辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机设计与试验
2021-09-16韩长杰肖立强李洪雷
韩长杰,肖立强,徐 阳,张 静,李洪雷
辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机设计与试验
韩长杰1,肖立强1,徐 阳1,张 静1,李洪雷2
(1.新疆农业大学机电工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830052;2. 德州福瑞特农业机械制造有限公司,德州 253000)
针对新疆广泛应用的半自动辣椒移栽机效率低、劳动强度大的问题,该研究设计了一种辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机。整机主要由全自动取投苗系统与栽植机构组成,采用整排取苗再分苗投苗的方式,实现128(16列×8行)穴辣椒穴盘苗的自动取苗、投苗。在分析现有移栽机结构和工作原理的基础上,确定了辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机的整体结构,完成了全自动取投苗系统的关键参数设计;制定了全自动取投苗系统的气动回路方案,并基于FluidSIM软件进行仿真及优化。采用平均苗高166.7 mm的辣椒苗,以取投苗成功率,栽植频率,株距变异系数,倒伏率为评价指标进行田间试验。试验结果表明:在工作气压0.4 MPa及移栽机作业速度1.4~1.7 km/h时,平均取投苗成功率为97.07%,栽植频率为123株/min,倒伏率1.67%,株距变异系数为3.67%,各项性能指标均满足辣椒穴盘苗移栽的农艺要求。该研究可为自动化移栽机的研究提供参考。
农业机械;设计;试验;自动移栽机;辣椒穴盘苗;气动
0 引 言
育苗移栽技术有提高蔬菜生长期间抗灾能力、增加幼苗成活率、提高蔬菜品质等优点,目前新疆的辣椒种植已经开始大力推广育苗移栽技术。新疆辣椒移栽作业以半自动辣椒移栽机为主,移栽作业时人工取苗、输苗,劳动强度大、成本高、效率低[1-4]。辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机可实现机械化自动取苗、投苗,提高工作效率,降低劳动强度,因此,辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机是新疆地区现阶段迫切需求的种植机械。
发达国家蔬菜移栽机的形式主要分为2类,以日本为代表的小型自动移栽机和以欧美为代表的大型自动移栽机[5-7]。小型自动移栽机如日本洋马株式会社生产的PA10型及PW10型自动移栽机,久保田株式会社生产的A500型及SKP-100mpci型自动蔬菜移栽机,其自动化程度高、稳定性好,但只适合小地块垄上移栽,不适合新疆大田作业。大型自动移栽机如意大利Ferrari公司生产的Futura自动移栽机,美国FMC及英国Pearson生产的全自动移栽机,其整机体积庞大、结构复杂,无法在新疆推广应用[8]。为满足国内作物移栽的农艺要求,一些学者提出了夹茎式[9-11]、夹钵式[12-16]、顶出式[17-20]等多种取投苗机构,文永双等[21]结合顶出式和插入夹持式取苗设计了一种插入顶出式取苗装置,解决了蔬菜穴盘苗自动取苗装置结构复杂、取苗性能差等问题。王蒙蒙等[22]基于辣椒穴盘苗抗压特性设计了一种曲柄摆杆式夹苗机构,对不同含水率穴盘苗适应性强、损伤小。张静等[23]设计了一种可实现整排取苗间隔投苗的机械驱动式自动取投苗系统,利用凸轮与齿轮齿条结合的机械驱动方式代替电气装置,完成自动取投苗作业,但取投苗效率不高、结构复杂、整机质量大。作者实地调研发现,新疆巴州良佳公司设计了一种回转夹茎式自动移栽机,移栽效率有所提高,但该机分苗漏斗有卡苗现象。山东青州火绒机械制造有限公司设计了一种单摆夹钵式自动移栽机,取苗适应性好,但需要2名作业人员在两侧放置苗盘,人工成本高。
基于以上分析,为进一步提高自动移栽机的工作效率及稳定性,本文采用整排取苗再分苗投苗的方式,由机械构件触发机械阀,按顺序控制气缸运动,完成穴盘苗的自动移栽。通过理论与试验,验证辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机设计的合理性。
1 辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机
1.1 整机结构
辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机如图1所示,由悬挂主梁、栽植机构、地轮、机架、全自动取投苗系统组成。全自动取投苗系统如图2所示,由取投苗机构、移盘机构、柔性链输苗机构、气动系统组成。
1.2 工作原理
辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机由拖拉机牵引,拖拉机动力输出轴驱动的空气压缩机产生压缩空气为全自动取投苗系统提供动力,地轮驱动栽植机构和柔性链输苗机构转动。穴盘苗被移盘机构输送至取苗位置,取投苗机构将取苗位置的穴盘苗移动至投苗位置并投入柔性链输苗机构的苗杯中,柔性链输苗机构将苗杯中的穴盘苗逐个投入栽植机构,由栽植机构将穴盘苗植入土壤中。
