Effects of Empathy Training on Sub-clinical Depression College Students’ Empathy
2021-11-26HouXiaohua
Hou Xiaohua
(Guangzhou Huashang Vocational College,Guangzhou 511300)
Abstract:Objective:To explore the intervention effect of empathy training on sub-clinical depression and empathy in college students with depression.Methods:20 sub-clinically depressed college students from a university in Guangzhou were divided into group (n=10) and control group (n=10).The empathy training group received empathy training once a week for 100 minutes for 8 weeks;the control group was not intervened and only participated in the pre-and post tests.After pretest and 8 weeks of intervention,the effect was assessed using Human Response Pointer Scale (I RI-C),Beck Depression Scale Second Edition (BDI-II),Adolescent Presocial propensity Scale (PTM)..056 Results:After the empathy training,the group scored higher than their pre-test scores,differences were close to significant levels (P=0),sub-clinical depression differences did not reach a significant level,and empathy and cognitive empathy scores were significantly higher than their pretest scores.No difference in the scores between the control group reached a significant level.Conclusion:Empathy training can significantly improve the level of empathy in sub-clinical depression.
Key words:Empathy training;Sub-clinical depression;College students;Intervention
Sub-clinical depression is an emotional state in which an individual shows depressive symptoms which have not met the diagnostic criteria for depression,also known as depressive symptoms,depressive states,or depressive mood.Studies have been conducted on depression in college students[1-4],subjects were screened using a depression scale (e.g.,to SDS,to CES-D,to BDI-).Clinically,depression is diagnosed according to the results of psychological measures,and it can not be diagnosed as depression,which is called sub-clinical depression.Previous studies have shown that the incidence of sub-clinical depression in Chinese college students is not low,with 39.1%[5]、31.2%[6]、13.2%[7]、23.6%[8]equal proportion.Sub-clinical depression exerts a negative impact on college students’learning and interpersonal communication,and is closely related to the tendencies of suicide,self-injury,suspension,withdrawal,etc[9],It is also a predictor of its development into depression[10].Therefore,it is necessary to intervene in the sub-clinical depression in college students.This study intends to explore the intervention effect of empathy training on sub-clinical depression and empathy ability.
Empathy training is a professional coaching training for an individual's cognition,emotion,and behavior to foster their empathic abilities[11].Objects with existing empathy training are mainly children and adults with externalizing problems (such as aggression,conduct disorders),as well as participants in the human aid field,such as social workers,psychologists,doctors,nurses,etc.Numerous studies have shown that[12-15],empathy training (e.g.,symptom simulation,positive behavior and socioemotional learning,group counseling) can nurture empathy among healthcare staff,disadvantaged children,adolescent schizophrenia,and college students,thereby inhibiting problem behavior in people with externalizing problems and improving the mental states of participants in the aid field.So what is the impact of empathy training on sub-clinically depressed individuals? To the knowledge of this study,no current study has directed at the effects of empathy training on sub-clinical depression and the effect of empathy training on the empathic ability of sub-clinical depressed individuals.Neurobiological studies have found that[16],the development of individual empathy neural networks begins in early infancy and matures in early adulthood.College students are in early adulthood,so it is neurobiologically possible to foster their empathy through empathy training.
In conclusion,this study aims to select college students with sub-clinical depression through questionnaire and interview,to apply a self-designed empathy training program for empathy training(including cognitive empathy and emotional empathy),to investigate the impact of empathy training on sub-clinical depression level,and to provide useful reference or basis for future research.
1 Method
1.1 The Participants
The subjects were recruited from a university in Guangzhou,and the score was more than 14 points or equal to 28.With good life with both parents and family economic conditions as the second and third screening conditions,20 college students with sub-clinical depression participated in this study.With informed consent,10 students were randomly chosen to join the training group and 10 students were enrolled in the control group to form two paired samples.Among them,8 lived in the training group and their parents,9 had good family financial conditions,9 lived in the control group,and 9 had good family financial conditions.According to Zhang Rui,Yang Chenyun,etc[17](2020) Metta-analysis of sub-clinical depression concluded that gender and grade were not significantly related to the occurrence of sub-clinical depression in college students,so this study takes no consideration of the team arrangement of the training group and controls.
