Experimental study of the anti-inflammatory activity of some compounds in Berchemia lineata(L.)DC
2023-11-14LIUJunyangTENGHongliZHAOJinmeiHONGJing
LIU Jun-yang, TENG Hong-li, ZHAO Jin-mei, HONG Jing
1.Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, China
2.Guangxi International Zhuang Medical Hospital, Nanning 530201, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To screen the anti-inflammatory monomeric compounds isolated from Berchemia lineata(L.)DC and explore the anti-inflammatory mechanism of some compounds based on NF-κB signaling pathway.Methods: LPS was used to induce RAW264.7 to establish a model of cellular inflammatory reaction.CCK-8 method was used to detect the effect of monomer compounds on the activity of RAW264.7 cells.The release of nitric oxide (NO)in the superneant was measured by Griess method, and NO inhibition rate was calculated.The anti-inflammatory activity gradient of some monomeric compounds was also measured.The effects of monomer compound 21 on the secretion of IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB, COX-2 and iNOS induced by LPS were detected by ELISA.Results: The concentration of monomer compound of Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.was 50 μmol/L, and it was administered for 24 h.The results showed that anthraquinone compound No.19 had obvious drug toxicity, while other compounds had weak or no obvious drug toxicity.The concentration was 50 μmol/L,and the drug was administered for 12 h.The results showed that all the monomer compounds could inhibit the release of NO to varying degrees, and the highest NO inhibition rate was over 90%, which showed obvious anti-inflammatory activity.NO inhibition rate of No.01 new skeleton compound can reach 70.81%.The results of anti-inflammatory activity gradient showed that the monomer compound of Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.could inhibit the release of NO in a dose-dependent manner.The results of ELISA showed that phenolic compound 21 could inhibit the secretion of IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB, COX-2 and iNOS in RAW264.7 cells.Conclusion: The monomer compound of Berchemia lineata(L.) DC.has a certain antiinflammatory activity, among which flavonoids and bibenzyl components isolated from this plant for the first time may be the material basis for its anti-inflammatory activity.The simple phenolic monomer compound 21 may play an anti-inflammatory role by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway.
1.Introduction
Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.is one of the iron bao-jin based medicinal materials, also known as oolong root, Ma Kou Zi, mouse ear, is the rhamnofamily kigechu catechu plant, with its roots and leaf rattan stem into medicine[1].Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.(Zhuang medicine name: Gaeuhouznou) was first published in Lingnan Herbs Collection and is commonly used in Zhuang medicine[2, 3].As a commonly used anti-inflammatory drug in Zhuang medicine,it is widely used in the combination of rheumatoid arthritis (RA),but there are few reports and most of them are ancient clinical literatures[4].Studies have shown that the total extract of iron coated gold has obvious anti-inflammatory effect and certain curative effect on ear swelling in mice[5, 6].The main chemical components include flavonoids, quinones, dimers, phenylpropanoids, terpenoids,glycosides and organic acids[7, 8].Although clinical and animal experiments have proved that iron-coated gold has good antiinflammatory effects, there has been no relevant report on the specific iron-coated gold monomer compounds with anti-inflammatory activities.The understanding on the molecular level of phyllocatechu restricts the promotion and use of this herb.Group fine leaf hook catechu stem leaf of n-butyl alcohol and ethyl acetate extract of the communist party of China the separation and identification of 23 compounds, chemical structure type present diversity, including new skeleton, naphthalene pian and alpha-pyrone, naphthalene pian gamma-pyrone, flavonoid glycosides, al benzyl, flavonoids and dihydrogen flavonoids, anthraquinones, terpenoids, simple phenolic compounds, New compounds and compounds isolated from the plant for the first time are covered.By screening its drug toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity, iron-clad gold monomer compounds with anti-inflammatory activity were preliminarily screened out, and the mechanism of action of phenolic compound No.21 with relatively sufficient drug dosage was preliminarily explored, in order to have further understanding of Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.at the molecular level, and provide experimental basis for further exploration.
