低渗透油气藏用阳离子型乳液表面活性和润湿性研究
2022-06-11刘淼罗根祥乔钰杨江
刘淼,罗根祥,乔钰,杨江
低渗透油气藏用阳离子型乳液表面活性和润湿性研究
刘淼,罗根祥,乔钰,杨江
(辽宁石油化工大学 石油化工学院,辽宁 抚顺 113001)
以自制的一种长链阳离子表面活性剂(SFC111)和低界面能物质(SFC115)构建出阳离子型乳液,研究其作为低渗透油气藏用表面活性剂性能。通过粒度仪考察乳液在水中的分散性,通过接触角测定仪考察经乳液处理前后岩心的接触角,通过旋转滴界面张力仪测试表面张力;通过计算得到乳液在20、70 ℃的热力学参数。结果表明,质量分数为0.5%的乳液在20 ℃时50=420.8 nm,70 ℃时50=728.0 nm;清水在岩心表面上的接触角从10°最大可增至120°;70 ℃下乳液可将清水的表面张力降至24 mN/m,表现出良好的防水锁性能。乳液符合langmuir吸附理论,其热力学结果表明,随着温度的升高,乳液表面吸附量降低,乳液表面分子所占面积减小,吸附层厚度降低。
低渗透油藏; 乳液; 表面张力; 接触角; 热力学计算
低渗透油气藏已经成为油气开发的热点,而低渗透油气藏通常具有泥质含量高、毛细管压力高、孔喉细、结构复杂、致密性差、油气流动阻力高等特点,在钻井过程中极易发生水锁损害[1⁃2]。
在钻井液中加入表面活性剂是处理水锁效应的较好方法[3]。特定的表面活性剂会有效地吸附在油水界面和低渗透储层岩石表面上,进而使储层岩石产生润湿反转作用[4⁃5]:当岩石接触角大于90°时,由于张力的作用,孔喉道的外来体使孔喉内出现向外排斥的倾向,进而极大地削弱储层岩石的自吸效应,从而降低溶液所受的毛细管力,减少孔喉道的自吸,缓解水锁效应[6⁃7]。
1 实验部分
1.1 材料和仪器
中石化胜利油田某区块天然岩心;低界面能疏水试剂(SFC115),分子质量17 000~25 000 g/mol,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;长链阳离子表面活性剂(SFC111),分子质量200~500 g/mol,实验室自制;SFC115和SFC111混合物分子质量16 000~23 000 g/mol;实验室用水均为去离子水。
OCA15EC接触角表面性能测定仪,德国Dataphysics公司;TX⁃500C型旋转滴界面张力仪,上海中晨数字技术设备有限公司;Winner 2000ZD型激光粒度仪,济南微纳颗粒技术有限公司;DF⁃101S集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器,山东鄄城华鲁电热仪器有限公司;SU8010场发射电子扫描显微镜,日本日立公司;YKA⁃100L高剪切乳化分散机(3 000 r/min),上海依凯机械制造有限公司;DZF⁃6050型真空干燥箱,上海精宏实验设备有限公司。
