功变化及甲功五项的相关性。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1孕妇甲状腺功能指标检测结果比较
甲亢组、甲减组和对照组的孕妇在G24时FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与G12相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05);甲亢组、甲减组的孕妇在G24时FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与G24时的对照组孕妇相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05);甲亢组孕妇在G24时FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与G24时的甲减组孕妇相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05)。甲亢组在G24时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最高,TSH水平最低,甲减组在G24时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最低,TSH水平最高,详见表1。
2.2各组孕妇子代甲状腺功能检测结果比较
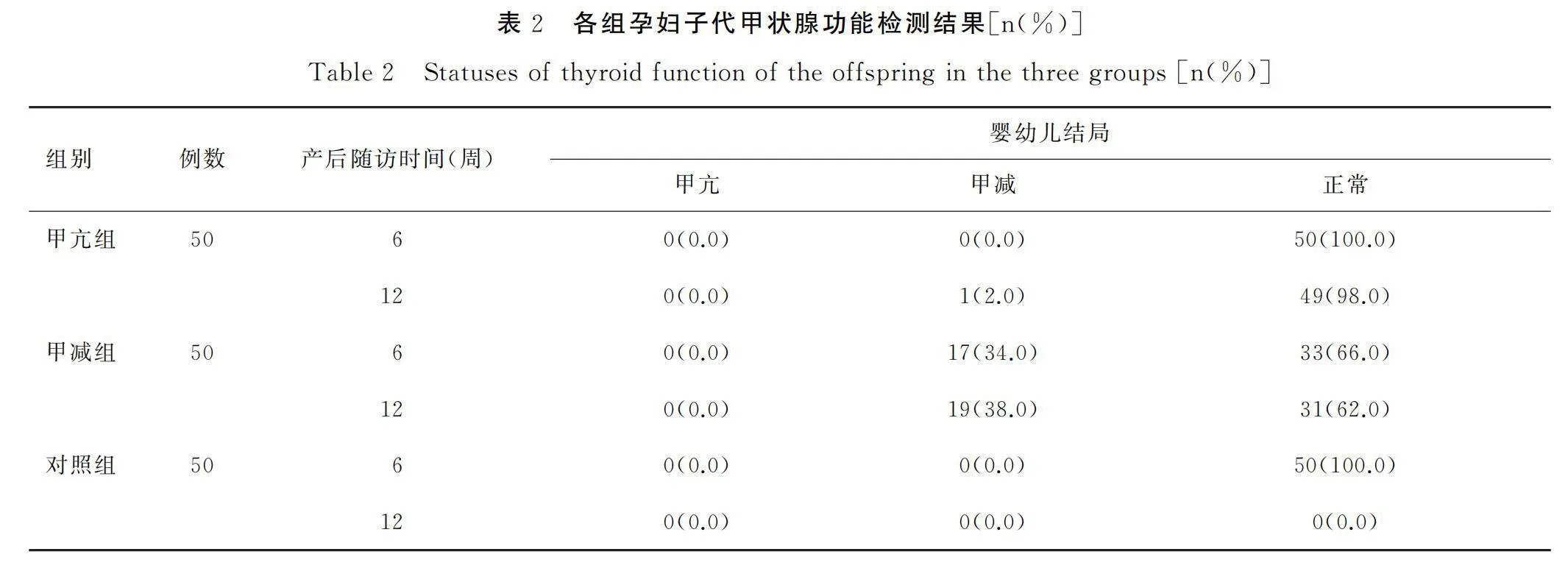
甲减组孕妇经产后随访发现,子代在出生后6周和12周时出现甲状腺功能减退的人数占比分别为34.0%、38.0%,详见表2。
2.3各组子代甲状腺功能指标检测结果比较比较
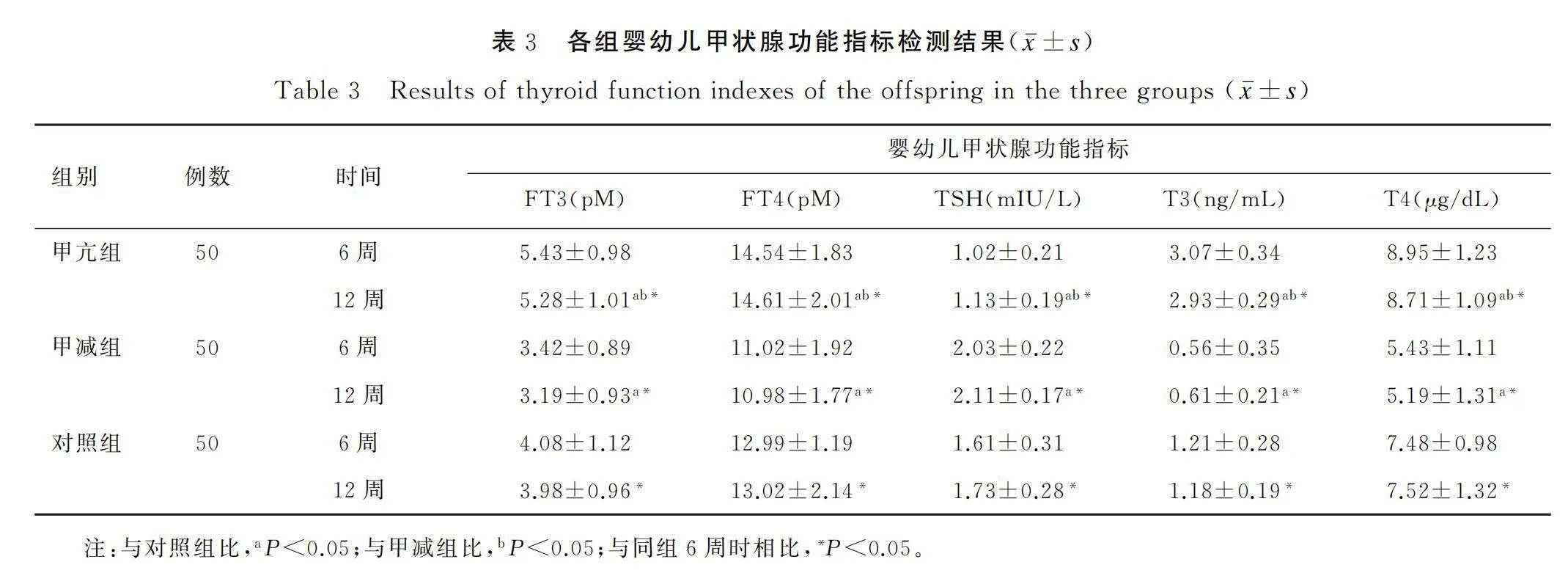
甲亢组、甲减组和对照组的子代在产后12周时FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与产后6周时相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05);甲亢组、甲减组的子代在产后12周FