The prevention of high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice by Fucoidan
2024-01-19LIUXipengSUNJuanZHANGHaifeng
LIU Xi-peng, SUN Juan, ZHANG Hai-feng
Department of Clinical Nutrition, Ninth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective:To study the preventive effect of fucoidan on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high fat diet.Methods: The experimental mice were randomly divided into three groups: control group, high-fat diet group and fucoidan intervention group.The control group was fed a standard diet, and the other two groups were fed a high-fat diet.The control group and the high-fat diet group were given normal saline intragastric administration every day,and the intervention group was given intragastric administration of fucoidan polysaccharide solution at a dose of 100 mg∙kg-1∙d-1 once a day for continuous intervention for 12 weeks.After the last intragastric administration for 12 h, the body weight and liver weight of each group of mice were measured, and the liver index was calculated.The contents of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) in liver tissues of mice in each group were detected by biochemical kit.Hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE) was used to compare the pathological morphological changes of liver tissue in each group.The contents of inflammatory factor interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and oxidative stress index malondialdehyde (MDA), and the activities of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in liver tissues of mice in each group were determined.Results: Compared with the control group, the body weight and liver index of mice receiving high fat diet increased significantly (P<0.01).In addition,the contents of TG, TC, AST and ALT in liver tissue of high-fat diet group were significantly increased compared with that of control group (P<0.01).The liver tissue of mice in the high-fat diet group also showed significant pathological changes, accompanied by increased expression of inflammatory factors and a significant increase in oxidative stress response.However,compared with the mice in the high-fat diet group, the above indexes were significantly improved in the liver tissue of the mice treated with fucoidan (P<0.01).Conclusion: Fucoidan can inhibit liver lipid deposition, liver inflammation and oxidative stress induced by high fat diet.
1.Introduction
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic metabolic liver disease characterized by excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells[1].NAFLD is a common cause of chronic liver disease[2, 3].If not effectively treated, NAFLD may evolve into life-threatening diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer[4].In addition to liver damage, NAFLD is also closely related to diabetes,hypertension, metabolic syndrome, arteriosclerotic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases[5, 6].With economic development and improvement of living standards, the increase in food convenience leads to excessive intake of energy and dietary fat, which further increases the risk of NAFLD[7].NAFLD poses a serious threat to human health and places a heavy burden on healthcare systems.However, current treatments for NAFLD are not effective enough.
Fucoidan is a water-soluble chemical found in brown algae such as kelp and is known as sulfated heteropolysaccharide.It has a variety of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory,antioxidant, anti-tumor and hypolipidemic effects[8-12].Some studies have shown that the combination of low-molecular weight fucosic polysaccharide with high-stability fucoxanthine can regulate the leptin-adiponectin axis in adipocytes and hepatocytes, thereby regulating lipid and glycogen metabolism, alleviating insulin resistance, and having a certain inhibitory effect on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[13].However, at present, there are not enough research results to prove whether the inhibitory effect of fucoidan on NAFLD alone exists.In this study, we focused on the effects of fucoplite polysaccharides on lipid accumulation,inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver of mice with high-fat diet-induced NAFLD, aiming to provide a new research direction for the prevention of high-fat diet-induced NAFLD.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Main materials and reagents
Algae polysaccharides, purchased from Beijing Qisong Biotechnology, The test kits for TC, TG, ALT and AST are from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, GSH, MDA assay kits are all from Shanghai Yuanye Biological Company.Mouse IL-6 and mouse TNF-ELISA kits were purchased from Beijing Tongli Haiyuan Biotechnology Company.
2.1.2 Experimental animals and forage
In this study, 18 SPF C57BL/6J male mice with body weights ranging from 18 to 25 grams were selected.These mice were routinely housed in animal houses with individual aerated cages(IVC) that provided 12 hours of light per day and a nighttime cycle.The temperature of the animal room is maintained at 22 ℃, and the humidity is controlled at 50% to 60%.We adopted the high-fat forage (XTHF60) provided by Nanjing Synergetics Bioengineering,which consists of 60% fat 20% carbohydrate and 20% protein.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Grouping, modeling, and administration
After 1 week of adaptive feeding, male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into three groups: control group, high-fat diet group and fucoplite polysaccharide intervention group, with 6 mice in each group.Mice in the control group continued to be fed a standard diet, while mice in the other two groups were fed a highfat diet.At the same time, the mice in the control group and the high-fat diet group were given normal saline, while the mice in the intervention group were given the fucoidan solution (100 mg∙kg-1∙d-1).The drug was administered once a day for a total of 12 weeks.
