不同运动项目对孤独症谱系障碍儿童干预效果的探讨
2024-03-25庞丽婷叶展辰
庞丽婷,叶展辰
不同运动项目对孤独症谱系障碍儿童干预效果的探讨
庞丽婷1,叶展辰2
(1.扬州大学体育学院,江苏 扬州,225000;2.成都教育科学院附属龙泉学校,四川 成都,610107。)
孤独症谱系障碍作为一种神经发育障碍疾病,其严重威胁到儿童的日常生活和身心健康,是每个家庭的沉重负担。目前,孤独症谱系障碍儿童发病率也呈上升趋势,其具体发病机制尚未完全清楚,有许多以运动干预为手段的治疗方法,其对孤独症谱系障碍儿童有效,但是仍存在运动方案不完整。本文针对不同运动项目对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果进行综述,以期为孤独症儿童的运动干预提供指导和借鉴。
运动项目;孤独症谱系障碍;儿童;干预效果
孤独症谱系障碍(autism spectrum disorder,ASD)是一种具有特定认知行为特征和相当普遍的共病(即癫痫、抑郁症和注意缺陷/多动障碍)等的神经发育障碍疾病[1]。近年来,孤独症患儿以飞快的速度在不断的增加,并成为当今儿童最常见的精神疾病之一。据最新统计显示,从2000年到2018年,美国儿童孤独症谱系障碍的发病率正在增加,从1/54到1/44只用了两年的时间,而中国的ASD儿童的发病率也逐年上升,其受到不同程度的ASD患病影响。调查研究发现,运动改善孤独症谱系障碍通过不同的运动项目、运动频率、运动时间、运动周期以及运动强度的变量,能达到改善孤独症的效果。研究表明,不同强度、周期、时间、频率、项目的运动能有效的改善孤独症谱系障碍儿童的心理健康、身体的协调能力以及平衡能力,合理的运动干预对孤独症儿童的治疗有一定的积极作用,然而在运动项目改善孤独症的认识体系并不健全[2]。本文旨综述不同运动项目对孤独症的干预康复效果,以期更全面的了解运动干预的康复方案,为孤独症儿童提供更多的抉择。
1 孤独症谱系障碍儿童的现状及原因分析
1.1 孤独症谱系障碍儿童的现状
当今,由于孤独症谱系障碍儿童的发病率逐年上升。丁宁等人在安徽芜湖某医院对13842名学龄前儿童的调查中发现,有748名儿童疑似为孤独症,最终确诊52名,孤独症儿童发病率达4.11%。孤独症的来临已经严重的影响家庭,使得家庭支离破碎[3]。沈锦红等人在对清远市4700名幼儿园就读的儿童调查分析中显示,确诊ASD的儿童有49名,其患病率达1.09%[4],主要原因在父母遗传、家庭养育方式以及家庭环境等因素,从而造成儿童患病率增高。
1.2 孤独症谱系障碍儿童的原因分析
儿童在幼儿时期的发病率较高,根据有关研究结果显示,父母内向、父母生育年龄较晚,文化程度低、孕期使用特殊药物等都会成为儿童患孤独症的独立危险因素[5]。沈锦红等人根据临床研究发现,家庭精神病史、新生儿窒息、新生儿黄疸、母亲月经初潮年龄等因素也会对儿童患孤独症有影响[4]。儿童窒息会过度激活血液中的多巴胺,导致脑干一种导致危险因素的疾病,如言语障碍,从而导致孤独症儿童发病率增高。