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与产后12周时对照组的子代相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05);甲亢组的子代在产后12周时FT3、FT4、TSH、T3、T4水平与产后12周时甲减组的子代相比存在显著差异(Plt;0.05)。甲亢组的子代在产后12周时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最高,TSH水平最低,甲减组的子代在产后12周时FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平最低,TSH水平最高,详见表3。
2.4孕妇甲状腺功能状况与其子代甲功变化的相关性
研究结果显示,孕妇甲状腺功能状况与子代甲状腺功能状况呈显著正相关关系,相关系数r=0.703,P=0.013。
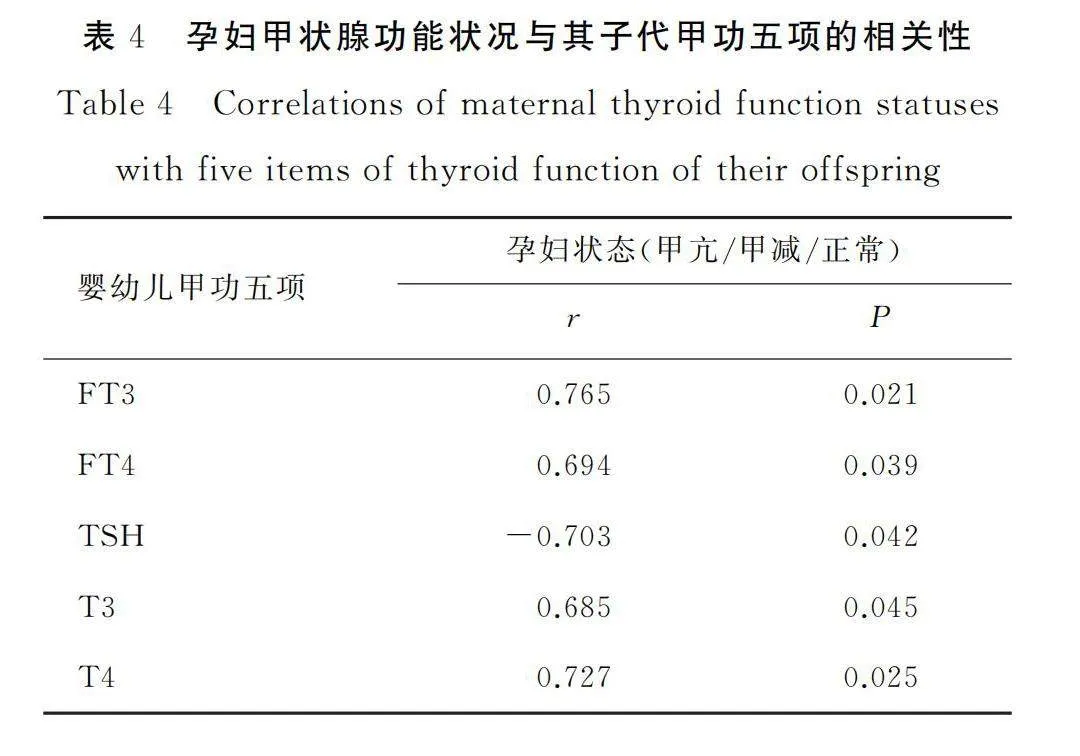
2.5孕妇甲状腺功能状况与其子代甲功五项的相关性
本组研究结果显示,孕妇甲状腺功能状况与其子代的FT3、FT4、T3、T4水平呈显著正相关关系,与TSH水平呈显著负相关关系,且差异存在统计学意义(Plt;0.05),详见表4。
3讨论
3.1妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常与婴幼儿甲状腺功能异常分析
妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常指在孕期,孕妇患有甲状腺功能异常,包括甲亢和甲减[7]。甲亢可能增加孕妇患高血压、心血管疾病、产后出血等并发症风险,甲减可能导致孕期贫血、子痫前期、胎盘早剥等并发症的发生[7]。此外,甲状腺功能异常还可能增加孕妇患产后抑郁症的风险[8]。对于妊娠期出现甲状腺功能异常的孕妇,应及早进行甲状腺功能检查,包括血清甲状腺激素水平和抗甲状腺抗体的检测。临床中,对甲亢或甲减合并妊娠患者进行干预时,需建立一个综合治疗团队,包括内分泌学专家、产科医生和其他相关专家,以确保母儿得到全面管理及照顾[9]。治疗方案根据孕妇具体情况制定,包括孕妇甲状腺功能异常的类型、病情严重程度、孕周及胎儿情况等[10]。