2.Materials
2.1 Relevant reagents and instruments
DMEM high glucose medium (Gibco), fetal bovine serum (FBS;Aoki), penicillin streptomycin (Gibco), Lipopolysaccharide (Sigma),dexamethasone (source foliar), CCK-8 (ABclonal), NO assay kit(Biyuntian), ELISA kit (Tetrapleurocypress,Rui Xin), enzyme marker (Thermo Scientific), CO2 incubator (Thermo Scientific)
2.2 Cell Lines
RAW264.7 (Wuhan Punosai Life Technology Co., LTD.)
2.3 Iron-clad gold monomer compounds
Source of iron-clad gold monomeric compounds: A total of 23 compounds were extracted from the aboveground part of Phyllocatechu[9], including new compounds (1-8) and known compounds (9-23).Among them, No.1 is a new skeleton compound; No.2 and No.3 have previously been found only in Marine organisms, and rarely in natural products.No.9 was the first bibenzyl compound discovered from this plant.All known compounds except 14, 15 and 16 were isolated from this plant for the first time.The name, molecular formula and structural formula of the compounds are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1 (Tab.1, Fig.1).

Tab 1 Compound name and molecular formula
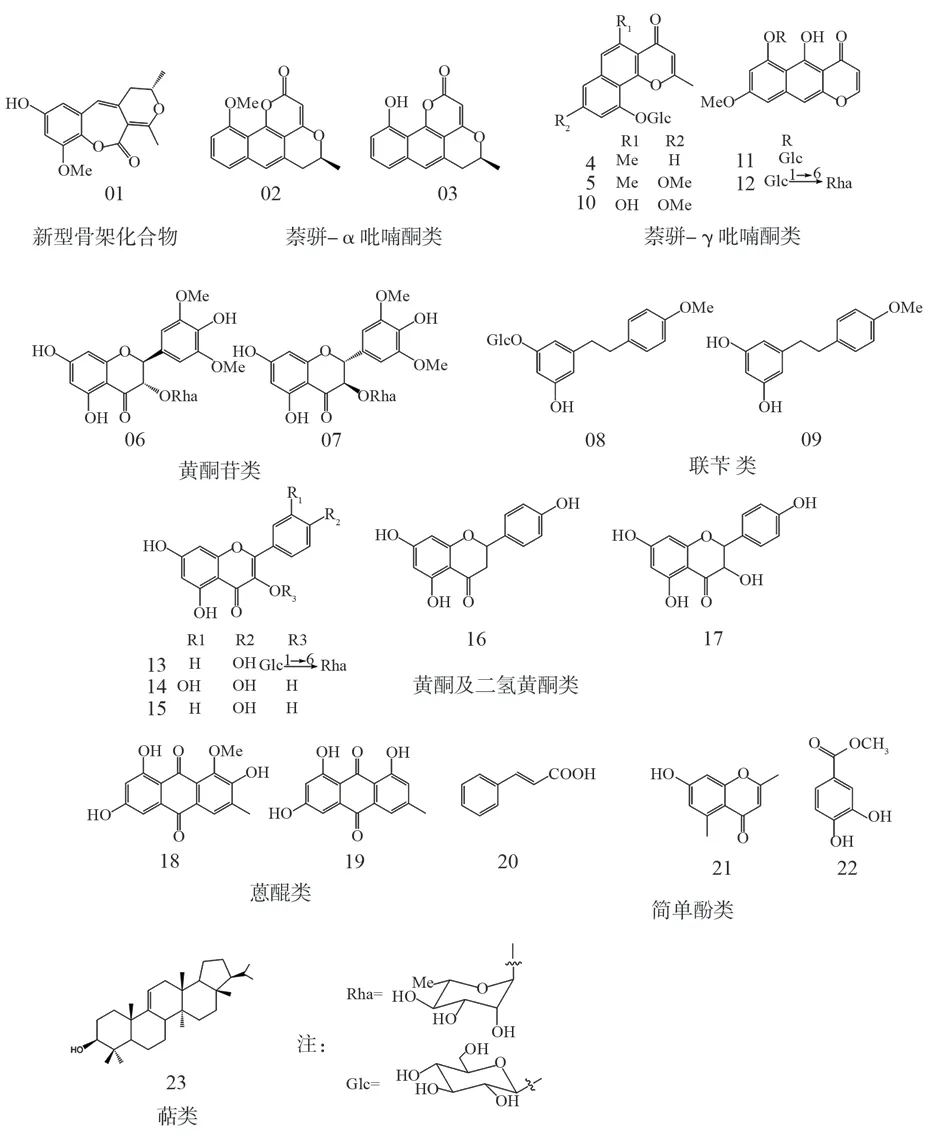
Fig 1 Classification and chemical structure formula
3.Methods
3.1 Cell culture
RAW264.7 was cultured with complete culture solution(DMEM+10% FBS+1%P/S) in a humid incubator at 37 ℃ and 5%CO2concentration.RAW264.7 cells were cultured every 24 h, and cells with logarithmic growth stage were selected for the experiment.
