能量法小电流接地方向判据的应用研究
2022-09-28金华锋曾兵元梁海东
杨 涛,金华锋,曾兵元,梁海东,赵 舫
能量法小电流接地方向判据的应用研究
杨 涛1,2,金华锋3,曾兵元3,梁海东2,赵 舫4
(1.杭州意能电力技术有限公司,浙江 杭州 310007;2.国网浙江省电力有限公司电力科学研究院,浙江 杭州 310007;3.南京智汇电力技术有限公司,江苏 南京 211100;4.浙江大学电气工程学院,浙江 杭州 310027)
为解决小电流接地系统中利用单点电气量难以准确判断接地故障方向的问题,提出了一种改进的能量法接地方向判据。根据叠加原理分析了单相接地故障暂态等值电路,指出了测量点处的零序能量由故障初始时刻的电容充电能量和维持LC振荡的稳态振荡能量两部分组成,分析了零序能量在不同接地方式和不同接地电阻下的特点。为了简化定值整定原则,对零序能量函数进行了离散化处理并作了二次积分,提出了实用的能量二次积分判据。对中性点不接地方式、中性点经消弧线圈完全补偿的接地方式下的金属性故障和经3000W电阻接地故障进行了仿真测试。仿真结果表明,上述各种故障情况下该判据均能判别故障方向。
小电流接地系统;能量法;分布电容;共振频率
0 引言
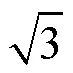
国内外学者对小电流接地选线方法进行了广泛深入的研究[3-4]。现有方法可分为主动式和被动式。主动式主要采用注入信号的方法[5-6],通常用于故障线路停电后的故障点定位。被动式利用故障时的电压、电流量进行接地选线,可分为基于稳态信息、基于暂态信息和基于综合信息的三类选线方法。
基于稳态信息的选线方法[7-8]有零序电流幅值法[9-10]、零序电流比相法[11-12]、零序无功功率方向法[13]、零序有功功率法[14-15]和5次谐波法[16-17]等。上述方法原理相对简单,但对于经消弧线圈补偿的小电流接地系统或间歇性故障,由于没有稳定的稳态电流,上述方法很难正确选出故障线路。
基于暂态信息的选线方法有首半波法[18]、基于小波变换的暂态零序电流比较法[19-27]和基于暂态零流波形特征的定位方法[28]等。通常情况下,故障产生的暂态电流远大于稳态电流且不受中性点接地方式的影响,因此该类方法具有较高的可靠性和灵敏度。但该类方法均需要采集高频信号进行分析。首半波法受故障相角、系统参数的影响较大,应用效果一般;基于小波变换的暂态零序电流比较法和基于暂态零序波形特征的定位法均需进行复杂的计算,对装置硬件的处理能力有较高的要求。
基于综合信息类方法主要为复合判据法[29-30]。复合判据法根据稳态法和暂态法的适用条件和优缺点,并利用信息融合和模糊决策理论进行故障选线,取得了较好的效果。但复合判据法需要的信息量比较多,适用于变电站的故障选线,但无法应用于架空线路或电缆线路的分段、分支线等仅能获取单点信息量的场合。
浙江大学何奔腾老师于1998年提出了能量法小电流接地选线原理[31]。能量法将零序电压和零序电流乘积的积分定义为能量函数,并根据能量函数值的正负判断故障方向。该方法算法简单,仅需单点的零序电压和零序电流而无需多点的综合信息,不受消弧线圈的影响,可实现配网架空线路或电缆线路的零序方向判别。但该方法未深入分析暂态能量和稳态能量对判据的影响,也未探讨系统模型、暂态频率和装置采样率之间的关系。对经消弧线圈完全补偿的接地故障,由于其故障后稳态零序电流为0,若按该方法所采用的每周波12点采样值进行能量积分,其值为0,将无法判断故障方向。
本文详细分析了系统模型和暂态电流频率之间的关系,指出对于短线暂态电流频率可能高达数千赫兹,采用能量法计算故障方向时的装置采样频率,至少需4800 Hz;提出了实用的能量法保护判据,为能量法小电流接地判别原理应用于配网架空线路或电缆线路接地故障定位提供有益探索。
1 原理