2 运动干预孤独症效果的背景
2.1 孤独症的干预现状
孤独症作为一种高发病率和终身疾病的当前精神发育障碍,其主要表现为社交障碍和重复性刻板行为等潜在症状。目前,孤独症的治疗主要包括:应用行为分析疗法、结构化教育疗法、药物治疗、肠道微生物疗法、中医药疗法等,但是由于孤独症发病机制的复杂性和多样性,大多数的疗法效果不明显。近些年研究表明,由于运动康复的独特疗法,孤独症患者可以通过体育运动,不服用药物,也可以对身体的发育障碍、运动协调、社交障碍以及重复刻板行为有明显的改善效果。
2.2 体育运动对孤独症干预的作用
体育运动对孤独症儿童干预的方式多种多样,首先,运动干预是指孤独症患者利用自身的重量,通过不同的运动方式,获得社会功能、感统功能以及运动技能的改善。孤独症儿童的运动技能会影响其社交、认知等方面的发展。体育运动也可以改善他们的执行功能、睡眠质量、情绪调节能力以及肥胖的风险,让他们身心健康得以发展。
3 不同运动项目对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
本文对2009—2021年的国内外文献在中国知网、百度学术以及万方数据库上进行中文检索,在Pub Med、Web of Science 以及Google Scholar进行英文检索。文献纳入标准:(1)纳入的受试者是孤独症谱系障碍患者。(2)实验组为体育运动干预,对照组为普通正常生活。排除标准:(1)文献中不完整的数据报告。(2)个案分析。搜索符合本文要求的文献23篇。通过对文献的梳理显示,近些年,越来越多的研究人员开始使用体育运动干预的模式来改善孤独症谱系障碍儿童的症状。
3.1 骑马运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
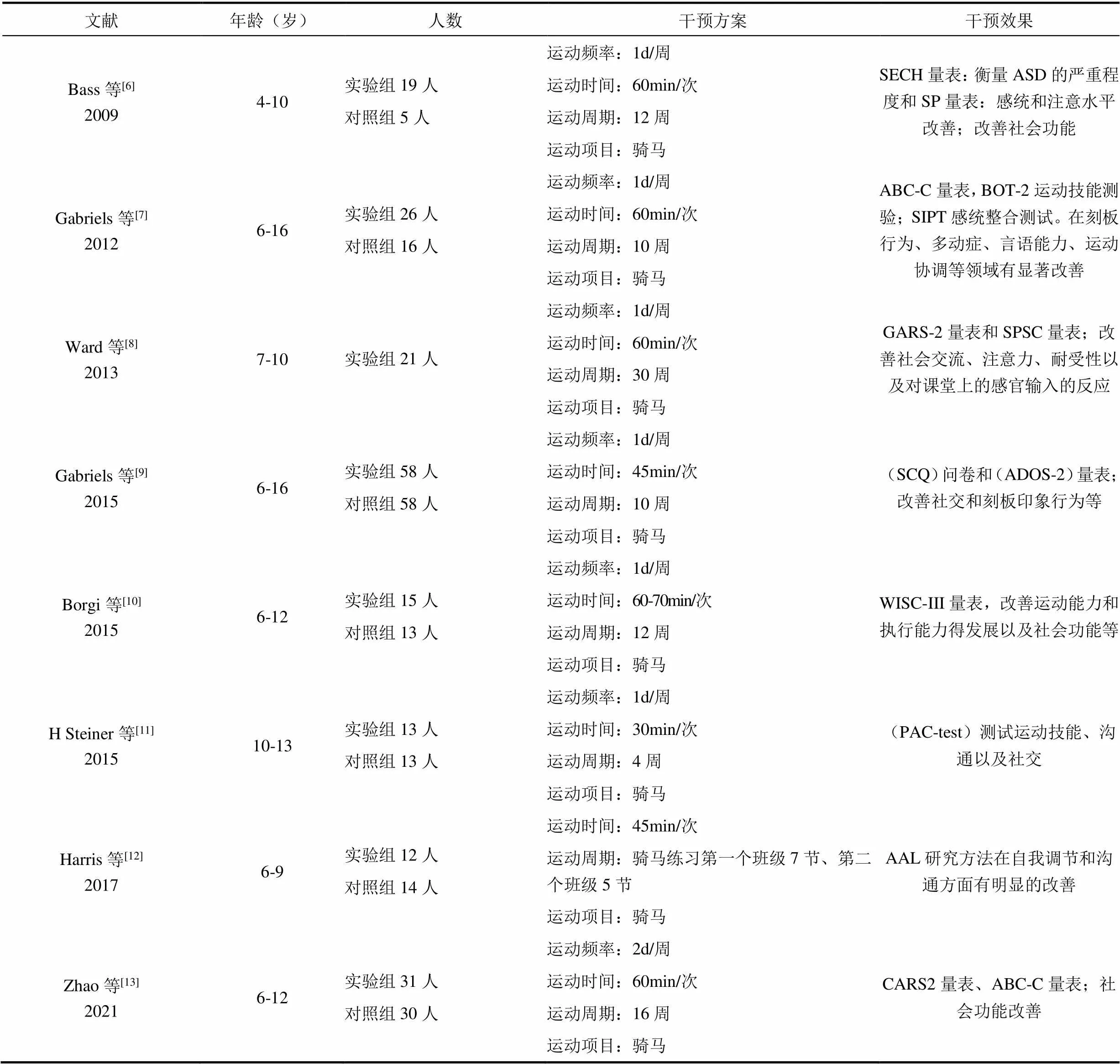
表1 骑马运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
Bass等[6]、Gabriels等[7]、Ward等[8]、Gabriels等[9]、Borgi等[10]、H Steiner等[11]、Harris等[12]、Zhao等[13]均对孤独症患者进行了马术练习,并得到较一致的结论。马术运动主要为单人练习,其分为骑马10min的热身(手臂绕圈、驱赶扭转等)、15min的骑马技能练习(直接控制、小跑、开放引导控制等)、马术游戏(红灯/绿灯和字母游戏等)等形式。马术运动后ASD患者睡眠状态更好、社会功能改善、刻板行为缓解、语言能力提高,见表1。
3.2 小篮球运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
