PACS-2在阿尔茨海默病发展中作用机制研究
2024-03-08王艳云叶群英钱军刘志鹏罗红波李芸
王艳云 叶群英 钱军 刘志鹏 罗红波 李芸

[摘要] 目的 探究磷酸呋喃酸性簇分選蛋白-2(phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein-2,PACS-2)在N2a/APP695swe细胞线粒体功能及细胞凋亡中的参与作用,进一步探讨PACS-2在阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimers disease,AD)发生、发展中的作用及意义。方法 CCK8法分析不同浓度的二苯乙烯苷(tetrahydroxy stilbene glycoside,TSG)处理N2a/APP695swe细胞48h后的细胞存活率,选择合适浓度的TSG用于后续实验。体外常规培养N2a/WT细胞和N2a/APP695swe细胞,实验细胞分为3个组:空白对照组(WT组):N2a/WT细胞;模型组(APP组):N2a/APP695swe细胞;治疗组(TSG组):N2a/APP695swe细胞,合适浓度的TSG干预。TUNEL法荧光显微镜观察细胞凋亡情况,JC-1法流式检测细胞线粒体膜电位,Western blot(WB)检测PACS-2的蛋白表达情况,RT-qPCR检测PACS-2的mRNA表达情况。结果 CCK8法分析不同浓度的TSG作用细胞48h后的细胞存活率:100μmol/L的TSG保护作用最显著,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);TUNEL法荧光显微镜观察细胞凋亡情况,与WT组相比,APP组的凋亡率升高,与APP组相比,TSG组的凋亡率降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);JC-1法检测细胞线粒体膜电位;与WT组相比,APP组的膜电位降低,与APP组相比,TSG组膜电位升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);WB检测PACS-2的蛋白表达:与WT组相比,APP组的PACS-2表达升高,与APP组相比,TSG组的PACS-2表达降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);RT-qPCR检测PACS-2的mRNA表达:与WT组相比,APP组的PACS-2表达升高,与APP组相比,TSG组的PACS-2表达降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 PACS-2在AD的发生、发展中有重要作用,其上调可能促进AD的发生,脑保护药物TSG可能通过下调PACS-2抑制AD模型细胞凋亡并改善线粒体功能发挥细胞保护作用。
[关键词] PACS-2;阿尔茨海默病;N2a/APP695swe细胞;线粒体功能障碍;细胞凋亡
[中图分类号] R741 [文献标识码] A [DOI] 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2024.05.003
Effect of PACS-2 on the development of Alzheimers disease
WANG Yanyun1, YE Qunying1, QIAN Jun1, LIU Zhipeng1, LUO Hongbo1, LI Yun2
1.Department of Neurology, the Fifth Affiliated (Zhuhai) Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong, China; 2.Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, the Fifth Affiliated (Zhuhai) Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the involvement of phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein-2 (PACS-2) in mitochondrial function and apoptosis in N2a/APP695swe cells and further explore the role and significance of PACS-2 in the development of Alzheimers disease (AD). Methods The CCK8 method was used to analyze the cell survival rate of N2a/APP695swe cells treated with different concentrations of tetrahydroxy stilbene glycoside (TSG) for 48h and to select the appropriate concentration of TSG for subsequent experiments. N2a/WT cells and N2a/APP695swe cells were routinely cultured in vitro, and the experimental cells were divided into 3 groups: blank control group (WT group): N2a/WT cells; model group (APP group): N2a/APP695swe cells; treatment group (TSG group): N2a/APP695swe cells with appropriate concentrations of TSG intervention. TUNEL method to observe apoptosis by fluorescence microscopy; JC-1 method for flow detection of cellular mitochondrial membrane potential; WB to detect protein expression of PACS-2; RT-qPCR to detect PACS-2 mRNA expression. Results CCK8 method was used to analyze the cell survival rate of different concentrations of TSG acting on cells after 48h: the protective effect of 100 μmol/L TSG was the most significant and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.01). The TUNEL method of fluorescence microscopy observed the apoptosis: compared with the WT group, the apoptosis rate of APP group was increased, compared with the APP group, the apoptosis rate of TSG group was decreased, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The JC-1 method was used to detect the mitochondrial membrane potential of cells: compared with the WT group, the membrane potential of APP group was decreased, compared with the APP group, the membrane potential of TSG group was increased, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05); Western blot (WB) detection of PACS-2 protein expression: compared with the WT group, PACS-2 expression was significantly higher in the APP group, and compared with the APP group, PACS-2 expression was significantly lower in the TSG group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05); The RT-qPCR detected the mRNA expression of PACS-2: the expression of PACS-2 was elevated in the APP group compared with the WT group and decreased in the TSG group compared with the APP group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). Conclusion PACS-2 has an important role in the development of AD, and its upregulation may promote the development of AD. The cerebroprotective drug TSG may exert cytoprotective effects by downregulating PACS-2 to inhibit apoptosis and improve mitochondrial function in AD model cells.
