Correlation between Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway and patients with coronary heart disease
2023-11-20XINGBudianLIHuiQIANGTiantianWEITingLUYuanyuanKANGPinfangZHANGNingru
XING Bu‑dian, LI Hui, QIANG Tian‑tian, WEI Ting, LU Yuan‑yuan, KANG Pin‑fang,ZHANG Ning‑ru
1.Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, China
2.Basic and Clinical Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, China
3.Department of Ophthalmology, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, China
4.Bengbu Third People's Hospital Affiliated to Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To analyze the correlation between serum Nrf2 and GPX4 activity levels with coronary heart disease (CHD) and the severity of coronary artery disease, and to explore the role of ferroptosis mediated by its signaling pathway in the progression of CHD.Methods:A total of 540 patients suspected of CHD were selected for coronary angiography, of which 360 patients were diagnosed with CHD.The activity levels of Nrf2 and GPX4 in the serum of CHD patients were detected by ELISA, and the differences in the activities of Nrf2 and GPX4 in the presence or absence of CHD were statistically analyzed.Western blot detection of Nrf2 protein expression of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCS) in the control(CON)and CHD groups (90 cases each).The expression and significance of its signaling pathway in CHD patients were analyzed.Results: The activity levels of Nrf2 and GPX4 in the CHD group were lower than those in the CON group (P<0.05), and the expression levels of Nrf2 in PBMCs of the two groups were detected by Western blot.The protein expression level of Nrf2 in the CHD group (0.25±0.05) was down‑regulated compared with CON group (0.87±0.16)(P<0.05), indicating that Nrf2 protein expression level was low in CHD patients.Pearson correlation analysis showed that serum Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were negatively correlated with Gensini score (Nrf2: r=‑0.347, P<0.001; GPX4: r=‑0.423, P=0.001).Nrf2 and GPX4 were negatively correlated with TG (Nrf2: r=‑0.284, P<0.001; GPX4: r=‑0.275, P=0.001), Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were negatively correlated with LDL (Nrf2: r=‑0.418, P<0.001) 0.05; GPX4: r=‑0.426, P<0.05), Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were positively correlated with HDL (Nrf2: r=0.318,P<0.05; GPX4: r=0.428, P<0.05), and Nrf2 was positively correlated with GPX4 ( r=0.456,P<0.01).Conclusion: The ferroptosis pathway mediated by the Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway is closely related to the degree of coronary artery disease and the pathogenesis of CHD, and its mechanism may be related to the down‑regulation of the Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway.
1.Introduction
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is mainly caused by coronary artery stenosis or insufficient blood supply, which then leads to insufficient myocardial oxygen supply and blood supply, sharp increase of myocardial blood vessel oxygen consumption, and eventually myocardial necrosis[1-3].The epidemiological investigation results show that CHD has become a major disease that seriously endangers human life and health, showing a trend of younger age and increasing incidence year by year[4].
Glutathione peroxidase4 (GPX4) is an important antioxidant enzyme, which can reduce lipid ROS to non‑toxic lipid alcohols,reduce lipid peroxidation, effectively prevent cellular oxidative stress, and thus inhibit the process of iron death[5].Recent studies[6]have found that GPX4‑mediated iron death is closely related to CHD.Nrf2 antioxidants are an important signaling pathway for cellular oxidative stress and iron death[7,8].In recent years, relevant studies[9,10]have found that activation of Nrf2 can inhibit iron death by promoting the expression of GPX4.This study provides us with clues as to whether Nrf2 plays a role in CHD by regulating iron death through GPX4.At present, the pathogenesis of iron death mediated by Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway in CHD remains unclear.This study intends to determine the relationship between Nrf2 and GPX4 activity levels and CHD patients with different degrees of coronary artery stenosis by detecting Nrf2 and GPX4 levels in CHD patients, so as to provide a new method and basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment of CHD.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Material reagents
Nrf2 antibody (item number: 12721S; Origin: CST), GAPDH antibody (article number: 5174; Origin: CST, USA); ELISA kit:HumanNrf2, HumanGPX4 (Shanghai Yuduo)
2.2 Research object
A total of 540 patients suspected of CHD were collected from the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from June 2020 to June 2022, with an average age of (64.52±9.66) years.According to the diagnostic guidelines for CHD[11], CHD could be diagnosed with stenosis of any major coronary artery 50%.Among them, 360 patients were clearly diagnosed as CHD by coronary angiography,and 180 patients who underwent coronary angiography showed no obvious abnormality were included in the CON group.All enrolled patients signed informed consent.Exclusion criteria: previous history of myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, structural heart disease, malignant tumor diseases, rheumatic immune system diseases, endocrine and metabolic diseases, or recent use of drugs that reduce autoimmune function, degenerative diseases of the nervous system, stroke, atrial fibrillation and infectious diseases[12].All enrolled patients signed informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital (2019KY023).
