Attack-Resilient Control Against FDI Attacks in Cyber-Physical Systems
2022-06-25BoChenYawenTanZheSunandLiYu
Bo Chen,, Yawen Tan, Zhe Sun, and Li Yu,
Dear editor,
This letter is concerned with the control of cyber-physical systems(CPSs) in the presence of malicious false data injection (FDI) attacks on actuators. The FDI attacks on actuators may result in faults of actuators or even the instability of CPSs. To tackle this problem, an unknown input observer (UIO) is proposed to estimate the system states and attack signals. For the aim of suppressing the impact of FDI attacks, a discrete-time sliding mode control (DSMC) algorithm is correspondingly put forward, where its reaching law is constructed based on then-th order difference of the estimation of attack signals.Finally, two simulation instances are presented to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Introduction: Cyber-physical system (CPS) plays a more and more pivotal role in the era of Industry 4.0 and attracts increasing attention from academy and industry profiting by the advantages of networks such as low cost, less wiring and convenient maintenance[1]-[3]. However, the introduction of communication networks breaks the closeness of conventional physical systems, and thus results in the threat of cyber attacks [4]-[6]. Among various cyber attacks, FDI attack is a typical and threatening one, whose working principle is to break the integrity and availability of data by injecting erroneous signals [7]. Therefore, it is of great significance to research effective defense strategies for CPSs.
In order to maintain the security and improve the robustness of CPSs under cyber attacks, the concept and methods of fault tolerant control (FTC) are proposed. According to different working principles, FTC is classified into two types, i.e., active ones and passive ones [8]. Active FTC utilizes attack-detection method to identify attacks or faults, and then appropriately manipulate the control input to compensate for the corresponding negative effect [9]. On the other hand, passive FTC normally ensures the stability of a control system by considering and addressing the worst case. In contrast with passive FTC, the active FTC input contains the estimating information of attacks or faults, which makes the control system less conservative. Hence, the investigation of active FTC has aroused keen interest from researchers and engineers.
As a robust and effective nonlinear control strategy, sliding mode control (SMC) is recognized as one of the most competent tools in dealing with uncertain systems owing to its robustness or even insensitivity to perturbations. Hence, SMC has been introduced for the purposed of ensuring the security of CPSs [10]. Specifically, Liet al. proposed an adaptive SMC law with a discontinuous input term to defense actuator attacks [11]. An SMC method is put forward by[12] to ensure that CPSs are stochastic finite-time bounded when subjected to random injection attacks. Note that the aforementioned studies are under the same assumption, i.e., the system states can be directly measured. Nevertheless, this strict requirement is normally difficult to be satisfied in reality. Consequently, observer-based SMC has drawn more and more attention. For instance, an observer-based event-triggered SMC method is developed for nonlinear networked control systems subjected to cyber attacks [13]. In [14], a novel technique based on neural network is presented to estimate the attack signals for attenuating the negative effect, and an adaptive SMC method is designed to guarantee the system’s security.
Motivated by the aforementioned research, this letter studies the control of CPSs under FDI attacks. An unknown input observer(UIO) is designed to jointly estimate the system states and attack signals, and a DSMC law is proposed to attenuate the impact of FDI attacks and maintain the stability of the control system. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed DSMC law is verified from two simulation examples.
The main contributions of this letter are summarized as follows:
1) For a system with unknown states, an UIO is put forward such that the system states and FDI attack signals can be accurately estimated.
2) A DSMC algorithm is accordingly designed by introducing the high-order terms with respect to the estimation of attack signals,which further reduces the width of the quasi-sliding mode domain(QSMD).



