The diagnostic value of the expression of the thymidine kinase 1 in lung cancer : A meta analysis
2023-11-14HUChanLIJingchengLIULingPENGQianSANGShenggang
HU Chan, LI Jing-cheng, LIU Ling, PENG Qian, SANG Sheng-gang
Department of Laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College, Haikou 570100, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To study is to evaluate the diagnostic value of the expression of thymidine kinase 1(TK1) in lung cancer through literature review and meta-analysis.Methods: Firstly, we searched Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane, Web of Science, CBM, CNKI, Wanfang and other databases up to June 2022.Then two researchers separately selected the clinical study on diagnosis of lung cancer by the expression of the TK1 and treatment and obtained the full text of the literature.Then we evaluated the systematic quality and bias risk of the included literatures by using Revman 5.3 software, and the consistency among the covariables in meta analysis.Finally, the Sensitivity (Sen), the Specificity (Spe) and other indicators were analyzed by using Stata16.0 software.Results: The study included 37 literatures, including 3 218 lung cancer cases and 2 976 control cases.The meta-analysis showed that the Ser and Spe of the expression of the TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer were 0.63 (95%CI: 0.57, 0.68) and 0.88 (95%CI: 0.84,0.91), while positive likelihood ratio (PLR) was 5.34(95%CI: 4.02,7.1)and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) was 0.42(95% CI: 0.37, 0.48), diagnostic odd sratio (DOR) was 12.69 (95%CI:8.91,18.08), and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.82 (95% CI: 0.79, 0.85).When TK1, CEA and CYFRA21-1 were used as combined diagnostic indexes of lung cancer, Sen was 0.82 (95%CI:0.76, 0.86), Spe 0.78 (95%CI:0.46, 0.94), PLR 3.69 (95%CI:1.28, 10.66),NLR 0.24 (95%CI:0.18, 0.31), DOR 15.59 (95%CI: 4.56, 53.36), AUC 0.84 (95%CI:0.80, 0.87).The Youden index of combined diagnosis was 0.60, which was higher than that of TK1 alone.Conclusion: TK1 alone as a diagnostic index of lung cancer has low Sen, but its Sep is higher.So it has a certain diagnostic value.TK1 combined with CEA and CYFRA21-1 has higher Sen in the diagnosis of lung cancer, and the diagnostic value is better.
1.Introduction
Lung cancer(LC) is one of the most common malignancies in the world, originating from bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells.According to the latest statistics, there are about 2.2 million new cases and 1.79 million death cases of LC every year[1].When the patient has clinical symptoms, the disease has worsened.About 75% of the patients are diagnosed as terminal-stage LC, and the overall 5-year survival rate is only about 21%[2], thus the prognosis is relatively poor[3].At present, there is still a lack of sensitive tumor markers in clinical diagnosis, so it is often difficult to diagnose early-stage LC[4].Therefore, there is an urgent need to find a tumor marker with higher diagnostic value, which can better monitor LC’s therapeutic effect.
Thymidine kinase 1(TK1), located in chromosome 16q22~q23.1,shows a tetramer structure, in which each subunit contains an α/ β domain[5].TK1 is involved in DNA synthesis, which is up-regulated in the S phase of the cell cycle, so it can be an indicator of cell proliferation activity[6].The content of TK1 in healthy people is very low.When malignant tumor cells proliferate, the number of cells in the S and G2 phases increases sharply in a short period, resulting in a large amount of TK1 released into the blood, so TK1 can be detected in serum[7].Several studies have shown that the expression level of TK1 is different between healthy people and patients with benign tumor disease or early lung cancer, so it has important reference value for early tumor diagnosis and prognosis evaluation and can be used as a routine serological marker detection index[8-11].Therefore, this study systematically evaluates the published literature to provide a reliable basis for the clinical diagnosis of lung cancer with TK1.
2.Data and methods
2.1 Retrieval approaches and strategies