全自动取投苗系统的升降气缸由机械阀DT0控制,步进气缸、移位气缸、分苗气缸由机械阀DT1控制,夹苗装置气缸及升降控制气缸由机械阀DT2控制。辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机工作原理如图3所示,柔性链输苗机构每输送8个苗杯,投苗控制装置触发一次机械阀DT2,夹苗装置将8株穴盘苗投入苗杯中,取苗中,升降控制气缸触发机械阀DT0,升降气缸驱动夹苗装置及行程槽板下降,行程槽板下降至最低位置时触发机械阀DT1,移位气缸及分苗气缸驱动各夹苗装置移位合并至取苗位置,夹苗装置固定架触发机械阀DT2,夹苗装置夹取8株穴盘苗;投苗中,机械阀DT0弹簧自动复位,升降气缸驱动夹苗装置及行程槽板上升,行程槽板上升至最高位置时触发机械阀DT1,移位气缸及分苗气缸驱动各夹苗装置移位分散至对应苗杯上方,等待投苗,同时移盘机构进行纵向移盘动作,准备执行下次取苗过程。
1.3 性能参数
辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机性能参数如表1所示。
2 关键部件设计
2.1 移盘机构
移盘机构用于苗盘的进给。如图4所示,该机构由主动轴、主动链轮、变步距角棘轮装置、步进气缸、链条、苗盘推杆、中心导向杆、从动轴、从动链轮组成。作业人员将苗盘倒V型间隙卡在移盘机构中的苗盘推杆上,机械阀DT1来控制步进气缸做往复直线运动,通过变步距角棘轮装置驱动主动轴作间歇转动,主动轴带动苗盘推杆移动,使穴盘向取苗位置进给;主动轴另一端部设有摩擦轮,产生一定的摩擦力,防止棘轮由于惯性转动,导致苗盘位移不准确。
2.1.1 苗盘推杆与苗穴的运动学分析
如图5所示,将苗盘的进给运动分2个阶段,第1阶段从放苗盘位置,直线进给至取苗位置;第2阶段取苗完成后,苗盘在左右侧板的限制下,进行曲线运动,随从动链轮向下弯曲,从移盘机构底部送出。为避免苗盘在运动过程中与苗盘推杆相互干涉,对苗盘推杆与苗穴的运动轨迹进行分析。
根据图5的几何关系有:
式中1为从动链轮齿数;l为苗盘推杆圆心至点的距离,mm;l为点至点的距离,mm。128穴软苗盘常规尺寸3≈100°,纵向苗穴间距为31.75 mm,l为半个纵向苗穴间距,取l=15.875 mm,且由式(1)可得1>36,为保证移盘机构动作顺畅及链轮齿数常选奇数,取1=51,计算得≥129 mm时,苗盘推杆与苗穴不相互干涉。
2.1.2 变步距角棘轮装置的运动学分析
变步距角棘轮装置用于苗盘的变步距角进给,实现两衔接苗盘间隙的跨越。如图6所示,变步距角棘轮装置由棘轮、棘爪摇臂、棘爪、棘爪固定转轴、棘爪弹簧组成,棘爪摇臂受往复运动的步进气缸驱动,做往复摆动,棘爪随棘爪摇臂往复摆动,棘爪受棘爪弹簧控制,始终与棘轮外边缘接触;棘爪摇臂带动棘爪每次滑过的步距角大于1个正常棘齿加特殊棘齿的距离,且接近2个正常棘齿距离,即每次棘爪推动棘轮转动1个步距角,仅当棘爪从特殊棘齿上滑过时,棘轮随棘爪向前推进2个步距角2。移盘机构中链条旋转1周可放置3个苗盘,每个苗盘对应5根(一组)苗盘推杆,每组首根苗盘推杆标记为红色,两衔接苗盘间隙为一个纵向苗穴间距,红色苗盘推杆与棘轮的特殊棘齿相对位置对应不变,放置苗盘时,将苗盘起始行置于红色苗盘推杆位置即可实现苗盘变步距进给。
1.主动轴 2.棘轮 3.棘爪弹簧 4.棘爪 5.棘爪摇臂 6.步进气缸 7.连杆 8.棘爪固定转轴 9.特殊棘齿
1.Driving shaft 2.Ratchet 3.Pawl spring 4.Pawl 5.Pawl rocker arm 6.Stepping cylinder 7.Connecting rod 8.Pawl fixed shaft 9. Special ratch
注:为步进气缸在初始位置时与连杆铰接点的位置;为步进气缸在初始位置时连杆与棘爪铰接点的位置;为步进气缸在终止位置时与连杆铰接点的位置;为步进气缸在终止位置时连杆与棘爪铰接点的位置;为步进气缸活塞杆中心轴线至轴的垂直距离,mm;φ为棘爪摇臂的工作转角,(°);为步进气缸在初始位置时棘爪摇臂与轴的夹角,(°)。
Note:is the position of the hinge point of the stepping cylinder and the connecting rod when the stepping cylinder is in the initial position;is the position of the hinge point of the connecting rod and the pawl when the stepping cylinder is in the initial position;is the position of the hinge point of the stepping cylinder and the connecting rod when the stepping cylinder is at the end position;is the position of the hinge point between the connecting rod and the pawl when the stepping cylinder is at the end position;is the vertical distance from the center axis of the piston rod of the stepping cylinder to theaxis, mm;φis the working angle of the pawl rocker arm, (°);is the angle between the pawl rocker arm and theaxis when the stepping cylinder is in the initial position, (°).