2.2.2 Measurement of body mass, liver mass and liver index
12 h after the last intervention, the mice were killed by cervical dislocation and blood samples were taken from the eyeballs.Subsequently, the liver tissue of the mice was isolated and the tissue fluid on the surface was removed using filter paper.Then, the mass of the liver was weighed using a precision balance and the liver index was calculated (liver index %= liver mass/body mass *100%).
2.2.3 The contents of total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride(TG) in mouse liver were determined
Mouse liver tissue from the same part was taken, put into precooled normal saline, placed in an ice water bath, cut up and homogenized with a tissue homogenizer.Then, centrifuge at 4 ℃,10 000 g for 10 min, take the supernatant and put it on the ice to be measured.The contents of TC and TG in liver tissue of mice in each group were determined according to the operation steps of the kit instructions.
2.2.4 HE staining of mouse liver tissue
In order to study the changes of liver histopathologic morphology of mice in each group, we need to obtain liver tissue from the same part and soak it in 10% formaldehyde solution for 24 h.Then, after the treatment steps of dehydration, transparency, wax dipping and paraffin embedding, the liver tissue was sliced using a microtome,and dried for use.Finally, staining was performed according to the instructions of HE staining kit, and the changes of liver histopathological morphology of mice in each group were observed under light microscope.
2.2.5 Determination of inflammation and oxidative stress in mouse liver tissue
Mouse liver tissue from the same part was taken and evenly stirred according to the above steps, centrifuged at 4 ℃,10 000 g for 10 min, and the supernatant was taken out and placed on the ice to be measured.According to the instructions of the kit, the contents of IL-6 and TNF-α in liver tissues of mice in each group were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The activity of SOD, GSH-Px and content of MDA in liver tissues of mice in each group were determined by spectrophotometry.
2.3 Statistical analysis of data
SPSS 26.0 software was used for statistical analysis of the collected data.Shapiro-Wilk method was used to test the normality of the data and Levene method to test the homogeneity of variance of the data.If the data conform to a normal distribution and the condition for homogeneity of variance is satisfied, these data are represented as±s.For the comparison of multiple groups, we will use one-way ANOVA, and for the comparison between groups, we will use t test.When the P-value is less than 0.05, it indicates that the difference is statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 The body weight, liver mass and liver index of mice in different groups were compared
The body weight and liver weight of mice were measured, and the liver index was calculated.The results showed that the body weight, liver mass and liver index of mice in the high-fat diet group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.01).These results suggest that a high-fat diet may lead to fat gain in mice and trigger non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).In addition,compared with the high-fat diet group, the body weight, liver mass and liver index of mice in the intervention group supplemented with fucoidan were significantly reduced (P<0.01).For details, see Table 1.
Tab 1 Determination results of body weight, liver weight and liver index of mice in each group (n=6,±s)

Tab 1 Determination results of body weight, liver weight and liver index of mice in each group (n=6,±s)
Note:vs.control group,*P<0.01;vs.HFD group,# P<0.01
group weight(g) Liver weight(g) Liver index(%)Control group 30.83±1.92 1.32±0.15 4.27±0.21 High-fat diet group 43.23±0.99* 2.60±0.21* 6.00±0.19*fucoidan intervention group(100mg/kg) 39.00±1.28# 1.97±0.15# 5.06±0.24#F 63.12 83.67 96.61
3.2 Comparison of lipid content in liver tissues of mice in each group
According to the experimental results, we can compare the difference of lipid content in the liver tissues of mice in each group.The contents of total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) in liver of mice in the high fat diet group were obviously higher than the control group (P<0.01).However, the contents of TC and TG in the liver of the intervention group were decreased to different degrees compared with those in the high-fat diet group (P<0.01).For details,see Table 2.