董晓晓等[14]、Cai等[15]、Wang等[16]、Yang等[17]通过12周小篮球运动可以改善孤独症儿童的社交障碍、刻板行为等核心症状。小篮球运动主要为小组练习和集体练习,其分为简单球性练习(拨球、抛接球等)、技术动作练习(传球、投篮等)以及体育游戏(运球比多游戏、抓鸭子等)等形式,见表2。
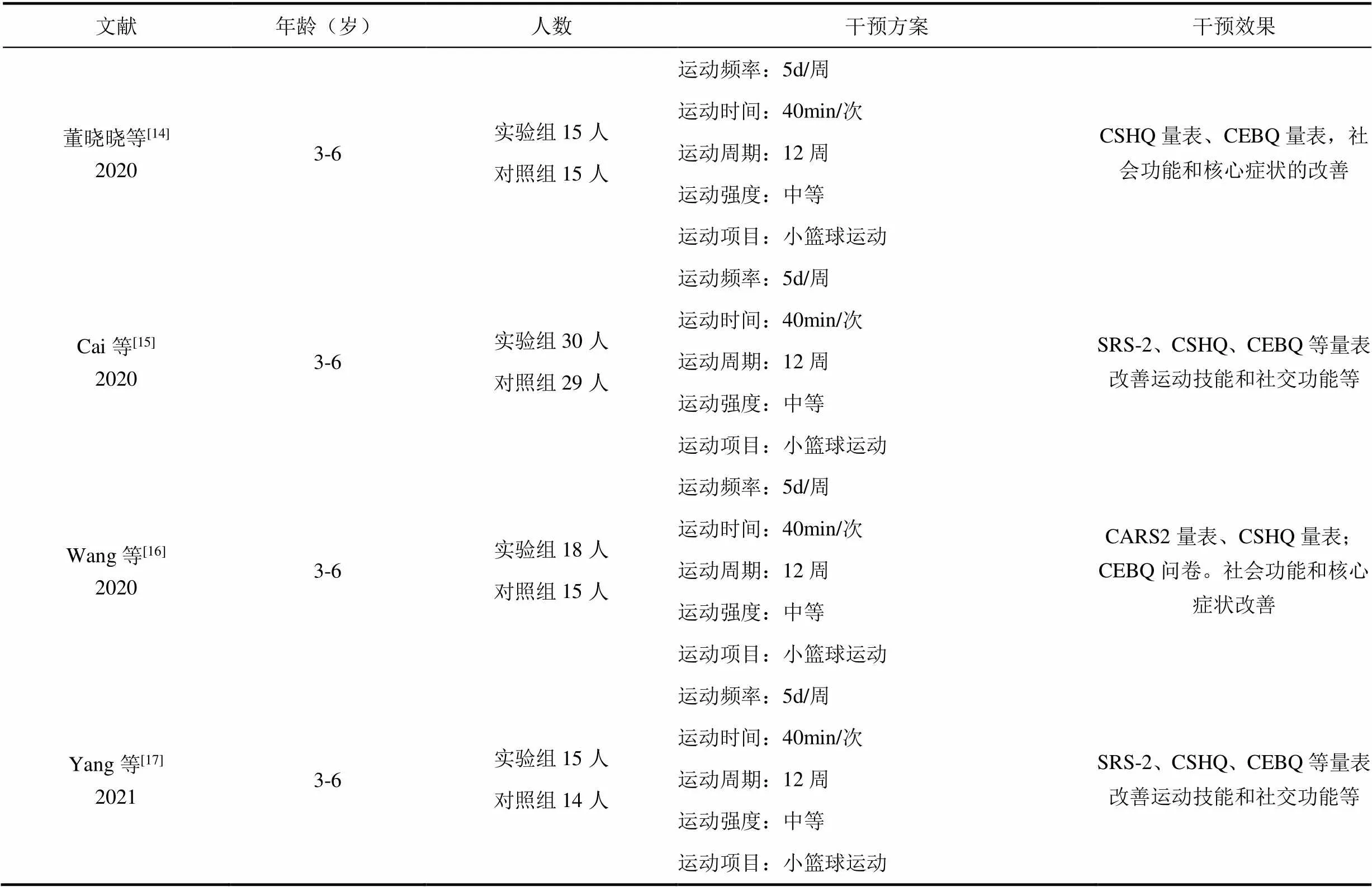
表2 小篮球运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
3.3 武术运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
Bahrami等[18]、Movahedi等[19]、张芹等[20]、Janice N.Phun[21]通过武术运动干预来改善孤独症患者得自我控制能力、社会功能、语言沟通能力以及平衡能力。武术运动主要为个人练习和小组练习,其分为姿势练习、防守进攻技术练习(阻挡、打、踢等)以及口头指导和口头线索(提示行动、引导注意力等)等形式,见表3。
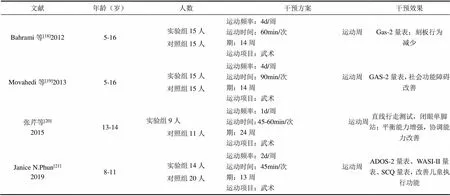
表3 武术运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
3.4 瑜伽运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
Sotoodeh等[22]、Narasingharao等[23]通过瑜伽运动干预发现孤独症儿童的模仿技能提高、平衡能力以及行为症状的改善。瑜伽运动主要为单人练习,其分为热身(向下姿势、坐姿等)、强化动作练习(树的姿势、战士的姿势等)以及静止动作练习(蝴蝶姿势、椎体收缩等)等形式,见表4。

表4 瑜伽运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
3.5 水上运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
Pan等[24,25]通过水上运动干预后发现孤独症儿童肌肉、耐力素质有明显得改善,水上技能提升。水上运动主要为单人练习和小组练习,其分为地板热身活动、呼啦圈游泳、直腿踢水、直臂独立、水中吹起泡以及组队游戏等形式,见表5。

表5 水上运动对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
3.6 韵律操对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
裴晶晶等[26]、杨毅等[27]通过韵律操干预后发现孤独症儿童得身体素质有着明显的改善、社交能力、语言沟通能力以及感知觉改善较大。韵律操主要为单人练习,其分为以Bobath 疗法、感觉统合疗法为主编排的垫上练习、徒手操以及器械操等形式,见表6。
