Mechanism of Qiliqiangxin capsule on the regulation of IP3Rs/GRP75/VDAC1 gene in myocardial infarction rat heart
2023-11-14JIXiaodiYANGDingCUIXiyuanLOULixiaNIEBoZHAOJiuliZHAOMingjingWUAiming
JI Xiao-di, YANG Ding, CUI Xi-yuan, LOU Li-xia, NIE Bo, ZHAO Jiu-li, ZHAO Ming-jing,WU Ai-ming
Dongzhimen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education and Beijing Key Laboratory of Internal Medicine of Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100700, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the regulatory effect of Qiliqiangxin Capsule on mitochondrial Ca2+related genes in rats with myocardial infarction(MI).Methods: The rat model of MI was established by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery.After operation, the rats were randomly assigned to the model group, the Qiliqiangxin group and the captopril group; a sham-operated group was also available as a control.After four weeks of treatment, the extent of infarction in rats was observed by gross cardiac structure and the morphological changes of myocardial histopathology were observed by HE staining.Detection of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport-related genes such as inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor 2 (IP3R2), glucose regulated protein 75 (GRP75), voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1), and mitofusion 2 (Mfn2) and mitochondrial apoptosis-related genes such as B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2 related X protein (Bax) mRNA expression changes was measured by RT-PCR in the infarct margins of the heart; Western blot was used to detect changes in Bcl-2, Bax protein expression in myocardial tissue.The rate of apoptosis in cardiac myocardial tissue was detected by TUNEL staining.Results: Compared with the sham group, the anterior left ventricular wall of the model group showed a large area of infarction, and the structure of myocardial tissue was disordered.The mRNA expression level of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport-related genes such as IP3R2, GRP75, VDAC1, and Mfn2 were significantly increased (P<0.05, P<0.01);The mRNA and protein expression of Bcl-2, a molecule related to mitochondrial apoptosis, were significantly decreased (P<0.01), while the mRNA and protein expression of Bax were significantly increased (P<0.01); and apoptosis rate was significantly increased (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the infarct size of cardiac gross specimens in the Qiliqiangxin group and the captopril group was reduced and myocardial fibers were relatively well ordered;The mRNA expression of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport-related genes such as IP3R2, GRP75,VDAC1, and Mfn2 were significantly reduced (P<0.01); the mRNA and protein expression of Bcl-2, a molecule related to mitochondrial apoptosis, were increased (P<0.05, P<0.01), and the mRNA and protein expression of Bax were significantly decreased (P<0.05, P<0.01).and apoptosis rate was significantly decreased (P<0.01).Conclusion: Qiliqiangxin Capsule can improve the morphological structure of the heart of rats with MI, and its mechanism is related to regulation of the gene expression of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport complex IP3R2/GRP75/VDAC1, thereby inhibiting apoptosis.✉Corresponding author: WU Ai-ming.
1.Introduction
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a common cardiovascular emergency that can cause a wide range of pathological changes in the heart, including apoptosis, inflammatory response, myocardial fibrosis, and disturbances in energy metabolism.Among them, the imbalance of Ca2+homeostasis is the basis of many pathological changes after MI[1].Our group found that there was excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress in MI rats, which in turn led to massive apoptosis [2, 3].However, the exact regulatory mechanism is not yet clear.A review of the literature revealed that myocardial ischemia is accompanied by mitochondrial Ca2+overload , and Ca2+-mediated apoptotic signals induce apoptosis in the mitochondrial pathway[4],This severely damages the morphological structure and function of the heart, leading to uncoupling of systolic and diastolic functions, which in turn induces arrhythmias and heart failure[5, 6].Therefore, correction of imbalance in mitochondrial Ca2+homeostasis is essential for the treatment of MI[7, 8].
Clinically, Qiliqiangxin Capsules (QLQX) is widely used in the treatment of heart failure after MI, which can improve patients’cardiac function and their quality of life[9, 10].Studies have shown that QLQX can directly regulate cardiomyocyte Ca2+signaling and exert myocardial protective effects[11, 12].However, its regulatory effect on the expression of genes related to the mitochondrial Ca2+transport complex has not been reported.The aim of this study was to preliminarily investigate the pharmacological mechanism of QLQX in regulating the gene expression of IP3Rs/GRP75/VDAC1 of mitochondrial Ca2+transport complex in the treatment of MI from the genetic level, and to provide new experimental evidence for the clinical application of QLQX.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Animal
Sprague-Dawley rat, weight (200±20) g, 6 weeks old, purchased from Weitonglihua Experimental Technology Ltd (Beijing), [license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2012-0001].The animals used in this study were approved by the Animal Management Committee of Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.All study protocols involved were in accordance with the guidelines of the Chinese Ethics Committee on experimental animals.