图1 单相接地故障暂态等效电路
假设金属性故障发生在电压峰值时刻,则


中性点零序补偿电流为

叠加电容和中性点电流后,零序电流为
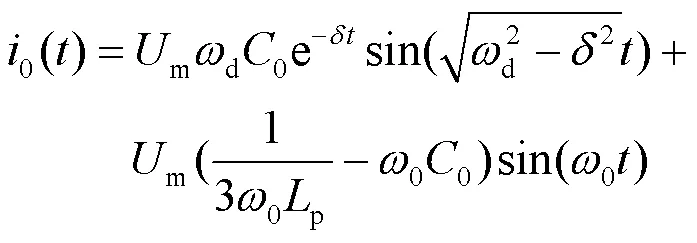

测量点处的零序能量定义为


其中:



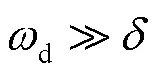

图2为中性点不接地系统单相接地故障时反向叠加电源产生的零序能量,红色曲线为电容充电能量,蓝色曲线为稳态振荡能量,绿色曲线为两者的叠加。从波形可以看出,衰减后的电容充电能量和稳态振荡能量同方向,暂态能量在故障发生瞬间快速由0增大到最大值,然后快速衰减,衰减到第一个波谷,其幅值也远大于0。叠加同方向的稳态振荡能量后,更能确保零序能量大于0。
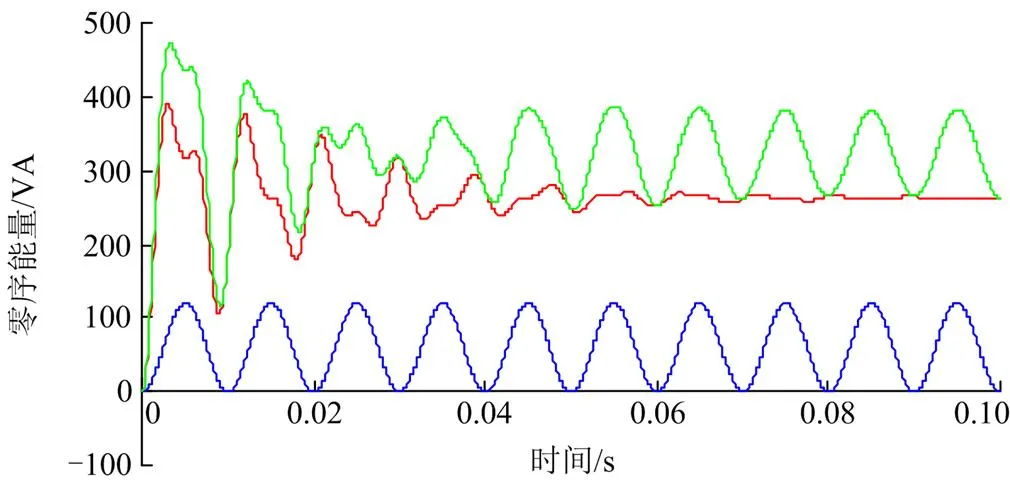
图2 中性点不接地系统单相接地时的故障能量
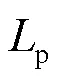

图3 中性点过补偿系统单相接地时的故障能量
2 保护判据
测量点安装于变电站线路出口处或线路分段。变电站线路出口处,规定电流方向由母线指向线路为正方向;线路分段处,规定电流方向由电源指向负荷为正方向。由第1节的分析可知,若单相接地故障发生在本线正方向,零序能量值为负;若单相接地故障发生在母线或其他线路,零序能量值为正。对式(6)进行离散化处理,得到基于暂态零序能量的单相接地方向判据,如式(11)所示。

由于零序电流暂态分量的共振主频率为300~ 1000 Hz[32],为了避免暂态能量泄漏引起方向误判,采样频率取4800 Hz。
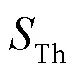