图6 变步距角棘轮装置结构示意图
Fig.6 Structure diagram of variable step angle ratchet device
为保证移盘位置精准,对棘轮的关键参数进行计算[24],设计要求棘轮转动1周进给1个苗盘并跨越两衔接苗盘间隙,共进给17个苗穴纵向间距,棘爪推动1个棘齿,驱动苗盘推杆前进1个纵向苗穴间距,故棘轮齿数3=17,棘轮的关键参数为:
式中为棘轮步距角,(°);为棘爪运动一次推过的棘齿数量;为送苗行程,mm;2为主动链轮齿数;为节距,mm;为棘轮模数;d为棘轮齿顶圆直径,mm;为棘齿齿高,mm;d为齿根圆直径,mm;1为棘齿齿距,mm;1为棘爪工作长度,mm;1为棘爪高度,mm。本文链条链号取10A,则=15.875 mm;128穴软苗盘纵向苗穴间距为31.75 mm,因此送苗行程31.75 mm;按照强度要求确定模数m为7,将代入式(2)得出≈21°、2=34、d=119 mm、=5.25 mm、d=108.5 mm、1≈22 mm、1≈44 mm、1=10.5 mm。
如图6所示,以棘轮转动中心为原点,竖直方向作为轴建立坐标系,记φ为棘爪摇臂的工作转角,图中棘轮转动中心及根据机构安装位置给定,可得到x==148mm,棘轮各关键参数已知,棘轮步距角≈21°,棘爪的工作转角应在42°~68°之间,取棘爪的工作转角为50°,由于棘爪随棘爪摇臂往复摆动,故棘爪摇臂的工作转角也为50°。
为满足机构工作要求,需同时满足以下约束:
当机构处于初始位置时,为保证棘爪在棘轮齿根圆上,有约束式[25]:
当机构在转动过程中,为保证摇臂转动正常,有约束式[26]:
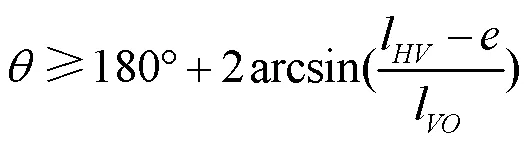
取不等式(4)作为设计的优化目标,使l与l在满足机构工作要求的条件下取得最小值,以保证变步距角棘轮装置结构紧凑,使用Matlab对不等式(4)进行求解,最终取整得到解l=25 mm,l=146 mm。
2.2 取投苗机构
取投苗机构用于从穴盘中自动取出穴盘苗并准确投入苗杯中。如图7所示,该机构主要由移位气缸、移位滑轨、分苗气缸、分苗滑轨、夹苗装置、升降气缸、投苗挡片、机械阀组成。取苗行程时,分苗气缸活塞杆收缩使夹苗装置合并,移位气缸活塞杆伸出使夹苗装置移动至取苗位置,夹苗装置夹取8株穴盘苗,升降气缸活塞杆收缩,将穴盘苗从苗穴中取出;投苗行程时,移位气缸活塞杆收缩使夹苗装置移动至投苗位置,同时分苗气缸活塞杆伸出使夹苗装置分散至对应苗杯上方,夹苗装置将8株穴苗准确投入苗杯中,完成1次取苗投苗的过程。取投苗机构纵向移动采用双滑轨倒挂设计,在风沙天气,可以减少磨粒磨损,延长使用寿命。
1.移位气缸 2.升降气缸 3.方管 4.夹苗装置 5.行程槽板 6.分苗气缸 7.机械阀DT1 8.机械阀DT2 9.移位滑轨 10.夹苗装置固定架 11.机械阀DT0 12.限位板 13.投苗挡片
1.Shift cylinder 2.Lifting cylinder 3.Square tube 4.Seedling clamping device 5.Stroke groove plate 6.Seedling dividing cylinder 7.Mechanical valve DT1 8.Mechanical valve DT2 9.Moving slide 10.Fixing frame of seedling clamping device 11.Mechanical valve DT0 12.Limit plate 13. Seedling dropping block
注:→表示气缸活塞杆移动方向;为移位气缸;为升降气缸;为分苗气缸;下标1和2为各气缸的运动次序。
Note: → the moving direction of cylinder rod;is shift cylinder;is lifting cylinder;is seedling dividing cylinder; subscript 1 and 2 refers to the order of movement of each cylinder.
图7 取投苗机构工作原理图
Fig.7 Working principle diagram of seedling picking and dropping mechanism
2.2.1 夹苗装置
夹苗装置用于夹取和投放辣椒苗,为实现准确夹取及投放苗的自动化控制,使用气缸控制夹苗装置的开合,夹苗装置机构简图如图8所示。
1.夹苗装置气缸 2.铰接点 3.固定支点 4.夹苗臂 5.辣椒苗茎秆
1.Cylinder of seedling clamping device 2.Hinge point 3.Fixed fulcrum 4.Seedling holding arm 5.Chili seedling stem
注:L为夹苗臂总长,mm;L为夹苗臂宽度,mm;1为气缸推力,N;F1和F2是两侧夹苗臂对辣椒苗的夹持力,N;为铰接点气缸压力方向与竖直方向夹角,(°)。
Note:Lis the total length of the seedling holding arm, mm;Lis the width of the seedling holding arm, mm;1is the cylinder thrust, N;F1andF2is the clamping force of the seedling holding arms on both sides of the chili seedling, N;is the angle between the cylinder pressure direction and the vertical direction at the hinge point, (°).