2.1.2 Medicines and Reagents
QLQX, provided by Yiling Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd (Shijiazhuang)(GMP Z20040141); Captopril, supplied by Sino-US Shanghai Squibb Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd (lot number: AAN9869);Trizol(Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA, lot number: 15596026); PCR amplification kit (Applied Biosystems, lot 4472897); TUNEL kit(Promega, lot G3250); cell fixative (Shanghai Beyotime, lot P0098),fluorescent blocker (Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao, lot ZLI-9557) RIPA lysate (Shanghai Beyotime, lot no.P0013B), B lymphocytoma-2(Bcl-2) antibody (proteintech, 26593-1-AP), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) antibody (proteintech, 60267-1-Ig), GAPDH antibody( proteintech, 60004-1-Ig).
2.1.3 Instruments
FX-7202 electrocardiograph (Beijing, Futian); ALC-V8S small animal ventilator (Shanghai Olcott Biological Company); Gene Amp PCR system 9700 instrument (Applied Biosystems, USA);embedding machine, paraffin slicer (Leica, Germany), DM300 optical microscope (Leica, Germany); JA1003N electronic precision balance (Shanghai Precision Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.); 4 ℃centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA); biological microscope(Zeiss Axio Scope.A1).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Model Preparation
Referring to the literature, the MI model was established by ligating the anterior descending branch of the left coronary artery method[13].First, the rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% sodium pentobarbital (45 mg/kg).Subsequently, tracheal intubation was performed and connected to a ventilator (inhalationexpiration ratio 1:2, tidal volume 7 mL, respiratory rate 80 breaths/min).The ligature was performed at the left edge of the sternum in the precordial region between the 3rd and 4th ribs transversely, and the ligature was performed at the lower edge 2 mm between the cone of the pulmonary artery and the left auricle, and intraoperatively, the myocardial ischemia under the ligature site was seen to turn white,followed by layer-by-layer suture closure of the chest.The sham group served as the control group, and only open-chest threading without ligature was performed.After surgery, 40 U of penicillin was injected intraperitoneally for 3 consecutive days to prevent infection.
2.2.2 Grouping and drug administration
Rats with ST-segment elevation on the ECG immediately after surgery and 6-8 pathological Q waves on the ECG 24 h after surgery were selected, and the animals were randomly and evenly divided into the model group, the QLQX group and the captopril group according to the number of pathological Q waves.In addition, there was a sham group and there were 8 rats in each group.The QLQX group was given QLQX drug suspension 0.32 g/(Kg-d), the captopril group was given captopril suspension 2.25 mg/(Kg-d), and the sham and model groups were given an equal volume of 10 mL/(Kg-d)of deionized water starting from the second postoperative day by gavage for 4 weeks.
2.2.3 Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining
NBT staining was performed to visualize the area of infarction in rat hearts with reference to the literature[14].The thoracic cavity was opened, and rat hearts were quickly removed and soaked in precooled saline to remove blood stains.Atrial tissue was removed, and we cut continuous transverse sections of approximately 2 mm thick along the long axis of the heart, which were then placed in 2% NBT staining solution, protected from light, and incubated at a constant temperature of 37 ℃ for 1h.
2.2.4 HE staining
The 4um thick tissue sections were subjected to HE staining: baked at 60 ℃ for 1h, followed by xylene dewaxing, gradient ethanol hydration, tap water rinsing for 5 min, hematoxylin stained nuclei for 10 min, water washing for 10 s, hydrochloric acid alcohol fractionation for 30 s, water washing for 10 min.eosin staining for 10 min, water washing for 1 min.Subsequently myocardial tissue was dehydrated in gradient ethanol, transparent in xylene.Finally,we sealed the slices with neutral gum, dried them and observed the myocardial tissue morphology under the microscope.
