面部皮脂腺痣伴多肿瘤及Muir-Torre综合征的临床病理学观察
2022-05-28谢新明王鸿雁张娇娇
谢新明 王鸿雁 张娇娇
[摘要]目的:探討1例皮脂腺痣患者,同时继发乳头状汗管囊腺瘤、皮脂腺腺瘤、皮脂瘤三种肿瘤并伴有Muir-Torre综合征的临床病理特征、免疫表型及预后。方法:对患者的临床资料、病理特点及免疫组化标记进行研究并复习相关文献。结果:患者,女性,56岁。左面部皮表中央见隆起性肿物,肿物表面局部较粗糙,切面灰黄色,颗粒状。组织学表现为两种结构,一种呈乳头状结构,乳头表面被覆双层立方和柱状上皮,乳头间质可见大量浆细胞;一种呈分叶状结构,由周围基底细胞样细胞和中心的多泡状皮脂腺细胞组成,基底样细胞和多泡状细胞分布比例不同,局部区基底样细胞<50%,局部区基底样细胞>50%;免疫组化示乳头状结构CK7、CK5/6均(+);分叶状结构CK5/6、EMA、P63、AR均(+),BerEP4(-);错配修复(Mismatch repair,MMR)蛋白显示,MLH1和PMS2的核阳性表达,而MSH2和MSH6表达缺失,Ki67阳性指数约3%。结论:患者在皮脂腺痣的基础上同时发生三种肿瘤,既往有乳腺癌病史并错配修复蛋白缺失,提示伴发Muire-Torre综合征,病理对肿瘤的正确认识有助于临床进行Muire-Torre综合征调查。皮脂腺痣的多种肿瘤潜能,此类病例需要在成年后预防性切除或至少密切的临床监测,以防止新的肿瘤发生。
[关键词]皮脂腺痣;乳头状汗管囊腺瘤;皮脂腺腺瘤;皮脂瘤;Muire-Torre综合征;临床病理学
[中图分类号]R644 [文献标志码]A [文章编号]1008-6455(2022)04-0031-03
Clinical and Pathological Observation of Facial Naevus Sebaceus with Multiple Tumors and Muir-Torre Syndrome
XIE Xinming, WANG Hongyan, ZHANG Jiaojiao
(Department of Pathology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061,Shaanxi,China)
Abstract: Objective Naevus sebaceus may develop into multiple epidermal and adnexal tumors.It is very rare to have more than three tumors at the same time on the basis of naevus sebaceus lesions, and it is even rare to be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome.The clinicopathological features,immunophenotype and prognosis of a patient with sebaceous nevus complicated with syringocystadenoma papilliferum, sebaceous adenoma and sebaceoma with Muir-Torre syndrome were studied. Methods The clinical data,pathological features and immunohistochemical markers of the patients were studied and the related literatures were reviewed. Results The patient was female, 56 years old. The tumor was seen in the left face, the surface of the tumor was rough, the section was grayish yellow and granular.Histology shows two kinds of structures, one is papillary structure,the surface of the papillary structure is covered with double cuboidal and columnar epithelium, and a large number of plasma cells can be seen in the papillary interstitium,the other is a lobulated structure, which is composed of surrounding basal-like cells and central polyvesicular sebaceous gland cells.The distribution proportion of basal-like cells and multi-vesicular cells is different,some region basal-like cells<50%,some region basal-like cells>50%.Immunohistochemistry showed that papillary structure CK7 and CK5/6 were all (+),lobulated structure CK5/6, EMA, p63, AR were all (+), BerEP4 (-). The mismatch repair results showed retained nuclear expressions of MLH1 and PMS2 while MSH2 and MSH6 proteins were absent,Ki67 positive index was about 3%. Conclusion This patient developed three kinds of tumors simultaneously on the basis of naevus sebaceus. The previous history of breast cancer and mismatch repair absent suggested that it was associated with Muire-Torre syndrome.The correct understanding of the tumor by pathology is helpful to the clinical investigation of Muire-Torre syndrome.This article emphasizes the multiple tumor potential of s naevus sebaceus.All cases of naevus sebaceus require prophylactic resection or at least close clinical monitoring to prevent new tumors.