婴幼儿甲状腺功能异常指出生后婴儿甲状腺功能异常,其中最常见的是婴幼儿甲减[11]。甲状腺激素对婴儿神经系统发育至关重要,婴幼儿甲减可能导致婴儿智力发育受损,包括认知能力、言语和运动技能的延迟[12]。甲状腺激素在婴儿体内调节能量代谢和骨骼发育,婴幼儿甲减可能导致婴儿生长缓慢、肌肉松弛、骨骼畸形,还可能影响心脏功能,引起心律不齐和心脏结构异常[13]。早发现、早治疗婴幼儿甲减对婴儿发展至关重要,通过及时纠正甲状腺激素不足以减少或避免智力发育障碍和身体发育障碍发生,提高生活质量[14-15]。
3.2妊娠合并甲状腺功能异常与子代甲功五项之间的相关性
在妊娠期间,母体与胎儿之间存在密切的甲状腺激素交流[16]。甲功五项,包括T4、FT4、T3、FT3、TSH,可反映甲状腺功能状态,在妊娠期上述指标会受多种因素影响,包括孕周的变化与孕妇体内的激素水平变化[17]。妊娠期甲亢孕妇,其甲状腺激素水平升高可能导致胎儿在子宫内受到高甲状腺激素刺激,对胎儿的甲状腺功能产生抑制作用[18]。因此,出生后,婴幼儿的甲功五项可能呈现异常模式:FT4和FT3水平可能升高,TSH水平通常较低。上述异常通常在几周内自行恢复正常,对婴儿的健康影响较小[19]。对于妊娠期甲减孕妇,胎儿受甲状腺激素不足影响,导致婴幼儿甲功五项异常[20]。婴幼儿可能出现婴幼儿甲状腺功能减退,表现为FT4和FT3水平降低,TSH水平升高,需及早干预治疗,防止对婴儿发育和智力产生不良影响[21]。本组研究结果显示,母亲孕期甲状腺功能状态与子代甲状腺功能状态呈显著正相关关系,进一步分析显示,母亲孕期甲状腺功能状态与子代的FT3、FT4、T3、T4呈显著正相关关系,与TSH呈显著负相关关系,同样验证了上述阐述。
本研究临床样本数较少,随访周期较短,后续将扩大样本量,开展长期追踪随访进行进一步探究。
综上所述,孕妇甲状腺功能状态与其子代甲功变化及甲功五项存在显著性相关关系,尤其是妊娠期甲减孕妇,应对其及时干预治疗并密切关注子代甲状腺功能状况,防止对婴儿发育和智力产生不良影响。
[参考文献]
[1]Eng L,Lam L.Thyroid function during the fetal and neonatal periods[J].Neoreviews,2020,21(1):e30-e36.