1.2 防水锁剂溶液制备
将SFC111和SFC115的混合物5 g加入到500 mL去离子水中,用高剪切乳化分散机搅拌10 min至完全分散,得到低渗透油气藏用阳离子型乳液防水锁剂母液。取适量母液于容量瓶中,稀释至质量分数为0.001%~1.000%,待用。
1.3 表面张力评价
1.3.1温度对表面张力影响实验 取不同质量分数阳离子型乳液防水锁剂于样品管中,向样品管注射约1 mL气泡,放置到保温套中,利用TX⁃500C型旋转滴界面张力仪于5 000 r/min下搅拌15 min,待气泡稳定,通过读取稳定气泡的直径(),分别记录溶液在20、70 ℃时的表面张力。
1.3.2吸附计算 根据20、70 ℃溶液表面张力测试所得数据,采用origin拟合,并根据Gibbs吸附式(式(1))、langmuir型等温吸附式(式(2))、标准吉布斯自由能式(式(3)),计算最大吸附量(max)、标准吸附自由能(Δθ)、饱和吸附层厚度()、最小分子面积(min)等热力学参数[10⁃13]。




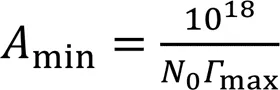

1.4 接触角测试
将天然岩心制备成1 cm×1 cm大小的小石块,使用600目砂纸将岩心两侧表面磨至光滑,准备不同质量分数的阳离子型乳液防水锁剂于50 mL烧杯中,为方便接触角测量,将打磨后岩心光滑面朝上放置在50 mL烧杯中,用保鲜膜封住烧杯,在不同质量分数乳液中浸泡8 h,用镊子轻轻取出,阴干24 h后,测试岩石表面的静态接触角及动态接触角。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 乳液粒径分析
将5 gSFC111和SFC115混合物放到高速搅拌机中搅拌10 min后,稀释至质量分数为0.5%的溶液,通过测试溶液粒径考察其分散性能。
乳液粒径分布如图1所示。随着温度的升高,降低了油相黏度,增强了相密度之间的差异,致使胶束碰撞次数增加,乳液发生破乳,故粒径增大[14]。胶束粒径分布较窄且为单峰分布,颗粒粒径达到微纳米级别。20 ℃时50=420.8 nm,70 ℃时50=728.0 nm。对于我国非常规油气致密储层微观结构,以胜利油田低渗油藏孔隙结构为例,一般低渗油藏平均孔喉半径为1 647 nm,故该乳液能进入到低渗油藏孔喉中,减少水锁损害[15]。
2.2 岩心扫描电镜分析
