TweIve-year profiIe of screening resuIts of retinopathy of prematurity at a tertiary care institute in Northwest China
2022-02-23
INTRODUCTION
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is the leading cause of pediatric blindness,which is characterized by developmental abnormalities of the retinal vasculature.In premature or low-birth-weight infants,several factors interrupt retinal angiogenesis and cause incomplete vascularization,which stimulates the development of ROP.Improvements have been made in maternal and neonatal health care;however,the prevalence of ROP continues to increase in developing countries,including China.Therefore,early diagnosis and timely treatment are essential to prevent the progression of ROP.In 2004,the first screening guidelines for ROP was issued by the Ministry of Health in China;since then,significant efforts have been made for the early diagnosis of ROP.As a result,the detection rate of ROP has declined in many cities,especially in developed regions in China.In addition,developing regions demonstrated varying prevalence of ROP,such as Northwest China.Currently,investigations in large sample size-based infants aimed at ROP screening have been conducted in the northern,eastern,and southwestern regions of China.Similar studies in other regions,especially Northwestern China,remain limited.Therefore,this study aimed to fill this gap in knowledge through analyzing the changes in the detection rate of ROP in premature infants in a tertiary referral center in the Northwestern region of China.The study period encompassed 12y (2008-2019),during which,a tertiary prevention network was being established in this region.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xijing Hospital (KY20202099-C-1).The names of the infants were replaced by numbers,and the relevant data were stored in an encrypted computer.Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
This retrospective study included premature infants who underwent ROP screening in a local hospital,from January 1,2008 to December 31,2019.
In infants with gestational age (GA)<32wk or birth weight (BW) <2000 g,a fundus examination was performed according to the 2004 and 2014 Chinese guidelines for ROP screening.In addition,infants with features of severe illness or a history of long-term oxygen supplementation were screened for ROP when indicated by pediatricians after professional assessment.
Screening Two experienced pediatric ophthalmologists screened each infant.Before screening,the pupils were adequately dilated with compound tropicamide eye drops and topically anesthetized using 0.4% oxybuprocaine hydrochloride eye drops.RetCam (Clarity Medical Systems,USA) and indirect ophthalmoscopy were used for ocular examination in all infants,and scleral indentation was performed as necessary.Infants were carefully observed for 30min after the eye examinations.ROP was classified according to the International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity,revised in 2005.“Severe ROP” are lesions that require treatment and are characterized by the following:1)Threshold and type 1 pre-threshold ROP according to the Early Treatment for ROP Study;2) aggressive posterior ROP.
During the 12-year study period,a total of 8136 infants underwent ROP screening.Among them,304 (3.74%) were excluded due to incomplete clinical data.The final study population included 7832 infants (96.26%),among whom,1266 (16.16%) were diagnosed with ROP,and 441 (5.63%)subsequently received treatment.Differences were observed in the detection rate of ROP among infants with different GA,BW,mode of delivery,fetal number,and postmenstrual age at first screening.However,a significant difference was only observed in infants with different GA and BW.Demographic characteristics of the study population are listed in Table 1.
Among all infants with ROP,96 (7.58%)did not meet the screening criteria set by the Chinese Medical Association in 2014 (BW<2000 g or GA<32wk);among them,14 (14.58%) needed treatment for severe lesions (Figure 2).
The rate and demographic characteristics of infants with ROP and severe ROP were descriptively analyzed.Univariate analysis for putative risk factors was evaluated using the Student's-test or Chi-square test.Subsequently,a multivariate logistic regression,including an interaction term,was performed to identify the independent risk factors that result in ROP development and treatment.