图5 单相高阻接地时的故障能量积分
3 仿真测试


图6 仿真系统模型

表1 模型参数


图7 中性点不接地系统的能量积分值
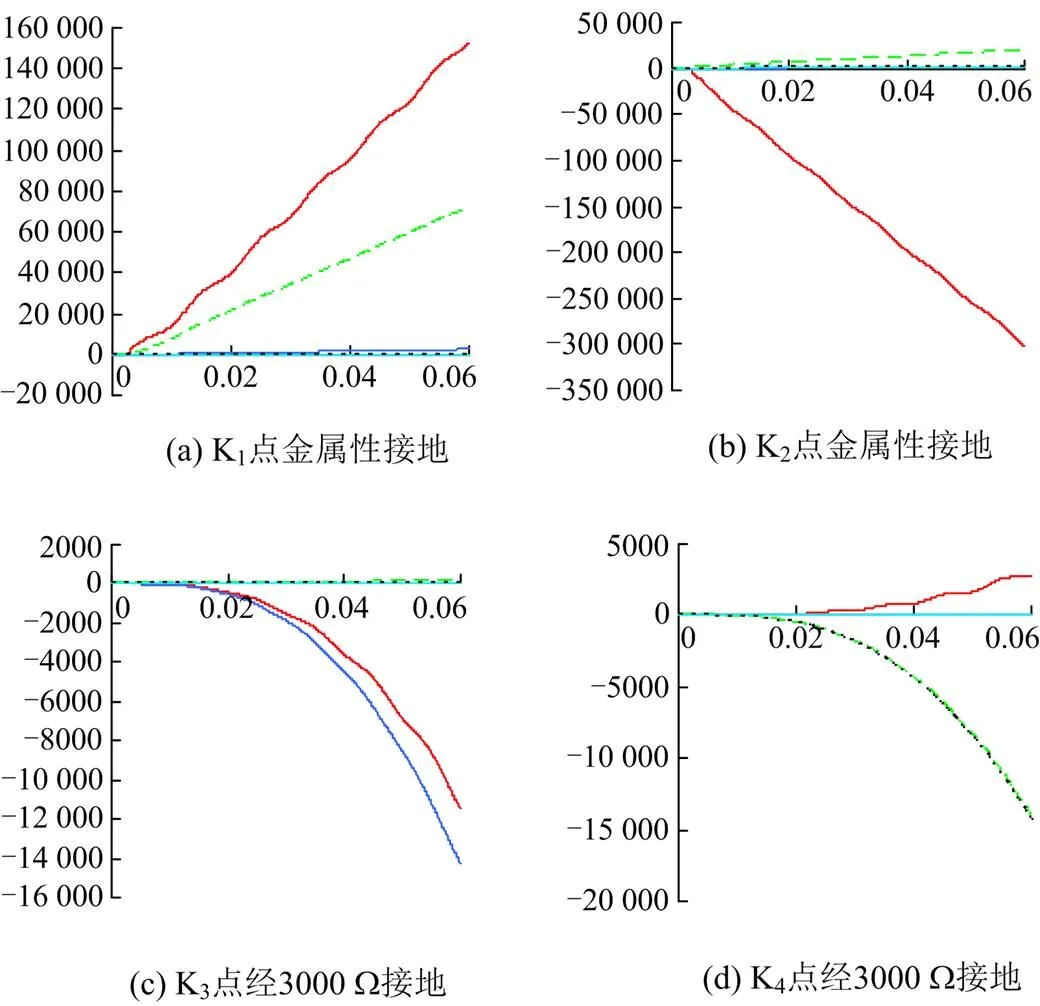
图8 经电抗完全补偿系统的能量积分值
仿真结果证明了能量积分的方向性,根据能量积分值可以判别单相接地故障方向,当能量积分值为负时,故障发生在观测点正方向;当能量积分值为正时,故障发生在观测点反方向。