3.2 Molding
RAW264.7 cells were induced by LPS for 12 h and the inflammatory cell model was established.
3.3 The effect on the proliferation activity of RAW264.7 cells was determined by CCK-8 method
RAW264.7 cells were uniformly inoculated on 96T plate with 100 μL per well, and the supernatant was discarded after cell adherence.Blank control group and drug group were set.Cell culture medium and 50 μmol/L or 75 μmol/L monomer compound 100 μL were added to the blank control group and drug group, respectively,and incubated for 24 h.The supernatant was abandoned.In strict accordance with the CCK-8 instructions, the absorbance was measured at 450nm wavelength to calculate the cell survival rate.
3.4 NO release in RAW264.7 cells was determined by Griess method
RAW264.7 cells were inoculated on 96T plate with 100 μL per well, and the supernatant was discarded after cell adherence.Blank control group (Con), model group (LPS), positive control group(DXM) and monomer compound group were set.Administration:Blank control group: DMEM medium; Model group: LPS with final concentration of 0.5 μg/mL; Positive control group: LPS with final concentration of 0.5 μg/mL was co-incubated with DXM with final concentration of 10 μmol/L.Monomer compound group:LPS with final concentration of 0.5 μg/mL was co-incubated with monomer compound of 50 μmol/L.The 96T plate was incubated in an incubator at 37 ℃ with 5% CO2concentration for 12 h.The supernatant of 50 μL cells was taken and the absorbance was measured at 540 nm wavelength in strict accordance with the instructions of the NO detection kit.The release amount and inhibition rate of NO were calculated.
3.5 Gradient detection of anti-inflammatory activity(Compounds 2, 15, 16, 18, 21)
The monomer compounds with good anti-inflammatory activity and relatively large amount of extraction were selected to detect the antiinflammatory activity gradient.Administration: Model group: LPS 0.5 μg/mL; Positive control group: LPS with final concentration of 0.5 μg/mL was co-incubated with DXM with final concentration of 10 μmol/L.The monomer compound group was incubated with LPS of 0.5 μg/mL and different concentrations of monomer compound.2, 21 setting concentration gradient: 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 75 μmol/L;15, 16, 18 Set the concentration gradient: 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 μmol/L.In strict accordance with the instructions of NO detection kit,absorbance was measured at 540 nm wavelength, and NO release and inhibition rate were calculated.
3.6 The contents of TNF-α, IL-6, NF-κB, COX-2 and iNOS were determined by ELISA
RAW264.7 cells were inoculated in 6T plates and were waiting for cell adherence.Blank control group, model group, positive drug group and leptocatechu monomer compound group were set.The supernatant was discarded when the cells adhered to the wall.Administration: Blank control group: DMEM medium; Model group: LPS 0.5 μg/mL; Positive control group: 0.5μg/mL LPS and 10 μmol/L DXM co-incubated; LPS of 0.5 μg/mL was co-incubated with LPS of 25, 50, 75 μmol/L.Incubate at 37 ℃ in an incubator with 5% CO2concentration for 12h.Cell supernatant was collected and tested according to ELISA kit instructions.
3.7 Statistical Analysis
Using GraphPad prism 9.0 software to analyze data, using±s, P <0.05 or P < 0.01 represents data difference is statistically significant.