Tab 2 Content determination results of TC and TG in liver tissue of mice in eachgroup(n=6, ±s, mmol/g protein)
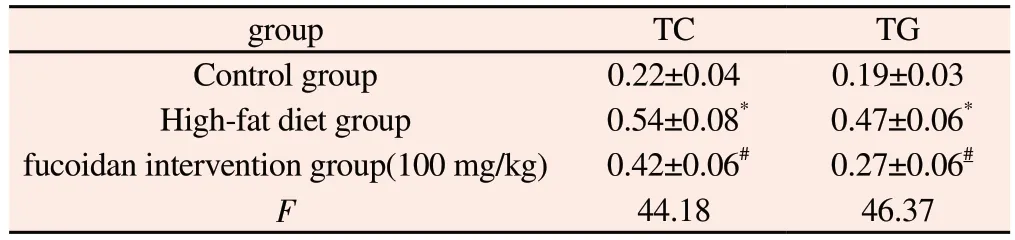
Tab 2 Content determination results of TC and TG in liver tissue of mice in eachgroup(n=6, ±s, mmol/g protein)
Note: vs.control group,*P<0.01;vs.HFD group,# P<0.01
group TC TG Control group 0.22±0.04 0.19±0.03 High-fat diet group 0.54±0.08* 0.47±0.06*fucoidan intervention group(100 mg/kg) 0.42±0.06#0.27±0.06#F 44.18 46.37
3.3 Results of histopathological analysis of mouse liver
After HE staining, it was observed that mice in the high-fat diet group showed significant pathological changes compared with the control group.These changes included hepatocyte enlargement,a marked increase in inflammatory cell infiltration, lipid droplets of varying sizes in hepatocytes, and balloon-like changes in some hepatocytes.Compared with the high-fat diet group, the liver histopathology of the fucoidan intervention group was significantly improved.These results further prove that fucoidan can reduce the liver lesions of non-alcoholic fatty liver induced by high fat diet,and also reduce the lipid accumulation in the liver.For details, See Figure 1.

Fig 1 Pathological conditions of liver tissues in each group (HE, ×200)
3.4 The liver function of mice in different groups was compared
During the experiment, it was found that the levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in liver tissue of mice receiving high-fat diet were significantly higher than those of control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.01).However, the levels of AST and ALT in liver tissue of mice in the high-fat diet group were significantly decreased after the intervention of fucoplite polysaccharide, and the difference was also statistically significant(P<0.01).For details, see Table 3.
Tab 3 Activity determination results of AST and ALT in liver tissue of mice in each group(n=6, ±s, U/L)

Tab 3 Activity determination results of AST and ALT in liver tissue of mice in each group(n=6, ±s, U/L)
Note: vs.control group,*P<0.01;vs.HFD group,#P<0.01
group AST ALT Control group 17.50±5.17 11.16±3.65 High-fat diet group 55.83±5.98* 42.17±4.71*fucoidan intervention group(100 mg/kg) 33.50±4.23# 31.33±5.16#F 83.02 71.62
3.5 The inflammation levels in liver tissues of mice in different groups were compared
The inflammatory factors in mouse liver tissue were detected by ELISA kit.The results showed that compared with the control group,the levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the liver tissue of mice in the highfat diet group were significantly increased (P<0.01).However,compared with the high-fat diet group, the levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the liver tissue of the mice in the intervention group were significantly decreased (P<0.01), which indicates that the fucoidan can inhibit the excessive increase of inflammatory factors caused by the high-fat diet.See Table 4 for details.