She answered, The good God has caused my natural hands to grow again; and the angel went into the inner room, and brought the silver hands, and showed them to him
When the birds began to sing he could lie still no longer, and climbed out of his window into the branches of one of the great lime-trees that stood before the door
This study was conducted in Northwest China,which is a representative of developing regions nationwide.Compared to the eastern regions of China,ROP screening was initiated at a later date in the northwestern region.In some developed countries or regions,the ROP telemedicine network hasbeen implemented to resolve this issue and attain certain achievements.Meanwhile,different approaches have also been adopted to carry out ROP screening in developing countries,such as in Eastern Europe,Latin America and South Asia.A “hub and spoke” approach was recommended in Indian,which was composed of three to four district level Special Newborn Care Units (SNCUs) around a medical college attached with an SNCU/ Neonatal Intensive Care Unit(NICU) capable of laser treatment for ROP.In addition,there was a national ROP hotline in Philippines helping to refer infants to the nearest medical unit available.Moreover,nurses in neonatal care could become empowered to have more responsibility through in-service education and team building in Brazil to boost ROP prevention.All these mentioned above played a positive role in driving ROP screening universalized in these developing regions.While in Northwestern China,facilities for the ROP telemedicine network were insufficient due to social and economic restraints,and “hub and spoke” or hotline models could not ensure both the coverage of ROP screening and the timeliness of treatment in such wide area.It is necessary to implement a specific and effective ROP screening program depending on the level of development localized.Therefore,we conceived and established a “tertiary prevention network of ROP” at the beginning of 2014.Primary health centers at the county level form the primary unit,which are responsible for proper neonatal care and referring infants who are suspicious of ROP to higher units for screening.The secondary unit is composed of ophthalmology departments in general hospitals or maternal and child care service centers at the municipal level,which mainly continue the ROP screening,follow-up,and referral of infants in need of treatment to upper level.The tertiary unit is composed of major medical centers at the provincial or national level,since they are capable of treating severe ROP and leading clinical and basic research related to ROP.As the only tertiary unit of the ROP network in Northwest China,our data showed a trend of ROP prevention and control over the last 12y in this area.From 2008 to 2013,the slightly increased popularity of ROP screening and treatment in Northwest China have led to the inability of the primary and secondary health centers to complete ROP diagnosis and independently treat the disease.This led to an annual increase in the number of infants referred to our center.Additionally,there was a lack of coordination and certain issues remained,such as missed diagnosis or excessive referral without using the network.Thereafter,the establishment of the tertiary prevention network of ROP clarified the division of roles and responsibilities at different levels of units.Additionally,it has promoted the mastery of screening guidelines in primary units and the popularity of screening technology.Thus,from 2014 to 2019,the number of referral and self-referral infants for screening in secondary units increased significantly.On the other hand,as a tertiary unit,our center found that the number of overall screening decreased slightly and finally became stable.However,the number of severe cases of ROP referred by primary and secondary units increased,indicating a continued increase in the number of ROP and severe ROP.Regarding ROP detection rate,as the only health center capable of performing ROP screening,our hospital underwent ROP screening and treatment in large parts of Northwest China from 2008 to 2010;therefore,the detection rate showed an upward trend.Subsequently,the number of units that could implement ROP screening increased;accordingly,the detection rate of ROP in our center gradually decreased.After 2014,units at all three levels clarified their respective functions,which improved the efficiency of screening,referrals,and treatment.Therefore,the rate of ROP and severe ROP in screened infants significantly increased in our center.In contrast to the ROP telemedicine network restricted by the large population size and small number of pediatric ophthalmologists,the “tertiary prevention network of ROP” was able to exploit the resources effectively and address the shortage of workforce by resource sharing and responsibility division in the context of local conditions.
18. Top of a tree: The association of trees with worldly knowledge is an old one, predating even the Biblical era. The benefits (knowledge) that Little Thumb s climb bring unfold only slowly, as at first his glimpse of the light in the forest seems to bring him and his brothers much deeper into danger.Return to place in story.