比较图7、图8各个故障点的仿真结果,对于金属性故障,不管是中性点不接地系统还是经消弧线圈补偿系统,各点的能量积分值差别不大;对于高阻接地故障,由于分布电容和消弧线圈产生LC共振,相当于末端开路,因此作用于分布式的零序电容越大,对应的零序电流和零序能量积分也更大,能量积分方向判据更灵敏。

4 结论
基于零序能量积分的单相接地故障方向判据,需要以较高的采样频率采集零序电压和零序电流,将两者瞬时值相乘进行两次积分;当能量积分小于0时,故障发生在观测点正方向;当能量积分大于0时,发生在反方向。不管是中性点不接地系统,还是中性点经消弧线圈完全补偿的小电流接地系统,采用能量积分方向判据,均能有效判别单相接地故障方向。
在实际应用中,还需要考虑采样误差、计算误差、零序不平衡分量以及外部干扰等因素对判据的影响。
[1] 李福志, 郑卫宾, 张文海, 等. 基于回路直流电阻测量的输电线路单相接地故障离线故障定位[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54(2): 140-146.
LI Fuzhi, ZHENG Weibin, ZHANG Wenhai, et al. Fault path direct-current resistance based off-line single-phase- to-ground fault location[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54(2): 140-146.
[2] 蒋原, 李擎, 冯茜, 等. 基于BP神经网络的直流电网故障定位与保护方法[J]. 高压电器, 2020, 56(8): 23-28.
JIANG Yuan, LI Qing, FENG Qian, et al. Fault location and protection method for DC power grid based on BP neural network[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2020, 56(8): 23-28.
[3] 王闰羿, 胡兵, 王良毅, 等. 分布式小电流接地保护研究与应用[J]. 供用电, 2020, 37(5): 56-63.
WANG Runyi, HU Bing, WANG Liangyi, et al. Research and application on distributed small-current grounding protection[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2020, 37(5): 56-63.
[4] 高俊青, 李题印, 胡晓琴, 等. 考虑频段筛选的配电网单相接地选线方法研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48(2): 92-97, 118.
GAO Junqing, LI Tiyin, HU Xiaoqin, et al. Line detection methods for single-phase grounding fault in distribution network considering frequency band selecting[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48(2): 92-97, 118.
[5] 刘斯琪, 喻锟, 曾祥君, 等. 基于零序电流幅值连调的小电流接地系统故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(9): 48-56.
LIU Siqi, YU Kun, ZENG Xiangjun, et al. Fault location method of a non-effective system based on zero sequence current amplitude continuous regulation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(9): 48-56.
[6] 张国军, 张文周, 葛群, 等. 基于补偿参数的多零序电流互感器的小电流接地系统单相接地故障选线方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(2): 1-9.
ZHANG Guojun, ZHANG Wenzhou, GE Qun, et al. Single-phase ground fault line selection method of small current grounding system of multiple zero-sequence current transformer based on compensation parameters[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(2): 1-9.
[7] WELFONDER T, LEITLOFF V. Location strategies and evaluation of detection algorithms for earth faults in compensated MV distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2000, 15(4): 1121-1128.
[8] SHALIN A I, POLITOV E N. Ground fault protection for 6-10 kV distribution system[J]. Power and Electrophysics, 2002, 2: 430-433.
[9] 潘贞存. 比相式和比幅式小接地电流系统接地选线保护[J]. 山东电力技术, 1991(3): 60-64.
PAN Zhencun. Protection for non-solid grounded system based on phase and amplitude comparison[J]. Shandong Electric Power Technology, 1991(3): 60-64.
[10]帅军强, 邹维, 赵高帅. 基于暂态零序电流幅值比较的配电网单相接地故障定位[J]. 电工电气, 2012(4): 33-37.
SHUAI Junqiang, ZOU Wei, ZHAO Gaoshuai. Power distribution network single phase grounding fault positioning based on amplitude comparison of transient zero-sequence current[J]. Electrotechnics Electric, 2012(4): 33-37.
[11]贺家李, 宋从矩. 电力系统继电保护原理[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2001.
[12]张大波, 刘志刚, 张亚军, 等. 基于相差统计的小电流单相接地选线新判据[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2007, 31(11): 77-79, 102.
ZHANG Dabo, LIU Zhigang, ZHANG Yajun, et al. A new criterion for small current single-phase grounding line selection based on phase difference statistics[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2007, 31(11): 77-79, 102.
[13]庞清乐. 基于智能算法的小电流接地故障选线研究[D].济南: 山东大学, 2007.