图8 夹苗装置机构简图
Fig.8 Schematic diagram of seedling clamping device
为保证成功取苗,对夹苗装置取苗状态进行受力分析。夹苗装置在夹持状态下,各力之间的关系如式(5)所示:
式中为辣椒苗的重力,N;为摩擦系数。当辣椒幼苗摩擦系数较小且重力较大时,夹苗装置可以牢固夹持辣椒幼苗,则证明夹苗装置可以保证取苗成功。故取L=50 mm,L=10 mm,=0.49[27],=0.4 N,=5°。将已知数值代入式(5)中,可得气缸所需的理论最小推力1=2.0 N。
2.2.2 分苗装置
由于取苗时苗穴间距与投苗时苗杯间距不同,所以采取整排取苗再分苗的方式投苗,分苗装置主要包括分苗导轨、分苗气缸、方管、限位板。8个夹苗装置安装在8个滑块上,相邻夹苗装置之间使用限位板连接,2个分苗气缸驱动8个夹苗装置在分苗导轨上运动,夹苗装置合并取苗时,夹苗装置间距L=32 mm;夹苗装置分散投苗时,夹苗装置间距L=127 mm,由结构关系可得
式中2为分苗气缸行程,mm;L为分散时夹苗装置间隔距离,mm;L为合并时夹苗装置间隔距离,mm;为夹苗装置气缸个数,为分苗气缸个数。将L、L、按式(6)计算得分苗气缸行程2=332.5 mm,取整后分苗气缸行程为333 mm。
2.3 柔性链输苗机构
柔性链输苗机构用于将苗杯中的穴盘苗逐个投入至栽植机构中。如图9所示,该机构由苗杯、柔性链主动链轮、活门托板、投苗控制装置、柔性链、支架组成。动力经地轮通过链轮链条及六方轴,变速箱,传递至柔性链,苗杯随柔性链移动,当苗杯移动到落苗口时,苗杯下方的活门打开,将苗落入栽植机构中。苗杯的间距127 mm,苗杯数量为18个。
投苗控制装置用于控制取投苗机构将取出的穴盘苗投入苗杯中。如图10所示,该装置由柔性链从动链轮、柔性链主动链轮、变速箱、六方轴、机械阀DT3、螺栓型滚动轴承、从动齿轮、主动齿轮组成,柔性链主动链轮和主动齿轮通过方轴连接,主动齿轮与从动齿轮啮合传动,螺栓型滚动轴承安装于从动齿轮侧面。设计要求每经过8个苗杯,螺栓型轴承触发一次机械阀DT3,控制取投苗机构将8株穴盘苗准确投入苗杯中。根据运动关系有:
式中L为苗杯间距,mm;为投苗数量,株;为链条节距,mm;4为柔性链主动链轮齿数,取4=16;5为从动齿轮齿数;6为主动齿轮齿数。将4L代入式(7)得主动齿轮与从动齿轮传动比为1∶4。
1.柔性链从动链轮 2.柔性链主动链轮 3.变速箱 4.六方轴 5.机械阀DT3 6.螺栓型滚动轴承 7.从动齿轮 8.主动齿轮