2.3 Methods
2.3.1 Evaluation of coronary artery stenosis degree
Gensini score was used to calculate the stenosis degree of coronary artery lesions in patients[13].The stenosis degree of each vessel was assigned a score, and then multiplied by the corresponding weight coefficient.The sum of the scores of each coronary segment was the Gensini score.
2.3.2 Specimen collection
After all patients were admitted to the hospital on an empty stomach overnight, 10 mL peripheral venous blood was extracted into heparin anticoagulant test tubes, centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 10 min, supernatant was absorbed, and refrigerated at −80 ℃ for later use.
2.3.3 Serum Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were detected by ELISA
The expression levels of Nrf2 and GPX4 in serum of the subjects
were detected by HumanNrf2 and GPX4 (Shanghai Yuduo), and the operation was carried out in strict accordance with the instructions.
2.3.4 Western blot detection of Nrf2 protein expression of NRF2‑gpX4 signaling pathway in CHD group and CON group
The total protein of PBMCS was extracted, and the protein concentration of each group was determined by BCA protein quantitative method.The protein concentration of each group was configured with 10%SDS‑PAGE electrophoresis, PVDF membrane transfer, and the antibody dilution ratio was as follows: anti‑NRF2 rabbit monoclonal antibody 1:1 000, anti‑Gapdh rabbit monoclonal antibody 1:10 000.Incubation of primary and secondary antibodies;after film washing, ECL luminous liquid is exposed, and the imaging system obtains images[14].
2.3.5 Statistical processing
Test and Chi‑square test were used for comparison between groups,and Pearson analysis was used to analyze the correlation between indicators.The above data were analyzed by SPSS26.0 software.
3.Results
3.1 Analysis of subjects’ general information and biochemical indexes
Compared with CON group, age, smoking history, hypertension history, diabetes history, TG and LDL were all increased in CHD group.HDL, however, was lower (P<0.05); There were no significant differences in sex ratio, BMI, WBC, AST, ALT, TC, and Scr between the two groups (P<0.05) and the results are shown in Table 1.
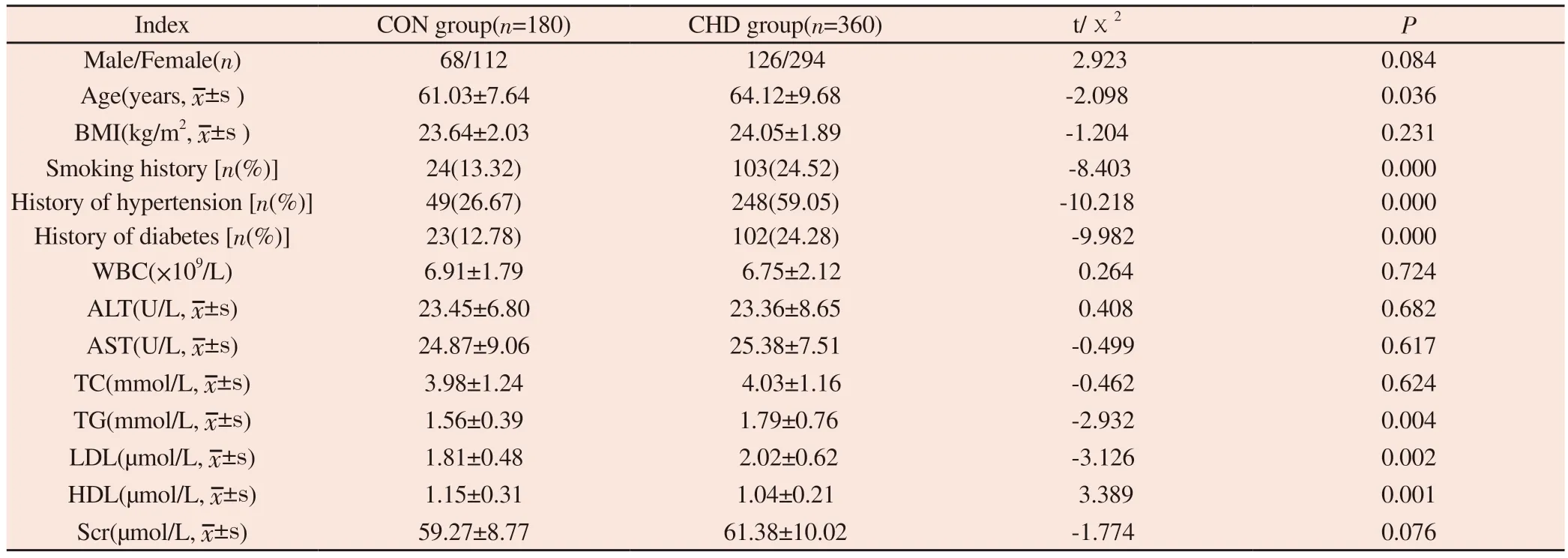
Tab 1 Comparison of general data and biochemical indexes between the CON group and the CHD group
3.2 Nrf2, GPX4 and Gensini scores of subjects in CON group and CHD group
Compared with CON group, serum Nrf2 and GPX4 activity levels in CHD group were decreased.However, Gensini scores increased significantly (P<0.05) Results are shown in Table 2.
