自噬流参与癫痫发作的研究进展
2022-11-11徐祖才
张 帆,肖 飞,徐祖才
(1.遵义医科大学附属医院 神经内科,贵州 遵义 563099;2.重庆医科大学第一附属医院 神经内科,重庆 渝中 400016)
Epilepsy is a common and frequently-occurring disease of the nervous system.It is a clinical syndrome with recurrent seizures and stereotyped characteristics caused by abnormal discharge of brain neurons with high synchronization.Its main feature is the repeated and unpredictable interruption of normal brain function.which are mainly characterized by repeated and unpredictable interruptions of normal brain function.Epilepsy is not a single disease,but reflects a variety of symptoms of potential brain dysfunction,which may be caused by many different causes.It can seriously affect the physical and mental health and quality of life of patients.However,there is still a lack of in-depth understanding of the pathogenesis and effective treatment of epilepsy[1-2].Autophagy is a highly dynamic,multi-step biological process,also known as "self-digestion",which is a physiological phenomenon widely present in eukaryotic cells,responsible for the removal of misfolded protein aggregates,lipids and damaged organelles that provide alternative energy sources under starvation and certain other adverse conditions to ensure cell survival and play an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis,health[3-4].It consists of several steps:(1)The formation of phagocytic vesicles; (2)The formation of autophagosomes; (3)Autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes to form autophagolysosomes; (4)Degradation and reuse of autophagolysosomes and substrates.Autophagic Flux refers to the complete process in which all four stages of autophagy are completed.Substrate degradation in autophagosomes can only be achieved when the entire autophagic flux is completed.Impairment of autophagic flux will lead to dysfunction of autophagosomes to degrade substrates[5].Previous studies have mostly used the number of autophagosomes to evaluate the strength of autophagy,and the level of autophagy flux requires a combination of multiple autophagy detection methods to effectively detect.Because from the perspective of autophagic flux,the number of autophagosomes is affected by both formation and clearance.The concept of autophagic flux can better reflect the dynamic and multi-step nature of autophagy,and help autophagy researchers to distinguish whether the increase in autophagosome comes from autophagy-induced activation or inhibition of autophagosome clearance.
Moderate autophagy plays a very important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and cellular health,while autophagy occurs excessively or is blocked,autophagy may also be detrimental,possibly leading to activation of apoptosis and cellular die[6].Excessive autophagy may lead to neuronal stress,but low degradation activity also affects the removal of toxic substrates,which in turn affects neuronal physiology and leads to disease.Neurons appear to be particularly dependent on autophagy because of their properties that make them highly sensitive to the accumulation of toxic proteins and damaged organelles[7].Autophagy is frequently dysregulated in aging and neurodegenerative diseases,and autophagy at synaptic sites appears to play a crucial role in neurodegenerative diseases.In addition,the role of autophagy in neurodevelopment,synaptogenesis,and establishing correct connections is being discovered.It is therefore not surprising that abnormalities in autophagy have been demonstrated in a range of neurodevelopmental disorders,often associated with early-onset epilepsy[8].Abnormal autophagy has also been reported to cause genetic epilepsy,such as Tuberous sclerosis and Lafora disease,and epilepsy can in turn trigger abnormal autophagy.Furthermore,autophagy also plays a protective or detrimental role under epileptic stress[9-10].Growing evidence suggests that autophagy is altered in various neurological diseases,such as neurodegenerative diseases and acute neurological injury[11].However,the relationship between the four stages of autophagy,that is,autophagic flux,and epilepsy remains unclear.Therefore,this article intends to review the possible mechanism of autophagic flux involved in epilepsy.
1 The formation of phagosomes and autophagosomes in epilepsy
Substrates of autophagy include cytoplasmic proteins,redundant and damaged organelles such as mitochondria,peroxisomes and nuclei,lipids,and invading microorganisms.When autophagy is initiated,an incomplete double-membrane structure called a phagophore is formed.Substrates are sequestered by phagocytic vesicles,which elongate and seal around the substrate,selectively or non-selectively engulf autophagic substrates and form more mature double-membrane structures known as autophagosomes[12].The formation of autophagosome is a complex molecular process,which involves the production of various protein complexes and the transduction of various signals.body,which eventually fuses with late endosomes or lysosomes[13].
Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.If autophagosome formation is impaired,it may lead to excessive accumulation of glutamate receptors and lead to abnormal neuronal excitability and protein homeostasis.And if the abnormal autophagic flux leads to the abnormal accumulation of autophagosomes in cells,it may lead to a variety of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD),Parkinson’s disease (PD),etc[14].It has been found that autophagosome accumulation increases the production of reactive oxygen species and leads to increased mitochondrial membrane permeability,leading to cell death[15].The formation and clearance of autophagosomes is an important process of autophagic flux.From the perspective of autophagic flux,both the formation of autophagosomes and the obstruction of autophagosome clearance can lead to an increase in the number of autophagosomes.The levels of autophagic flux represented by these two conditions are opposite.If the formation of autophagosomes increases,it means that the level of autophagic flux and autophagy is up-regulated.If the clearance of autophagic flux is restricted,it means that the autophagic flux and autophagy Phagocytosis level decreased[16].Therefore,autophagy cannot be judged only by the number of autophagosomes.It is more scientific and reliable to judge the level of autophagy by the combination of multiple detection methods and whether the autophagy flux is unobstructed.
Sodium valproate (VPA) is a classic antiepileptic drug,which is widely used in clinical practice.Some studies have found that VPA has the function of histone deacetylase inhibition,which can increase the number of autophagosomes by increasing the degree of histone acetylation,thereby affecting the level of autophagy[17].Therefore,as an anti-epileptic drug,VPA can reduce the level of epileptic seizures and reduce neuronal damage caused by epilepsy during epilepsy treatment.Therefore,when using VPA-type drugs to treat epilepsy,it can be considered to antagonize its effect on activating autophagy,thereby inhibiting the excessive activation of autophagy and reducing neuronal damage.
2 The fusion of lysosome and autophagosome in epilepsy
After autophagosomes are formed,they are transported to lysosomes and fused with lysosomes to degrade substrates.Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles present in animal cells and are the cellular center for signal transmission,metabolism and quality control,controlling cell growth,division and differentiation[18-19].Consists of more than 50 acid hydrolases with digestive functions and 120 membrane proteins that maintain lysosomal integrity and regulate lysosomal transport,fusion,and intralysosomal pH,lysosomes are essential for eliminating cellular debris,damaged organelles and invading microbes.The function of lysosomes is not limited to protein degradation and recycling of cellular waste through the activity of lysosomal hydrolases,but rather these organelles are also involved in fundamental processes such as secretion,plasma membrane repair,signaling and energy metabolism[20].Lysosomes as independent organelles have been implicated in human disease long before their formal discovery.Mutations in about 50 genes encoding luminal hydrolases and membrane-piercing cells trigger a series of disorders known as lysosomal storage disorders,which possess properties that result in amino acids,lipids,sugars and nucleotides in the lysosomal lumen accumulation of digestive products.Pathophysiological consequences of these storage phenotypes include neurodegenerative diseases,metabolic imbalances,and severe growth retardation[19].
Bafilomycin A1 (bafa1) is a classical autophagy inhibitor,which can inhibit the level of autophagy by affecting the fusion of autophagosome and lysosome.Some studies have found that most of the DRG neurons treated with 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) will die after 24 hours,while the simultaneous treatment with bafa1 can almost completely block the cell death[21].It shows that inhibiting the fusion of autophagy and lysosome has a protective effect on neurons in the pathological process of epilepsy.
More recently,lysosomal dysfunction has been implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of neurodegenerative diseases,such as Parkinson’s disease,Alzheimer’s disease,and Huntington’s disease,in which initial protein-inhibitory damage may be progressively diminished the ability of the autophagy-lysosomal system to perform degradative functions,resulting in a domino effect that ultimately impairs cell viability[22].Loss of lysosomal function may be a major disease mechanism leading to neuronal death[23].If lysosomal function is abnormal or specific substrates cannot be degraded,resulting in abnormal accumulation of autophagosomes,it will affect many tissues and organs,such as early-onset neurodegeneration in the central nervous system[24],causes apoptosis and severe cortical atrophy and triggers epilepsy[25].Moreover,the accumulation of abnormal proteins or damaged organelles is also a common cause of neurodegenerative diseases[26].For example,Niemann-Pick disease (NPC) is a lysosomal storage disorder that manifests as a progressive neurodegenerative disease associated with abnormal cholesterol transport between lysosomes and other cellular compartments[27].Moreover,studies have found that autophagosome accumulation also occurs in the hippocampus of patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy (rTLE) and hippocampal sclerosis (HS),leading to neuronal degeneration and damage[28].Autophagy lysosomal function is also impaired in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases[29].The triggering mechanism of each case is different,but the destruction of protein balance and quality control through autophagy injury may be the ultimate common consequence of the death of the affected neural cell population.