1.Flexible chain driven sprocket 2.Flexible chain driving sprocket 3.Gearbox 4.Hexagonal shaft 5.Mechanical valve DT3 6.Bolt type rolling bearing 7.Driven gear 8.Driving gear
图10 投苗控制装置结构示意图
Fig.10 Structure diagram of seedling dropping control device
3 气动系统的设计
辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机中的气动元件包括升降气缸A、步进气缸B、移位气缸C、分苗气缸D、夹苗装置气缸E、升降控制气缸F、投苗控制气缸G。如图11所示,升降气缸由机械阀DT0控制,由节流阀1及2进行调节速度。步进气缸、移位气缸、分苗气缸由机械阀DT1控制,由节流阀3及4进行调节速度。夹苗装置气缸及升降控制气缸由机械阀DT2控制。投苗控制气缸由机械阀DT3控制。
3.1 气动系统的仿真分析
为验证气动系统中各气缸动作时序是否满足设计要求,对气动回路进行仿真分析,首先利用FluidSIM对系统进行建模,设置各个元气件的有关参数,如气源气体的压力、节流阀的开度、气缸的缸径、行程一系列参数,再运用软件的查错功能对所建立的系统模型进行检查,完成模型的建立[28]。
在完成系统建模后,针对不同的系统参数对气动系统进行仿真,观察各缸完成规定行程所用的时间,各气缸动作时序是否满足要求,从而可以设计出结构简单、工作可靠、效率较高的最优回路。
在表2所示的系统建模参数下,对气动系统运行仿真。图12为各气缸动作时序图,横坐标为时间,纵坐标为各气缸活塞杆位置,从夹苗装置气缸活塞杆第一次收缩至0 mm开始至第二次收缩至0 mm结束为一个工作循环,整个动作循环时间约4s。整个过程气缸时序动作为:夹苗装置气缸活塞杆收缩且升降控制气缸活塞杆伸出,升降气缸活杆伸出,移位气缸及步进气缸活塞杆伸出且分苗气缸活塞杆收缩,夹苗装置气缸活塞杆伸出且升降控制气缸收缩,升降气缸活塞杆收缩,移位气缸及步进气缸活塞杆收缩同时分苗气缸活塞伸出,夹苗装置活塞杆收缩。各气缸动作时序符合全自动取投苗系统投苗-下降-移位合并-取苗-提升-移位分散及纵向移盘-投苗动作次序的要求。
3.2 耗气量的计算
根据气缸参数计算总耗气量,并依据总耗气量选择较合适的空气压缩机。各气缸往返一次的平均耗气量按式(8)[29]计算。计算总耗气量时,按自动移栽机每行栽植频率为128株/min。各气缸耗气量计算结果见表3。