Key words: naevus sebaceus; syringocystadenoma papilliferum; sebaceous adenoma; sebaceoma; Muire-Torre syndrome; clinicopathology
皮脂腺痣是一種皮肤错构瘤,Mehregan等首次报道皮脂腺痣有分化为各种表皮和附属器来源肿瘤的潜能[1]。继发肿瘤的发生率为10%~30%,随着年龄增长而增加[2]。在皮脂腺痣病变基础上同时出现三个以上的肿瘤非常罕见,Stavrianeas等报道了第一例[3]。Muire-Torre综合征(Muir-Torre syndrome,MTS)是指同时或相继发生至少一种皮脂腺肿瘤和内脏肿瘤,由Muire[4]和Torre[5]分别在1967和1968年描述报道,故得名。在皮脂腺痣病变基础上同时继发三种以上肿瘤,国外文献报道不足10例[6-8],国内文献尚未见报道。本文报道1例皮脂腺痣基础上继发乳头状汗管囊腺瘤、皮脂腺腺瘤及皮脂瘤三种肿瘤,同时伴发MTS,研究其临床病理特征、免疫组化特点、诊断及鉴别诊断。
1 资料和方法
1.1 一般资料:某女,56岁,出生时即发现左面部斑块,20年前无意间发现左面部皮肤结节,大小约0.2 cm×0.2 cm,无红肿破溃,缓慢增大,现可见结节状物,大小约3.5 cm×2.5 cm×1.5 cm,完整切除结节。患者既往于3个月前因乳腺癌行左侧乳腺单切术。
1.2 方法:标本经4%中性甲醛固定,常规取材,石蜡包埋制片,HE染色及免疫组化染色,免疫组化采用MaxVision二步法。CK7、EMA、P63、AR、BerEP4、MLH1、PMS2、MSH2和MSH6单克隆抗体均购自福州迈新生物技术开发有限公司。DAB显色、苏木精复染。
1.3 结果判定:免疫组化以阳性细胞准确定位为有效。
2 结果
2.1 大体检查:左面部皮肤组织,体积5.0 cm×3.5 cm×2.0 cm,皮表中央见隆起性肿物,体积3.5 cm×2.5 cm×1.5 cm,表面局部较粗糙,切面灰粉、灰黄色,周界清楚,质中。
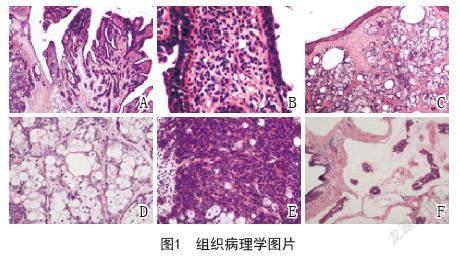
2.2 镜下所见:组织病理学显示三种肿瘤(乳头状汗管囊腺瘤、皮脂腺腺瘤、皮脂瘤),周边可见皮脂腺痣病变。组织学表现为一种为乳头状结构(图1A),有两层上皮细胞,外层细胞高柱状,胞浆丰富,嗜酸性,核大,内层细胞小立方状,胞浆稀少,核为卵圆形且深染,乳头间质水肿,可见毛细血管扩张,炎细胞浸润,可见淋巴细胞和大量浆细胞(图1B);另一种为结节分叶状结构,小叶外周较致密,中心疏松,呈外密中空样,小叶内可见大小不等囊腔,囊腔内壁可见嗜酸性物质(图1C),小叶周围为基底样细胞,大小一致,并有小的核仁,核分裂像不显著,中间皮脂腺细胞胞浆疏松,分泌脂质,挤压核,可见切迹,呈扇贝状,外周基底样细胞与中间皮脂腺分布比例不同,部分区以中间皮脂腺细胞为主,基底样细胞<50%(图1D)。部分区以周围实性基底细胞样细胞为主,周围基底细胞样细胞>50%(图1E)。既往有乳腺癌病史,组织学显示黏液癌,可见癌细胞漂浮于黏液中(图1F)。