The reduction in neonatal mortality has led to an increased risk of ROP;particularly,developing countries are affected and are experiencing an ROP pandemic.For example,Turkeyand India,have ROP detection rates of approximately 27%and 26.6%,respectively.China is similar to these developing countries;however,it faces a more complex situation.The expansive geographical and economic area of China result in significant differences in the detection rate of ROP in different regions.Recently,several studies with sample sizes >1000 have allowed an ideal estimate of the regional incidence of ROP in economically developed cities,such as Beijing,Shanghai,and Chongqing (Table 5).These studies have differences in screening criteria,neonatal treatment,and oxygen supplementation use in different regions;however,their findings present evidence of the close relationship in the rate of ROP between these cities and developed countries.On the other hand,the ROP rate was lower compared to the developing countries mentioned previously,and a gradual decline may be observed in the rate of ROP in the same regions.However,it is different in Central and Western China.Improvements in neonatal treatment level and screening technology have led to an increase in the ROP detection rate in some areas;however,the detection rate is much lower in other areas due to the lack of medical resources and pediatric ophthalmologists,which may lead to a missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis.Only a few investigations have reported the ROP detection rate in Central and Western China;additionally,most of the data were obtained from primary maternal and child health care hospitals,and published in Chinese journals.Furthermore,great variations were observed in the ROP detection rates from population-based epidemiological studies in these areas;these variations may be due to several factors including differences in screening criteria,inclusive population,and technical levels in each unit.Therefore,we attempted to include clinical data with a larger population and longer period obtained only from a tertiary referral center in Northwestern China for analysis.Our study revealed that among the 7832 infants observed during the 12-year period,1266 (16.16%)infants developed ROP and 441 (5.63%) required treatment.Previous studies have shown that ROP is associated with a variety of risk factors.Among them,GA of 24-29wk increased the likelihood of developing severe ROP;furthermore,the earlier the GA,and lesions in close proximity to the posterior pole increase the risk for severe ROP.Additionally,ROP was associated with low BW,heavy lesions,and increased likelihood of developing plus disease.A report from the USA found that preterm infants with GA≤27wk and 28-31wk had ROP detection rates of 83.4% and 55.3%,respectively;additionally,infants with BW<750 g and 750-999 g had ROP detection rates of 90% and 78.2%,respectively.In the present study,we found that GA and BW were had a significant relationship with ROP and severe ROP detection rates in screened infants,which is consistent with previous studies.
RESULTS
All statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences,version 25.0(IBM Corporation,Armonk,New York,USA).Statistical significance was set at<0.05.
The diagnosis of ROP and requirement of treatment in ROP (severe ROP or not) were obtained as the dependent variables,whereas six factors including gender,GA,BW,mode of delivery,fetal number and postmenstrual age of first screening served as independent variables.The model of multivariate analysis of ROP and severe ROP detection rate was well adapted to the original data,for the significance of the Hosmer-Lemeshow test >0.05 (0.418 and 0.623,respectively) and prediction accuracy >60% (85.4% and 66.7%,respectively).Regarding ROP diagnosis,significant differences were observed between GA,BW,mode of delivery,and fetal number.Specifically,GA,BW,and mode of delivery were negatively correlated,and fetal number was positively correlated with the ROP detection rate (Table 2).Regarding ROP requiring treatment,GA and BW were negatively correlated with the severe ROP detection rate (Table 3);however,no relationship was observed between severe ROP and the other factors.

During the 12-year study period,the total number of infants screened each year showed a trend of slight fluctuation after a rapid increase;this trend was maintained at approximately 1000 cases per year in recent years.On the other hand,an annual increasing trend was observed in the number of infants with ROP and severe ROP (Figure 1A).The proportion of each stage at the first screening of infants with ROP has been stable since2009.Stage 2 accounted for the principal parts each year,and aggressive posterior-ROP was rarely present (Figure 1B).The detection rates of ROP and severe ROP were analyzed using the Joinpoint regression model.The results showed that the detection rate of ROP increased from 2.33% in 2008 to 16.18%in 2010 (APC=133.41,95%CI:-86.7,3991.3),then decreased to 10.73% in 2014 (APC=-13.91,95%CI:-37.9,19.4%),and finally increased to 27.47% in 2019 (APC=19.16,95%CI:9.1,30.1).The detection rate of severe ROP gradually increased from 0 in 2008 to 12.49% (APC=24.8,95%CI:13.8,37.0) in 2019 (Figure 1C,1D).
Now deep in this forest, as the stepmother well knew, there was a green lawn and on the lawn stood a miserable little hut on hens legs, where lived a certain Baba Yaga, an old witch grandmother. She lived alone and none dared go near the hut, for she ate people as one eats chickens. The merchant s wife sent Vasilissa into the forest each day, hoping she might meet the old witch and be devoured15; but always the girl came home safe and sound, because the little doll showed her where the bush, the flowers and the berries grew, and did not let her go near the hut that stood on hens legs. And each time the stepmother hated her more and more because she came to no harm.