式中平均为气缸耗气量,L/min;为气缸动作频率;为气缸缸径,cm;为气缸行程,cm;为气缸工作压力,MPa。
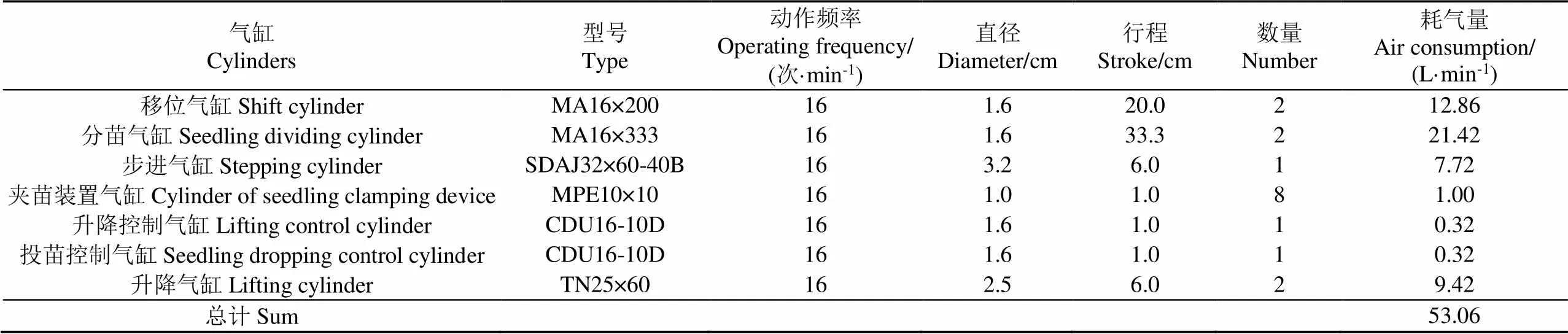
表3 耗气量计算
由表3可知全自动取投苗系统耗气总量为53.06 L/min,为保证气源压力稳定,辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机中2组全自动取投苗系统应选择容积流量160 L/min以上的空气压缩机提供压缩空气。
4 田间试验
4.1 试验条件
如图13所示,田间试验于2020年8月在德州福瑞特农业机械制造有限公司试验地进行,试验前,对试验地进行旋耕作业保证土壤疏松平整。采用育苗大棚所培育的辣椒苗,苗龄为60 d,平均苗高为166.7 mm;基质为草炭、蛭石、珍珠岩按照体积比1∶1∶1混合制得,基质含水率24%~32%。
4.2 试验方法及评价指标
移栽机与拖拉机挂接方式为三点悬挂,拖拉机额定功率为36.8 kW,参照JB/T 10291-2013[30],在工作气压0.4 MPa及移栽机作业速度1.4~1.7 km/h时进行试验,以取投苗成功率,栽植频率,株距变异系数,倒伏率为性能评价指标。
4.2.1 取苗投苗成功率试验
对穴盘苗移栽机进行取投苗成功率试验,任选8盘辣椒穴盘苗分别进行试验。试验前,确认穴盘内辣椒苗株数为128株;试验中,分别统计取苗成功的株数,投苗成功的株数,苗杯输苗成功的株数;试验后,对试验结果进行分析。
4.2.2 栽植频率试验
移栽机进行3次单程作业,每次每行移栽1盘辣椒苗,栽植时间用秒表计时,试验后,分别测定每次作业一个栽植行内的栽植株数并按式(9)计算栽植频率。
式中为栽植频率,株/min;为栽植株数;为栽植时间,s。
4.2.3 株距变异系数及倒伏率试验
在测定栽植频率的同时,分别测定株距变异系数及倒伏率。每行选取中间连续的120株辣椒苗进行测定,共测定6行。
理论株距为X(mm),相邻两株的实测株距为X(mm),株距变异系数按(10)计算。
式中CV为株距变异系数,%;S为株距标准差,cm;为实测株距数,株。
每行选取中间连续的120株辣椒苗测定倒伏率,共测定6行。行业标准规定秧苗主茎与地面夹角小于30°为倒伏,试验采用万能角度尺测量移栽后辣椒苗主茎与地面的夹角,并用式(11)计算倒伏率。
式中为倒伏率,%;N为倒伏株数,株;为测定株数。
4.3 试验结果与分析