2.2.5 Real-time fluorescence PCR
Total RNA from myocardial tissue was extracted by Trizol method,and its purity was ensured in the normal range with OD(260/280)between 1.8 and 2.0.The total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA according to the instructions.Real-Time PCR was used to detect the relative expression of target genes in each group.Amplification conditions: pre-denaturation 95℃ for 10 min,denaturation 95 ℃ for 30 s, annealing 55 ℃ for 30 s, extension 72℃ for 20 s, total 40 cycles.The relative expression of the target gene was calculated by the 2-△△CTmethod using GAPDH as the internal reference.The primer sequences are shown in Table 1.

Tab 1 PCR primer sequences
2.2.6 Western Blot
Total myocardial tissue proteins were extracted by RIPA lysis.Electrophoresis was performed by SDS-PAGE gels, followed by wet transfer method to electro-transfer the proteins onto NC membranes, then we used 5% skim milk powder for 1h closure,followed by incubation of primary antibodies Bcl-2 and Bax at 4 ℃ overnight.The next day, protein strips were incubated for 1h at room temperature using secondary antibodies, followed by chemiluminescence for observation.
2.2.7 TUNEL staining
The excised myocardial tissue sections were fully dewaxed in xylene and down-hydrated in gradient ethanol; subsequently immersed in cell fixative for 5 min, 20 μg/mL proteinase K solution was added and incubated for 10 min at room temperature, immersed again in cell fixative for 5 min, rinsed in PBS and incubated for 10 min with equilibration solution.rTdT buffer was added dropwise under light-proof environment and incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h.The reaction was finally terminated with 2X SSC.Anti-fluorescence quenching blocker containing DAPI was added dropwise.The green fluorescence indicating apoptotic nuclei and the blue fluorescence indicating normal nuclei can be observed under the microscope.The number of apoptotic nuclei as well as normal nuclei was counted using Image-Pro Plus, and the apoptosis rate was calculated for each group.
2.2.8 Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 25.0 software.The measurement data were expressed using the mean ± standard deviation (±s), and one-way ANOVA was used for comparison between groups.Data conforming to normal distribution with equal variance between groups were analyzed by LSD method and vice versa by Dunnett's T3 method.Differences were considered statistically significant at P<0.05.
3.Results
3.1 Evaluation of animal models
ECG measurements were performed before, immediately after,and 24 h after the left coronary artery ligation surgery.The results showed that the ECGs of the rats before surgery were in the normal range.The ECGs of the sham group showed no significant abnormal changes in the immediate postoperative period and 24 h postoperative period, while the ECGs of the model group showed ST-segment elevation in the immediate postoperative period and pathological Q waves in the 24 h postoperative period, suggesting myocardial ischemic injury and successful modeling of MI.The results are shown in Figure 1A.In addition, we further evaluated the modeling of MI by NBT staining, and the non-infarcted area showed purple-black coloration after staining, while the infarcted area was not colored.The results showed that the hearts of the sham rats showed a uniform purple-black color, which means no infarcted area, while the model rats had large unstained infarcted areas, which again proved the successful establishment of the MI model.The results are shown in Figure 1B.

Fig 1 Evaluation of myocardial infarction model
3.2 Gross cardiac structure observation
Compared with the sham group, the rats in the model group had a larger heart size and a white ischemic infarct zone, especially the thinning of the anterior wall of the left ventricle, and the infarcted myocardial tissue was replaced by connective tissue and collapsed extensively; compared with the model group, the rats in the QLQX and captopril groups had an improved heart structure and a smaller ischemic white infarct zone.The results are shown in Figure 2.
