高速逆流色谱法分离纯化大风艾中的黄酮类成分
2021-11-10谭道鹏郭振虎何芋岐
谭道鹏,郭振虎,何 莉,秦 琳,何芋岐
(1.遵义医科大学 药学院,贵州 遵义 563009; 2.贵州医科大学省部共建药用植物功效与利用国家重点实验室,贵州 贵阳 550014; 3.贵州黄果树立爽药业有限公司,贵州 贵阳 550014; 4.贵州苗药生物技术有限公司,贵州 铜仁 554300)
Blumeabalsamiferais a medicinal plant widely growing in Southeast Asia such as Malaysia,Philippines,Vietnam,Thailand and China.B.balsamiferashowed lots of biological effects such as sudorific[1],antifungal[2],anti-cancer[3]and anti-obesity[4]effects.B.balsamiferacontains abundant flavonoids[5-6]that are a ubiquitous group of polyphenolic substances.Consequently,to study on intrinsic relations about medical functions and chemical constitutes ofB.balsamifera,systematic phytochemical investigation is necessary firstly.However,a mixture of three compounds was very difficult to isolate in the process of phytochemical study.Among them,compound 1 can be separated from the mixture by common column chromatography (CC),but the other two compounds can not be isolated by the traditional methods,such as CC (including normal phase,reversed phase) and thin-layer chromatography (TLC) because of their similar polarity.While 20 mg the mixture removed compound 1 was separated by size-exclusion chromatography on the Sephadex LH20 column (100×3) cm with 80% methanol as mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min at ambient temperature.Compound 2,3 can be separated partly.So,development of an efficient separation and purification method of these active compounds is needed.High-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) is a separation method with liquid-liquid partition[7].It provides a highly efficient separation and less loss of complex samples,especially in the study of natural products chemistry[8].
In the present,an efficient HSCCC method was developed to isolate and purify the flavonoids glycosides inB.balsamifera.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Materials All analytical grade solvents were purchased from Shanghai Chemical Reagent Co.Ltd.Distilled water and HPLC grade acetonitrile (Fisher Scientific,Santa Clara,USA) were used for HPLC analysis.The leaves ofB.balsamiferawere collected from Luodian,Guizhou province of PR China in October 2015.It was identified by associate professor Daopeng Tan of the Zunyi medical university.The voucher specimen ofB.balsamiferawas deposited in the Herbarium of Guizhou Miaoyao biotechnology Co.,Ltd.
1.2 Apparatus A high-speed counter-current chromatography instrument (TBE-300A,Shanghai Tauto Biotech Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai) coupled with a polytetrafluoroethylene coils and a sample loop was employed in the present separation.The centrifuge (R) was 5 cm,and the β-values of the multilayer coil varied from 0.5 to 0.8.The revolution speed can be regulated between 0 and 1 000 r/min.The temperature was controlled by HX1050 circulating implement (Beijing Boyikang,Beijing).The instrument was also equipped with a constant flow pump (S-1007,Shengyitong Tech & Exploitation,Beijing),and an UV detector (8823B,Binda Yingchuang E-Tech Co.,Ltd.,Beijing).A N2000 workstation (Zhejiang University,Hangzhou) was used to collect the data.An Agilent 1100 Series HPLC apparatus (Agilent,Palo Alto,USA),equipped with a G1311A quaternary pump,a G1322A continuous vacuum degasser,a G1313A thermostated auto-sampler and a G1316A diode array detector was used.This system was operated by Agilent Chemstation software.NMR spectrometer was Bruker AM-400 MHz (Bruker,Switzerland).
1.3 Preparation of crude extract The air-dried leaves ofB.balsamifera(5 kg) were exhaustively extracted with 80% ethanol under reflux.The extract was evaporated in vacuum to yield a syrupy residue (500 g).The ethanol extract was fractionated by CC on silica gel using petroleum ether,dichloromethane,and methanol,respectively.The methanol solution was evaporated to obtain a residue (300 g) under reduced pressure,which was subjected to chromatography over silica gel using a gradient of 100% CH2Cl2to 100% MeOH to yield 21 fractions (Fr.1-Fr.21) based on TLC analysis.The targeted components were located in Fr.18 (7 g).
