基于指数增益迭代学习的机械臂二阶滑模控制方法
2023-10-05王策杨升张磊左信白小波
王策 杨升 张磊 左信 白小波


摘 要 机械臂系统具有非线性和不确定性,针对其精确跟踪控制问题,提出基于指数增益迭代学习的二阶滑模控制算法。首先,采用滑模控制增强系统对外界非重复干扰的鲁棒性,采用二阶滑模方法使控制器产生连续的控制信号,以减轻传统滑模控制的抖振问题;其次,结合指数增益迭代学习控制逼近由摩擦力等周期性扰动引起的有界重复性扰动,通过设置指数增益系数以提高迭代的收敛速度,该方法既能减小系统的跟踪误差又能保证系统的全局渐近稳定性,提高系统的动态性能;最后,分析算法收敛的充分条件,以二自由度机械臂为例对所提方法进行理论数值仿真。仿真结果表明:所提控制方法可以保证系统的稳定运行,输出跟踪误差收敛到接近零的邻域,提高了系统的控制精度,对干扰保持了良好的鲁棒性。
关键词 二阶滑模控制 指数增益迭代学习控制 机械臂系统 轨迹跟踪 抖振 控制精度
中图分类号 TP18 文献标志码 A 文章编号 1000-3932(2023)05-0644-08
机械臂在工业生产中广泛应用,越来越受到工业界和学术界的重视,轨迹跟踪控制是机械臂的重点研究方向之一。机械臂轨迹跟踪控制的主要目标是通过给定各关节的驱动力矩,使得机械臂的位置、速度等状态变量跟踪给定的理想轨迹。在实际控制工程中,难以用精确的数学模型描述其动态特性,因为机械臂系统是一个具有非线性、不确定性的系统,存在很多不利于提高系统性能的因素,如:非线性因素,包括电机力矩波动、驱动饱和、耦合力矩、干扰力矩等;参数变化,包括负载变化导致的转动惯量变化、温度升高导致的参数变化等;测量延迟及测量噪声等因素。因此,在建立数学模型时需要对不确定因素作合理的近似处理,然而由近似模型来设计控制器,设计中被忽略的不确定因素往往会影响控制系统的品质,甚至导致系统不稳定[1]。
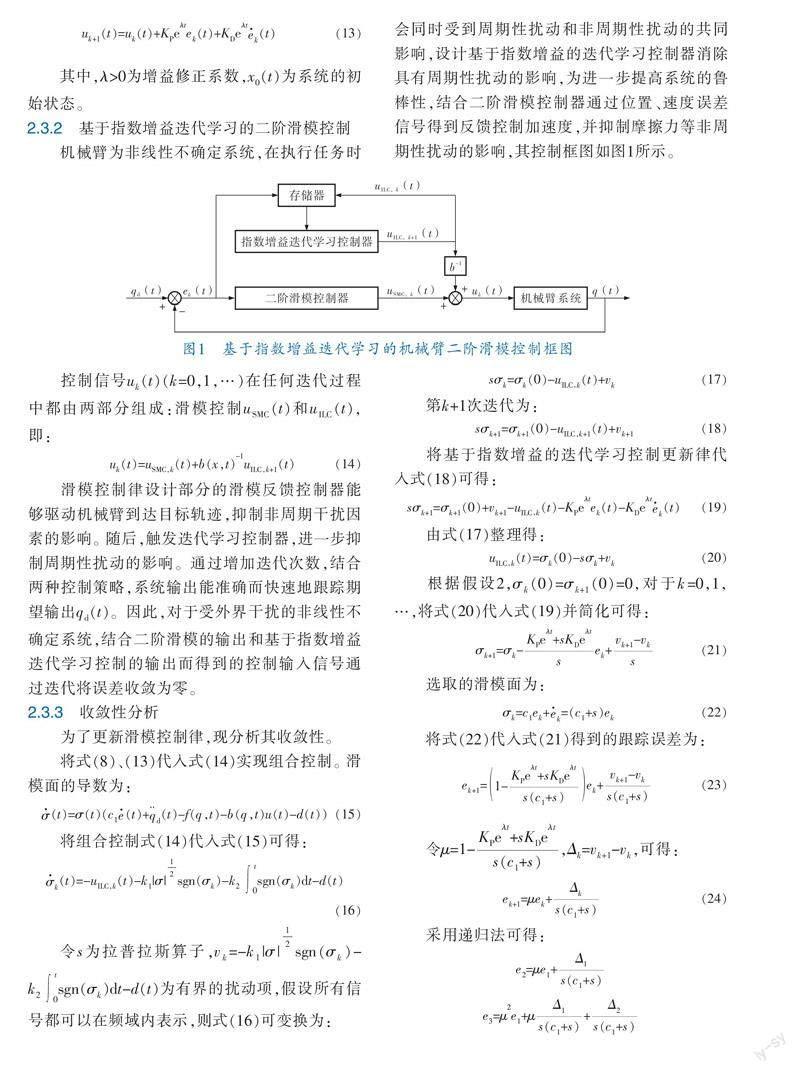
滑模控制[2~4]提出通过切换控制变量使系统按照预定的滑动模态的状态轨迹运动,保证被控系统在参数摄动和外界扰动情况下的稳定性,具有较强的鲁棒性,在机器人控制中得到了广泛的应用。文献[5]针对参数未知和外界干扰条件下的移动机械臂,提出了一种基于模糊小波神经网络的自适应分数阶非奇异终端滑模控制,仿真实验验证了方法的可行性和有效性;文献[6]设计了滑模控制器调节机械臂的死区和重力未知行为。然而,传统滑模控制输出的不连续切换会引起抖振效应,在实际操作中,控制信号的不连续会损坏执行器或控制装置。边界层法和饱和函数法是解决抖振问题的常用方法[7,8]。但是,饱和函数替代符号函数法在减小抖振和保证控制精度之间难以两全,高阶滑模算法是一种利用滑模积分项有效减轻抖振的方法[9,10]。文献[11,12]提出的高阶滑模理论被认为是减小滑模抖振且保持系统较高控制精度的有效手段,并提出几种二阶滑模控制算法。二阶滑模的核心思想是将不连续切换项转移到滑模面的二阶导数上,进而通过积分作用实现控制输出的连续性,因此可以有效抑制抖振,同时保持鲁棒性。文献[13]提出一种二阶滑模控制算法,应用于一类多输入多输出系统,该算法不需要滑动曲面的导数,所得到的控制是动态的,减轻了系统输入的抖振。尽管滑模控制算法简单、鲁棒性强,但实际机械臂控制系统中模型不确定性的存在使得仅使用该算法时跟踪效果不够理想。