由表4试验结果可知,辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机平均取投苗成功率为97.07%,取苗成功率为97.85%,投苗成功率为99.50%,苗杯输苗成功率为99.70%。各运动部件配合良好,但由于部分试验辣椒幼苗枝叶过于紧凑,一定程度上影响了取苗成功率。由表5试验结果可知,辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机栽植频率为每行123株/min,满足设计要求。由表6试验结果可知,辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机倒伏率为1.67%,满足行业标准要求。由表7试验结果可知,辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机株距变异系数为3.67%,结合观察试验过程,发现地轮存在打滑现象,导致地轮传动存在误差,影响了株距变异系数。
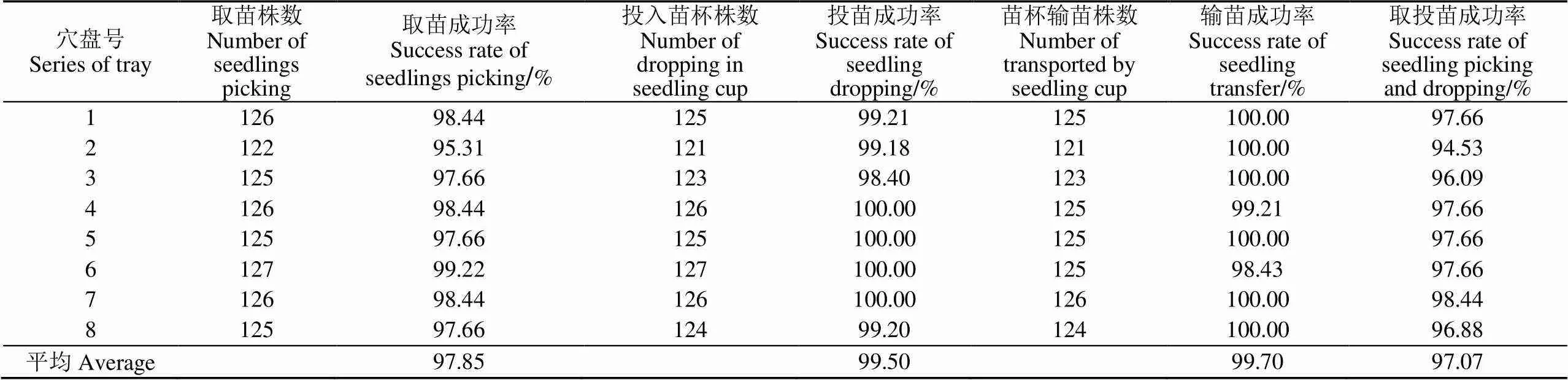
表4 取投苗成功率试验结果
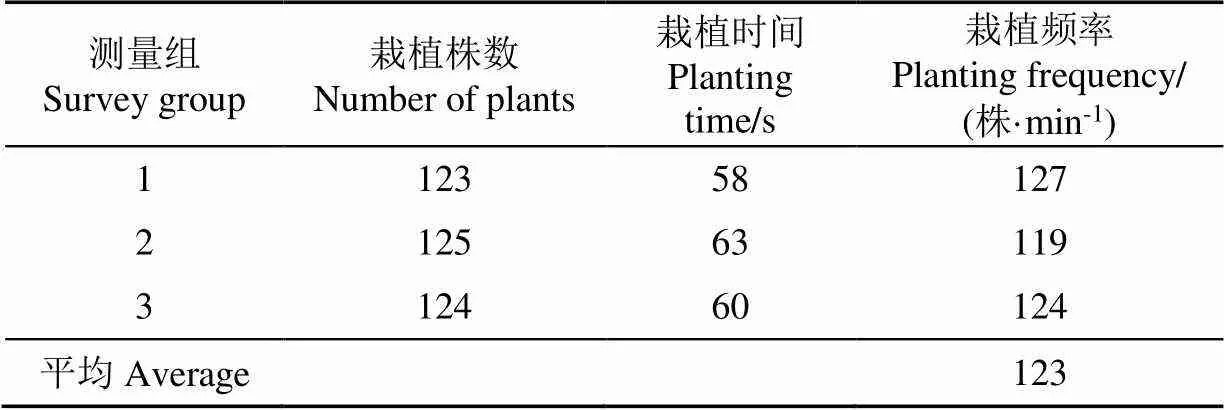
表5 栽植频率测量结果
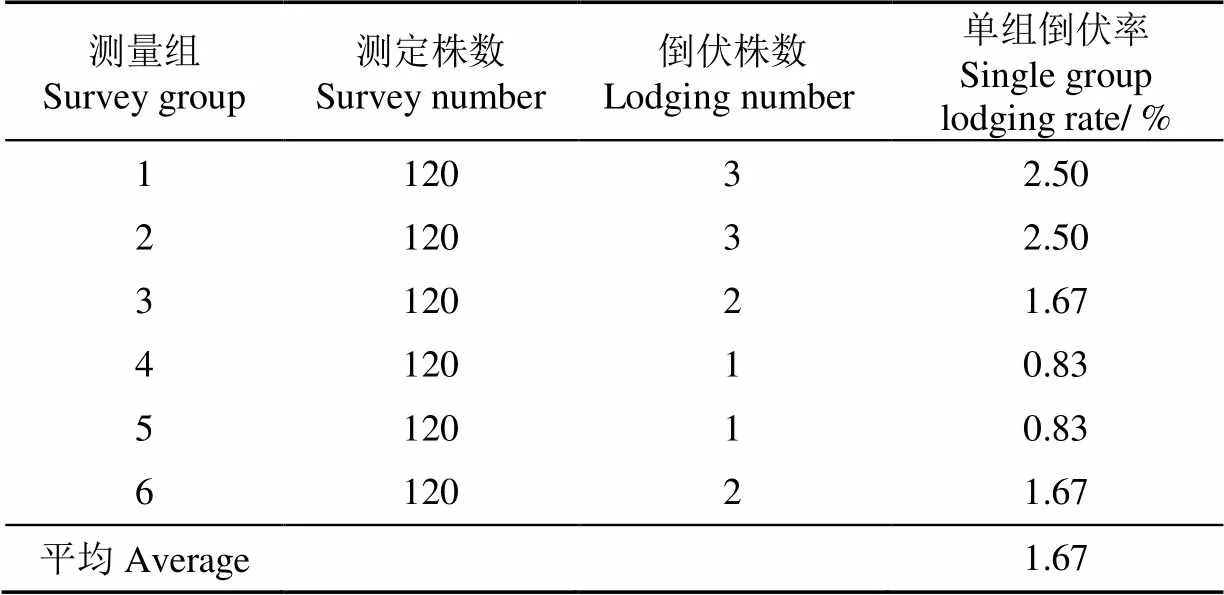
表6 倒伏率测量结果
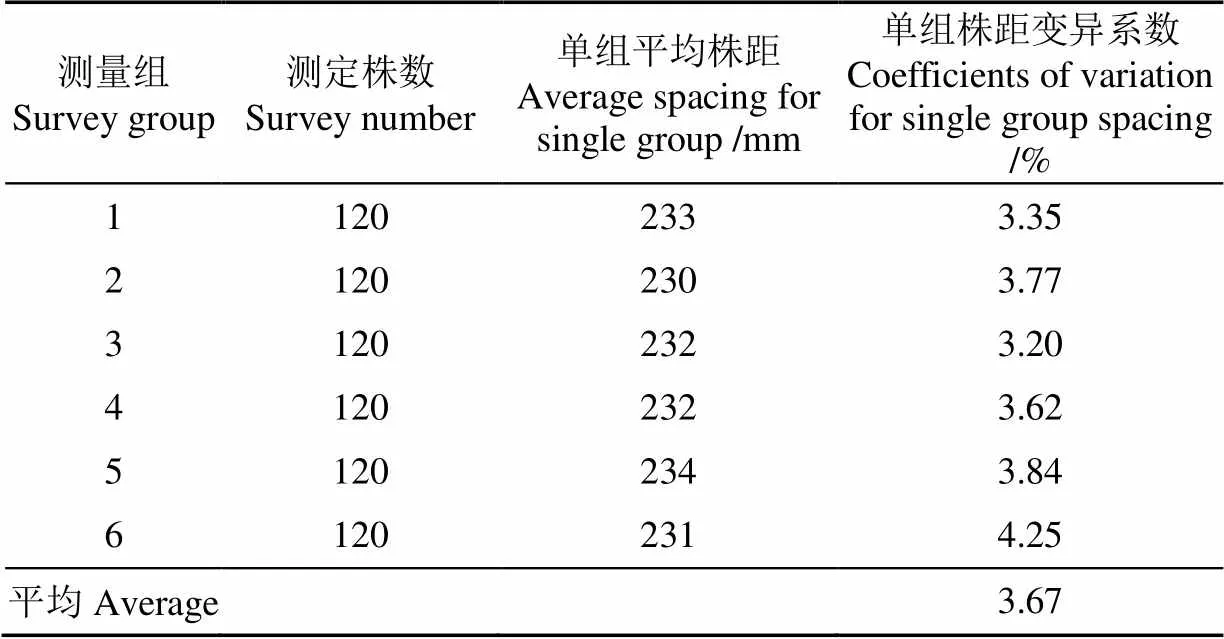
表7 株距测量结果
5 结 论
1)本文将机械结构与气动控制原理结合设计了一种以全自动取投苗系统为关键部件的辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机,可完成自动送苗、取苗、投苗、栽种等多道作业环节,其控制系统简单,结构紧凑。
2)对全自动取投苗系统进行运动学及力学分析,完成了关键参数设计。制定了全自动取投苗系统气动回路方案,并基于FluidSIM软件进行仿真,气动系统运行满足设计要求。
3)通过田间试验测得,在工作气压为0.4 MPa及移栽机作业速度为1.4~1.7 km/h时,平均取投苗成功率达97.07%,栽植频率为123株/min,倒伏率1.67%,株距变异系数为3.67%,各项性能指标可以满足新疆地区辣椒作物移栽的农艺要求。在前期机械驱动式辣椒穴盘苗自动取投苗系统的研究基础上,进一步提高了工作效率及取投苗成功率。
[1] 吕志军,单伊尹,王杰,等. 蔬菜移栽装备研究现状和钵苗移栽装备展望[J]. 中国农机化学报,2017,38(11):30-34.