We searched databases including Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane, Web of Science, CBM, Zhiwang, and Wanfang until June 2022.And the keywords are “lung cancer”, “lung neoplasm”, “pulmonary cancer”,“pulmonary neoplasm”, “lung adenocarcinoma”, “Lung squamous cell carcinoma”, “non-small-cell lung cancer”, “NSCLC”, “small cell lung cancer”, “TK1”, “TK1 protein”, “Thymidine kinase 1”.Finally, we search all the literature about TK1 in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.2.1 Inclusion criteria
(1) The gold standard of Lung cancer is the histopathological diagnosis, the sample size of both the case groups and the control groups were more than 20 cases; (2) The case groups are not complicated with other malignant tumors and have not been treated with surgery and chemotherapy before detection, the control groups are healthy or patients with benign tumors or benign nodules.(3)Data, including TP, TN, FN, Sen, and Spe can be directly extracted or calculated indirectly.(4) The language of the literature is Chinese or English.(5) Complete data and full text can be obtained.
2.2.2 Exclusion criteria
(1) Literature of non-clinical studies; (2) No histopathological diagnosis; (3) Lack of full text or complete data; (4) repeatedly reported studies.
2.3 Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers conducted literature retrieval and screened 1197 articles.Then the two researchers screen out the literature and downloaded the full text and finally reached an agreement.After rescreening, we extracted the relevant literature data, including the author, publication year, publication region, type of study, number of cases in case groups, control groups, and detection methods of TK1.The extracted data included TP, TN, FP, FN, Sen, Spe, and cut-off values.
2.4 Quality evaluation
The quality of the studies was assessed based on the quality evaluation tool of QUADAS[12], and by using RevMan5.3 software,the inclusion study was rated as high-risk, unclear, or low-risk.Finally, a visual risk bias map was obtained to judge whether there existed risk bias in the study.
2.5 Statistical methods
Statistical methods were analyzed by RevMan5.3, Stata16.0,and MetaDiScv1.4 software.The main results are as follows: (1)Data are merged, such as Sen, Spe, PLR, NLR, and DOR, and the corresponding 95%CI were calculated.(2) Through the Spearman test, if P >0.05, there was no threshold effect, so it was feasible to analyze by meta-analysis.(3) When the P value of CochranQ<0.05or I2>50%, the heterogeneity existed.It was necessary to explore the source of heterogeneity and carry out Meta-regression analysis and subgroup analysis.(4) If there was still heterogeneity,the random effect model would be used.
3.Results
3.1 The result of the screening of the literature
Two researchers screened 1197 articles, including Pubmed (n=75),Embase (n= 116), Cochrane (n=8), WebofScience (n=215), CBM(n=119), CNKI (n=183), Wanfang (n=481).After re-screening,37 articles were included (Figure 1).The first author, publication year, publication region, number of cases included in the study,pathological stage, detection means, sample type, Cut-off value, and so on were classified( Table 1).
3.2 The quality evaluation results
According to the quality evaluation results of the included studies,the overall risk bias of the literature is low (Figure 2 &Figure 3).
3.3 Diagnostic value of TK1 in lung cancer
Deek’s funnel diagram of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer showed that there was no publication bias (Figure 4).TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer Sen=0.63 (95%CI: 0.57, 0.68), Spe=0.88(95% CI: 0.84, 0.91); AUC=0.82 (95% CI:0.79, 0.85), indicating that there was a certain degree of accuracy (Figure 5&Figure 6).The values of PLR were 5.34 (95% CI: 4.02,7.1) and NLR was 0.42(95% CI: 0.37,0.48) (Figure 7).The DOR is 12.69 (95% CI:8.91)(Figure 8).When the test result was positive, the prior probability of the patient diagnosed with lung cancer increased from 30% to 70%;if the test result was negative, the prior probability decreased from 30% to 15% (figure 9).The above results showed that TK1 had a certain diagnostic value in lung cancer.
3.4 Meta-regression analysis