1.4 Preparation of sample and solvents The solvents of water-methanol-ethyl acetate-n-hexane (5∶1∶5∶1,v/v/v/v) were thoroughly equilibrated,and then separated using a separating funnel.The upper layer was used as stationary phase,while the lower layer was the mobile phase.The sample was dissolved by the lower layer and used for the separation.
1.5 Sample separation Firstly,the column was filled entirely with the upper layer solvent.And then,when the rotation rate of HSCCC reached at 800 r/min,the lower layer solvent was pumped into the column at 2 ml/min rate.The temperature was set at 30 ℃.After the mobile phase front emerged from the column,about 10 ml sample solution was injected into the column.The effluent was monitored using a UV detector under 254 nm.Fractions were collected based on the elution peaks.
1.6 Peak fractions analysis and identification Original sample and all of fractions were analyzed by HPLC with a reversed phase column [Diamonsil-C185 μm (4.6×250) mm,Dikma,Beijing].the column temperature was 40 ℃.The mobile phase was performed by acetonitrile (A) and 0.2% aqueous acetic acid (B) as follow gradient elution mode:0-5 min,12% A; 5-25 min,12%-18% A; 25-37 min,18% A,at 1.0 ml/min rate.The detection wavelength was set at 254 nm.The targeted constituents were elucidated by NMR and ESI-MS.
2 Results
In the present study,three fractions (1,2 and 3) were obtained in one step separation by HSCCC (Fig 1),The compounds corresponding to peaks 1,2 and 3 were elucidated as hyperoside (9.3 mg),astragalin (5.7 mg) and quercitrin (7.6 mg) respectively,on the basis of the information from1H-NMR and ESI-MS values.As shown in Fig 2, compared to the extract of Fr.18,the purity analysis of each fractions revealed that these three flavonoid glycosides were 97.1%,82.8% and 98.8%,respectively.

Fig 1 HSCCC chromatogram of the crude extract from B.balsamifera
Peak fraction 1:yellow powder,mp 235-236 ℃,ESI-MS (m/z):465 [M+H]+,1H-NMR (CD3OD,400 MHz) δ:7.83 (1H,d,J=2.1 Hz,H-5′),7.61 (1H,dd,J=8.5,2.4Hz,H-6′),6.87 (1H,d,J=8.5 Hz,H-2′),6.39 (1H,d,J=2.1 Hz,H-8),6.20 (1H,d,J=2.1 Hz,H-6),5.16 (1H,d,J=7.8 Hz,H-1″),3.45-3.84 (6H,m,sugar Hs).Comparing to the literature[9],the compound 1 was elucidated as hyperoside.
Peak fraction 2:yellow powder,mp 170-171 ℃,ESI-MS (m/z):449 [M+H]+,1H-NMR (CD3OD,500 MHz) δ:8.04 (2H,d,J=8.0Hz,H-2′,6′),6.86 (2H,d,J=7.8 Hz,H-3′,5′),6.35 (1H,brs,H-8),6.16 (1H,brs,H-6),5.20 (1H,d,J=6.6 Hz,H-1″),3.21-3.69 (5H,m,sugar Hs).Comparing to the literature[10],the compound 2 was elucidated as astragalin.
Peak fraction 3:yellow powder,mp 251-253 ℃,ESI-MS (m/z):449 [M+H]+,1H-NMR (CD3OD,400 MHz) δ:7.33 (1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-2′),7.31 (1H,dd,J=8.3,2.0 Hz,H-6′),6.91 (1H,d,J=8.3 Hz,H-5′),6.37 (1H,d,J=2.1 Hz,H-8),6.21 (1H,d,J=2.1 Hz,H-6),5.34 (1H,d,J=1.4 Hz,H-1″),3.34-4.21 (4H,m,sugar Hs),0.94 (3H,d,J=6.1 Hz,H-6″).Comparing to the literature[9],the compound 3 was elucidated as quercitrin.