为了直观地了解吸附情况,以复配体系在岩心上的吸附为例,用扫描电镜观察阳离子型乳液防水锁剂吸附前后岩心表面的微观结构,结果如图2所示,其中图2(b)为用质量分数为0.5%阳离子型乳液防水锁剂浸泡后的岩石表面微观形貌。由图2可知,粗糙的岩石表面经处理后,阳离子型乳液在岩石表面发生了吸附[16⁃17],表面由颗粒状变为网状结构。

图1 20、70 ℃时SFC111和SFC115混合物质量分数为0.5%的乳液粒径分布
2.3 接触角测量
岩心处理前后接触角测试结果如图3、表1所示。由图3、表1可知,经乳液处理后的岩心接触角普遍大于90°,动态接触角前进角、后退角差值均小于2°,前进角均大于后退角,表现出良好的润湿反转性能[18⁃20];但是,随着阳离子型乳液防水锁剂质量分数的增加,接触角有所减小。这是由于阳离子型乳液防水锁剂吸附密度增大,空间排布方式由平面单层变为横向双层[21⁃22],亲水性有所增强,接触角减小。
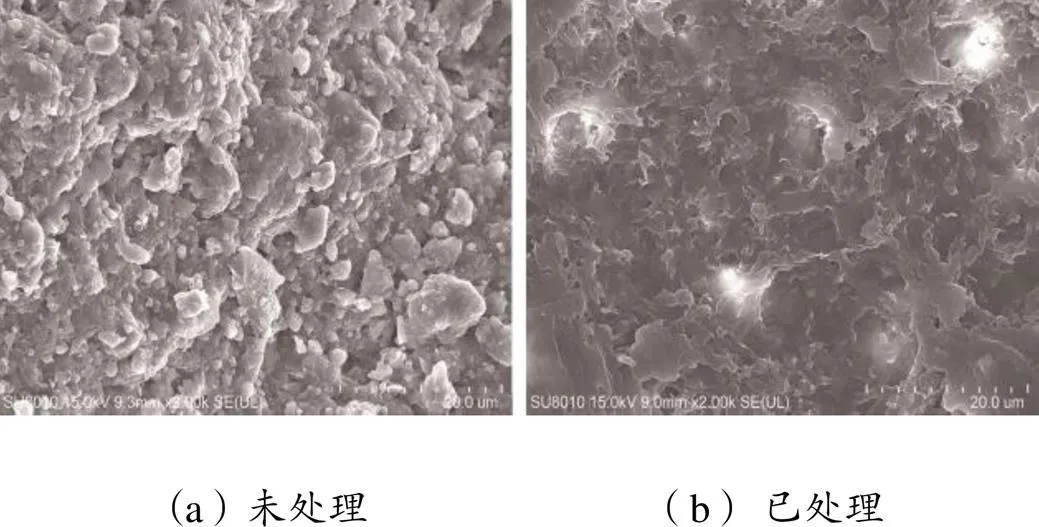
图2 岩石表面微观形貌

图3 阳离子型乳液防水锁剂质量分数对岩心接触角的影响

表1 阳离子型乳液防水锁剂处理岩心前后接触角测量结果
2.4 表面张力测试及吸附量计算

图4 阳离子型乳液防水锁剂在不同温度下的表面张力
2.4.2吸附量计算 为了更好地理解表面活性剂的表面张力与吸附的关系,利用表面张力origin拟合曲线,采用Szyszkowsk公式及式(1)计算乳液的吸附量[24],并运用langmuir吸附公式[25]拟合出吸附量曲线,结果如图5所示。
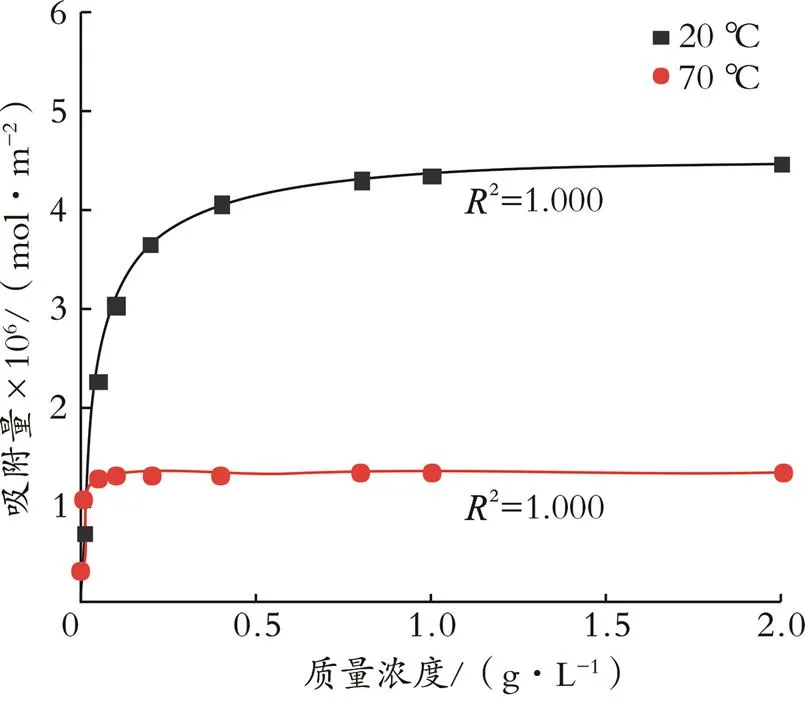
图5 阳离子型乳液防水锁剂在20、70 ℃时的吸附曲线
由图5可知,阳离子型乳液防水锁剂的吸附量随温度升高而降低,这是由于吸附为放热过程,温度升高会阻碍吸附过程,且较高的温度增加了阳离子型乳液防水锁剂在溶液中的溶解度,降低了阳离子型乳液防水锁剂的吸附量,故吸附量随着温度升高而降低[17]。同时,随着阳离子型乳液防水锁剂质量浓度的增加,吸附量先增加后趋于稳定,这是由于随着阳离子型乳液防水锁剂质量浓度的增加,阳离子型乳液防水锁剂以单分子层的形式吸附在吸附剂表面,阳离子型乳液防水锁剂质量浓度进一步增加,吸附量趋于稳定。
由图4和式(1)拟合出吸附量和质量浓度的关系曲线,结果如图6所示。根据图6得到式(2)中的饱和吸附量和吸附平衡常数,再由式(1)-(5)计算出体系热力学参数[25],结果如表2所示。
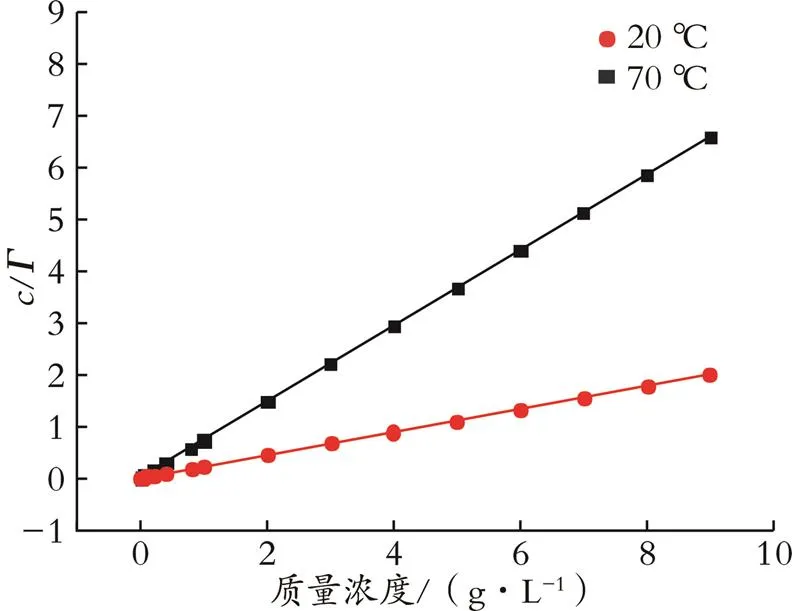
图6 阳离子型乳液防水锁剂在20、70 ℃时c/Γ⁃c曲线