[Key words] Phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein-2; Alzheimers disease; N2a/APP695swe cell; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Apoptosis
阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimers disease,AD)是一种以认知功能障碍和记忆力减退为主要临床表现的神经退行性变性疾病,主要病理改变为β淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β peptides,Aβ)沉积、Tau蛋白(Tau protein,Tau)高度磷酸化,以及它们所形成的老年斑、神经纤维缠结[1]。AD的发病人数逐年上升,在未来30年中国AD的患病人数将大幅度上升[2]。然而目前并无有效的预防或治疗措施,因此寻找AD的有效治疗药物刻不容缓。研究报道,在AD的典型病理改变发生之前AD患者存在一些与线粒体相关内质网膜(mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane,MAM)结构和功能异常相关的早期病理变化,如线粒体动力学改变、细胞凋亡等[3]。MAM是线粒体外膜与内质网膜之间距离约为10~30nm的物理连接,调节MAM上存在的蛋白质及其相关蛋白复合物可参与细胞生命活动过程及MAM的形成,如磷酸呋喃酸性簇分选蛋白-2(phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein-2,PACS-2)、线粒体融合蛋白2(mitofusion2,Mfn2)、三磷酸肌醇受体(inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor,IP3R)等[4-5]。MAM如何参与并影响AD的发生、发展的机制目前研究尚未完全阐明。近年来MAM及其上的蛋白及蛋白复合物成为神经退行性变性疾病研究中的热点,但PACS-2在阿尔茨海默病中的报道目前相对少见。PACS-2是MAM上的一种多功能分选蛋白,在细胞稳态和细胞凋亡中发挥一定作用[6]。研究报道通过抑制PACS-2可以阻止线粒体裂变及细胞凋亡[7]。AD患者同样表现出线粒体功能障碍及细胞凋亡,是否PACS-2在AD的发生、发展中有一定的意义呢?二苯乙烯苷(tetrahydroxy stilbene glycoside,TSG)是中药何首乌特有的关键活性成分,化学名为2,3,5,4-四羟基二苯乙烯2-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷,相对分子质量为406.39[8]。相关报道及课题前期研究表明,TSG具有显著且明确的神经保护作用[9–13]。因此,本研究使用TSG干预细胞作为治疗对照组。在AD的多种发病机制假说中被大量的研究者普遍认可的假说是淀粉样蛋白级联反应,N2a/APP695swe细胞具有很好的Aβ堆积和淀粉样斑块沉积特点[14]。因此,本研究使用N2a/APP695swe细胞作为模型细胞,通过分析 N2a/APP695swe细胞与N2a细胞的凋亡情况、膜电位变化、PACS-2的蛋白和基因表达情况,初步探究PACS-2在阿尔茨海默病发生发展中的作用及意义,为AD的防治药物研究提供新理论及新靶点。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验细胞