1.2 Tool
1.2.1 The Chinese Version of Interpersonal Reactivity Index[18](Interpersonal Reactivity Index-C,IRI-C)
A 5-point Likert scale questionnaire was used to measure the participants’ ability to empathize,which consists of 22 items (including reverse scoring items) and 4 dimensions,namely,viewpoint selection and imagination measure cognitive empathy,and personal pain and empathy concern measure emotional empathy.For each item,0 indicates“inappropriate”,1 for“somewhat appropriate”,2 for“moderately appropriate”,3 for“appropriate”and 4 for“highly appropriate”.The higher the score,the better the empathy.In this study,the Cronbachα coefficients of the training group and the control group were 0.875,0.758,0.738 and 0.803 respectively.
1.2.2 The Baker Depression Scale,2nd Edition[19](Beck Depression Inventory-II,BDI-II)
The questionnaire was revised by Beck in 1996 and translated by Wang Zhen et al.[20]in 2011 to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in the past week,and has good reliability and validity among Chinese college students.It consists of 21 items,each of which is rated on a scale of 0 to 3,and the total score is equal to the sum of the 21 item scores.The total score of 0 to 13 stands for no depression,14 to 19 for mild depression,20 to 28 for moderate depression,and 29 to 63 for severe depression.In this study,subjects with an overall score greater than or equal to 14 and less than or equal to 28 were classified as sub-clinical depressed college students.In this study,the Cronbachα coefficients of the training group and the control group were 0.617,0.817,0.603 and 0.882 respectively.
1.2.3 Juvenile Prosocial Tendency Scale[21](Prosocial Tendencies Measure,PTM)
A five-point Likert scale was applied to measure prosocial tendencies,which was composed of 26 items,six dimensions,with a gradual transition from“very unlike me”of 1 to“very much like me”of 5.A large number of studies[22-26]have found that empathy is closely related to prosocial behavior,and empathy exerts a motivational and informational effect on prosocial behavior.Therefore,this study takes its total score as the criterion validity.In this study,the Cronbachα coefficients of the training group and the control group were 0.946,0.921,0.878 and 0.794,respectively.
1.3 Intervention Method
The training group received empathy treatment for 90 to 100 minutes once a week for 8 weeks.As the training day just happened to be a holiday,two consecutive training canceled,so the whole time span of empathy training is 10 weeks.During this period,two team members asked for leave for one time each,and arranged separate training afterwards.