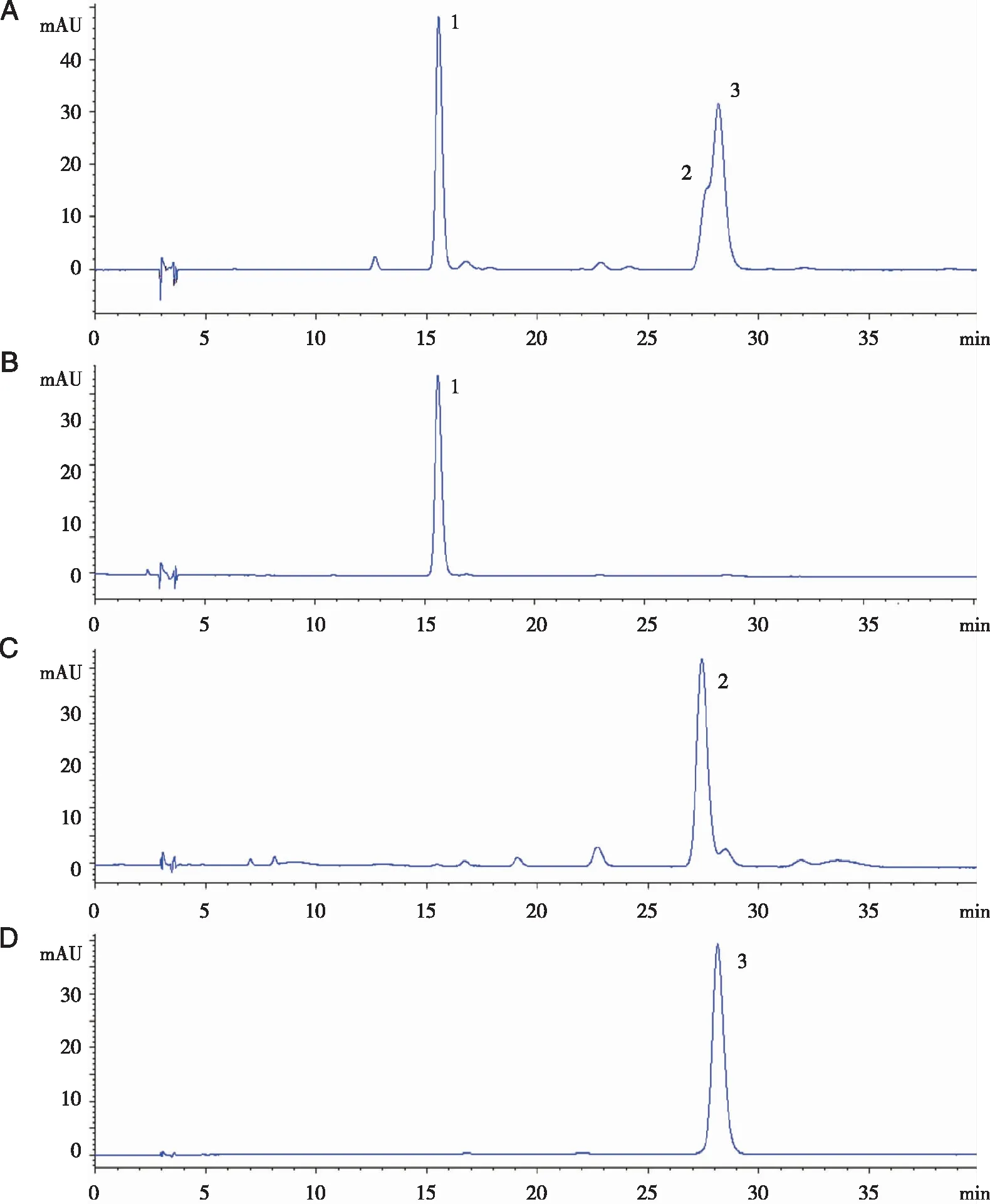
Conditions:Diamonsil-C18 column [5 μm,(4.6×250)mm,Dikma,Beijing,China] at column temperature of 40 ℃; mobile phase:acetonitrile and 0.2% aqueous acetic acid in gradient mode as follows:0-5 min,12% acetonitrile; 5-25 min,12%-18% acetonitrile; 25-37 min,18% acetonitrile; flow-rate:1 ml/min; detection wavelength:254 nm.A:The Fr.18 of B.balsamifera;B-D:the three targeted compounds (peak fractions 1-3) purified by HSCCC.Fig 2 HPLC chromatograms of Fr.18 of B.balsamifera and the three targeted compounds (peak fractions 1,2 and 3) purified by HSCCC
3 Discussion
3.1 Solvent system selection HSCCC is a pure liquid-liquid partition chromatography which is entirely based on the difference in partition coefficient (K) of solutes.To obtain efficient separation,it is essential to optimize theK-values of each targeted constituent by selecting a proper solvent system.A smallerK-value elutes compounds with lower resolution,while a largerK-value tends to give a longer elution time.In the present,ethyl acetate-water,n-hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol-water,and ethyl acetate-n-butanol-water,different solvent systems,were employed to optimize the separation condition.TheK-values of the three targeted compounds corresponded to peak fraction 1,2 and 3 in different solvent systems were measured and summarized in Table 1.When ethyl acetate-water (1∶1,v/v),and water- n-butanol-acetate (5∶1∶4,v/v) were selected as solvent systems,theirK-values were too large,and smallKvalues