小鼠脑神经瘤细胞(neuro-2a,N2a)野生型(wildtype,N2a/WT)购自武汉益普生物科技有限公司,稳定表达Swedish家族突变基因人APP695的N2a细胞(N2a/APP695swe)由河南文特尔生物技术有限公司构建(伦理审查批件编号[2023] 2023ZH0050号)。
1.2 主要药品、试剂及仪器
二苯乙烯苷(纯度98%)购自南京道斯夫生物科技有限公司;TUNEL细胞凋亡检测试剂盒(一步法)、线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒(JC-1)购自广州碧云天生物科技公司;Takara RNAiso Plus(Total RNA 提取试剂)购自北京宝日医生物技术有限公司;FlexCycler PCR仪购自德国耶拿公司。
1.3 细胞的培养与分组
完全培养基比例为40ml DMEM基础培养基:4ml胎牛血清:400μl青链霉素,细胞在二氧化碳培养箱(37℃,5%CO2)中培养。将实验分为3组,WT组:N2a/WT细胞;APP组:N2a/APP695swe细胞;TSG组:N2a/APP695swe细胞,CCK8篩选出最适浓度的TSG进行干预。
1.4 检测方法
按照CCK8试剂盒进行实验,用酶标仪检测样本在450nm处的A值,计算细胞存活率,细胞存活率=(实验组A值?空白组A值)/(对照组A值?空白组A值)?100(%)。按照TUNEL细胞凋亡检测试剂盒进行实验,荧光显微镜下观察并计算细胞凋亡率,细胞凋亡率(%)=Cy3与DAPI重合细胞数/DAPI细胞数(%)。按照线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒检测膜电位,线粒体膜电位较高时产生红色荧光,线粒体膜电位较低时产生绿色荧光,检测完成后使用Flow Jo软件分析,膜电位变化水平=红/绿。采用Western blot(WB)法检测蛋白表达,以GAPDH为内参,按照说明书裂解细胞,提蛋白,蛋白定量、变性,制胶,跑胶,转膜,封闭,孵育一抗和二抗,取适量ECL发光液滴于膜上(注意避光),曝光成像并采集,用Image J软件对条带进行灰度值分析测定。采用实时定量荧光RT-qPCR检测mRNA表达,反应条件:95℃ 5min,95℃ 15s,60℃ 30s,总共40个循环。以GAPDH为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算PACS-2的mRNA相对表达量。设计引物序列见表1。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 26.0统计学软件对数据进行处理分析。实验独立重复3次,计量资料先进行正态性检验、方差齐性检验,符合正态分布或近似正态分布的均采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用两独立样本t检验,多组间比较使用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)和LSD-t检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
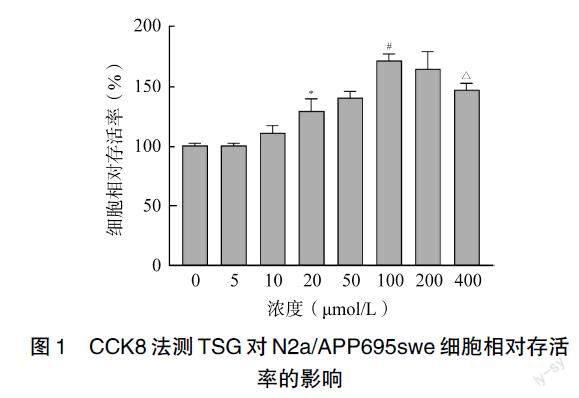
2.1 二苯乙烯苷的最适浓度
通过CCK8法检测N2a/APP695swe细胞的存活率,实验结果发现不同浓度的TSG(0、5、10、20、50、100、200、400μmol/L)处理细胞48h后,细胞的相对存活率均在100%以上,其中100μmol/L的TSG对细胞存活率的影响最顯著(P<0.01,图1),因此笔者选择100μmol /L的TSG进行后续实验。
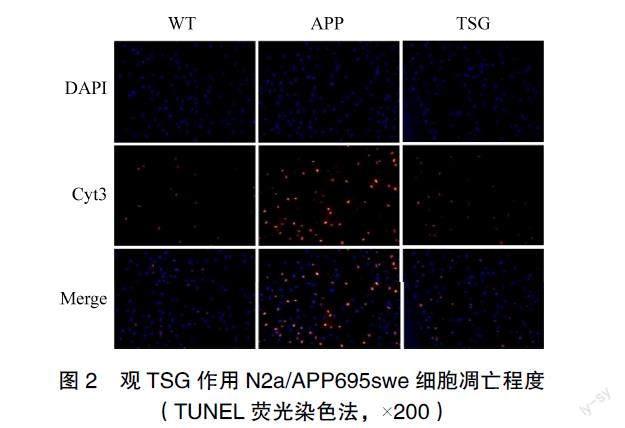
2.2 细胞凋亡程度比较