4.Results
4.1 Toxic effects of monomeric compounds of Phyllocatechu on RAW264.7 cells
The results showed that 24 h after administration (50 μmol/L),No.19 had toxic effects on RAW264.7 cells, and the survival rate was 59.25%.No other compounds had obvious toxicity on RAW264.7 cells, and the survival rate of RAW264.7 cells was over 80%.The survival rates of compound 2 and 21 cells at 75 μmol/L were 117% and 108 %.When compound concentration was 50 μmol/L, the survival rate of RAW264.7 cells was shown in Table 2 (Tab.2).
4.2 Effects of monomeric compounds of Phyllocatechu on NO release from RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS
The results showed that 12 h after administration, the isolated and extracted monomer compounds could inhibit the release of NO to varying degrees.NO inhibition rate of NO 9 bibenzyl compounds,No 15 flavonoids and No 19 anthraquinones reached more than 90%, showing strong anti-inflammatory activity.Compound 19 at this concentration can reduce cell survival rate and affect the detection result of NO.NO inhibition rates of NO 1 novel skeleton compound, No 6, No 7 flavonoid glycosides, No 8 bibenzyl, No 16,No 17 dihydroflavonoids, No 18 anthraquinones and No 21 simple phenolic compounds ranged from 54.65% to 80.57%.Among them,the inhibitory rate of NO of the new skeleton compound No.1 was 70.81 %, which not only had good anti-inflammatory effect but no obvious drug toxicity, so it has the value of further exploration.Theresults of NO inhibition rate are shown in Table 3 (Tab.3).
Tab 2 Cell survival rate(n=3, ±s)
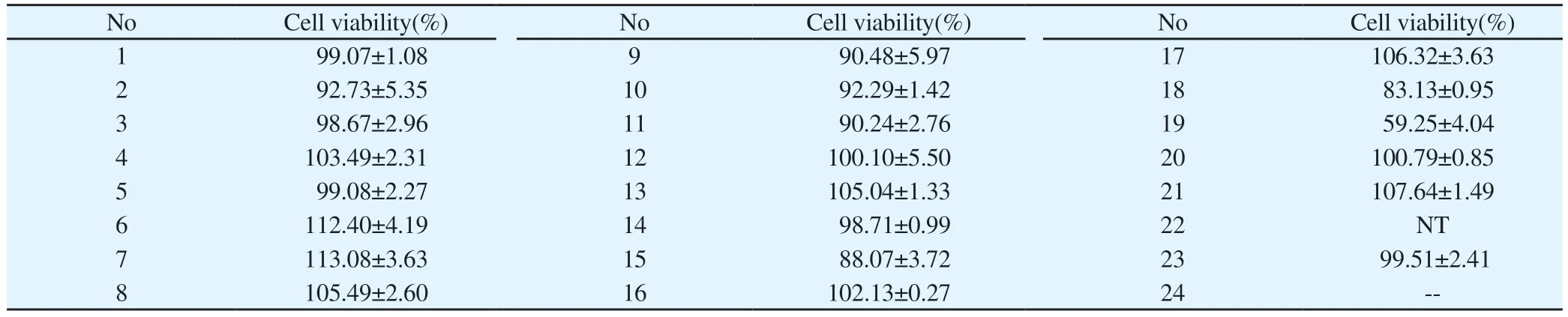
Tab 2 Cell survival rate(n=3, ±s)
Note: NT: not test
No Cell viability(%) No Cell viability(%) No Cell viability(%)1 99.07±1.08 9 90.48±5.97 17 106.32±3.63 92.73±5.35 10 92.29±1.42 18 83.13±0.95 3 98.67±2.96 11 90.24±2.76 19 59.25±4.04 2 103.49±2.31 12 100.10±5.50 20 100.79±0.85 5 99.08±2.27 13 105.04±1.33 21 107.64±1.49 4 112.40±4.19 14 98.71±0.99 22 NT 7 6 113.08±3.63 15 88.07±3.72 23 99.51±2.41 8 105.49±2.60 16 102.13±0.27 24 --
Tab 3 Nitric oxide inhibition ratio (n=3, ±s)

Tab 3 Nitric oxide inhibition ratio (n=3, ±s)
No NO inhibition ratio (%) No NO inhibition ratio(%) No NO inhibition ratio (%)1 70.81±0.79 9 90.02±0.48 17 80.57±3.87 2 41.82±2.98 10 5.41±1.38 18 57.61±3.23 3 15.15±1.49 11 0.90±1.11 19 101.7±2.25 4 27.81±3.10 12 NT 20 20.48±1.21 5 38.32±6.04 13 NT 21 58.81±7.64 6 54.65±6.42 14 NT 22 NT 7 56.87±2.49 15 99.07±1.82 23 18.09±3.50 8 63.12±0.19 16 71.22±1.78 24 -