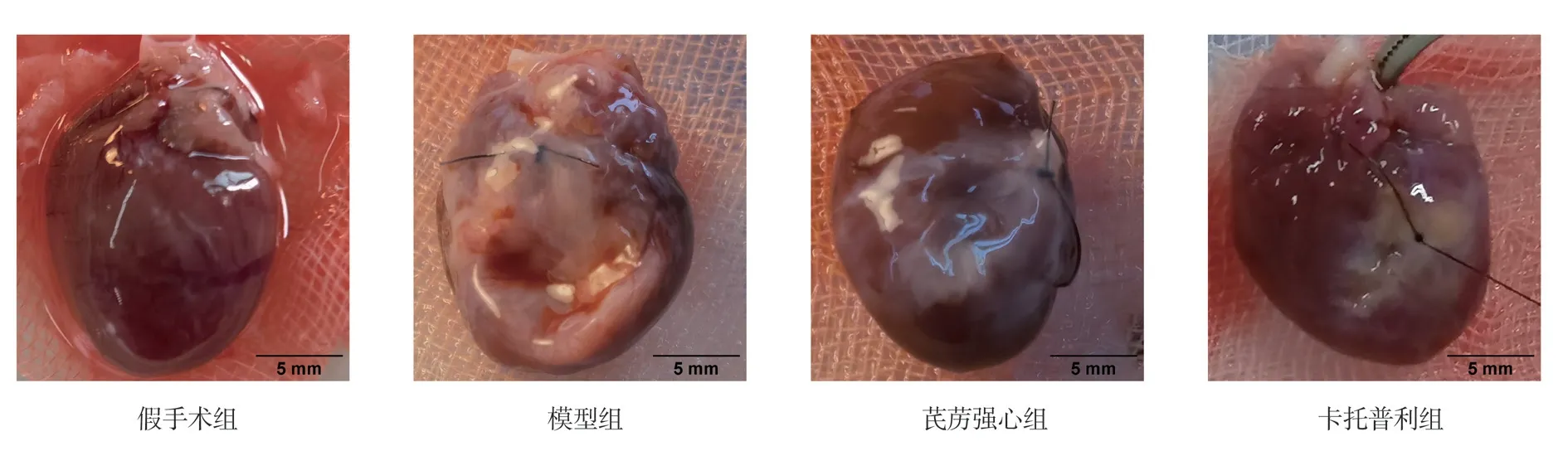
Fig 2 Gross structure of the heart of rats in each group
3.3 HE staining results of myocardial tissue
HE staining showed no abnormal changes in myocardial tissue morphology in the sham group, with clear myocardial fiber transverse lines, dense and neat arrangement, basically uniform nuclei size, and uniform red staining of cytoplasm.In the model group, myocardial tissue showed obvious cell degeneration and necrosis, myocardial fibers were broken, and the remaining myocardial cells were hypertrophied, with nuclear fixation and uneven cytoplasmic staining.Compared with the model group, the myocardial cell structure was improved and the histopathological damage was relatively less in the QLQX and captopril groups.The results are shown in Figure 3.

Fig 3 HE staining results of myocardial tissues of rats in each group (400 ×)
3.4 The mRNA expression of mitochondrial Ca2+ transportrelated genes
Compared with the sham group, the mRNA expression levels of inositol triphosphate receptor 2 (IP3R2), glucose regulatory protein 75 (GRP75), voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1), and mitochondrial fusion protein 2 (Mfn2) were significantly higher in the model group (P<0.05, P<0.01); compared with the model group,the mRNA expression levels of IP3R2, GRP75, VDAC1, and Mfn2 were significantly lower in the QLQX group and the captopril group(P<0.01).The results are shown in Table 2, Figure 4.
Tab 2 Expression of Ca2+ transport-related genes in each group(n=8, ±s)
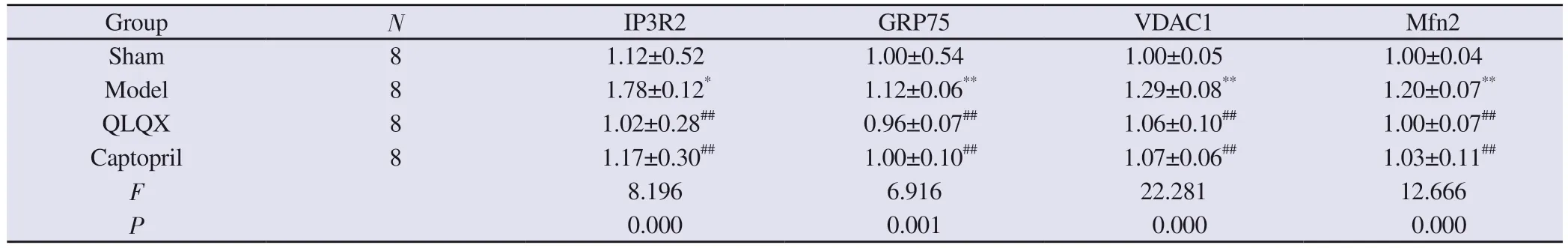
Tab 2 Expression of Ca2+ transport-related genes in each group(n=8, ±s)
Note: Compared with the sham group, *P<0.05,**P<0.01; compared with the model group, ##P<0.01.