Tab 4 Content determination results of NF-κB,TNFα and IL-6 in liver tissue of mice in each group (n=6, ±s, pg/mL)

Tab 4 Content determination results of NF-κB,TNFα and IL-6 in liver tissue of mice in each group (n=6, ±s, pg/mL)
Note: vs.control group,*P<0.01;vs.HFD group,#P<0.01
group IL-6 TNF-α Control group 10.93±1.07 23.69±4.79 High-fat diet group 54.37±6.56* 75.67±6.02*fucoidan intervention group(100 mg/kg) 32.09±5.34# 48.90±5.73#F 116.74 132.00
3.6 The oxidative stress levels in liver tissues of different groups of mice were compared
The results showed that the activities of superoxide dismutase(SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in liver tissue of mice were significantly lower than those of the control group (P<0.01),while the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.01).This suggests that a high-fat diet causes oxidative stress responses in the liver of mice.In addition, the experimental results showed that the activities of SOD and GSH-Px in the liver tissue of mice in the intervention group were lower than those in the control group, but significantly higher than those in the high-fat diet group (P<0.01).MDA content was significantly lower than that of high fat diet group (P<0.01).These results indicate that the fucoidan can activate the anti-oxidative stress response in the liver tissue of mice and reduce the level of peroxidation stress in the liver.See Table 5 for details.
Tab 5 Determination results of SOD and GSH-Px activities and MDA content in liver tissue of micein each group (n=6, ±s)
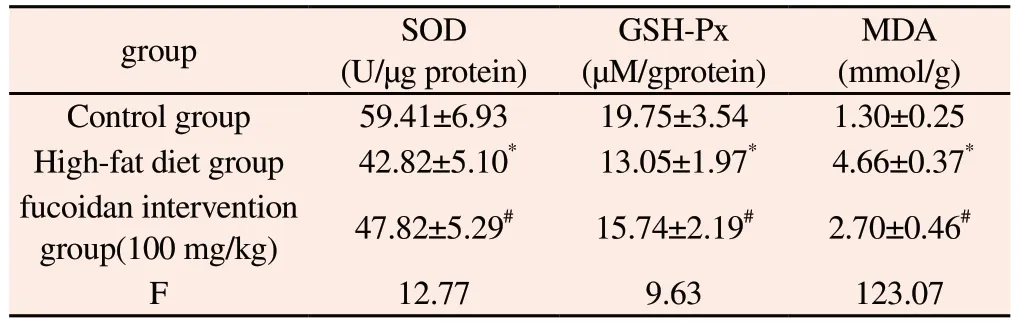
Tab 5 Determination results of SOD and GSH-Px activities and MDA content in liver tissue of micein each group (n=6, ±s)
Note:vs.control group,*P<0.01; vs.HFD group,#P<0.01
MDA(mmol/g)Control group 59.41±6.93 19.75±3.54 1.30±0.25 High-fat diet group 42.82±5.10* 13.05±1.97* 4.66±0.37*fucoidan intervention group(100 mg/kg) 47.82±5.29# 15.74±2.19# 2.70±0.46#F 12.77 9.63 123.07 group SOD(U/μg protein)GSH-Px(μM/gprotein)
4.Discussion
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) was originally a chronic metabolic liver disease characterized by ectopic fat deposition in the liver[14, 15].According to the degree of NAFLD, it can be divided into different stages such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFL),non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[4, 7, 16, 17].The incidence of NAFLD is increasing worldwide and is closely related to the incidence of obesity.Studies have shown that the prevalence of NAFLD in the world is about 25%, and the prevalence of NAFLD in obese people is much higher than that in the general population, reaching 65% to 85% [18].China is also one of the countries with a high prevalence of NAFLD.According to epidemiological survey data, the prevalence of NAFLD in mainland China ranges from 12.5% to 38%, becoming the second major cause of liver dysfunction and chronic liver disease in China[19].
The liver is the body’s main organ involved in fat metabolism.When people consume a high-fat diet rich in fat for a long time,the liver will increase the absorption of fat in the diet[20].If the rate of liver fat uptake exceeds the rate of expulsion, excessive accumulation of fat in the liver will result in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[21].The occurrence and development of human NAFLD can be effectively simulated by feeding mice with a highfat diet, and has been widely used in research[14,17, 22].Therefore, in this study, C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat diet to construct an animal model of NAFLD.In our study, we found that after feeding a high-fat diet for 12 weeks, the body weight, liver weight and liver index of mice increased significantly, and the liver histomathological examination showed that a large number of fat droplets accumulated in the liver, accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration,indicating that the high-fat diet caused obesity and fat accumulation in the liver of mice.However, a comparison of the mice that were simultaneously fed fucoidan (100 mg∙kg-1∙d-1) with those fed a highfat diet alone showed that fucoidan could significantly reduce the body weight, liver weight and liver index of the mice, and improve the pathological status of liver tissue.The results of this study indicate that the polysaccharide of fucoidan has the ability to inhibit the occurrence and development of NAFLD caused by high fat diet.