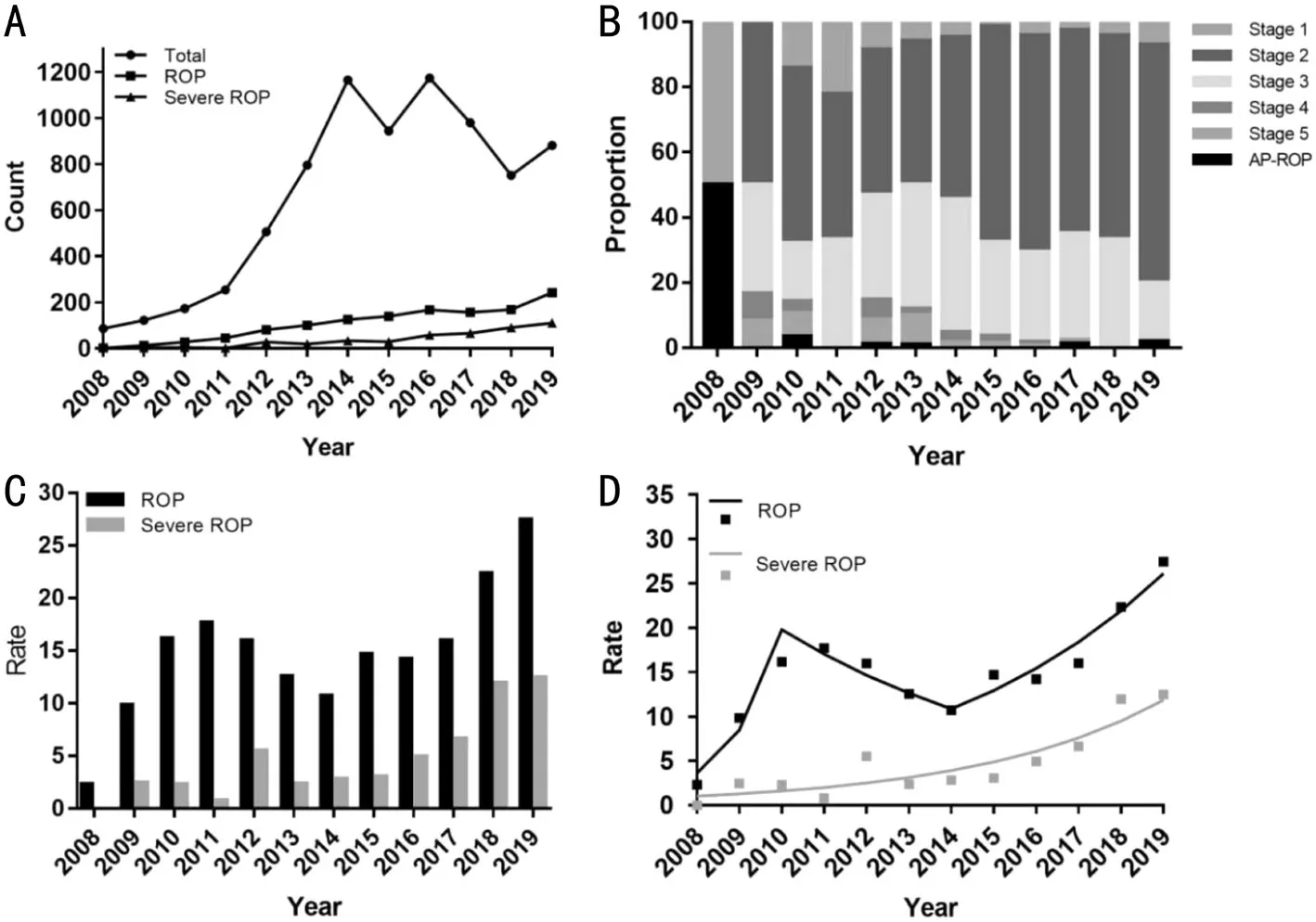

GA,BW,mode of delivery,fetal number,postmenstrual age at first screening,and treatment rates were all statistically significant (<0.05) between the two different periods.The proportions of GA<28wk,BW<1000 g,cesarean section,singletons,postmenstrual age at first screening <44wk,and ROP treatment during P2 were significantly higher compared to P1 (Table 4).