could be produced in water-methanol-ethyl acetate-n-hexane solvent system at the ratios of 1∶1∶1∶1 and 2∶1∶2∶1 (v/v).At last,water-methanol-ethyl acetate-n-hexane (5∶1∶5∶1,v/v/v/v) was selected the solvent system in the present separation,which provided a suitableK-values and the target compounds could be well separated from the other compounds.
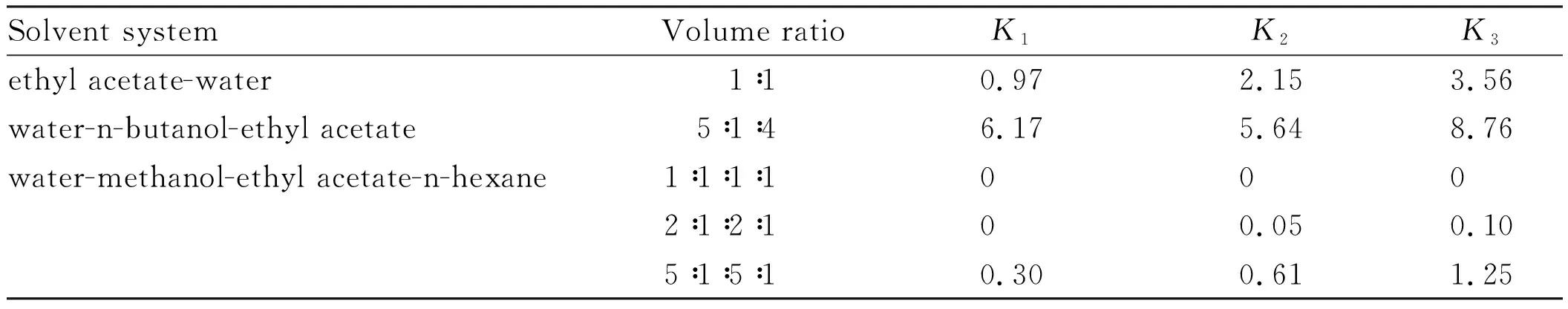
Table 1 The partition coefficient (K) of three target compounds in various solvent systems
3.2 HSCCC separation In this HSCCC experiment,the flow rate,the rotation rate,and the column temperature were confirmed.The results showed that slower flow rate could produce a good separation,but its chromatogram peaks was extended and more time was needed,the slower rotation rate could decrease stationary phase retained in the column leading to lower peak resolution; and higher temperature would produce more air in the column and degrade the separation efficiency.Accordingly,the flow rate was set as 2.0 ml/min and a revolution speed of 800 r/min and a column temperature of 30 ℃ were employed for the separation.
In the present study,a HSCCC method was successfully employed to isolate and purify three flavonoid glycosides inB.balsamifera.Three compounds,hyperoside (9.3 mg),astragalin (5.7 mg) and quercitrin (7.6 mg) were obtained from the crude extract by one-step HSCCC separation.The results suggested that the method is of great value to investigate the natural products of chemistry especially in separation of similar polarity compounds.