Group N IP3R2 GRP75 VDAC1 Mfn2 Sham 8 1.12±0.52 1.00±0.54 1.00±0.05 1.00±0.04 Model 8 1.78±0.12* 1.12±0.06** 1.29±0.08** 1.20±0.07**QLQX 8 1.02±0.28## 0.96±0.07## 1.06±0.10## 1.00±0.07##Captopril 8 1.17±0.30## 1.00±0.10## 1.07±0.06## 1.03±0.11##F 8.196 6.916 22.281 12.666 P 0.000 0.001 0.000 0.000
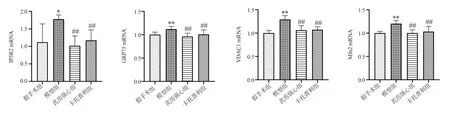
Fig 4 Comparison of the expression of Ca2+ transport-related genes in each group
3.5 The mRNA expression of mitochondrial apoptosis-related genes
Compared with the sham group, the B lymphocytoma-2 (Bcl-2)mRNA expression level was significantly lower and the Bcl-2-related X protein (Bax) mRNA expression level was significantly higher in the model group (P<0.01); compared with the model group, the Bcl-2 mRNA expression level was significantly higher and the Bax mRNA expression level was significantly down-regulated in the QLQX group and the captopril group (P<0.01).The results are shown in Table 3 and Figure 5.
Tab 3 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in each group(n=8, ±s)

Tab 3 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in each group(n=8, ±s)
Note: Compared with the sham group, **P<0.01; compared with the model group, ##P<0.01.
Group N Bcl-2 Bax Sham 8 1.04±0.32 1.03±0.29 Model 8 0.57±0.11** 1.80±0.27**QLQX 8 0.98±0.21## 1.13±0.14##Captopril 8 0.96±0.27## 1.22±0.32##F 6.520 13.477 P 0.002 0.000
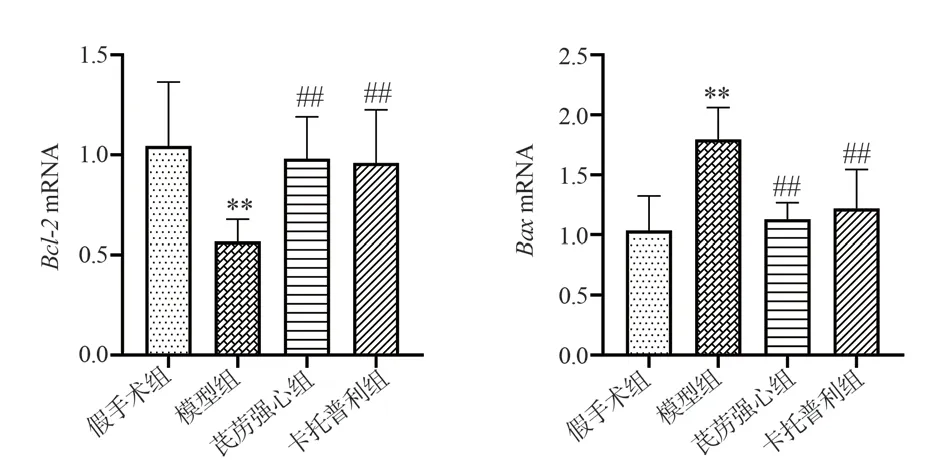
Fig 5 Comparison of the expression of apoptosis-related genes in each group
3.6 Expression of mitochondrial apoptosis-related proteins
Compared with the sham group, the expression of Bcl-2 protein in the model group was significantly decreased, and the expression of Bax protein was significantly increased (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the expression level of Bcl-2 protein in QLQX group and captopril group was significantly increased, and the expression level of Bax protein was significantly decreased (P<0.05,P<0.01).The results are shown in Table 4 and Figure 6.
