雾化吸入多黏菌素辅助治疗呼吸机相关性肺炎疗效与安全性的Meta分析
2021-10-15罗梦林王璇白浩陈万一
罗梦林 王璇 白浩 陈万一


中圖分类号 R563.1;R974 文献标志码 A 文章编号 1001-0408(2021)19-2400-06
DOI 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.19.16
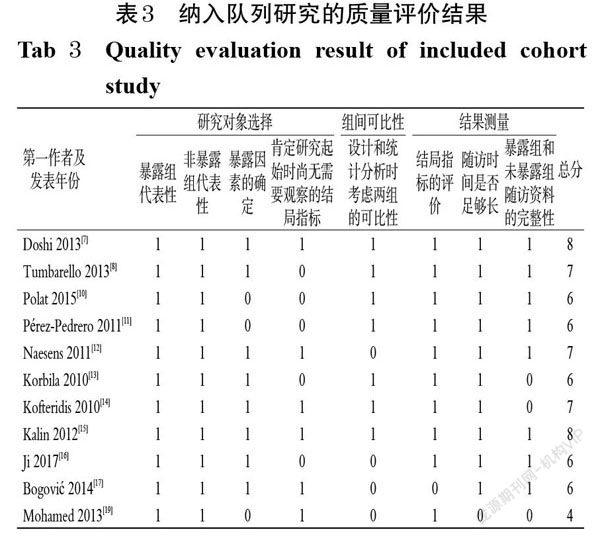
摘 要 目的:系统评价雾化吸入多黏菌素辅助治疗呼吸机相关性肺炎的疗效与安全性,为临床治疗提供循证参考。方法:计算机检索Cochrane Library、Embase、PubMed、Web of Science、中国期刊全文数据库、中国生物医学文献数据库、中文科技期刊数据库、万方数据库(检索时限均为建库至2021年3月)中关于雾化吸入多黏菌素联合常规治疗(试验组)对比常规治疗(对照组)对呼吸机相关性肺炎的疗效和安全性的随机对照试验(RCT)及队列研究。对符合纳入与排除标准的文献进行资料提取和质量评价后,采用RevMan 5.4软件进行Meta分析。结果:共纳入13项临床研究,包括2项RCT和11项队列研究,共计1 066例患者。Meta分析结果显示,试验组患者的临床有效率[OR=1.53,95%CI(1.17,2.00),P=0.002]、微生物清除率[OR=1.46,95%CI(1.11,1.91),P=0.007]均显著高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义;两组患者的全因死亡率[OR=0.88,95%CI(0.68,1.14),P=0.32]、肾功能损害发生率[OR=1.04,95%CI(0.72,1.49),P=0.85]比较,差异均无统计学意义。结论:基于现有临床证据,雾化吸入多黏菌素联合常规治疗能显著提高呼吸机相关性肺炎患者的临床有效率和微生物清除率。但本结论尚需要更多设计严格、长期随访的大样本RCT加以证实。
关键词 雾化吸入;多黏菌素;呼吸机相关性肺炎;Meta分析;疗效;安全性
Efficacy and Safety of Atomization Inhalation of Polymyxin in the Adjunctive Treatment of Ventilator- associated Pneumonia: A Meta-analysis
LUO Menglin1,WANG Xuan1,BAI Hao2,CHEN Wanyi2(1. Dept. of Pharmacy, the Second Affiliated Hospital of the Army Medical University, Chongqing 400037,China;2. Dept. of Pharmacy,Chongqing University Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Chongqing 400030,China)
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of atomization inhalation of polymyxin combined in the adjunctive treatment for ventilator-associated pneumonia, and to provide evidence-based reference for clinical treatment. METHODS: Retrieved from Cochrane Library, Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI, CBM, VIP and Wanfang database (from their inception to March 2021), randomized controlled trials (RCTs) about efficacy and safety of atomization inhalation of polymyxin combined with conventional treatment (trial group) versus conventional treatment (control group) for ventilator- associated pneumonia were collected. After data extraction and quality evaluation of included literatures met inclusion and exclusion criteria, Meta-analysis was performed by using RevMan 5.4 software. RESULTS: A total of 13 clinical studies were included, involving 2 RCTs and 11 cohort studies with a total of 1 066 patients. The results of Meta-analysis showed that clinical response rate [OR=1.53, 95%CI (1.17,2.00) ,P=0.002], microbial clearance rate [OR=1.46, 95%CI(1.11,1.91), P=0.007] of trial group were significantly higher than those of control group, with statistical significance. There was no statistical significance in the mortality rate [OR=0.88, 95%CI(0.68,1.14), P=0.32] and the incidence of renal impairment [OR=1.04, 95%CI (0.72, 1.49), P=0.85] between 2 groups. CONCLUSIONS: Based on current evidence, atomization inhalation of polymyxin combined with conventional treatment can significantly improve clinical response rate and microbial clearance rate of patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. However, more strictly-designed, long-term follow-up and large-scale RCTs are needed.