Fig 1 flow chart of literatures screening

Tab 1 Basic characteristics of included literature
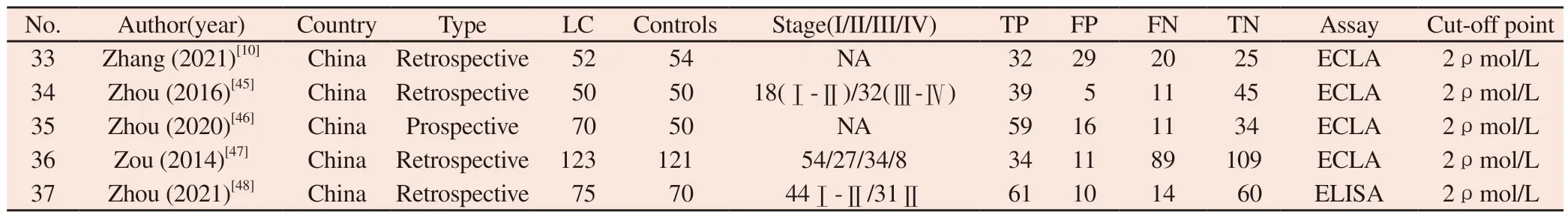
Note: “NA” indicates that the data is not mentioned in the literature.

Fig 2 The summary chart of literature bias risk

Fig 3 The summary of the applicability of the literature and the entres of risk bias

Fig 4 Deek’s funnel diagram of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer
The results of the Spearman test showed that there was no threshold effect in this study(P=0.101).The results of the CochranQ test and inconsistency I2 test of the sensitivity and specificity showed that P<0.01, I2>50%, and there was heterogeneity in sensitivity and specificity (Figure 5).Meta-regression analysis showed that the heterogeneity mainly came from the type of study, the number of cases, different tumor types, detection methods, and Cut-off value(P<0.05).Furthermore, through subgroup analysis, it was found that the calculation value of Spe, PLR, DLR, and AUC of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was superior to that of enhanced chemiluminescent (ECLA).There are relatively few studies in small cell lung cancer groups, thus it is not included in the subgroup analysis, but we found that non-small cell lung cancer has better Sen, Spe, PLR, and NLR than unclassified lung cancer, while unclassified lung cancer groups had better AUC value (Table 2).
3.5 Comparison of diagnostic value of TK1 single test and combined CEA and CYFRA21-1 test
From the 37 articles screened previously, we further screened out the literature of TK1 item combined CEA and CYFRA21-1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer.There were 409 lung cancer patients and 399 benign control group.The diagnostic values of TK1, CEA,CYFRA21-1 alone, and combined diagnosis of lung cancer were compared.The results of the Spearman test showed that there was no threshold effect in the diagnosis of TK1 and CEA alone and the combined diagnosis of TK1, CEA, and CYFRA21-1, but there was a threshold effect in the diagnosis of CYFR21-1 alone (Table 3).Therefore, Meta-analysis was performed on TK1, CEA, and the three combined diagnoses.When TK1, CEA, and CYFRA21-1 were used as indicators for combined diagnosis of lung cancer, Sen=0.82(95% CI:0.76,0.86).It was higher than TK1 and CEA alone.The Youden index of Spe=0.78 (95% CI:0.46,0.94), which was lower than that of TK1 and CEA alone, and the Youden index of combined diagnosis was higher than that of TK1 alone (95% CI:0.80,0.87).DOR=15.59 (95% CI: 4.56, 53.36); AUC=0.84 (95%CI:0.80,0.87), higher than that of TK1 and CEA alone, which had a certain diagnostic value.(Table 4).

Fig 5 Sensitivity and specificity of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer

Fig 6 SROC curve of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer
4.Discussion
CA125, NSE, CYFRA21-1, CEA, and ProGRP are the common tumor markers of lung cancer.CYFRA21-1 is a sensitive indicator of non-small-cell lung cancer, with a sensitivity of 55.38% and a specificity of 58.97%[32].Meanwhile, NSE is a sensitive marker of small-cell lung cancer.The sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing SCLC are 77.1% and 66% respectively[14].A study has found that the specificity of ProGRP, NSE, CEA, and CYFRA21-1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer and benign lung diseases is more than 60%,while the sensitivity is about 31% to 56%[49].To sum up, the current diagnostic value of tumor indicators is limited, so it is necessary to seek tumor indicators with higher sensitivity and specificity.
In recent years, there are many studies to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of TK1 in lung cancer.Chen’s study has shown that the sensitivity and specificity of TK1 in lung cancer are 84.29%and 72.90% respectively[14], while LanYongle finds that the sensitivity and specificity of TK1 in lung cancer are 43.3% and 97% respectively[27].The diagnostic value of TK1 in lung cancer is controversial.Therefore, We use Meta-analysis to explore the clinical value of TK1 as a diagnostic index of lung cancer, which can provide a more reliable reference for clinical research.