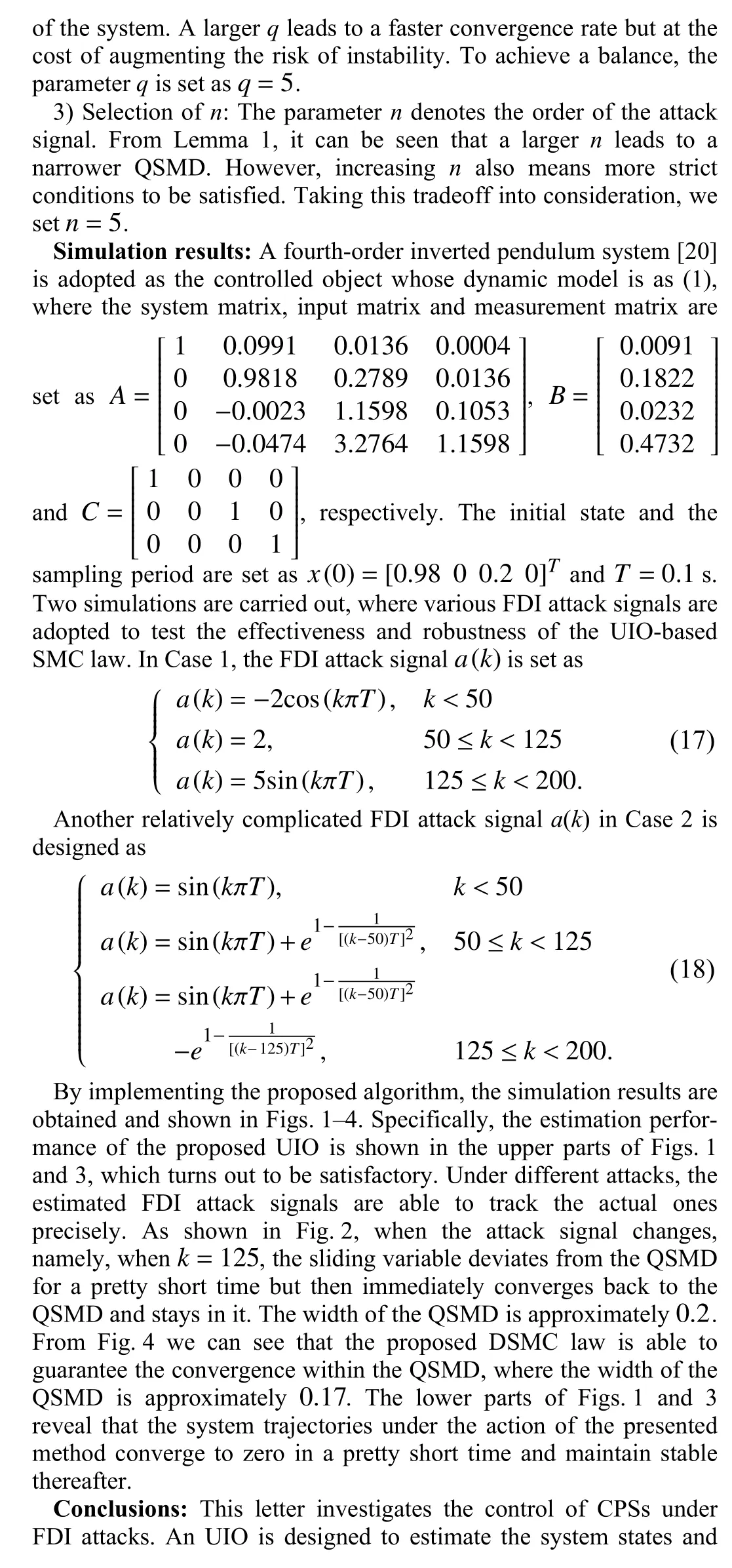
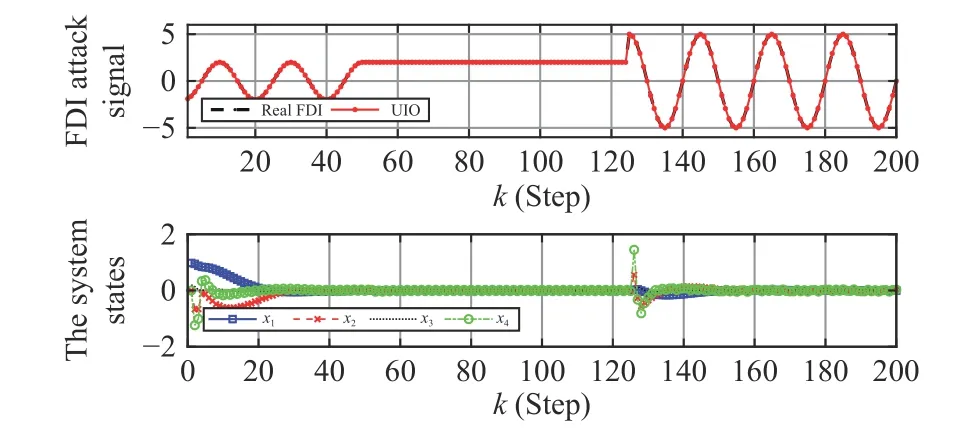
Fig. 1. Estimation of FDI attack signal and system states in Case 1.
