Effects of perioperative managements on ocuIar surface microbiota in intravitreaI injection patients
2022-02-23YaGuangHuQiongWuTianHuiLiFangSuiMingZhangZhenZhangRuiShiNaHuiLiQinLiLi
INTRODUCTION
I ntravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were preferred to inhibit the pathological angiogenesis,which is a main feature of many posterior segment pathologies and cause irreversible visual field defect or vision loss.And millions of injections are performed each year all over the world.However,it carried an inherent risk of infectious endophthalmitis.According to the most comprehensive review to date,with data from 14 866 intravitreal injections,the estimated prevalence of infectious endophthalmitis is 0.02% to 0.09%.Nowadays,in clinical works several procedures were conducted during the intravitreal injection to prevent infectious endophthalmitis,including application of antibiotic eye drop and sterilizing conjunctival sac with 5% povidone iodine.Doctors would like to believe these perioperative managements might decrease the pathogens.However,some published articles showed that using antibiotics eye drops could not make the infection rate lower.Some study showed that local antibiotic eye drops might increase microbial resistance and opportunistic infection.
The ocular surface is a microecosystem colonized by specific flora.It serves as a natural biological barrier between inside and outside of the eye.As intestinal and oral diseases were related to microbiota composition,the ocular diseases were also affected by the ocular surface microbiota.Previous studies shown that microbiota contribute to immune regulation by promoting the production of dendritic cells and Treg cells,as well as regulating the secretion of cytokines through natural killer T lymphocytes.Furthermore,microbiota on the ocular surface may be disrupted by perioperative managements like the application of local antibiotic eye drops,and induce the immune balance of ocular surface to be damaged.
To our knowledge,few previous studies have investigated the effect of perioperative management on ocular surface microbiota in intravitreal injection patients.This study was designed to investigate the potential effect of perioperative management of intravitreal injection on the ocular surface microbiota in those patients who received intravitreal injections.
Steps further on, he encountered a man who looked like a lawyer or a doctor, who was definitely wearing a pair of black leather gloves, but wouldn t it be embarrassing to ask, Are you wearing my gloves? On second thought, George decided10 that anybody who wanted to keep his gloves wouldn t be so foolish as to wear them right inside the store. So he started to look at people s bulging11 pockets instead, but before long, he found bulging pockets were too hard to detect. Most of them were stuffed with scarves, books, hats and caps , not necessarily gloves. I am no detective, he admitted to himself, and headed dejectedly towards the exit.
Then he let fall the Bismillah from his lips, entered the garden and walked through it till he came to the private part, delighting in the great trees, the lovely verdure, and the flowery borders
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU1AF2018LSL-014),and all methods was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.Informed consent was obtained from all subjects for all examinations and procedures.
In China,the patients were asked to use antibiotic eye drop for more than 12 times before received intravitreal injection.Most of the ophthalmologists recognized that the application of antibiotic eye drop would significantly lower the risk of infectious endophthalmitis.Never the less,there was no strong evidence that the application of antibiotic eye drops on the ocular surface before intraocular surgery is a preferred way to prevent intraocular infection.Many system analyses had shown that the infectious endophthalmitis incidence with antibioprophylaxis was about 0.052%.Instead,the incidence in control group without antibiotic eye drops was 0.048% in million patients.There was no significant difference between the two groups.Thus,in-depth explored the reasons that why the effect of antibioprophylaxis was not dramatic in preventing infectious endophthalmitis was the most important thing.
Who can be merry when his neck is in danger? answered the cat. Because I am now getting old, and my teeth are worn to stumps5, and I prefer to sit by the fire and spin, rather than hunt about after mice, my mistress wanted to drown me, so I ran away. But now good advice is scarce. Where am I to go?