PANG Qingle. Research on line selection of small current grounding fault based on intelligent algorithm[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2007.
[14] 牟龙华. 零序电流有功分量方向接地选线保护原理[J].电网技术, 1999, 23(9): 60-62.
MOU Longhua. Principle of zero sequence current active component directional grounding line selection protection[J]. power System Technology, 1999, 23(9): 60-62.
[15] 杜丁香, 徐玉琴. 消弧线圈接地电网有功选线[J]. 继电器, 2002, 30(5): 33-36.
DU Dingxiang, XU Yuqin. Arc suppression coil grounding, active line selection of power grid[J]. Relay, 2002, 30(5): 33-36.
[16] 郝玉山, 高曙, 杨以涵, 等. MLN系列小电流接地微机选线装置动作原理[J]. 电力情报, 1994, 2(2): 7-11.
HAO Yushan, GAO Shu, YANG Yihan, et al. The principle of MLN series devices for detecting earth fault line in neutral ungrounded power system[J]. Information on Electric Power, 1994, 2(2): 7-11.
[17] 郝玉山, 齐丽芳, 尹永生, 等. 零序网络中的谐波电流分布[J]. 华北电力学院学报, 1995, 22(3): 12-17.
HAO Yushan, QI Lifang, YIN Yongsheng, et al. Harmonic current distribution in zero sequence network[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power Institute, 1995, 22(3): 12-17.
[18] 徐丙垠, 李天友, 薛永端. 智能配电网建设中的继电保护问题[J]. 供用电, 2012, 29(5): 16-26.
XU Bingyin, LI Tianyou, XUE Yongduan. Relay protection issues in construction of smart distribution network[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2012, 29(5): 16-26.
[19] 操丰梅, 苏沛浦. 小波变换在配电自动化接地故障检测中的应用研究[J]. 电力系统自动化, 1999, 23(13): 33-36.
CAO Fengmei, SU Peipu. application of wavelet transform in grounding fault detection of distribution automation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 1999, 23(13): 33-36.
[20] 毛鹏, 孙雅明, 张兆宁, 等. 小波包在配电网单相接地故障选线中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 2000, 24(6): 9-13.
MAO Peng, SUN Yaming, ZHANG Zhaoning, et al. Application of wavelet packet in single-phase grounding fault line selection of distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2000, 24(6): 9-13.
[21] 贾清泉, 肖鹏, 杨以涵, 等. 小电流接地电网单相接地故障的小波选线方法[J]. 继电器, 2001, 29(3): 5-8.
JIA Qingquan, XIAO Peng, YANG Yihan, et al. Wavelets method to select single phase faulted circuit for small current grounding power systems[J]. Relay, 2001, 29(3): 5-8.
[22] 贾清泉, 刘连光, 杨以涵, 等. 应用小波检测故障突变特性实现配电网小电流故障选线保护[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2001, 21(10): 78-82.
JIA Qingquan, LIU Lianguang, YANG Yihan, et al. Abrupt change detection with wavelet for small current fault relaying[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2001, 21(10): 78-82.
[23] 戴剑锋, 张艳霞. 基于多频带分析的自适应配电网故障选线研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2003, 23(5): 44-47.
DAI Jianfeng, ZHANG Yanxia. Study on adaptively choosing fault line under single-phase to ground fault based on analysis of multi-frequency bands[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2003, 23(5): 44-47.
[24] CHAARI O, MEUNIER M. A recursive wavelet transform analysis of earth fault currents in Petersen-coil-protected power distribution networks[C] // Proceedings of the IEEE-SP International Symposium on Time-Frequency and Time-Scale Analysis, October 25-28, 1994, Philadelphia, PA, USA: 162-165.
[25] ASSEF Y, CHAARI O, MEUNIER M. Classification of power distribution system fault currents using wavelets associated to artificial neural networks[C] // Proceedings of the IEEE-SP International Symposium on Time- Frequency and Time-Scale Analysis, June 18-21,1996, Paris, France: 421-424.
[26] HUANG S J, HSIEH C T. Hi-impedance fault detection utilizing a Morlet wavelet transform approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1999, 14(4): 1401-1407.
[27] 邱进, 田野, 李冠华, 等. 基于现场实录波形的小电流接地故障暂态选线研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(6): 180-187.