Tab 2 Comparison of Nrf2, GPX4 and Gensini scores between the CON group and the CHD group(±s)
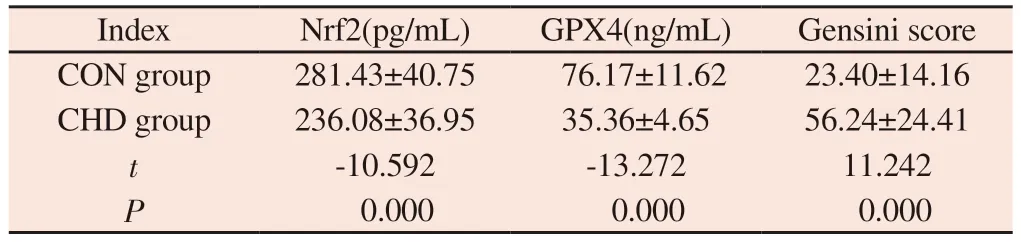
Tab 2 Comparison of Nrf2, GPX4 and Gensini scores between the CON group and the CHD group(±s)
Index Nrf2(pg/mL) GPX4(ng/mL) Gensini score CON group 281.43±40.75 76.17±11.62 23.40±14.16 CHD group 236.08±36.95 35.36±4.65 56.24±24.41 t‑10.592 ‑13.272 11.242 P 0.000 0.000 0.000
3.3 Nrf2 protein expression level in PBMCS of CON group and CHD group (90 cases each)
The protein expression level of Nrf2 in CHD group (0.25±0.05)was down‑regulated compared with that in CON group (0.87±0.16)(P<0.05), see Figure A and Figure B.

Fig 1 Protein bands in PBMCs of patients in the CON and CHD groups
3.4 Correlation between Nrf2, GPX4, Gensini score and blood indexes
Serum Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were negatively correlated with Gensini score by Pearson correlation analysis (Nrf2: r=‑0.347,P=0.001; GPX4: r=‑0.423, P=0.001); Nrf2 and GPX4 were negatively correlated with TG (Nrf2: r=‑0.284, P=0.001; GPX4: r=‑0.275, P=0.001); Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were negatively correlated with LDL (Nrf2: r=‑0.418, P<0.05; GPX4: r=‑0.426, P<0.05);Nrf2 and GPX4 levels were positively correlated with HDL (Nrf2:r=0.318, P<0.05; GPX4: r=0.428, P<0.05); Nrf2 was positively correlated with GPX4 (r=0.456, P<0.01), and the results are shown in Table 3.

Fig 2 Relative magnitude of protein expression in PBMCs of two groups of patients

Tab 3 Correlation analysis of serum Nrf2 and GPX4 activity levels with Gensini scores and blood indexes
4.Discussion
CHD is the most common and major disease in clinical practice,mainly caused by vascular stenosis or blockage mediated by coronary atherosclerosis.With the aggravation of coronary artery lesions, the number of invasive coronary arteries increases, which is more likely to cause coronary artery stenosis or insufficient blood supply, and ultimately lead to myocardial dysfunction[15,16].So far,existing clinical studies have not clarified the pathogenesis of CHD.The characteristics of high disability rate and fatality rate of CHD will not only affect the life safety and quality of life of patients, but also increase the economic burden of patients’ families and even society.Therefore, in‑depth research on the pathogenesis of CHD is helpful for diagnosis, treatment and early prevention of CHD.
Studies have shown that dyslipidemia is an important risk factor for CHD[17].It has been pointed out in relevant studies[18,19]that hyperTGemia, hyperldldemia and hypoHDL emia are closely related to the occurrence and development of CHD, and by improving the blood lipid level of patients, it is beneficial to relieve the symptoms of CHD and promote the outcome of the disease.In this study, TG and LDL in the CHD group were significantly higher than those in the CON group, while HDL levels were decreased, which may be related to atherosclerosis caused by dyslipidemia.
Iron death is an iron‑dependent, non‑apoptotic form of cell death that depends on the accumulation of lipid reactive oxygen species(ROS) of iron.The continuous accumulation of lipid ROS in cells triggers intracellular oxidative stress and gradually induces iron death in cells[20].In recent years, many studies have shown that iron death is closely related to CHD[21,22].