表2 阳离子型乳液防水锁剂吸附计算结果
由表2可知,阳离子型乳液防水锁剂在20、70 ℃下的Δθ分别为-40.93、-56.54 kJ/mol,故在标准状态下表面吸附可以自发进行;提高温度减少了阳离子型乳液防水锁剂单位表面吸附量,增大了分子平均占有面积[26⁃27],降低了表面吸附层厚度。初步分析认为,温度升高使阳离子型表面活性剂溶解度升高达到krafft点,低界面能物质开始析出并在溶液表面发生聚集,故虽然表面吸附量降低,但是溶液的表面张力仍然减小。
3 结 论
(1)该阳离子型乳液防水锁剂在较低质量浓度时具有良好的表面活性,在70 ℃时表面张力值低至24 mN/m。亲水岩石表面经表面活性剂处理后,接触角大于90°。
(2)胶束粒径分布较窄且为单峰分布,颗粒粒径达到微纳米级别:20 ℃时50=420.8 nm,70 ℃时50=728.0 nm。
(3)该阳离子型乳液防水锁剂表面吸附属于Langmuir型吸附,根据热力学计算可知,温度升高时,乳液表面吸附量降低,乳液表面分子所占面积减小,吸附层厚度降低。吉布斯自由能均为负数,该阳离子型乳液防水锁剂表面吸附在标准状态下可自发进行。
[1] Liang T B,Gu F Y,Yao E D,et al.Formation damage due to drilling and fracturing fluids and its solution for tight naturally fractured sandstone reservoirs[J].Geofluids,2017,5(8):1⁃9.
[2] Wang W,Yue X A,Chen Y X.A laboratory feasibility study of surfactant⁃polymer combinational flooding in low permeability reservoirs[J].Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2013,34(5):639⁃643.
[3] 耿学礼,吴智文,黄毓祥,等.低渗储层新型防水锁剂的研究及应用[J].断块油气田,2019,26(4):537⁃540.
Geng X L,Wu Z W,Huang Y X,et al,Research and application of new waterproof locking agent for low permeability reservoir[J].Fault⁃Block Oil & Gas Field,2019,26(4):537⁃540.