In the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD), the accumulation of triacylglycerol (TAG) in liver cells is considered to be an initial step[1].Therefore, reducing the excessive accumulation of fat in liver tissue, especially reducing the accumulation of tags in liver cells, is essential for the treatment and prevention of NAFLD.In this study, we found that the contents of TG and TC in the liver tissues of mice fed a high-fat diet were significantly higher than those of the control group, while the contents of TG and TC in the liver tissues of mice treated with fucoidan were significantly lower than those of mice fed a high-fat diet alone.In addition, the study also found that the intervention of fucoidan significantly reduced the increase of ALT and AST in the liver tissue of mice induced by a high-fat diet.This result suggests that fucoidan can reduce the accumulation of lipids in liver tissue and improve liver dysfunction caused by high fat diet.
Inflammatory response plays an important role in the occurrence and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [23,24].Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is the most serious phenotype in NAFLD.Besides the steatosis of liver tissue, the pathological features of NASH include hepatocyte swelling, inflammation of liver lobules, and hepatic fibrosis with or without[25].This study found that a high-fat diet significantly increased levels of the inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 in the liver tissue of mice.Inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 can promote hepatocyte steatosis,peripheral lipolysis, necrosis, apoptosis and inflammatory reaction,ultimately leading to NASH[26].In the intervention group of mice supplemented with fucoidan, we found that the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in the liver tissue of mice were significantly reduced compared with those in the high-fat diet group alone, suggesting that fucoidan can inhibit the inflammatory response in the liver tissue of NAFLD mice induced by high-fat diet.In addition, studies have shown that oxidative stress is an important cause of high-fat dietinduced liver damage and plays a crucial role in the progression of NAFL to NASH.MDA is an important marker of lipid peroxidation and is often used to evaluate the degree of tissue oxidative damage,while SOD and GSH-Px are important components of the body’s endogenous antioxidant system, which can clear ROS and prevent lipid peroxidation[1, 6].Therefore, this study also detected the levels of SOD, GSH-Px and MDA in mouse liver tissues[6, 25].The results showed that the fuoidan can significantly inhibit the decrease of SOD and GSH-Px levels and the production of MDA, a lipid peroxidation marker, in the liver tissues of mice induced by high fat diet, indicating that fucoidan has a certain inhibitory effect on the peroxidation stress of liver tissues of mice induced by high fat diet.
In summary, fucoidan can improve fatty ectopic deposition in hepatocytes induced by high fat diet, and inhibit the development of NAFL to NASH through anti- inflammatory and inhibition of oxidative stress levels, but the specific molecular mechanism remains to be further studied.
Ethics Statement: This study protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Ninth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine on February 8 2022, lot number: SH9H-2022-A023-SB, which complies with the guidelines for the management and use of laboratory animals.
Author contribution description:
Liu Xipeng was responsible for project design, relevant experiments, data analysis, writing ideas and writing papers; Sun Juan participated in data analysis and revised the paper; Zhang Haifeng was responsible for guiding the writing and finalizing the article.
Laboratory support: Central Laboratory of Ninth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Mechanism of Qishen Decoction inhibition of macrophage M1 type polarization by targeting TGR5-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome
- Epidemiological characteristics of hyperuricemia in metabolic syndrome and its different components in the physical examination population
- Analysis of E2F3 gene variants, expression and clinical significance in melanoma based on multiple databases
- Meta analysis and data mining of the method of yishenhuoxue in the treatment of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy
- Evaluation of the diagnostic efficacy of noninvasive diagnosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis B complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and significant liver fibrosis
- Discover the key genes for glomerular inflammation in patients with type II diabetic nephropathy based on bioinformatics and network pharmacology