迭代学习控制(ILC)的优势以其在控制具有部分未知和时变参数的重复系统方面的性能得以体现,并在控制领域得到广泛运用[14]。基本的ILC方法是根据过去迭代得到的跟踪或性能误差,在下次系统运行时调整控制输入,从而改善瞬态响应,最终达到预期轨迹[15~17]。文献[18]设计了一种迭代学习控制器,以选择适当的学习增益实现任意高精度的输出跟踪,而不考虑测量误差。文献[19]对具有初始状态误差的p型迭代学习控制的收敛性进行分析,仿真结果证明了算法的有效性。文献[20,21]提出通过将滑模控制作为鲁棒部分和学习控制作为智能部分相结合的控制,既具有滑模控制的鲁棒性又具有迭代学习的高精度。文献[22]提出一种具有连续滑模的鲁棒迭代学习策略,并在SRV02旋转装置中进行验证,实验结果表明该算法的控制信号是连续的,具有良好的输出跟踪性能。
笔者提出一种基于指数增益迭代学习的二阶滑模控制算法,首先利用二阶滑模控制提高系统对外界非重复性干扰的鲁棒性,二阶滑模方法用以减轻抖振效应,然后采用指数增益迭代学习控制对系统模型和外界重复性扰动进行逼近,摆脱对特定数学模型的依赖,通过设置指数增益系数来提高迭代的收敛速度。
显示了系统的控制输入状态性能。闭环系统的输入信号是有界的,证明笔者设计的控制算法具有良好的控制性能,达到了设计指标。
仅采用迭代学习控制算法对机械臂系统进行位置和速度跟踪,给出了各关节的仿真结果如图9~12所示,可以看出,控制效果较差,抖振现象较为明显,且关节1的位置跟踪和速度跟踪始终存在误差。
对比分析实验结果可以看出,笔者设计算法的跟踪控制效果较为满意,控制系统具有良好的鲁棒性,能够有效抑制不同时变扰动,并提高了控制精度,实现了有效的轨迹跟踪。
4 结束语
針对非线性不确定机械臂系统的输出跟踪问题,提出基于指数增益迭代学习的二阶滑模控制方法。首先采用二阶滑模控制消除外界非重复性干扰的影响,二阶滑模方法可以使控制器产生连续的控制信号以削弱抖振效应,将连续二阶滑模方法综合到迭代学习控制系统的设计中对系统模型和有界外界扰动进行逼近,通过设置指数增益系数以提高迭代的收敛速度,在李亚普诺夫方法的基础上,进一步研究和阐明了所提方法的收敛性和稳定性。仿真实例表明,在不同时变扰动环境下,基于指数增益迭代学习的二阶滑模控制具有良好的输出跟踪性能。
参 考 文 献
[1] LIU J K,ER L J.Sliding Mode Controller Design for Position and Speed Control of Flight Simulator Servo System with Large Friction[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics(China),2003,14(3):59-62.
[2] TRAN D T, TRUONG H V A, AHN K K.Adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control of robotic manipulator based neural network approach[J].Precis Eng Manuf,2021,22(3):417-429.
[3] PHAM D B,KIM J,LEE S G,et al.Double-loop control with hierarchical sliding mode and proportional integral loop for 2D ridable ballbot[J].Precis Eng Manuf,2019,20(9):1519-1532.
[4] WANG H, PAN Y,LI S, et al. Robust sliding mode control for robots driven by compliant actuators[J].IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol,2019,27(3):1259-1266.