3 Degradation and release of substrates in epilepsy
Autophagy is a totality degradation process in which cytoplasmic entities such as proteins,sugars,lipids,RNA,and sometimes even entire organelles are engulfed in autophagosomes.The autophagosome then fuses with the lysosome,where the engulfed product is degraded.The final products are amino acids and lipids,which are released back into the cytoplasm and recycled by the cell.Thus,autophagy is a catabolic pathway that assists protein homeostasis by removing dysfunctional cellular components and promoting the production of new ones,activation of autophagy is very important for the production of amino acids and free fatty acids and the maintenance of intracellular ATP levels[30].
Glutamate is a neurotransmitter released by excitatory neurons,and it is also the most abundant excitatory amino acid in the brain.It plays a key role in various physiological and pathological brain functions in the central nervous system[31-32].Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity has been shown to contribute to the neurobiology of epilepsy.Specifically,it has been found to cause epilepsy-induced cell death,increased sensitivity to neuronal synchronization,and network alterations through oxidative stress or excitotoxicity[33-35].And the high content of glutamate in extracellular fluid will cause excitotoxicity,which is related to nervous system disorders (such as epilepsy)[36].Astrocytes represent most of the nerve cells of the central nervous system.They play a fundamental role in the clearance of neurotransmitters,such as glutamate and γ Aminobutyric acid (GABA)[37].glutamate and γ Aminobutyric acid can regulate synaptic transmission and electrochemical behavior of both cells.Astrocytes also maintain neuronal homeostasis by scavenging neurotransmitters in extracellular fluid.The activity of these astrocytes can be altered in diseases with neuronal abnormalities,such as epilepsy,Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease[38].Recent studies suggest that astrocytes may influence the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of epilepsy through homeostatic control of synaptic transmission from glutamate release[39].In status epilepticus,persistent neuronal activation results in the reduction in clearance of synaptic extracellular fluid glutamate.This leads to the accumulation of glutamate,increasing the chance of neuronal excitotoxicity[40].Glutamate does not easily penetrate the blood-brain barrier,so it can accumulate in the brain,and excessive release of glutamate can lead to excessive accumulation of calcium ions in mitochondria,which can be toxic to nucleotides and proteins in nerve cells,resulting in synchronous potential and epilepsy[41-42].This indicates that the excessive release of amino acids caused by enhanced autophagy may lead to the occurrence of epilepsy.
Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is the most prevalent form of epilepsy in humans and is often accompanied by neurodegenerative changes in the hippocampus.Like other neurological disorders,it may disrupt lipid balance[43].Lipids are important biomolecules involved in building various biofilms and represent 60% of the human brain.The major lipid components of membrane bilayers are phospholipids,which are involved in different cellular functions such as regulation of membrane fluidity/structure,permeability barriers,neurotransmitter release,membrane trafficking,signal transduction,etc[44].It plays a messenger role in the signal transduction of downstream lipid signals,which are related to pathology and normal physiology.Many animal epilepsy models have shown that phospholipid metabolism plays a key role in the pathological progress of epilepsy[45-47].Recent studies have shown significantly reduced triglycerides in the hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy compared with patients with other temporal lobe space-occupying lesions[48].
In summary,the obstruction of autophagy flux will directly affect autophagy function,and is closely related to neuronal apoptosis,network abnormalities,transmitter changes and other damage mechanisms,thus participating in the process of epilepsy formation and seizure (Figure1).At present,the mechanism of autophagy involved in the formation of epilepsy is still unclear.In the future research work,it is necessary to further study the relationship between autophagy and epilepsy,which will provide new targets for the treatment of epilepsy and help to develop new drugs for the treatment of epilepsy.
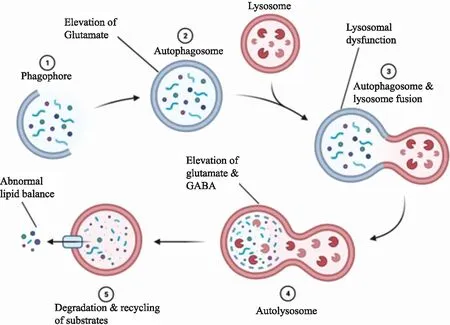
Figure 1 Autophagy may be involved in the mechanism of epilepsy(Made with biorender)
If there are obstacles in the transformation from phagosome to autophagosome,it will lead to the excessive accumulation of glutamate receptors and the abnormal excitability and protein homeostasis of neurons.If lysosomal dysfunction,it will lead to abnormal accumulation of autophagosomes,neurodegeneration and even neuronal death.When neurotransmitters such as glutamate and γ aminobutyric acid are released excessively,they will be toxic to nerve cells,which may lead to synchronous potential and seizures.γ aminobutyric acid lipid metabolism caused by blocked autophagy degradation substrate may also block neurotransmitters and signal transduction.