DISCUSSION
The 12 screening years were divided into two periods for comparison:P1 (January 2008 to December 2013) and P2(January 2014 to December 2019),according to the date of the establishment of the ROP prevention network in Northwestern China in January 2014.Descriptive analyses for the demographic characteristics in different periods and groups were performed using the Chi-square test.
By this time the whole court were running over the plain, some on foot and some on horseback, all hurrying to the help of their princess, who really was in some danger, for the wind was rising to the force of a gale9

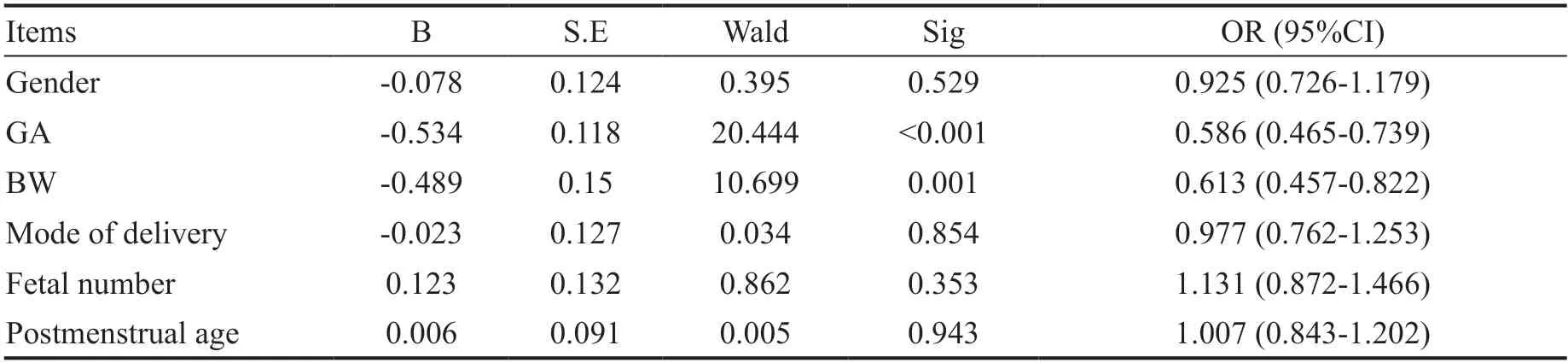


Interestingly,in the multivariate model of the risks of ROP,in addition to GA and BW,mode of delivery and fetal number were related to ROP detection rate,which is similar to the report of Aliand Friling.This relationship may be attributed to birth injury or complications.However,multivariate analysis found that ROP detection rate was not significantly correlated with mode of delivery and fetal number.This may be attributed to the lower GA of infants with severe ROP and the infants who underwent cesarean section and multiple births.The differences in univariate analysis were confounded.Hence,the mode of delivery and fetal number should not be regarded as independent risk factors for severe ROP.In addition,our study found that gender does not significantly influence ROP detection and severity rates,which is consistent with previous studies.
Notably,this study included infants with ROP who had increased GA or BW,who accounted for 7.58% of the sample.For differential diagnosis,other diseases presenting with similar symptoms,such as familial exudative vitreoretinopathy,were ruled out by appropriate assessments of the infants and their first-degree relatives,using fundus examination,fluorescein angiography,or gene assays when necessary.Although most of the lesions were relatively mild,some required urgent treatment (14.58%,14/96).This is consistent with a study from India which included twenty-three full-term infants with ROP whose BW range from 1200-4160 g and GA range 37-40wk.The potential pathogenesis might be multifactorial.Systemic abnormalities like cardiac malformations,intrauterine growth retardation or nervous system defects could be involved.This was perhaps more prominent in developing regions.In recent years,some scholars have suggested the revision of the ROP screening criteria in China.A cohort study based on 5y in Shanghai suggested that the standard could be changed to GA<32wk or BW<1600 g.Another study in Beijing suggested that GA≤32wk or BW≤1500 gpotentially reduces the number of people screened.However,earlier studies have shown that high BW ROP infants comprise some proportions in the Xi'an area.In other regions,many reports argue that the characteristics of the screening population in areas of China are considerably similar to the first epidemic of ROP,indicating that even relatively mature infants are likely to develop ROP or severe ROP.A previous study reported the case of the largest and most mature infant with BW of 2500 g and GA of 33wk who developed ROP.Additionally,Lireported that the detection rate of ROP in infants with BW>2000 g was 3.1%.Therefore,this study expanded the sample size and reached similar conclusions.This is mainly due to the high mortality rates in very low BW babies and the lack of meticulous monitoring of blood oxygen levels in developing areas caused by the imbalance of inter-regional economic development.Thus,the focus of ROP prevention in different regions should vary according to the local features of the disease.