[5] WU X R,HUANG Y Y.Adaptive fractional-order non-singular terminal sliding mode control based on fuzzy wavelet neural networks for omnidirectional mobilerobot manipulator[J].ISA Transactions,2022,121:258-267.
[6] JD JESUS RUBIO.Sliding mode control of robotic arms with deadzone[J].IET Control Theory & Applications,2017,11(8):1214-1221.
[7] CHEN M, YU J. Disturbance observer-based adaptive sliding mode control for near-space vehicles[J].Nonlinear Dynamics,2015,82(4):1671-1682.
[8] INCREMONA G P,CUCUZZELLA M,FERRARA A.Adaptive suboptimal second-order sliding mode control for microgrids[J].International Journal of Control,2016,89(9):1-37.
[9] UTKIN V I,POZNYAK A S.Adaptive sliding mode control with application to super-twisting algorithm:Equivalent control method[J].Automatica,2013,49(1):39-47.
[10] SHTESSEL Y,TALEB M,PLESTAN F.A novel adap-
tive-gain super-twisting sliding mode controller:Methodology and application[J].Automatica,2012,
48(5):759-769.
[11] LEVANT A.Higher Order Sliding Modes and Their Application for Controlling Uncertain Processes[D].Moscow:Institute for System Studies of the USSR Academy of Science,1987.
[12] LEVANT A.Sliding Order and Sliding Accuracy in Sliding Mode Control[J].International Journal of Control,1993,58(6):1247-1263.
[13] KHAN M K,SPURGEON S K.Robust MIMO Water Level Control in Interconnected Twin-Tanks Using Second Order Sliding Mode Control[J].Control Engineering Practice,2006,14(4):375-386.
[14] LU J, CAO Z,ZHANG R, et al.Nonlinear monotonically convergent iterative learning control for batch processes[J].IEEE Trans Ind Electron,2018,65(7):5826-5836.
[15] BRISTOW D A, THARAYIL M, ALLEYNE A G.A survey of iterative learning control[J].IEEE Control Systems Magazine,IEEE,2006,26(3):96-114.
[16] ARDAKANI M M G, KHONG S Z, BERNHARDSSON B.On the convergence of iterative learning control[J].Automatica,2017,78:266-273.
[17] SHEN D,WANG Y.Survey on stochastic iterative lea-rning control[J].Process Control,2014,24(12):64-77.
[18] WANG Y, GAO F, DOYLE F J. Survey on iterative learning control,repetitive control,and run-to-run co-ntrol[J].Process Control,2009,19(10):1589-1600.
[19] LIU X,LI Y.The convergence of iterative learning control for some fractional system[J].Advances in Difference Equations,2017,132:4221-4360.
[20] ONIZ Y,KAYNAK O.Control of a direct drive robot using fuzzy spiking neural networks with variable structure systems-based learning algorithm[J].Neurocomputing,2015,149:690-699.
[21] XU J X,CAO W J.Learning variable structure control approaches for repeatable tracking control tasks[J].Automatica,2001,37(7):997-1006.
[22] CHEN W, CHEN Y Q, YEH C P.Robust iterative learning control via continuous sliding?鄄mode technique with validation on an SRV02 rotary plant[J].Mechatronics,2012,22(5):588-593.
(收稿日期:2023-02-07,修回日期:2023-03-22)
The Second-order Sliding Mode Control Method for Manipulator
Based on Exponential Gain Iterative Learning
WANG Ce1, YANG Sheng2, ZHANG Lei1, ZUO Xin1, BAI Xiao-bo1
(1. College of Information Science and Engineering, China University of Petroleum (Beijing);
2. PetroChina Northwest Marketing Co.Wuhan Branch)
Abstract Considering manipulator systems nonlinearity and uncertainty and its poor precision tracking control, a second-order sliding mode control algorithm based on exponential gain iterative learning was proposed. Firstly, having the sliding mode control used to enhance robustness of the system against external non-repetitive disturbances and the second-order sliding mode adopted to make the controller generate continuous control signals to weaken chattering in the traditional sliding mode control; secondly, having the exponential gain iterative learning control used to approximate the bounded repetitive disturbances caused by periodic disturbances such as friction and the exponential gain coefficient set to improve convergence speed of the iteration. This method can reduce tracking error of the system and ensure global asymptotic stability of the system as well as improve dynamic performance of the system; finally, having the sufficient conditions for convergence of the algorithm analyzed, and the theoretical numerical simulation of the proposed method carried out through taking a two-degree-of-freedom manipulator as an example. The simulation results show that, the control method proposed can ensure stable operation of the system, and the output tracking error converges to the neighborhood near zero to improve control accuracy of the system and maintain good robustness against interference.
Key words two-order sliding mode control, iterative learning control with exponential gain, manipulator system, trace tracking, chattering, control precision
作者簡介:王策(1997-),硕士研究生,从事控制工程的研究。
通讯作者:左信(1964-),教授,从事计算机模式识别、先进控制理论与应用和智能控制的研究,zuox@cup.edu.cn。
引用本文:王策,杨升,张磊,等.基于指数增益迭代学习的机械臂二阶滑模控制方法[J].化工自动化及仪表,2023,50(5):644-651.