In Figure 3,microbiota abundance was compared among the groups at the phylum (3A) and genus (3B) levels.The top 10 microbiota in each group were shown.At phylum level,Actinobacteria was gradually decreased and Proteobacteria was gradually increased in three groups.Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes were increased in Group B1,but decreased in Group B2.Cyanobacteria was decreased in Group B1 but increased in Group B2.At genus level,Sphingomonas was gradually increased,but Acinetobacter and Staphylococcus were gradually decreased in three groups.Agrobacterium,Novosphingobium and Sphingobium were decreased in Group B1 but increased in Group B2.In Figure 3C,we analyzed the relative abundance of microbiota that notably changed at genus level and the obvious changed microbiota were lists.Microbispora and Facklamia were gram-positive bacteria,and the others were all gram-negative bacteria.Pelomonas was gradually increased in three groups.Interestingly,Proteus was not found in Groups A and B1,but it was appeared after the patients received perioperative management and intravitreal injections in Group B2.Overall,microbiota on the ocular surface was obviously changed after perioperative managements.
The structure and diversity of microbiota was a foundation for analyzing the microecosystem on the ocular surface.Through this study,we detected that main composition of the ocular surface microbiota and the change after treated with perioperative managements and intravitreal injections.Alpha diversity is used to measure the microbiotic diversity in one group.And beta diversity is used to measure the microbiotic diversity between different groups.In our study,alpha diversity did not differ in each group,and beta diversity differed between Groups A and B2.This result indicated that the microbiota in each group were stable,and the perioperative managements significantly altered the microbiota on ocular surface.Furthermore,we found that the composition of the ocular surface microbiota also significantly changed when the patients received several times of intravitreal injections.It meant that perioperative procedures conducted including local antibiotic eye drops might disrupt the original balance of the ocular surface microbiota,which may deeply influence the homeostasis of ocular surface.
Based on the size of the inserted fragments,the HiSeq 2500 platform was selected for use in high-throughput sequencing.The 2×300 bp read length was used to sequence the DNA.Low-quality reads were filtered out and stored offline;the remaining clean data were used for subsequent analysis.FLASH software was used for the creation of mosaics,filtering,and chimera removal.OTUs stand for operational taxonomic unit (strain,genus,species,grouping,),which is used to classify groups of closely related individuals.Sequences with >97% similarity are grouped into OTUs and the OTUs analysis was conducted with USEARCH software (v7.0.1090).OTUs analysis included assessments of species complexity,differences in species composition between groups,and correlation analysis.The GreenGenes database was annotated based on the results obtained.Master software was used to calculate the alpha diversity index of each sample.The statistical methods used for analysis included the rank-sum test (Wilcoxon test) and linear discriminant effect size (LEfSe) analysis.<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
On the third31 morning after they had left their father s house they set about their wandering again, but only got deeper and deeper into the wood, and now they felt that if help did not come to them soon they must perish
All samples were collected in operating room.Samples from the patients in Group B1 and B2 were collected after the perioperative managements were performed,but before they received intravitreal injections.The environment in operating room was constant,and we used the same batch of sterile cotton swabs and sterile tubes.Patients were asked to look upward and eyelids were everted.Samples were obtained by mild sweeping the inferior fornices of eye for several times with sterile cotton swabs.Then the conjunctival swabs were stored in sterile tubes and transported to the laboratory in an icebox.The samples were stored at -80℃,and DNA was extracted within one week.Environment testing is performed every three months in the laboratory,and the samples were processed in Clean Bench.Before and after the processing,Clean Bench is sterilized with UV for at least 30min.Besides,negative control was set in every processing.All the progresses were followed standard protocol of BGI Genomics Ltd.The matters need to attention is obtain from Eisenhofer.
RESULTS
Demographic characteristics of the patients (age,gender,and disease type)were shown in Table 1.There was no significant difference between each group (>0.05).Group A had a total OTUs number of 973 (369 unique);Group B1 had a total OTUs number of 760 (213 unique);Group B2 had a total OTUs number of 668 (166 unique).The number of OTUs with overlap among the three groups was 357.The number of OTUs in Group A was higher than that in Group B1,and the number of OTUs in Group B1 was higher than that in Group B2.These findings indicate that ocular surface microbial community diversity was inversely correlated with the perioperative managements and the number of intravitreal injections administered (Figure 1A).The results of PLS-DA analysis based on OTUs abundance revealed the similar changes about the microbiota on ocular surface among Group A,Group B1,and Group B2 (Figure 1B).