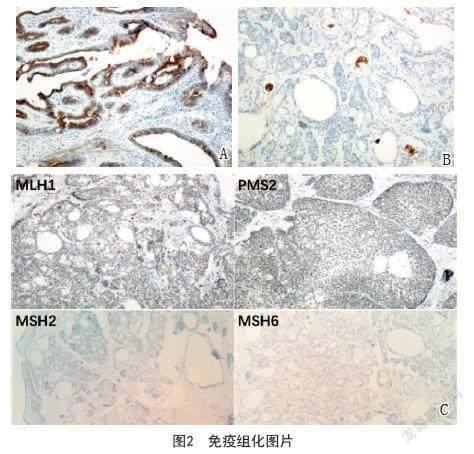
2.3 免疫组化:乳头状结构CK7(图2A)、CK5/6均阳性; 分叶状结构CK5/6、P63、AR均呈阳性,成熟皮脂腺EMA呈特征性泡沫状阳性(图2B),BerEP4阴性;错配修复蛋白(图2C)MLH1、PMS2阳性,而MSH2、MSH6阴性;Ki67阳性指数约3%。
2.4 病理诊断:头皮乳头状汗管囊腺瘤、皮脂腺腺瘤和皮脂瘤。结合临床病史及免疫组化结果提示伴发MTS。患者行手术切除左面部肿瘤后未做任何治疗,随访至今10个月,无复发及其他不适症状。
3 讨论
皮脂腺痣是一种表皮错构瘤,包括表皮、皮脂腺、毛囊及汗腺的错构瘤[9]。表皮常有不同程度的乳头状瘤样增生及角化亢进;真皮内可见分化成熟的皮脂腺体,皮脂腺错构瘤样增生;毛囊可数量减少或形状异常,在皮损区域通常无终毛毛囊;真皮和皮下组织大汗腺数量常增加, 以上是青春期皮脂腺痣的典型组织学表现[10]。成年后,约10%的皮脂腺痣可能发展为继发性肿瘤,Munir等[11]对707例皮脂腺痣患者回顾性研究提示,最常见的良性肿瘤为毛母细胞瘤,其次为汗腺起源的乳头状汗管囊腺瘤[12]。
乳头状汗管囊腺瘤是皮脂腺痣较常见的继发性良性肿瘤[11],50%的病例在出生时或儿童早期出现,15%~30%的病例在青春期发现。少部分可能会向基底细胞癌和导管腺癌转变[13]。本例皮脂腺痣继发的乳头状汗管囊腺瘤组织学表现为表皮乳头状瘤样增生、不规则的导管样结构和内衬双层上皮,间质浸润大量浆细胞的乳头状突起。乳头状汗管囊腺瘤部分病例可检测GCDFP和CK7,支持大汗腺分化。EMA是向皮脂腺分化肿瘤的有用标记物,且呈特征性泡沫状分布,特别是在低分化肿瘤中,在基底细胞样细胞中不表达。肿瘤细胞通常表达高分子量的细胞角蛋白。它们通常对CK7呈阳性,但对CK20呈阴性,p63和p40表达,但BerEP4始终为阴性。
乳头状汗管囊腺瘤需与乳头状汗腺腺瘤和管状大汗腺腺瘤鉴别。乳头状汗腺腺瘤通常发生于女性大阴唇、会阴和肛周区,表现为数毫米的真皮结节,组织学上结节界限清晰,囊腔与表面不相通,乳头状分支衬覆单层柱状细胞,向腔内顶浆分泌;管状大汗腺腺瘤通常含有大量形状不规则的管状结构,衬覆两层细胞,部分含有乳头状突起,类似乳头状汗管囊腺瘤,但此病变与被覆表皮不相通。
皮脂腺腺瘤和皮脂瘤在形态学上有一定重叠,差异在于基底细胞样细胞和成熟皮脂腺细胞的分布比例不同,皮脂腺腺瘤小叶主要由高度分化的空泡状皮脂腺细胞构成,这类细胞数目远远多于基底细胞样细胞,而皮脂瘤是由基底细胞样细胞构成的结节状病变,只有少量小的空泡状皮脂细胞团。本例皮脂腺腺瘤和皮脂瘤组织学上均可表现为分叶状结构、多泡状外观和三种细胞形态。Troy和Ackerman[14]建议将皮脂腺腺瘤和皮脂瘤看成一组良性皮脂腺肿瘤,用皮脂母质瘤一词将其简化,但没有得到广泛认可。