Tab 4 Expression of apoptosis-related proteins in each group(n=4, ±s)
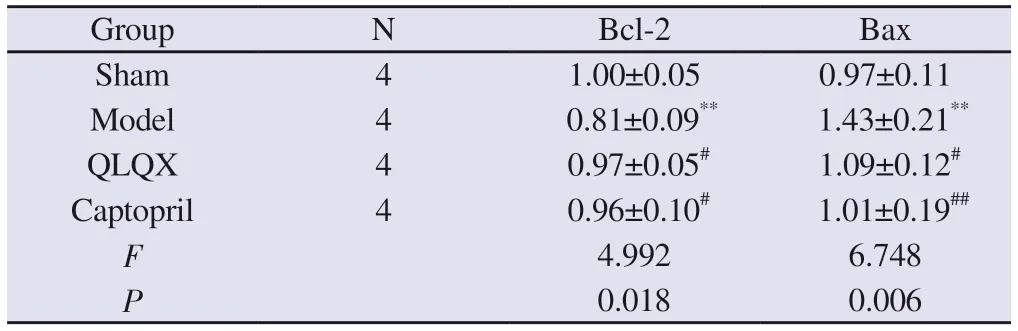
Tab 4 Expression of apoptosis-related proteins in each group(n=4, ±s)
Note: Compared with the sham group, **P<0.01; compared with the model group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01.
?
3.7 Myocardial cell apoptosis rate results
Compared with the sham group, the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells in the model group was significantly increased (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells in QLQX group and captopril group was significantly decreased(P<0.01).The results are shown in Table 5, Figure 7-9.
Tab 5 Results of apoptosis rate of cardiac myocytes in each group of rats(n=8, ±s)
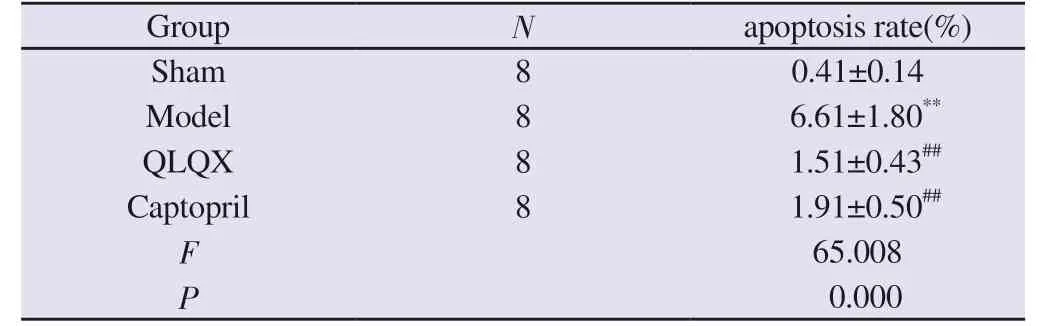
Tab 5 Results of apoptosis rate of cardiac myocytes in each group of rats(n=8, ±s)
Note: Compared with the sham group, **P<0.01; compared with the model group, ##P<0.01.
Group N apoptosis rate(%)Sham 8 0.41±0.14 Model 8 6.61±1.80**QLQX 8 1.51±0.43##Captopril 8 1.91±0.50##F 65.008 P 0.000

Fig 6 Comparison of the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in each group
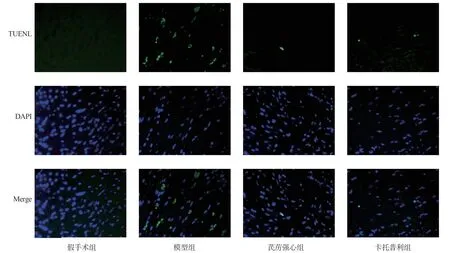
Fig 7 TUNEL staining results of myocardial tissues of rats in each group (400 ×)
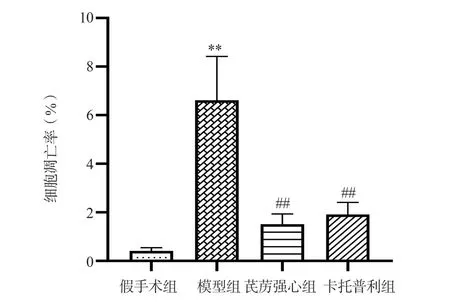
Fig 8 Comparison of apoptosis rates in cardiac myocytes of each group of rats
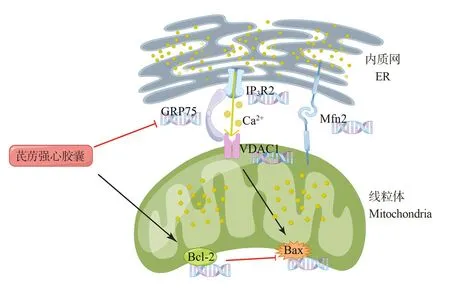
Fig 9 Regulation of Qiliqiangxin Capsule on Ca2+ transport in rats with myocardial infarction
4.Discussion
MI is a pathological event of sustained ischemia leading to myocardial injury, accompanied by an imbalance in cellular homeostasis and damage to cardiac structure and function[15].The imbalance of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+release and mitochondrial Ca2+ overload associated with MI is an important mechanism that causes organelle damage and thus triggers apoptosis[16].Therefore,the molecular changes of abnormal mitochondrial Ca2+uptake after MI and the regulatory role of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)deserve in-depth study.