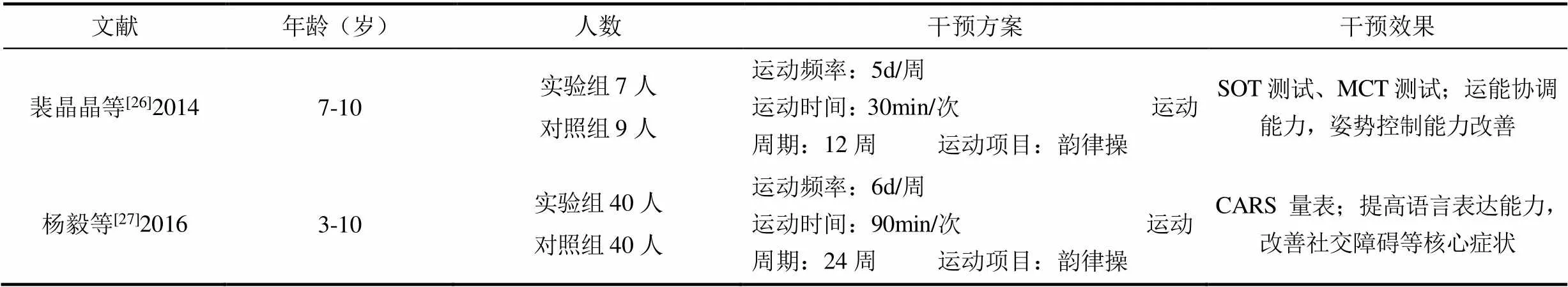
表6 韵律操对孤独症谱系障碍儿童的干预效果
4 结 论
不同运动项目对孤独症儿童的干预起着不同的作用,运动项目、频率、时间、周期的不同,会对孤独症儿童的身体也有着不同的影响。从中发现,多种运动干预的方式,通过各自的运动方案对每个年龄段的儿童都有一定的效果,但是仍存在不完整。在对孤独症儿童的干预过程中,要根据孤独症儿童的症状选择合适的运动项目,为其身体改善效果达到更好。
[1] Cai K, Yu Q, Herold F, et al. Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Social Communication and White Matter Integrity in Children with Autism[J]. Brain Sciences, 2020, 10(803): 803.
[2] 赵凌霄,范静怡.孤独症谱系障碍儿童社会沟通与交往障碍的表现与发生机制[J].中国儿童保健杂志,2017,25(06):585~587.
[3] 丁 宁,徐 慧,沈棫华,等.芜湖市学龄前儿童孤独症谱系障碍患病现状及影响因素研究[J].华南预防医学,2021,47(11):1384~1387.
[4] 沈锦红,吴文华,罗 炼,等.清远市清城区2~6岁孤独症谱系障碍的现状调查及相关因素分析[J].中国医学创新,2020,17(26):71~77.
[5] 王光霞,李 霞,方鲁阳,等.枣庄市2~6岁儿童孤独症谱系障碍的现况调查及相关因素分析[J].中国儿童保健杂志,2015,23(12):1322~1325.
[6] Bass M M, Duchowny C A, Llabre M M . The effect of therapeutic horseback riding on social functioning in children with autism.[J]. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 2009, 39(09): 1261~1267.
[7] Gabriels R L, Agnew J A, Holt K D , et al. Pilot study measuring the effects of therapeutic horseback riding on school-age children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders[J]. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2012, 6(02): 578.
[8] Sandra, C, Ward, et al. The Association Between Therapeutic Horseback Riding and the Social Communication and Sensory Reactions of Children with Autism[J]. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 2013.
[9] Gabriels R L, Pan Z, Dechant B , et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of Therapeutic Horseback Riding in Children and Adolescents With Autism Spectrum Disorder[J]. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2015.
[10] Effectiveness of a Standardized Equine-Assisted Therapy Program for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder[J]. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 2015, 46(01): 1~9.
[11] Steiner H, Kertesz Z. Effects of therapeutic horse riding on gait cycle parameters and some aspects of behavior of children with autism[J]. Acta Physiologica Hungarica, 2015, 102(03): 324.
[12] Harris A, Williams J M. The Impact of a Horse Riding Intervention on the Social Functioning of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 2017, 14(07): 776~.
[13] Zhao M, Chen S, You Y , et al. Effects of a Therapeutic Horseback Riding Program on Social Interaction and Communication in Children with Autism[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(05): 2656.