[4] 安一梅,李丽华,赵凯强,等.低渗透油气藏用防水锁剂体系的制备与性能评价[J].油田化学,2021,38(1):19⁃23.
An Y M,Li L H,Zhao K Q,et al.Preparation and performance evaluation of waterproof lock agent system for low permeability oil and gas reservoir[J].Oil Field Chemistry,2021,38(1):19⁃23.
[5] Guan Q Z,Dong D Z,Zhang H L,et al.Types of biogenic quartz and its coupling storage mechanism in organic⁃rich shales:A case study of the upper ordovician Wufeng formation to lower silurian Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan basin, SW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(4):813⁃823.
[6] Edwards A M J,Rodrigo L A,Newton M,et al.Not spreading in reverse:The dewetting of a liquid film into a single drop[J].Science Advances,2016,2(9):160⁃183.
[7] Liu X F,Kang Y L,Li J F,et al.Percolation characteristics and fluid movability analysis in tight sandstone oil reservoirs[J].ACS Omega,2020,5(24):14316⁃14323.
[8] 周毓棠,唐雨佳,金勇.含氟表面活性剂的复配及其应用研究进展[J].皮革科学与工程,2020,30(5):26⁃32.
Zhou Y T,Tang Y J,Jin Y.Progress in research and application of fluorinated surfactants mixed systems[J].Leather Science and Engineering,2020,30(5):26⁃32.
[9] Yayayürük A E,Yayayürük O.Applications of green chemistry approaches in environmental analysis[J].Curr.Nal.Chem.,2019,15(7):745⁃758.
[10] Ishiguro M,Koopal L K.Surfactant adsorption to soil components and soils[J].Advances in Colloid & Interface Science,2016,231:59⁃102.
[11] Mao J C,Wang D L,Yang X J,et al.Adsorption of surfactant on stratum rocks:Exploration of low adsorption surfactants for reservoir stimulation[J].Journal Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers,2019,95:423⁃431.
[12] Zhang D,Sha M,Pan R M,et al.Synthesis and properties study of novel fluorinated surfactants with perfluorinated branched ether chain[J].Journal of Fluorine Chemistry,2019,219:62⁃69.
[13] Chen W D,Schechter D S.Surfactant selection for enhanced oil recovery based on surfactant molecular structure in unconventional liquid reservoirs[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,196:107702.
[14] Elise A,Christophe B,Ahmad M,et al.Mesoporous silica colloids:Wetting,surface diffusion,and cationic surfactant adsorption[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2019,123(43):26226⁃26235.
[15] Zolfaghari R,Razi A F,Luqman C,et al.Demulsification techniques of water⁃in⁃oil and oil⁃in⁃water emulsions in petroleum industry[J].Separation and Puridication Technology,2016,170:377⁃407.
[16] 苏海波,王晓宏,张世明,等.低渗透油藏油水相对渗透率模型的分形表征方法[J].东北石油大学学报,2019,43(5):88⁃94.
Su H B,Wang X H,Zhang S M,et al.Fractal characterization method of oil water relative permeability model in low permeability reservoirs[J].Journal of Northeast Petroleum University,2019,43(5):88⁃94.
[17] Huang K,Peng H L.Solubilities of carbon dioxide in 1⁃ethyl⁃3⁃methylimidazolium thiocyanate,1⁃ethyl⁃3⁃methylimidazo⁃lium dicyanamide,and 1⁃Ethyl⁃3⁃methylimidazolium tricyanomethanide at (298.2 to 373.2) K and (0 to 300.0) kPa[J].J. Chem. Eng. Data,2017,62(12):4108⁃4116.
[18] 王克亮,张伟,庄永涛,等.碱和表面活性剂用量对弱碱三元体系乳状液稳定性的影响[J].东北石油大学学报,2020,44(4):48⁃55.
Wang K L,Zhang W,Zhuang Y T,et al. Effect of alkali and surfactant concentration on the stability of weak alkali ASP composition emulsion[J].Journal of Northeast Petroleum University,2020,44(4):48⁃55.