Fig 7 Positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio forest map of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer

Fig 8 TK1 diagnostic ratio forest map for the diagnosis of lung cancer
Our study’s results showed that the Sen of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer was 0.63 and specificity was 0.88.As a tumor marker of lung cancer, it had high specificity and moderate sensitivity.The PLR was 5.4 and the NLR was 0.42, which indicated that the diagnostic accuracy of lung cancer was 5.34 when TK1 was positive,while the misdiagnosis rate was 0.42 when TK1 was negative.When DOR>1, the higher ratio of the DOR was, the higher accuracy of the diagnostic test was.Moreover, the DOR value in this study was 12.69, indicating that the accuracy of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer was higher.And the value of our study was 0.82,which showed that the TK1 had higher accuracy as an index for the diagnosis of lung cancer.
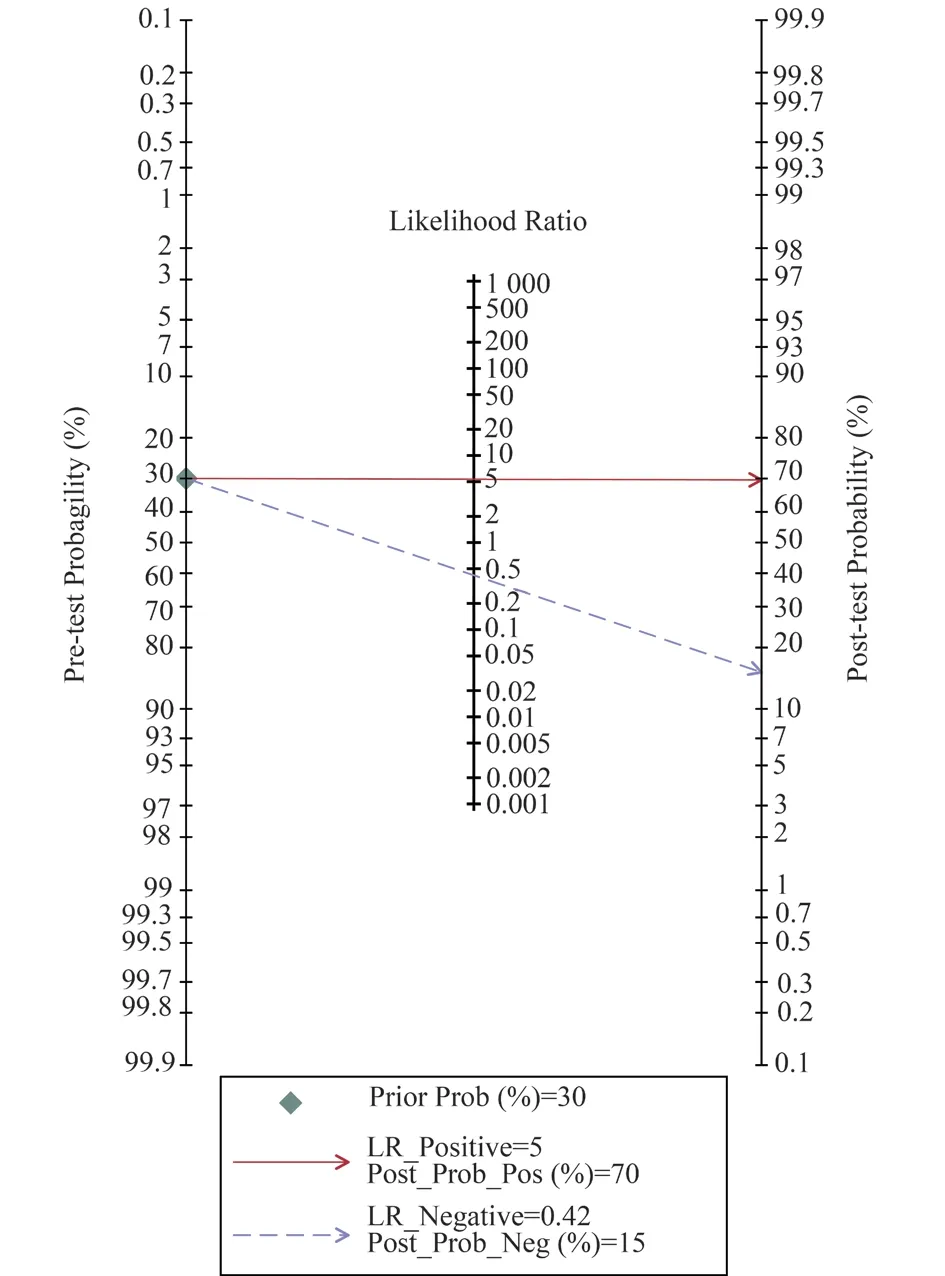
Fig 9 Fagan diagram of TK1 in the diagnosis of lung cancer