[14] 董晓晓,陈爱国,刘智妹,等. 小篮球运动对学龄前孤独症儿童重复刻板行为及脑灰质体积的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2020,56(11):7.
[15] Cai K L, Wang J G, Liu Z M , et al. Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Physical Fitness and Social Communication in Preschool Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders[J]. Journal of Human Kinetics, 73.
[16] Jin-Gui Wang, Ke-Long Cai, Zhi-Mei Liu, Fabian Herold, Liye Zou, Li-Na Zhu, Xuan Xiong, Ai-Guo Chen. Effects of Mini-Basketball Training Program on Executive Functions and Core Symptoms among Preschool Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders[J]. Brain Sciences, 2020, 10(05).
[17] Yang Sixin, Liu Zhimei,Xiong Xuan, Cai Kelong, Zhu Lina,Dong Xiaoxiao, Wang Jingui, Zhu Hao, Shi Yifan, Chen Aiguo. Effects of Mini-Basketball Training Program on Social Communication Impairment and Executive Control Network in Preschool Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(10).
[18] Fatimah Bahrami, Ahmadreza Movahedi, Sayed Mohammad Marandi, Ahmad Abedi. Kata techniques training consistently decreases stereotypy in children with autism spectrum disorder[J]. Research in Developmental Disabilities , 2012, 33(04).
[19] Ahmadreza Movahedi, Fatimah Bahrami, Sayed Mohammad Marandi, Ahmad Abedi. Improvement in social dysfunction of children with autism spectrum disorder following long term Kata techniques training[J]. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2013, 7(09).
[20] 张 芹. 体育锻炼对轻度自闭症少年平衡能力的影响研究[J]. 牡丹江师范学院学报:自然科学版,2015(02):2.
[21] JN. Promoting Executive Functioning in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Through Mixed Martial Arts Training[J]. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 2019, 49(09): 3669~3684.
[22] Sotoodeh M S, Arabameri E, Panahibakhsh M, et al. Effectiveness of yoga training program on the severity of autism[J]. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice, 2017, 28: 47~53.
[23] Narasingharao K. Efficacy of Structured Yoga Intervention for Sleep, Gastrointestinal and Behaviour Problems of ASD Children: An Exploratory Study[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2017, 11(03).
[24] Pan, C.-Y. Effects of water exercise swimming program on aquatic skills and social behaviors in children with autism spectrum disorders.[J]. Autism, 2010, 14(01): 9~28.
[25] Pan C Y. The efficacy of an aquatic program on physical fitness and aquatic skills in children with and without autism spectrum disorders[J]. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2011, 5(01): 657~665.
[26] 裴晶晶,蒋宇乐. 韵律操练习干预对自闭症儿童姿势控制能力的影响[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2014(04):4.
[27] 杨 毅,杨 阳. 运动干预对自闭症儿童的治疗效果分析[J]. 中国当代医药,2016.
Discussion on the Effects of Different Sports Programs on Interventions in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
PANG Liting1, YE Zhanchen2
(1.Sports Department of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou Jiangsu, 225000, China; 2.Longquan School affiliated to Chengdu Academy of Educational Sciences, Chengdu Sichuan, 610107, China.)
As a neuro developmental disorder, autism spectrum disorder has seriously threatened children's daily lives and physical and mental health, and is a heavy burden on every family. At present, the incidence of autism spectrum disorder in children is also on the rise, the specific pathogenesis is not yet fully understood, there are many treatment methods with exercise intervention as a means, they are effective for children with autism spectrum disorder, but there are still incomplete exercise regimens. This paper reviews the intervention effects of different sports programs on children with autism spectrum disorder, in order to provide guidance and reference for exercise interventions in children with autism.
Exercise program; Autism spectrum disorder; Children; Intervention effect
G804.83
A
1007―6891(2024)01―0055―05
10.13932/j.cnki.sctykx.2024.01.11
2022-03-21
2022-03-25
江苏省研究生科研与实践创新计划项目(KYCX22_3421)。
庞丽婷,1998-,女,内蒙古锡林浩特人,在读硕士研究生,专业:体育人文社会学,研究方向:学校体育心理学,电子邮箱:1031523445@qq.com。