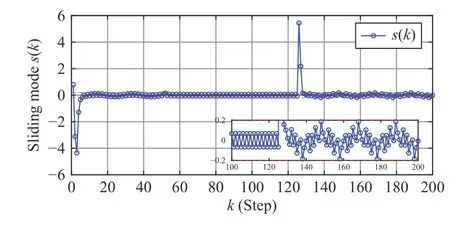
Fig. 2. Sliding mode dynamics in Case 1.
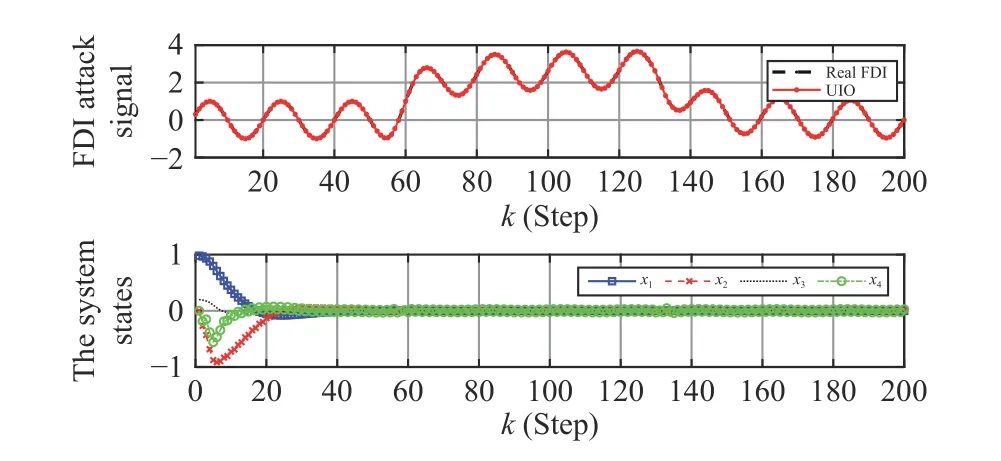
Fig. 3. Estimation of FDI attack signal and system states in Case 2.
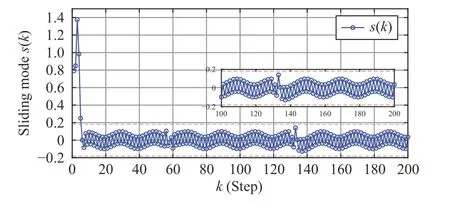
Fig. 4. Sliding mode dynamics in Case 2.

杂志排行
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Exponential Continuous Non-Parametric Neural Identifier With Predefined Convergence Velocity
- Exploring Image Generation for UAV Change Detection
- Wearable Robots for Human Underwater Movement Ability Enhancement: A Survey
- A Scalable Adaptive Approach to Multi-Vehicle Formation Control with Obstacle Avoidance
- Fuzzy Set-Membership Filtering for Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems
- Distributed Fault-Tolerant Consensus Tracking of Multi-Agent Systems Under Cyber-Attacks