与WT组相比,APP组的凋亡率升高,与APP组相比,TSG组的凋亡率降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图2~3。
2.3 线粒体膜电位的比较
与WT组相比,APP组膜电位降低,与APP组相比,TSG组膜电位升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图4。
2.4 PACS-2蛋白表达比较
与WT组相比,APP组的PACS-2表达升高;与APP组相比,TSG组的PACS-2表达降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图5。
2.5 PACS-2的mRNA表达比较
与WT组相比,APP组的PACS-2表达增加,与APP组相比,TSG组的PACS-2表达降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图6。
3 讨论
AD是国际上重大的医学和社会问题,威胁老年人的生命和健康、降低老年人的生命质量、给每个家庭以及社会带来沉重负担,然而当前并无有效的预防或治疗措施。大量研究证明通过调节线粒体功能障碍诱导的细胞凋亡是中药治疗神经退行性疾病的潜在治疗策略之一[15]。线粒体是一个不断的移动、融合和分裂的动态细胞器,通过融合和分裂改变其形状以适应其代谢环境维持线粒体功能,调节线粒体内环境平衡并维持细胞活力[16]。研究报道,在MAM上,淀粉样前体蛋白被γ分泌酶切割形成Aβ,Aβ与多种蛋白质相互作用破坏线粒体膜电位使其下降,引起线粒体功能障碍并释放大量细胞色素C,诱导细胞凋亡[17]。PACS-2是MAM形成的关键调节因子[18]。PACS-2基因敲除的糖尿病小鼠出现MAM破坏,内质网应激,线粒体自噬与分裂,线粒体功能不良及肾凋亡,其过表达可通过稳定MAM完整性减轻糖尿病肾小管损伤[19]。PACS-2的敲低破坏了 MAM接触并损害了线粒体的形成和线粒体自噬,增强了血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[20]。PACS-2的高表达有助于富集内质网-线粒体相互作用[21]。PACS-2的基因突变型PACS-2 e209K 改变了PACS-2蛋白的抑制作用,增加细胞死亡增加[22]。PACS-2通过介导抗凋亡Bcl-xL促进细胞存活[23]。另有研究报道,PACS-2可作为一个促凋亡蛋白,抑制PACS-2后能够阻止Caspases触发的细胞凋亡[7]。以上提示不同研究者之间存在差异,可能是由于不同实验条件及PACS-2在不同疾病中的作用及意义不同所致。
本研究结果提示,与N2a细胞相比,N2a/APP695swe细胞凋亡程度增加、线粒体膜电位降低、PACS-2的蛋白和基因表达增加,而经过脑保护药物TSG处理后,细胞的凋亡程度降低、线粒体膜电位升高、PACS-2的蛋白和基因表达降低,提示PACS-2上调可能引起线粒体功能障碍、加重细胞凋亡,进一步促进AD的发生、发展。但这仅仅是初步的探索结果,后期课题组将增加PACS-2的过表达及抑制组,进一步探究PACS-2在AD中的作用通路,为防治AD的提供有效作用靶点,为后期开发针对分子连接结构的靶向性疗法提供新的研究思路和治疗策略。
利益冲突:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
[参考文献]
[1] 周玲玲, 钱康, 杨鹏, 等. 阿尔茨海默病的线粒体氧化应激及靶向递送系统研究进展[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57(6): 1630–1640.
[2] 王英全, 梁景宏, 贾瑞霞, 等. 2020-2050年中国阿尔茨海默病患病情况预测研究[J]. 阿尔茨海默病及相关病, 2019, 2(1): 289–298.