皮脂腺腺瘤和皮脂瘤的诊断需要与皮脂腺增生、皮脂腺癌、基底细胞癌和Merkel细胞癌鉴别。皮脂腺增生通常皮脂腺腺体单纯性增大,小叶大部分由成熟的皮脂腺细胞构成,开口于单个扩张导管;皮脂腺癌呈浸润性生长、细胞异型性明显、可见肿瘤坏死、淋巴管或神经侵犯;基底细胞癌表现为周围细胞核的栅栏样排列及肿瘤收缩裂隙形成,基底细胞癌通常BerEp4阳性表达;Merkel细胞癌与低分化皮脂腺癌相似,但缺乏皮脂腺分化,免疫组化显示CK20和神经内分泌分化标记阳性。
Muire-Torre综合征(MTS)[15]是一种罕见的常染色体显性遗传性疾病,男多于女,发病年龄在30岁以上,常见于41~60岁,皮肤肿瘤常常发生于内脏肿瘤之后或同时发生,也可早好几年出现。MTS的诊断标准:①患者至少有一个皮脂腺肿瘤或具有向皮脂腺分化的腫瘤;②虽然无皮脂腺肿瘤,但有多发皮肤病变,如基底细胞癌,鳞状细胞癌特别是角化棘皮瘤并伴发内脏恶性肿瘤;③微卫星不稳定性和DNA错配修复基因缺失,绝大多数突变发生在MSH2或MLH1基因上,它们参与DNA错配修复[16],但组织化学阴性并不除外。在临床工作中的鉴别尤为重要,需要与MTS鉴别的病症主要包括面部和/或身体出现多发性皮肤丘疹和结节的其他综合征,例如:Cowden综合征、Birt-Hogg-Dube综合征和Brooke-Spiegler综合征等。Cowden病是一种由PTEN基因胚系突变引起的一种常染色体显性病变。其特征是多发的错构瘤,可累及生殖细胞所有三个胚层的器官,并对乳腺癌、子宫癌和非髓性甲状腺癌有高度危险度。与MTS在临床特点、形态学及分子生物学上差异明显,易鉴别[17]。Birt-Hogg-Dube综合征的皮损表现为小的肤色丘疹,好发于面部、头皮,也可发生于躯干上部,丘疹通常多发,其皮损组织病理检查显示真皮内细胞性纤维组织形成,同心圆状排列,在正常毛囊周围形成“洋葱皮”样结缔组织鞘[18]。Brooke-Spiegler综合征是一种常染色体显性遗传的良性多发性皮肤附属器肿瘤综合征,肿瘤主要包括真皮圆柱瘤、毛发上皮瘤和/或汗腺螺旋腺瘤,确诊以病理学检查及免疫组化染色证实包含两种以上肿瘤细胞为金标准,本病大多数为良性,极少发生恶变及转移[19]。
综上所述,本文报道1例皮脂腺痣基础上继发皮脂腺肿瘤并合并乳腺癌病史伴发MTS,研究其临床病理特征、免疫组化特点、诊断及鉴别诊断,病理对皮脂腺病变与MTS关系的正确认识及与临床医生的交流对患者至关重要。因此,建议对皮肤皮脂腺肿瘤患者应全面体检,检查是否有内脏恶性肿瘤,早期筛查,早期诊断,有助于提高预后。
[参考文献]
[1]Mehregan AH,Pinkus H.Life history of organoid nevi. special reference to nevus sebaceus of jadassohn[J].Arch Dermatol,1965,91:574-588.