4.3 Anti-inflammatory activity gradient test results
The results showed that the monomeric compounds of phyllocatechu could inhibit the release of NO to varying degrees in a dosedependent manner.No.02 Naphthalene α-Pyranones,flavonoids 15, 16 and dihydroflavonoids, anthraquinones 18, simple phenolic compounds 21 all inhibited NO release in a dose-dependent manner.Compound 21 inhibited 22.15%, 28.61%, 30.57%, 52.45% and 61.22% of NO at 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 75 μmol/L, respectively, and inhibited NO release from RAW264.7 induced by LPS in a dosedependent manner.See Table 4 (Tab.4) for details.
4.4 The effects of compound 21 on the secretion of IL-6,TNF-α, NF-κB, iNOS and COX-2 in RAW264.7 were detected by ELISA
ELISA results showed that compared with blank control group,the levels of IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB, COX-2 and iNOS in cell supernatant were significantly increased in model group.Compared with the model group, compound 21 inhibited the secretion of IL-6,TNF-α, NF-κB, COX-2 and iNOS in a dose-dependent manner.See Table 5 (Tab.5) for details.
Tab 4 Effects of compound on production of NO in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS(n=3, ±s)

Tab 4 Effects of compound on production of NO in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS(n=3, ±s)
Note: NT: not test; ##P<0.01 means comparison with blank control group, **P<0.01 means comparison with model group
组别 02 15 16 18 21 Con 2.19±0.06 2.48±0.36 0.84±0.03 1.86±0.27 2.51±0.12 LPS 17.45±1.12## 16.52±1.14## 22.19±0.60## 27.69±0.32## 19.01±0.48##DXM 3.52±0.23** 5.10±0.51** 5.32±0.23** 15.75±0.22** 3.99±0.58**6.25 16.79±0.11 14.55±0.93 20.95±0.92 26.46±0.18** 15.36±0.83**12.5 16.10±0.50 12.76±1.06** 17.61±1.00** 22.53±0.28** 14.29±0.71**25 14.74±0.21** 12.20±0.80** 14.05±0.71** 17.36±0.15** 13.97±0.81**50 12.56±0.60** 5.71±0.36** 7.94±0.51** 9.93±0.27** 10.36±0.09**75 10.66±0.56** NT NT NT 8.91±0.26**372.0 137.8 465.1 4230 310.7 P<0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 F
Tab 5 Effects of compound 21 of IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB, iNOS and COX-2 in RAW264.7 cells (n=3, ±s)

Tab 5 Effects of compound 21 of IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB, iNOS and COX-2 in RAW264.7 cells (n=3, ±s)
Note: ##P<0.01 means comparison with blank control group, **P<0.01 means comparison with model group.