[19] Ding B,Xiong C M,Geng X F,et al.Characteristics and EOR mechanisms of nanofluids permeation flooding for tight oil[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2020,47(4):810⁃819.
[20] Xu D R,Li Z,Bai B J,et al.A systematic research on spontaneous imbibition of surfactant solutions for low permeability sandstone reservoirs[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,206:109003.
[21] Zeng F H,Zhang Q,Guo J C,et al.Mechanisms of shale hydration and water block removal[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(3):752⁃761.
[22] Magdalena A,Tomasz B.Modifification of bentonite with cationic and nonionic surfactants:Structural and textural features[J].Materials,2019,12(22):3772.
[23] Yin Q Y,Xian W Z,Ping F X.Effects of temperature on the emulsification in surfactant⁃water⁃oil systems[J].International Journal of Modern Physics B,2003,17(14):2773⁃2780.
[24] 王梦霞,车晓宇,吕梦璇,等.无机盐与表面活性剂在低阶煤表面的协同吸附[J].洁净煤技术,2019,25(1):77⁃85.
Wang M X,Che X Y,Lü M X,et al.Synergistic adsorption of inorganic salt and surfactants onthe surface of low rank coal[J].Clean Coal Technology,2019,25(1):77⁃85.
[25] 李从虎,刘文涛,田振华,等.未变性胶原生物表面活性剂的表面张力及其表面吸附[J].功能材料,2014,45(23):23075⁃23079.
Li C H,Liu W T,Tian Z H,et al.Surface tension and surface absorbption of undenatured collagen bio⁃surfactant[J].Journal of Functional Materials,2014,45(23):23075⁃23079.
[26] Hu W R,Wei Y,Bao J W.Development of the theory and technology for low permeability reservoirs in China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(4):125⁃137.
[27] Qin L,Wang X B.Surface adsorption and thermodynamic properties of mixed system of ionic liquid surfactants with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide[J].RSC Advances,2017,7(81):51426⁃51435.
Study on the Surface Activity and Wettability of Cationic Emulsions for Low Permeability Oil and Gas Reservoirs
Liu Miao, Luo Genxiang, Qiao Yu, Yang Jiang
(School of Petrochemical Engineering, Liaoning Petrochemical University, Fushun Liaoning 113001,China)
A self⁃made long⁃chain cationic surfactant (SFC111) and a low interfacial energy substance (SFC115) were used to prepare a cationic emulsion for further application as surfactant for low permeability oil and gas reservoirs. The dispersion of the emulsion in water, the contact angle of the core before and after the emulsion treatment and the surface tension were investigated by particle size analyzer, contact angle meter, and rotating drop interfacial tension meter, respectively. The thermodynamic parameters of the emulsion at 20 ℃ and 70 ℃ were calculated. Particle size of 0.5% concentration emulsion is50=420.8 nm at 20 ℃,50=728.0 nm at 70 ℃.The contact angle of clear water on the surface of the core increases from 10° to 120°. The emulsion could reduce the surface tension of water to 24 mN/m at 70 ℃, indicating the good waterproof lock performance. The adsorption characteristic of emulsion conforms to the langmuir adsorption theory. The thermodynamic results show that as the temperature increases, the amount of adsorption on the surface of the emulsion decreases, the area occupied by the molecules on the surface of the emulsion goes down, and the thickness of the adsorption layer decreases.
Low permeability reservoir; Emulsion; Surface tension; Contact angle; Thermodynamic calculation
TE258
A
10.3969/j.issn.1006⁃396X.2022.02.009
1006⁃396X(2022)02⁃0056⁃06
2021⁃05⁃13
2021⁃06⁃22
中国石化科技部项目(219032⁃3);辽宁省兴辽英才计划项目(XLYC1902053);辽宁石油化工大学大学生创新创业训练计划项目(2020101480093)。
刘淼(1996⁃),男,硕士研究生,从事表面活性剂方面研究;E⁃mail:366431939@qq.com。
罗根祥(1965⁃),男,硕士,教授,从事无机化学研究;E⁃mail:gxluo1965@163.com。
(编辑 王戬丽)