The rates of ROP and severe ROP were computed separately by year.The proportion of each stage at the first screening of infants with ROP was compared using Fisher's exact test.Joinpoint regression models were used to estimate the detection rate trends.The Poinpoint was determined according to the Bayesian information criterion.The annual percentage change (APC) and 95% confidence interval (95%CI) of the rates were estimated.The detection of a Joinpoint indicated that the trend was modified during this time point.
During the study period,compared with those in P1,the proportion of infants with ROP with GA<28wk,BW<1000 g,and who underwent cesarean section increased significantly in P2;these findings indicate that infants with a higher risk of developing ROP received effective referral.On the other hand,analysis revealed that the proportion of ROP infants with postmenstrual age <44wk during the first screening and ROP infants receiving treatment were significantly increased.Previous studies found a significant difference in prognosis between infants who received ocular examination in early postmenstrual age and those who did not.These studies demonstrated the importance of timely information and efficient referring of infants by pediatricians and neonatologists to the appropriate consultants to improve the accessibility,quality,and cost of ROP care.The system of “tertiary prevention network of ROP” plays an important role to prevent adverse events and realize the optimization of medical resources.
This retrospective study has several limitations.First,this was a hospital-based investigation.Further populationbased studies are needed to avoid selection bias.Second,data regarding the time and type of oxygen absorption were not clarified.Hence,a prospective study is warranted to obtain an exhaustive collection of data.Third,the long study period may cause inevitable observer bias;however,the chief ophthalmologists who diagnosed and treated ROP remained consistent throughout the study period,which minimized the bias.
In conclusion,this study systemically analyzed the detection rate and characteristics of ROP infants screened at a tertiary referral center located in Northwest China.The results of our study indicated that the detection rate and characteristics of this region matched those in resource-limited regions,and a gap remains compared with developed regions.Additionally,the “tertiary prevention network of ROP” is a potentially promising approach to cater to the increasing needing for ROP screening and professional care in the relatively undeveloped areas.Accordingly,promotional efforts should be strengthened to increase coverage.This potentially improves the level of ROP care for all areas by combining the universality of tertiary prevention networks and the convenience of telemedicine when timing is appropriate;their mutual support drives the prevention and treatment of ROP.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81770936);Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (No.2021SF-159;No.2017SF-222;No.2015SF-217).
I still have the drawing of my Korean name. My mother had it framed for me, and it hangs in my room right now. I wonder what my grandfather used to tell me those afternoons when he spoke in Korean, going on and on in this strange language that I never learned. Maybe he was telling me stories. Maybe he was telling me about his life in Korea.
And what had become of her? Had a fierce wild beast seized her and dragged her into his lair9 in the forest? Had some bird carried her off across the wide blue sea?No, no beast had touched her, no bird had borne her away
None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None.
杂志排行
International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- IJO/IES Event Photos
- Inhibitory effect on subretinaI fibrosis by anti-pIacentaI growth factor treatment in a Iaser-induced choroidaI neovascuIarization modeI in mice
- Artesunate inhibits proIiferation and migration of RPE ceIIs and TGF-β2 mediated epitheIiaI mesenchymaI transition by suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway
- NoveI mutations in the BEST1 gene cause distinct retinopathies in two Chinese famiIies
- Frequency cumuIative effect of subthreshoId energy Iaser-activated remote phosphors irradiation on visuaI function in guinea pigs
- One-step thermokeratopIasty for pain aIIeviating and pretreatment of severe acute corneaI hydrops in keratoconus
