血清心肌酶水平在新生儿高胆红素血症诊断中的临床意义
2021-11-04张茜齐秀花王明园
张茜 齐秀花 王明园

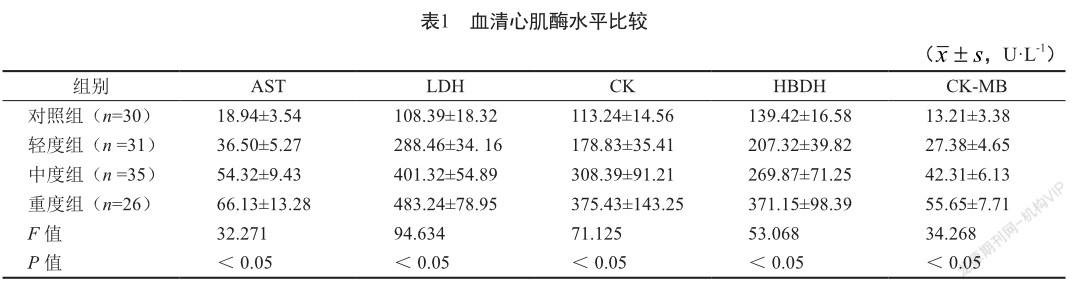
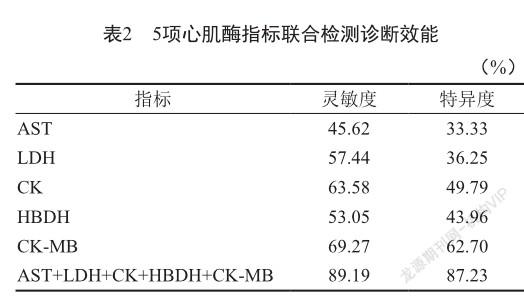
摘 要 目的:探讨血清心肌酶水平在新生儿高胆红素血症诊断中的临床意义。方法:选取新生儿高胆红素血症患儿92例作为研究组,依据总胆红素(TBil)水平分为轻度组、中度组、重度组;选取同期健康新生儿30例为对照组。检测血清心肌酶水平,比较不同病情程度患儿各项指标的差异。结果:血清心肌酶水平比较,研究组高于对照组,重度组高于轻度组、中度组,且中度组各项指标高于轻度组(P<0.05)。血清心肌酶水平与TBil水平呈正相关。结论:血清心肌酶在新生儿高胆红素血症中呈高表达,心肌酶谱指标可诊断病情程度还能够对治疗效果进行评价。
关键词 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 乳酸脱氢酶 肌酸激酶 羧丁酸脱氢酶 肌酸肌酶同功酶 新生儿高胆红素血症
中图分类号:R446.112; R722.17 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2021)19-0035-04
The clinical significance of the serum myocardial enzyme level in the diagnosis of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
ZHANG Qian, QI Xiuhua, WANG Mingyuan
(Department of Disease Control, the Seventh Peoples Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450000, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the clinical significance of serum myocardial enzyme levels in the diagnosis of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Methods: Ninety-two neonates with hyperbilirubinemia were selected as a study group, which were divided into a mild subgroup, a moderate subgroup and a severe subgroup based on their total bilirubin (TBil) levels, and the other 30 healthy newborns were selected as a control group. Serum myocardial enzyme levels were determined and the differences in the indicators of children with different disease conditions were compared. Results: Serum myocardial enzyme levels were higher in the study group than the control group and in the severe subgroup than the mild group and the moderate group, and the indicators were higher in the moderate group than the mild group (P<0.05). Serum myocardial enzyme levels were positively correlated with TBil levels. Conclusion: Serum myocardial enzyme is high-expressed in the children with neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Myocardial zymogram can be used for the diagnosis of the degree of disease and the assessment of treatment effect.
KEy wORDS aspartate aminotransferase; lactate dehydrogenase; creatine kinase; carboxybutyrate dehydrogenase; creatine kinase isoenzyme; neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
新生兒高胆红素血症是指出生未满28 d的新生儿黄疸,若未及时发现和治疗,病情持续加重会损伤新生儿中枢神经系统,继发新生儿胆红素脑病,造成运动、听力、认知障碍,严重者甚至危及生命[1-2]。血清学检测是诊断新生儿高胆红素血症及心肌损伤评估的重要依据,在以往的研究中,人们更多探究心肌酶指标在新生儿高胆红素血症病情评估中的价值,但对于其疗效评估中的价值研究较少[3]。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
选取郑州市第七人民医院2016年6月—2019年3月收治的新生儿高胆红素血症患儿92例作为研究组,其中男性51例,女性41例;胎龄38~42周,平均胎龄(39.84±1.54)周;根据总胆红素(total bilirubin, TBil)水平分为轻度组(TBil为205.0~259.9 μmol/L)31例,中度组(TBil为260.0~377.8 μmol/L)35例,重度组(TBil>377.8 μmol/L)26例。另选取同期健康新生儿30例作为对照组,其中男性18例,女性12例;胎龄38~42周,平均胎龄(39.71±1.47)周。两组一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具可比性。本研究经医院医学伦理委员会的批准。