[3] AREA-GOMEZ E, SCHON E A. Alzheimer disease[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 997: 149–156.
[4] MAO H, CHEN W, CHEN L, et al. Potential role of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins in diseases[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, 199: 115011.
[5] 周娟平, 蘇刚, 陈丽霞, 等. 线粒体相关内质网膜在神经退行性疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2020, 42(8): 1465–1471.
[6] SIMMEN T, ASLAN J E, Blagoveshchenskaya A D, et al. PACS-2 controls endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria communication and Bid-mediated apoptosis[J]. EMBO J, 2005, 24(4): 717–729.
[7] LI C, LI L, YANG M, et al. PACS-2: A key regulator of mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs)[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 160: 105080.
[8] WANG C, DAI S, GONG L, et al. A Review of pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics of 2, 3, 5, 4?-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucosid[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 12: 791214.
[9] LUO H B, LI Y, LIU Z, et al. Protective effect of tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside on learning and memory by regulating synaptic plasticity[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2016, 11(9): 1480.
[10] GAO Y, HU K, YANG J, et al. Tetrahydroxy stilbene glycoside regulates TGF-β/fractalkine/CX3CR1 based on network pharmacology in APP/PS1 mouse model[J]. Neuropeptides, 2021, 90: 102197.
[11] LUO H, LI Y, GUO J, et al. Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside improved the behavioral disorders of APP695V717I transgenic mice by inhibiting the expression of Beclin-1 and LC3-II[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2015, 35(3): 295–300.
[12] GAO D, CHEN C, HUANG R, et al. Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside ameliorates cognitive impairments and pathology in APP/PS1 transgenic mice[J]. Curr Med Sci, 2021, 41(2): 279–286.
[13] 羅红波, 杨金升, 石向群, 等. Aβ诱导内质网应激性凋亡通路的启动及二苯乙烯苷的影响[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版), 2011, 30(6): 855–860.
[14] PARONI G, BISCEGLIA P, SERIPA D. Understanding the amyloid hypothesis in alzheimers disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2019, 68(2): 493–510.
[15] LI R, WANG L Y, DUAN H X, et al. Regulation of mitochondrial dysfunction induced cell apoptosis is a potential therapeutic strategy for herbal medicine to treat neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 937289.
[16] MARTORELL-RIERA A, SEGARRA-MONDEJAR M, MU?OZ J P, et al. Mfn2 downregulation in excitotoxicity causes mitochondrial dysfunction and delayed neuronal death[J]. EMBO J, 2014, 33(20): 2388–2407.
[17] H?RAUD C, GOUFAK D, ANDO K, et al. Increased misfolding and truncation of tau in APP/PS1/tau transgenic mice compared to mutant tau mice[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2014, 62: 100–112.
[18] LI C, LI L, YANG M, et al. PACS-2 Ameliorates tubular injury by facilitating endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria contact and mitophagy in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Diabetes, 2022, 71(5): 1034–1050.
[19] XUE M, FANG T, SUN H, et al. PACS-2 attenuates diabetic kidney disease via the enhancement of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane formation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(12): 1107.
[20] MOULIS M, GROUSSET E, FACCINI J, et al. The multifunctional sorting protein PACS-2 controls mitophagosome formation in human vascular smooth muscle cells through mitochondria-ER contact sites[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(6): 638.
[21] CHEN S, CHE S, LI S, et al. High-fat diet exacerbated decabromodiphenyl ether-induced hepatocyte apoptosis via intensifying the transfer of Ca2+ from endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria[J]. Environ Pollut, 2022, 292(Pt A): 118297.
[22] ZANG R X, MUMBY M J, DIKEAKOS J D. The phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (PACS-2) E209K mutation responsible for PACS-2 syndrome increases susceptibility to apoptosis[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(38): 34378–34388.
[23] BARROSO-GONZ?LEZ J, AUCLAIR S, LUAN S, et al. PACS-2 mediates the ATM and NF-κB-dependent induction of anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL in response to DNA damage[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2016, 23(9): 1448–1457.
(收稿日期:2023–04–19)
(修回日期:2023–11–24)