1.3.1 Training group Training Method
Based on the experience of empathy training at home and abroad,we designed our own empathy training program,and adopted the forms of role-playing,situational perception,perspectivetaking and other therapies,as well as psychological painting and sand table games.There is a theme for each training session,aiming at different aspects of empathy from superficial to deep,and gradually improving the empathy ability of the subjects.The materials used in the training,such as facial expressions,video materials,story scenes,question cards are all carefully selected and made by the trainers and training assistants according to the training theme.The trainer is a mental health education and counseling teacher who has been working for more than ten years,and the training assistants are two undergraduates.Specific procedures are shown in Table 1.
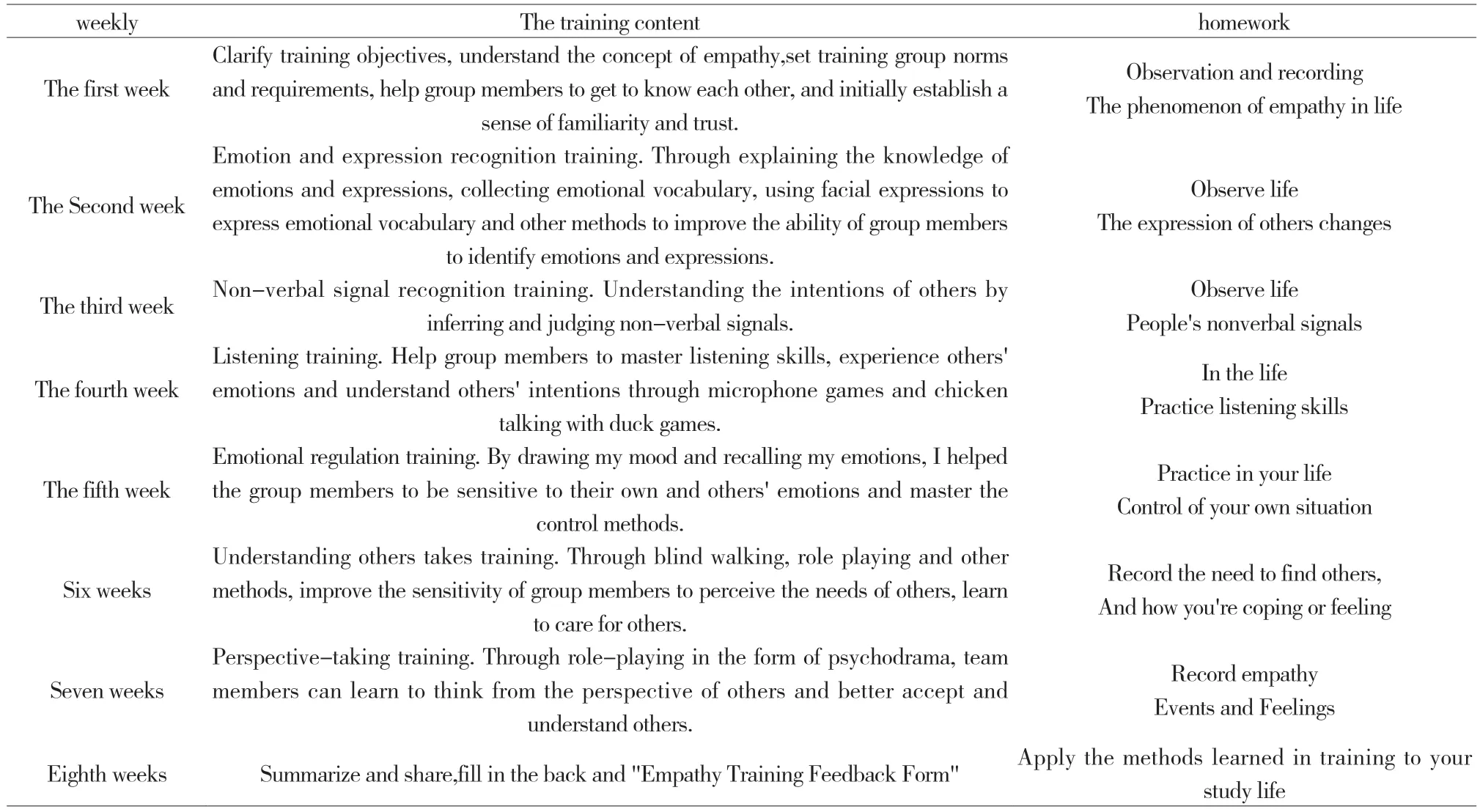
Table 1 empathy training
1.3.2 Control Group Treatment
The control group did not participate in the training,but only joined a common control group Wechat group and took the before and after tests,during which they were asked,“Are your emotions the same as they were 10 weeks ago? What causes the sameness or difference?”To find out the causes of their mood swings.
1.3.3 Research Design
This study used 2 (time:pretest,8 weeks post-intervention test)x 2 (group:training group,control group).Among them,the time is within-group factors,and the group is between-group factors.
1.3.4 Statistical Method
Using S PSS 19.0 soft ware,the pre-and post scores were compared,and the paired sample t-test for the pre-intervention scores was conducted.
2 The Results
2.1 Comparison of the Scores of Each Scale between the Two Previous Groups
As shown in Table 3,the difference in scores between the training and control scales reached the pre-test period.
2.2 Comparison of Each Scale before and after Intervention Groups
As shown in Table 3,the total empathy scores,cognitive empathy,emotional empathy and total kinship scores in the training group were higher than the previous scores,the total sub-clinical depression scores were lower than the previous test,and the difference between the total empathy scores reached significant levels,and the difference before and after the total kinship scores was very close to a significant level.No difference in the control group reached asignificant level.