Tab 2 Subgroup analysis of included studies

Tab 3 Statistics of threshold effect

Fig 10 Meta regression analysis of included studies

Tab 4 Comparison of diagnostic value of TK1 alone and combined with CEA and CYFRA21-1
Due to the limited diagnostic value of a single tumor index,combined detection has become a commonly used clinical detection method before we found more sensitive and specific tumor markers.Wang’s study showed that the sensitivity of tumor detection alone in the lung cancer group was 36%~52%, while the sensitivity of combined detection of TK1, VEGF, CYFRA21-1, and NSE increased to 91%, and the specificity increased from 65% to 92%[38].The AUC was 0.981, and the positive predictive value and negative predictive value were higher than those detected by each index alone.In addition, other studies had shown that the level of serum TK1 in patients with malignant pulmonary nodules was higher,and the sensitivity and specificity of serum TK1, CYFRA21-1, and SCC-Ag combined with chest CT in the diagnosis of malignant pulmonary nodules were higher (86.67% and 88.89% respectively)[37].In our study, we compared the diagnostic and therapeutic values of TK1, CEA, and CYFRA21-1 alone with combined diagnosis of lung cancer.The sensitivity and AUC of combined diagnosis were significantly higher than those of single diagnosis, which indicated that the combined detection of TK1, CEA, and CYFRA21-1 had better diagnostic value.However, the specificity was lower than that of single detection, indicating that the true negative rate of combined detection was slightly lower, and the diagnosis of lung cancer can only be diagnosed with the support of imaging and pathological techniques, such as CT, MRI, and so on.To sum up, the diagnostic value of single tumor marker of TK1 was limited, and the efficiency of combined diagnosis was higher.
In the early diagnosis of lung cancer, it is very important to select appropriate combined diagnostic indexes.Xiange’s study has explored the diagnostic value of the combination of TK1,CYFRA21-1, CA125, CEA, SCC, and NSE in lung cancer.The results show that the best four combinations of lung adenocarcinoma are TK1 CA125 CEA CYFRA21-1, with a sensitivity of 88.89% and a specificity of 80%.The best three combinations in lung squamous cell carcinoma are TK1 CYFRA21-1 SCC with a sensitivity of 90%and a specificity of 87.5%[41].Because the combinations of several tumor indexes are not the same in different literature, our study can only analyze the diagnostic value of TK1 combined with CEA and CYFRA21-1.In the future, we need to compare the diagnostic value of TK1 combined with other indicators to find the most suitable combination group of tumor indicators.
To sum up, the high expression of TK1 in lung cancer, as a good observation index for non-invasive detection, still shows its potential application prospect in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.However, our study still has some limitations.Due to the lack of abroad clinical studies, our study only provides a certain clinical reference for patients with lung cancer in China.Finally, the sample size of the case groups and control groups included in the metaanalysis is smaller, so our follow-up studies need a larger sample size of clinical studies to confirm the diagnostic value of TK1 expression in lung cancer in the real world.
Author contribution
Hu Chan designed the study, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; Li Jingcheng, Liu Ling, and Pengqian Participated in the experimental design and analyzed the results; Sang Shenggang was responsible for the project concept and review of the paper.All authors read and agreed on the article.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of complications related to spinal cord injury
- Research progress on the safety of nail placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery
- Study on the protective mechanism of Yizhiren regulating lipid metabolism in mice with diabetic nephropathy
- Differential expression analysis of coronary heart disease related genes in Hainan residents
- Experimental study of the anti-inflammatory activity of some compounds in Berchemia lineata(L.)DC
- Mechanism of Qiliqiangxin capsule on the regulation of IP3Rs/GRP75/VDAC1 gene in myocardial infarction rat heart