According to TCM, MI belongs to the category of vascular lesions,and Qi deficiency and blood stasis is its basic pathogenesis, while blockage and accumulation is another key pathogenesis of disease progression[17].QLQX is a patent medicine developed under the guidance of the theory of Chinese medicine, which has the effect of benefiting Qi, warming Yang, activating blood circulation,promoting water circulation and reducing swelling, and is effective in preventing and treating heart failure after MI[18, 19].However,the molecular mechanisms behind this cardioprotective effect have not yet been fully elucidated.The dynamic control of Ca2+uptake by mitochondria, the powerhouse of cells, is fundamental to the achievement of physiological functions or pathological stress in cardiomyocytes[20].In this study, we observed the interventional effects of QLQX in regulating the expression of genes related to mitochondrial Ca2+uptake channels, hoping to provide new laboratory evidence to elucidate its pharmacological mechanism.
Recent studies have found that mitochondrial-associated endoplasmic reticulum (MAMs) channel proteins including VDAC1,GRP75, and IP3Rs are the basis for maintaining mitochondrial Ca2+homeostasis[21].Among them, IP3Rs are mainly expressed in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, mediating endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+release; VDAC1 is located in the Ca2+uptake channel on the outer membrane of mitochondria.Hadar et al.found that VDAC1 was significantly overexpressed in patients with MI[22].In addition, VDAC1 can increase the permeability of the mitochondrial outer membrane and is considered to be an essential molecule for inducing apoptosis[23, 24].Zhao et al.found that the up-regulation of MAMs channel proteins VDAC1 and GRP75 was associated with the progression of cardiac hypertrophy[25].GRP75 interconnects IP3Rs and VDAC1 through the cytoplasmic to form the IP3Rs/GRP75/VDAC1 channel complex mediating mitochondrial Ca2+uptake[26, 27].In this study, we found that the expression levels of IP3R2, GRP75, and VDAC1 mRNA in myocardial tissues of rats in the model group were significantly elevated, this explains at the genetic level the cause of over-opening of mitochondrial Ca2+uptake channels after MI, which subsequently leads to mitochondrial Ca2+overload.In contrast, the overexpression of related genes was improved after treatment with QLQX, indicating that the drug could exert myocardial protective effects by regulating the gene expression of IP3Rs/GRP75/VDAC1 channel complex.
Mfn2 is an indispensable multifunctional protein for cells,promoting biological processes such as mitochondrial fusion,formation of MAMs, and apoptosis under physiological and pathological conditions[28].Current studies suggest that Mfn2 is closely related to the pathogenesis of heart failure.However, whether this biological effect is protective or damaging seems to be related to the degree of damage and the balance between its protective and damaging effects [29].
As the bearers of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake channels, MAMs are dynamic structures that are mainly regulated by Mfn2 and provide a stable platform for mitochondrial Ca2+ transport in the physiological state.However, MAMs channel proteins do not always seem to be favorable.Riba et al.found elevated Mfn2 expression in isoproterenol-induced heart failure [30], and Zhao et al.showed that downregulation of the MAMs pathway may have a protective effect on the heart [25].In addition, myocardial tissue with Mfn2 knockout was more tolerant to Ca2+ overload [31].In this study,the mRNA expression of Mfn2 was significantly elevated in the rat hearts of the model group, which seemed to be a causative factor for excessive Ca2+ exchange between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria, and eventually led to mitochondrial Ca2+overload.In contrast, QLQX was able to significantly suppress the overexpression of Mfn2 mRNA compared with the model group,which would help to alleviate the excessive mitochondrial Ca2+uptake after MI.