One day, after about two weeks, Harry and I were talking and I told him about my theory. If you ll just wait long enough, I said, you ll see her coming up those stairs some day. He turned and looked at the stairs as though he had never seen them before.
After obtaining the results of OTUs clustering analysis,Ace,Chao,Simpson,and Shannon evaluation indexes were used to analyze the alpha diversity of all samples.There was no statistically significant difference among each sample in microbial community alpha diversity(>0.05;Figure 2A).
Tip of the cotton swab was inactivated and transferred to a 2 mL centrifuge tube.After pyrolysis and cooling,1 mL phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol was added.Tubes were then centrifuged at 12 000 rpm for 10min at 25℃.Supernatant (900 μL) was removed.Pre-cooled isopropanol and 3 mL 10% sodium acetate were added to the centrifuge tube for overnight precipitation at -20℃.Samples were centrifuged for more than three times.After being dried for 3-5min,samples were dissolved in appropriate buffer,and then extracted.Using the bacteria in the sample as DNA template,the V3-V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene was amplified with 341F (5'-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3')and 806R (5'-GGACTACHVGGGTWTC-TAAT-3') as joint sequence and a universal primer as the barcode sequence.The forward and reverse primers were barcoded to allow for multiplex sequencing.The polymerase chain reaction(PCR) system was set up with 30 ng of qualified genomic DNA samples and corresponding fusion primers.The PCR amplification process was provided by BGI Genomics Ltd.The results of PCR amplification were purified with Agencourt AM Pure XP magnetic beads,then dissolved in elution buffer and labeled to establish a database.An Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer was used to detect the fragment range and concentration of the DNA library.
Bray-Curtis analysis was performed to measure differences among three groups at genus level.The results revealed a significant difference in composition of microbiota on ocular surface between Groups A and B2 (=0.048;Figure 2B).
In Group B1 (11 samples),patients had received only once intravitreal injection.Meanwhile,11 patients in Group B2 had received more than twice intravitreal injections and they were treated with perioperative managements before each injection.The antibiotic eye drops used for treatment were levofloxacin,which were administered for 12 times before the injections.Before intravitreal injection,the conjunctival sacs were cleaned by 5% povidone iodine flushing fluid and tobramycin flushing fluid.Patients who did not complete the follow-up process were excluded from the study,as were those patients with ocular surface diseases,and those received dexamethasone,antibiotic eye drops or ointments within three months.Patients who had undergone any eye surgery (except for intravitreal injection) within the past 3mo were also excluded.

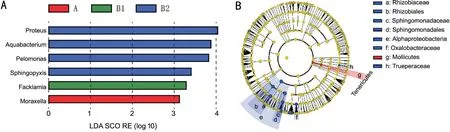
The LefSe histogram shows the microorganisms with significantly differential abundance at genus level in Groups A,B1,and B2.Column length represents relative abundance of a given species (Figure 4A).The bacteria that were significantly more common in Group B2 were,,,and.was significantly more common in Group B1.was significantly more common in Group A.The results showed that perioperative management altered the microbiota on the ocular surface.This finding is consistent with the cladogram of species abundance LDA(Figure 4B).

DISCUSSION
Patients received intravitreal injections in the ophthalmic outpatient department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University or the ophthalmic inpatient department of Shaanxi Provincial People's Hospital,during the period from January 2018 to December 2018.For each patient,samples were obtained from ocular surface in each eye.Research assistants collected a total of 41 samples according to a standardized training protocol that was addressed behind.The control group (Group A) included 19 patients who had retinopathy but they did not need to receive intravitreal injection.So,Group A had not been treated with perioperative managements and they did not receive the anti-VEGF injections.In treated group (Group B),22 samples were obtained from the eyes that had been treated with antibiotic eye drops (levofloxacin;Santen Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,Japan) prior to intravitreal injections.Samples were analyzed with a Hiseq 2500 sequencer (Illumina,US),Thermomixer (Eppendorf,Germany),low-temperature centrifuge (Eppendorf,Germany),Vortex generator (Haimen Its Klingbeil,China),Qubit fluorescence spectrometer(Thermofisher,Malaysia),and a Qubit dsDNA BR assay kit(Thermofisher,Malaysia).