QIU Jin, TIAN Ye, LI Guanhua, et al. Study on transient line selection of small current grounding fault based on field recorded waveforms[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(6): 180-187.
[28]李卫国, 许文文, 乔振宇, 等. 基于暂态零序电流凹凸特征的配电网故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(9): 48-56.
LI Weiguo, XU Wenwen, QIAO Zhenyu, et al. Fault section location method for a distribution network based on concave and characteristics of transient zero sequence current[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(9): 48-56.
[29] 曾祥君, LI K K, CHAN W L, 等. 信息融合技术在故障选线中的应用[J]. 继电器, 2002, 30(9): 15-20.
ZENG Xiangjun, LI K K, CHAN W L, et al. Earth fault feeder detection with information fusion[J]. Relay, 2002, 30(9): 15-20.
[30] 肖静. 中低压配电网单相接地故障检测的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2002.
XIAO Jing. Research on single-phase grounding fault detection in medium and low voltage distribution network[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2002.
[31] 何奔腾, 胡为进. 能量法小电流接地选线原理[J]. 浙江大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 32(4): 451-456.
HE Benteng, HU Weijin. A new principle to detect the grounded line in a neutral point indirectly grounded power system based on the energy function[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Natural Science Edition), 1998, 32(4): 451-456.
[32] 徐丙垠. 配电网继电保护与自动化[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2017.
Application of the criterion of small current grounding direction of the energy method
YANG Tao1, 2, JIN Huafeng3, ZENG Bingyuan3, LIANG Haidong2, ZHAO Fang4
(1. Hangzhou Yineng Electric Power Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310007, China; 2. State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. Electric Power Research Institute, Hangzhou 310007, China; 3. Nanjing Zhihui Power Technology Co., Ltd.,Nanjing 211100, China; 4. College of Electrical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China)
It is difficult to accurately determine the ground fault direction using a single-point electrical quantity in a small current grounding system. Thus an improved energy method-based grounding direction criterion is proposed. From the superposition principle, a single-phase ground fault transient equivalent circuit is analyzed, and the zero-sequence energy at the measurement point is composed of the capacitor charging energy at the initial moment of the fault and the steady-state oscillation energy to maintain the LC oscillation. The characteristics of the zero-sequence energy in different grounding modes and resistances are analyzed. To simplify the setting principle, the zero-sequence energy function is discretized and quadratic integration and a practical quadratic integral criterion is proposed. Simulation tests for a metallic fault and a 3000Wresistance grounding fault are conducted on the neutral point ungrounded or the neutral point fully compensated ground via the arc suppression coil. Results show that the criterion can distinguish the fault direction in the above fault conditions.
small current grounding system; energy method;distributed capacitance;resonance frequency
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.211519
2021-11-10;
2022-02-16
杨 涛(1978—), 男,硕士,高级工程师,研究方向为继电保护、稳控和配电自动化等;E-mail: 27462690@qq.com
金华锋(1972—),男,通信作者,博士,研究员级高级工程师,研究方向为继电保护、稳控和配电自动化等;E-mail:475774491@qq.com
曾兵元(1981—),男,硕士,高级工程师,研究方向为继电保护、稳控和配电自动化等。E-mail: 18311640@qq.com
国家重点研发计划项目资助(2017YFB0903100)
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFB0903100).
(编辑 姜新丽)