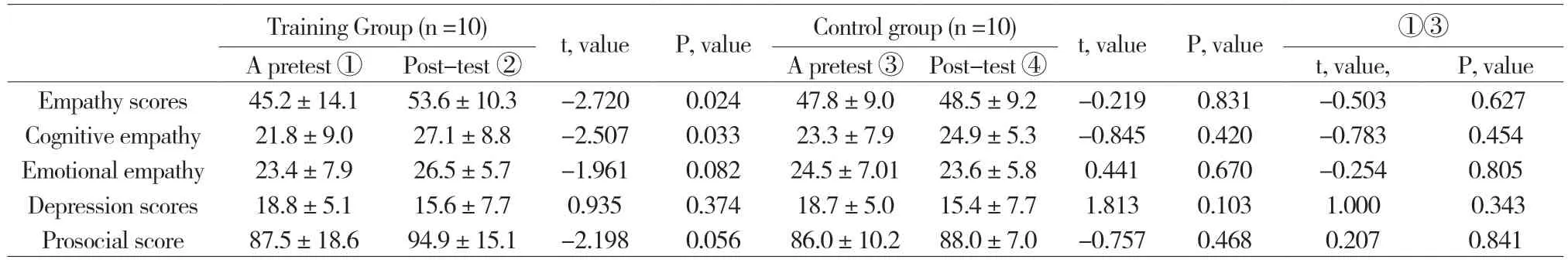
Table 2 Comparison of each scale score between before and after the two groups (M±SD)
2.3 Feedback of Qualitative Results from Empathy Training
After the last training session,the training group members filled in the Empathy Training Feedback Form,in which they were asked two questions,“What was the most impressive activity during the eight empathy training sessions?”,“What was your biggest gain from the eight empathy training sessions?”The results turned out that all the 10 team members acclaimed that the 10-week empathy training gave them a happy experience,most impressed by the activities such as blind walking,joint house building and psychological dramas.Most of the team members agreed that the biggest harvest was that they knew better about empathy.One team member said that there was no obvious benefit.
3 Discuss
Empathy plays a very important role in individual daily life and social interaction.College students are in the development stage of life.It is of great significance to the society and individual students to conduct empathy training for the special group of college students with sub-clinical depression,foster their empathy ability and alleviate their sub-clinical level.In this study,the intervention effect of empathy training on subclinical depression was not significant,but the improvement of empathy(especially cognitive empathy) reached a significant level.
According to the empathic altruism hypothesis[26],individuals with high empathy are more likely to understand others’ feelings and needs,and then the altruistic motivation is stimulated and prosocial behaviors tend to occur.In this study,prosocial total score increased after training,and the difference was close to significant level (t=-2.198,P=0.056).The prosocial total score was used as the calibration validity of this study,which indicated that the empathy training was effective.
3.1 Effects of Empathic Training on Sub-clinical Depression
In this study,sub-clinical depression scores were lower in the training group than in the pretest,but not significantly different from their pretest scores.This is not quite what we expected.Specifically,empathy training alleviated the level of sub-clinical depression in college students,but the effect was not statistically significant.The reasons may be as follows:(1)some group members experienced great setbacks during training,such as exam failure and love-life problems;(2) The time span of the whole training is long,lasting for 10 weeks,but the training frequency is low;(3)The validity of the sub-clinical depression pretest can not be guaranteed,and there is a suspicion that the answers are not completely true;(4) There are other unknown factors influencing sub-clinical depression.
3.2 Effects of Empathy Training on Empathy
T test before and after the training group showed that empathy training could significantly improve the empathy of college students with sub-clinical depression,which was consistent with the results of other individuals as research objects [26].Specifically,in this study,empathy training can significantly improve the cognitive empathy of students with sub-clinical depression,but not their emotional empathy.In the study of adolescents with schizophrenia,the main improvement was in the recognition of emotions and the understanding of gaffes.In addition to the differences in subjects,the differences may also result from the increasing emphasis on cognitive empathy and the diminishing of personal pain during training.For example,from the qualitative feedback results of empathy training,it can be seen that the training content involving cognitive empathy is the most applauded by everyone,and the most important gain in people’s life is to learn to take others’ place.This result is also supported by the dual-process perspective of empathy,in which cognitive empathy,as an adjustable cognitive process,can be improved in the short term through targeted training.Emotional empathy,on the other hand,is more of an automated process,which can not be easily regulated by short-term intervention.
3.3 Lack of Research
The study results call for leaders to pay attention to the needs of each group member and make corresponding responses in time,promote training participation,and ensure and improve training quality.However,the conclusions drawn from a small sample are not convincing enough to be directly extended to all the college students with sub-clinical depression .
In this study,due to the fact that there were fewer students with subclinical depression whose training time matched,different group members did not confirm the time of enrollment,so the two groups of members did not achieve complete paired grouping in terms of demographic variables.The experimental design of intervention should be further perfected in future studies.
In addition,in terms of the reliability of the sub-clinical depression pretest of the two groups,the pretest reliability was low because the group members may have expectations and assumptions about the training before joining the group.In the future,more attention should be paid to the expression of recruitment words and the screening of team members.