组别 Compound No.21 TNF-α(pg/mL) IL-6(pg/mL) NF-κB(pg/mL) iNOS(ng/mL) COX-2(ng/mL)Con 79.80±3.20 6.84±0.07 36.96±3.65 0.1467±0.01 4.097±0.04 LPS 40388±1443## 109.1±1.04## 170.8±4.04## 6.277±0.36## 18.90±0.11##DXM 5283±133.6** 18.28±0.20** 41.24±2.63** 2.507±0.06** 8.887±0.14**25 37744±488** 102.4±0.55** 121.4±5.84** 3.70±0.13** 11.55±0.92**50 17502±229.8** 35.86±0.38** 91.58±7.86** 3.58±0.16** 9.28±0.20**75 5323±54.47** 9.53±0.16** 85.33±4.60** 1.70±0.10** 8.247±0.45**F 2308 24451 298.3 431.5 390.4 P<0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001
5.Discussion
Based on the fact that [Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.] is mainly used in the clinical treatment of RA, the NF-κB signaling pathway is closely related to the occurrence of RA, and the previous study of our group found that the total extract of [Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.]can dose-dependent down-regulate the basic level of NF-κB activity in RAW264.7 cells.TNF alpha or inflammatory markers and be able to block the activity of LPS induced the nf-kappa B increases the fact that the experiment of fine leaf hook catechu monomer compounds screening of anti-inflammatory activity and based on the nf-kappa B signaling pathway to explore its action mechanism.Due to the large amount of compounds required for animal experiments, monomer compounds extracted from traditional drugs are often insufficient.Therefore, LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells were selected to establish classical in vitro inflammation model, and monomer compounds that may have anti-inflammatory activity in [Berchemia lineata(L.)DC.] were screened at the cellular level.Using a small amount of the compound could point the way for further research.
NO is an important secondary inflammatory mediator, and the formation of NO is closely related to iNOS[10, 11], which is an important indicator of inflammatory response[12].NF-κB signaling pathway is a classical pathway that regulates various inflammatory responses[13].Activation of NF-κB dimer can enhance the secretion of inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α while promoting the expression of NF-κB, forming a positive feedback mechanism and forming a vicious cycle[14].While causing inflammation,TNF-α can promote macrophages to produce a large amount of NO and intensify the secretion of IL-6, thus promoting inflammation[15-18].In addition, the NF-κB signaling pathway was activated and phosphorylated by inflammatory factors, which further induced the secretion of iNOS and COX-2.iNOS and COX-2 play a key role in the production of inflammatory mediators in the process of inflammatory response, and overexpression can aggravate the inflammatory response[19-22].COX-2 aggravates inflammatory response by regulating the synthesis and release of NO and iNOS mediators[23-25].
The results showed that no significant drug toxicity was detected in RAW264.7 cells after administration for 24 h(50 μmol/L), and no significant effect was found on cell survival rate of RAW264.7 cells.The anti-inflammatory activity screening results of Griess method showed that 50 μmol/L of phyllocatechu monomeric compound inhibited the release of NO from RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS in different degrees for 12h, indicating that it had certain anti-inflammatory activity.Among them, No.9 bibenzyl, No.15 flavonoid and No.19 anthraquinone compounds showed strong antiinflammatory activities, suggesting that these compounds may be the basis of efficacy substances for clinical anti-inflammatory therapy of phyllocatechu.However, compound 19 had good anti-inflammatory effect but certain drug toxicity, while compound 9 and Compound 15 not only had good anti-inflammatory effect but little drug toxicity,providing a new idea for further anti-inflammatory research.The results of the anti-inflammatory activity gradient test showed that the anti-inflammatory activity of the monomeric compounds (No.2, 15, 16, 18, 21) was dose-dependent.In addition, simple phenolic monomeric compound No.21 can reduce the secretion of NF-κB,COX-2, iNOS, TNF-α and IL-6 in RAW264.7 cells.
In conclusion, the results hint fine leaf hook catechu zhonglian benzyl class(09), anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids compounds(15) monomer compounds is a plus, could be a play the efficacy of the anti-inflammatory activity of material base.As a new skeleton compound, No.1 should be further explored.Simple phenolic compound No.21 can reduce the level of inflammatory cytokines in LPS-induced inflammatory models, and its mechanism may be related to the inhibition of abnormal activation of NF-κB pathway.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of complications related to spinal cord injury
- Research progress on the safety of nail placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery
- Study on the protective mechanism of Yizhiren regulating lipid metabolism in mice with diabetic nephropathy
- Differential expression analysis of coronary heart disease related genes in Hainan residents
- Mechanism of Qiliqiangxin capsule on the regulation of IP3Rs/GRP75/VDAC1 gene in myocardial infarction rat heart
- LINC00662 affects the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib drug by regulating miR‑106a‑5p/CAV1 axis