[2]Derakhshan A,Peeters R P,Taylor P N,et al.Association of maternal thyroid function with birthweight:a syste-matic review and individual-participant data meta-analysis[J].The lancet Diabetes amp; endocrinology,2020,8(6):501-510.
[3]Geno K A,Nerenz R D.Evaluating thyroid function in pregnant women[J].Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences,2022,59(7):460-479.
[4]洪琼,时晓丽,吴萍,等.血清TSH、FT4联合预测妊娠合并甲减不良结局的研究[J].中国妇幼健康研究,2022,33(12):51-56.
[5]《妊娠和产后甲状腺疾病诊治指南》(第版)编撰委员会,中华医学会内分泌学分会中华医学会围产医学分会.妊娠和产后甲状腺疾病诊治指南(第2版)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2019,35(8):636-665.
[6]陈肖肖,秦玉峰,周雪莲,等.婴幼儿亚临床甲状腺功能减退症的诊断标准和治疗探讨[C]//2007年浙江省儿科学、小儿外科学学术年会,2009.
[7]张铮,王苓,王红红.妊娠期甲状腺功能正常范围的探讨[J].中国妇幼健康研究,2022,33(11):36-42.
[8]Andersson M,Braegger C P.The role of iodine for thyroid function in lactating women and infants[J].Endoc-rine reviews,2022,43(3):469-506.
[9]刘克芳,陈凤莹,沈怡.甲状腺功能系统性治疗妊娠合并甲亢症患者的临床效果分析[J].实用妇科内分泌电子杂志,2021,8(27):7-9.
[10]Hales C,Taylor P N,Channon S,et al.Controlled antenatal thyroid screening II:effect of treating maternal suboptimal thyroid function on child behavior[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology amp; Metabolism,2020,105(3):e417-e427.
[11]Rotondi M,Bendotti G,Croce L,et al.A unique presentation of Graves’ disease in a pregnant woman with severe hypothyroidism[J].Gynecological Endocrinology,2022,38(8):697-701.
[12]Costantine M M,Smith K,Thom E A,et al.Effect of thyroxine therapy on depressive symptoms among women with subclinical hypothyroidism[J].Obstetrics and gynecology,2020,135(4):812.
[13]Petca A,Dimcea D A M,Dumitracu M C,et al.Management of Hyperthyroidism during Pregnancy:A Systematic Literature Review[J].Journal of Clinical Medicine,2023,12(5):1811.
[14]林小燕,钟振强,陈伟林.不同剂量左甲状腺素治疗妊娠期甲减的效果及对母婴结局的影响[J].当代医学,2021,27(16):80-82.
[15]Lee S Y,Cabral H J,Aschengrau A,et al.Associations between maternal thyroid function in pregnancy and obstetric and perinatal outcomes[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology amp; Metabolism,2020,105(5):e2015-e2023.
[16]Lee S Y,Pearce E N.Testing,monitoring and treatment of thyroid dysfunction in pregnancy[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology amp; Metabolism,2021,106(3):883-892.
[17]Pop V J,Hulsbosch L P,Boekhorst M G B M,et al.Hypothyroid symptoms throughout pregnancy are predominantly associated with thyroxine and not with thyrotropin concentrations[J].Thyroid,2022,32(10):1249-1258.
[18]杜德奇.甲状腺激素水平测定在不同妊娠期妇女病情评估中的意义[J].医学检验与临床,2021,32(10):11-15.
[19]Ilias I,Milionis C,Koukkou E.Further understanding of thyroid function in pregnant women[J].Expert Review of Endocrinology amp; Metabolism,2022,17(4):365-374.
[20]Knezevic J,Starchl C,Tmava Berisha A,et al.Thyroid-gut-axis:how does the microbiota influence thyroid function?[J].Nutrients,2020,12(6):1769.
[21]齐志业,张彩营,王琼,等.新生儿高促甲状腺素血症与妊娠期甲状腺功能关系的病例对照研究[J].中国妇幼健康研究,2022,33(8):1-5.
[专业责任编辑:肖延风]
[中文编辑:冯佳圆;英文编辑:杨周岐]