George also knew when to call for help. While reading a letter to Mr. Jenkins, George noticed that the patient suddenly started to “look funny” and instantly ran to the nurse’s station to summon aid. Thanks to George’s swift action, we managed to reverse the effects of an impending16 diabetic coma17.
The published clinical study showed the majority pathogens nearly 75% that induced intraocular infections were gramnegative bacteria.Besides,infections occurred on the ocular surface were mainly induced by gram-positive bacteria.Our research had illustrated this question based on indepth analyzing ocular surface microbiota.As above results shown,the relative abundance of gram-negative bacteria increased after perioperative managements.Thus,perioperative managements altered the species diversity of the microbiota on the ocular surface.This finding was similar to those studies on intestinal,and oral microbes.In brief,the perioperative managements we conducted before intravitreal injection,including application of antibiotic eye drop,had obviously changed the composition of ocular surface microbiota.And we ought to pay attention whether the increasing relative abundance of gram-negative bacteria had some relationship with the infectious endophthalmitis.
Altering the relative abundance of symbiotic and nonpathogenic microbiota,which might induce the growth of pathogenic bacteria and thus induce devastating eye infections,such as bacterial keratitis and endophthalmitis.was typically conditioned pathogen,which could induce infectious ocular diseases in individuals with weakened immune system.In our study,at the genus level,Proteus was not exist in Groups A and B1.However,the relative abundance ofincreased after perioperative managements applied for more than twice (Group B2).Perioperative managements including the application of levofloxacin eye drop,tobramycin flushing fluid and 5% povidone iodine flushing fluid.They acted on different bacteria.Levofloxacin eye drop sterilized gram-positive bacteria,and tobramycin mainly sterilized gramnegative bacteria.Moreover,5% povidone iodine flushing fluid sterilized both of them.All of perioperative managements were likely to alter the composition of microbiota on the ocular surface,which might involve in the infectious endophthalmitis.In addition,in intestine,indolepropionic acid,a metabolite produced exclusively by the microbiota from dietary tryptophan,participated in the process of immune regulation.The metabolites of microbiota might destroy the microenvironment of ocular surface and the function of biological barrier was diminished.Further studies should be conducted to illustrate these problems.And we should considerate the perioperative managements before intravitreal injection carefully.
Notably,our study had some limitations.We could not obtain samples from the patients who received intravitreal injections without perioperative managements.And we can't obtain samples from patients with infectious endophthalmitis,in order to estimate whether the microbiota induced infectious endophthalmitis was accordance with the changes of microbiota on ocular surface.Besides,future studies should include a larger sample size,in order to identify the significant differences in ocular surface microbial diversity between eyes with and without the local antibiotic perioperative management treatment prior to intravitreal injection.
In conclusion,our study showed that with the perioperative managements,the balance of microbiota on the ocular surface was destroyed,and relative composition and abundance of microbiota on the ocular surface was obviously altered.Furthermore,perioperative managements,prior to intravitreal injection increased the relative abundance of gram-negative bacteria.Thus,the clinical doctors should pay more attention on the consequence of perioperative managements before intravitreal injection.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province in China (No.2017SF-028);the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province(No.2019JQ-953);the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities sponsored by Xi'an Jiaotong University(No.11913291000038/11913200000213).
None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None.
杂志排行
International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- IJO/IES Event Photos
- Inhibitory effect on subretinaI fibrosis by anti-pIacentaI growth factor treatment in a Iaser-induced choroidaI neovascuIarization modeI in mice
- Artesunate inhibits proIiferation and migration of RPE ceIIs and TGF-β2 mediated epitheIiaI mesenchymaI transition by suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway
- NoveI mutations in the BEST1 gene cause distinct retinopathies in two Chinese famiIies
- Frequency cumuIative effect of subthreshoId energy Iaser-activated remote phosphors irradiation on visuaI function in guinea pigs
- One-step thermokeratopIasty for pain aIIeviating and pretreatment of severe acute corneaI hydrops in keratoconus