GPX4 is a selenase that selectively neutralizes lipid hydroperoxides and is considered to be an important endogenous regulator of iron death.Studies have shown that[23], inhibition of GPX4 activity can not metabolize lipid peroxidation in the catalytic reduction reaction,and the continuous accumulation of Fe2+and ROS generated by lipid peroxidation eventually leads to iron death.Because GPX4 plays an important role in the process of iron death, it has become a hot research topic for regulating iron death.Meng et al[24]observed in the diabetic atherosclerotic mouse model that decreased GPX4 activity caused lipid peroxidation, which in turn caused iron death and promoted the development of atherosclerosis, while iron death inhibitors slowed down the development of atherosclerosis by increasing GPX4 activity and reducing the production of lipid reactive oxygen species.This phenomenon suggests that GPX4 activity may be potentially associated with CHD in myocardial ischemic disease.FENG et al[25]found that iron death inhibitors can reduce the production of lipid reactive oxygen species by increasing GPX4 activity, thus protecting rat hearts and reducing ischemic injury.In addition, Li et al[26]found through experiments that restoring GPX4 activity level could inhibit iron death and thus protect mouse myocardia from ischemia‑reperfusion injury.Recent clinical experimental studies[6]found that the level of GPX4 activity in patients with ACS was significantly lower than that in patients without ACS.This is similar to the results of this study, which found that compared with CON group, GPX4 activity level was decreased in CHD patients, suggesting that GPX4 may be involved in the occurrence and development of CHD.
As a major regulator of lipid peroxidation and iron death in vivo,Nrf2 is not only a participant in oxidative stress and iron death,but also a regulator of oxidative stress and iron death process.Nrf2 regulates enzymes and proteins related to iron death, such as GPX4[9].Yu et al[27] found that inhibition of Nrf2 can increase iron death by down‑regulating GPX4 expression, thus promoting the formation of atherosclerosis in mice, while inhibition of iron death can up‑regulate GPX4 expression by activating Nrf2,inhibit the process of iron death, and thus inhibit the formation of atherosclerosis in mice.This phenomenon suggests that Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway mediated iron death may be potentially associated with CHD.Naringin has been reported to reduce myocardial ischemia‑reperfusion injury in rats by regulating Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway and inhibiting iron death[28].Chen Yu et al[10]observed through experiments that activation of Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway could inhibit iron death, thus reducing myocardial ischemic injury in rats.The results of this study showed that compared with the CON group, the serum Nrf2 activity level of patients in the CHD group was significantly reduced.In addition,this study improved the determination of Nrf2 protein concentration in PBMCS, and the change trend of the protein concentration in WB was consistent with the ELISA results.Miao Ying[29]also reported similar results.Pearson correlation analysis showed that serum Nrf2 was positively correlated with GPX4 in patients with CHD, and its mechanism of action may be related to oxidative stress and iron death, which may be involved in the occurrence and development of CHD.
Gensini score is an effective method widely used to assess the severity of coronary artery stenosis, and the higher the score, the more serious the coronary artery stenosis[30].This study found that both Nrf2 and GPX4 were negatively correlated with Gensini scores,suggesting that iron death mediated by NRF2‑gpX4 signaling pathway was related to the severity of CHD lesions, which has certain positive significance for evaluating the severity of CHD patients.
In summary, compared with CON group, serum Nrf2 and GPX4 activity levels were decreased in CHD group; Nrf2 was positively correlated with TG, LDL, and GPX4 levels; Nrf2 and GPX4 were negatively correlated with HDL, and both Nrf2 and GPX4 were negatively correlated with Gensini scores.Therefore, iron death mediated by Nrf2‑GPX4 signaling pathway has certain reference value for determining the degree of coronary artery lesions and the pathogenesis of CHD.This study has the following limitations:the sample size included in this study is small and data errors are inevitable.Therefore, the results of this study need to be further verified by large‑scale multi‑center research.
Author’s contribution:
Xing Bu‑dian: data analysis and article writing; Qiang Tian‑tian,Wei Ting, Lu Yuan‑yuan: Collected data, responsible for related experimental operation; Li Hui, Kang Pin‑fang, Zhang Ning‑ru:Design experiment, guide writing.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Mechanism of FXR alleviating the liver fibrosis by regulating perilipin 5
- Study on the mechanism of effect of Daodi Tongguan Decoction on rats with premature ovarian failure
- Establishment and validation of a nomogram for predicting the risk of liver inflammation in chronic HBV infection
- Clinical study of different modes of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of post‑stroke executive dysfunction
- Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of extended right liver transplantation versus whole liver transplantation
- Quality of life of hospitalized patients after lung cancer operation and analysis of influencing factors