[2]Jaqueti G,Requena L,Sánchez Yus E.Trichoblastoma is the most common neoplasm developed in nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a clinicopathologic study of a series of 155 cases[J].Am J Dermatopathol,2000,22(2):108-118.
[3]Stavrianeas N G,Katoulis A C,Stratigeas N P,et al.Development of multiple tumors in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn[J].Dermatology(Basel,Switzerland),1997,195(2):155-158.
[4]Muir E G, Bell A J,Barlow K A.Multiple primary carcinomata of the colon, duodenum,and larynx associated with kerato-acanthomata of the face[J].Br J Surg,1967,54(3):191-195.
[5]Torre D.Multiple sebaceous tumors[J].Arch Dermatol,1968,98(5):549-551.
[6]Izumi M,Tang X,Chiu C S,et al.Ten cases of sebaceous carcinoma arising in nevus sebaceus[J].J Dermatol,2008,35(11):704-711.
[7]Kazakov D V,Calonje E,Zelger B,et al.Sebaceous carcinoma arising in nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a clinicopathological study of five cases[J].Am J Dermatopathol,2007,29(3):242-248.
[8]Miller C J,Ioffreda M D,Billingsley E M.Sebaceous carcinoma,basal cell carcinoma,trichoadenoma,trichoblastoma,and syringocystadenoma papilliferum arising within a nevus sebaceus[J].Dermatol Surg,2004,30(12 Pt 2):1546-1549.
[9]Aslam A,Salam A,Griffiths C E,et al.Naevus sebaceus:a mosaic RASopathy[J].Clin Exper Dermatol,2014,39(1):1-6.
[10]Pradhan S,Ran X.Cover image:naevus sebaceus affected by overgrowth of Malassezia globosa[J].Br J Dermatol,2018,179(6):1432-1433.
[11]Idriss M H,Elston D M.Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn:a study of 707 cases[J].J Am Acade Dermatol,2014,70(2):332-337.
[12]Wali G N,Felton S J,McPherson T.Management of naevus sebaceous: a national survey of UK dermatologists and plastic surgeons[J].Clin Exper Dermatol,2018,43(5):589-591.
[13]Duman N,Ersoy-Evans S,Erkin Özaygen G,et al.Syringocystadenoma papilliferum arising on naevus sebaceus:A 6-year-old child case described with dermoscopic features[J].Australas J Dermatol,2015,56(2):e53-e54.
[14]Troy J L,Ackerman A B.Sebaceoma.A distinctive benign neoplasm of adnexal epithelium differentiating toward sebaceous cells[J].Am J Dermatopathol, 1984,6(1):7-13.
[15]Eisen D B,Michael D J.Sebaceous lesions and their associated syndromes:part II[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2009,61(4):563-578;quiz579-580.
[16]Abbott J J,Hernandez-Rios P,Amirkhan R H,et al.Cystic sebaceous neoplasms in Muir-Torre syndrome[J].Arch Pathol Lab Med,2003,127(5):614-617.
[17]Miguelote S,Silva R,Fougo J L,et al.Cowden syndrome is a risk factor for multiple neoplasm: a case report[J].World J Surg Oncol,2020,18(1):211.
[18]Guo T, Shen Q,Ouyang R,et al.The clinical characteristics of East Asian patients with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome[J].Ann Translat Med,2020,8(21):1436.
[19]Cüre K,Kocatürk E,Koku Aksu A E,et al.Brooke-Spiegler syndrome:focus on reflectance confocal microscopy findings of trichoepithelioma and flat cylindroma[J].Clin Exper Dermatol,2017,42(8):906-909.
[收稿日期]2020-12-23
本文引用格式:謝新明,王鸿雁,张娇娇.面部皮脂腺痣伴多肿瘤及Muir-Torre综合征的临床病理学观察[J].中国美容医学,2022,31(4):31-34.