Ca2+ homeostasis in mitochondria plays a key role in the respiratory chain complex and enzyme activity in the Krebs cycle.Excessive Ca2+ uptake by mitochondria leads to dysfunctional biology, which in turn activates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in cells [32].The anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 is a key regulator of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.It acts not only in mitochondria but also in the endoplasmic reticulum, affecting Ca2+ dynamics and thus counteracting apoptosis by targeting IP3Rs [33, 34].Ca2+-mediated apoptotic signaling can cause Bax activation and translocation to the outer mitochondrial membrane to induce the release of pro-apoptotic factors such as cytochrome c from mitochondria [35].VDAC1 is not only an important upstream molecule for the activation of Bax, but also oligomerizes and provides a channel for cytochrome c release[23, 36, 37].In addition, Mfn2 is involved in the recruitment of Bax to the mitochondrial membrane to induce apoptosis [38].Bcl-2 and Bax are mutually regulated to maintain mitochondrial membrane stability
In this study, Bcl-2 mRNA and protein expression were decreased and Bax mRNA and protein expression were increased in the model group rats; meanwhile, TUNEL staining showed that the apoptosis rate of cardiomyocytes was significantly increased in the model group compared with the sham group.It suggested that the high expression of IP3Rs escaped the inhibitory effect of Bcl-2 and released Ca2+ apoptotic signal when MI occurred.The Ca2+apoptotic signal activated Bax membrane translocation through VDAC1, which finally led to the activation of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.The treatment with QLQX for 4 weeks could increase the expression of Bcl-2 mRNA and protein, decrease the expression of Bax mRNA and protein, restore the dynamic balance of Bcl-2 and Bax and significantly reduce the rate of apoptosis.
The MAMs channel proteins IP3R2, GRP75, and VDAC1 have been shown to be hubs for stress signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the mitochondria, most notably involved in unfolded protein responses in the context of loss of endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis [39].Our previous experiments revealed that MI is accompanied by excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress [3].The results of the present study further suggest that the process of endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling to mitochondria and thus activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is associated with overexpression of the mitochondrial Ca2+ transport complex IP3R2/GRP75/VDAC1 gene.QLQX was able to regulate the genes overexpression of IP3R2/GRP75/VDAC1 channel complex after MI,thus inhibiting the activation of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and exerting cardioprotective effects.
In conclusion, this study revealed a novel mechanism at the genetic level that QLQX targets the gene expression of IP3R2/GRP75/VDAC1 channel complex and thus inhibit apoptosis.However,mRNA level regulation was not sufficient to fully demonstrate the intrinsic association between inhibition of Ca2+ pathway and apoptosis.This is the limitation of this study and the future research direction of our group, and further experimental evidence will be added at the protein level subsequently, hoping to elucidate the regulatory mechanism of IP3R2/GRP75/VDAC1 channel complex by QLQX in a more in-depth and comprehensive manner.
Author conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Author Contributions
Corresponding author Ai-Ming Wu conducted the overall design of the experiment and reviewed the article; Ming-Jing Zhao guided the idea and writing of the article; Li-Xia Lou, Bo Nie and Jiu-li Zhao provided technical guidance for the experiment; Xiao-di Ji, Ding Yang and Xi-Yuan Cui were responsible for animal rearing and index testing; first author Xiao-di Ji drew Figure 9 through Figdraw platform and wrote the article.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- A meta-analysis of risk factors for epilepsy after acute ischaemic stroke and the development of a predictive model
- The diagnostic value of the expression of the thymidine kinase 1 in lung cancer : A meta analysis
- Analysis on the formation principle and present situation of nano phase state of multi-component self-assembly of traditional Chinese compound medicine decoction
- LINC00662 affects the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib drug by regulating miR‑106a‑5p/CAV1 axis
- Experimental study of the anti-inflammatory activity of some compounds in Berchemia lineata(L.)DC
- Differential expression analysis of coronary heart disease related genes in Hainan residents