Lv Zhijun, Shan Yiyin, Wang Jie, et al. Research progress of vegetable transplanting machine and prospects of seed-ling-picking machinery of transplanter[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2017, 38(11): 30-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 周海燕,杨炳南,颜华,等. 旱作移栽机械产业发展现状及展望[J]. 农业工程,2015,5(1):12-13,16.
Zhou Haiyan, Yang Bingnan, Yan Hua, et al. Status quo and development prospects of dry land transplanting machine industry[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 5(1): 12-13, 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 于晓旭,赵匀,陈宝成,等. 移栽机械发展现状与展望[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(8):44-53.
Yu Xiaoxu, Zhao Yun, Chen Baocheng, et al. Current situation and prospect of transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(8): 44-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张雪琪,弋景刚,张秀花,等. 国内外蔬菜移栽机研究现状及发展[J]. 河北农机,2018(4):39-40.
[5] 张振国,曹卫彬,王侨,等. 穴盘苗自动移栽机的发展现状与展望[J]. 农机化研究,2013,35(5):237-241.
Zhang Zhenguo, Cao Weibin, Wang Qiao, et al. Development status and prospect of plug seedlings automatic transplanting machine[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2013, 35(5): 237-241. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 崔巍,徐盼,王海峰,等. 旱地自动移栽技术发展现状及分析[J]. 农机化研究,2015,37(6):1-5,28.
Cui Wei, Xue Pan, Wang Haifeng, et al. Present status and analysis of dry-land auto-transplanting seedling technique[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(6): 1-5, 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张开兴,吴昊,王文中,等. 夹紧式番茄移栽机取苗机构的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2020,42(12):64-68.
Zhang Kaixing, Wu Hao, Wang Wenzhong, et al. Design and sxperiment of clamping picking seedling mechanism for tomato transplanter[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2020, 42(12): 64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘洋,李亚雄,李斌,等. 新疆地区作物移栽与移栽机研究现状[J]. 广东农业科学,2013,40(09):189-191.
Liu Yang, Li Yaxiong, Li Bin, et al. Research of China’s Xinjiang Region crop transplanting machines[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 40(09): 189-191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李华,马晓晓,曹卫彬,等. 夹茎式番茄钵苗取苗机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(21):39-48.
Li Hua, Ma Xiaoxiao, Cao Weibin, et al. Design and experiment of seedling picking mechanism by stem clipping for tomato plug seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(21): 39-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 韩长杰,杨宛章,张学军,等. 穴盘苗移栽机自动取喂系统的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(8):51-61.
Han Changjie, Yang Wanzhang, Zhang Xuejun, et al. Design and test of automatic feed system for tray seedlings transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(8): 51-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 徐广鹏,张闯闯,杨铁钢,等. 一种种苗移栽机自动取苗送苗装置[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(6):249-252.
Xu Guangpeng, Zhang Chuangchuang, Yang Tiegang, et al. An automatic picking seedling and feeding aeedling device of the seedling transplanting machine[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(6): 249-252. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李华,曹卫彬,李树峰,等. 2ZXM-2型全自动蔬菜穴盘苗铺膜移栽机的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(15):23-33.
Li Hua, Cao Weibin, Li Shufeng, et, al. Development of 2ZXM-2 automatic plastic film mulching plug seedling transplanter for vegetable[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(15): 23-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 孙良,沈嘉豪,周誉株,等. 非圆齿轮-连杆组合传动式蔬菜钵苗移栽机构设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(10):26-33.
Sun Liang, Shen Jiahao, Zhou Yuzhu, et, al. Design of non-circular gear linkage combination driving type vegetable pot seedling transplanting mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(10): 26-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王永维,何焯亮,王俊,等. 旱地蔬菜钵苗自动移栽机栽植性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(3):19-25.
Wang Yongwei, He Zhuoliang, Wang Jun, et, al. Experiment on transplanting performance of automatic vegetable pot seedling transplanter for dry land[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(3): 19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘念聪,杨程文,刘保林,等. 全自动单摆式蔬菜钵苗取苗系统研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(22):87-95.
Liu Niancong, Yang Chengwen, Liu Baolin, et al. Development of automatic single pendulum vegetable pot seedling picking and feeding system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(22): 87-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 吴国环,俞高红,项筱洁,等. 三移栽臂水稻钵苗移栽机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(15):15-22.
Wu Guohuan, Yu Gaohong, Xiang Xiaojie, et, al. Design and test of rice potted-seedling transplanting mechanism with three transplanting arms[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(15): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 韩绿化,毛罕平,赵慧敏,等. 蔬菜穴盘育苗底部气吹式钵体松脱装置设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(4):37-45.
Han Lühua, Mao Hanping, Zhao Huimin, et al. Design of root lump loosening mechanism using air jets to eject vegetable plug seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(4): 37-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Wan Ishan W I, Awal M A, Elango R, et al. Development of an automatic transplanter for the gantry system[J]. Asian Journal of Scientific Research, 2008, 1(4): 451-457.
[19] Ye Bingliang, Yi Weiming, Yu Gaohong, et al. Optimization design and test of rice plug seedling transplanting mechanism of planetary gear train with incomplete eccentric circular gear and non-circular gears[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(6): 43-55.
[20] Xin Jin, Li Daoyi, Ma Hao, et al. Development of single row automatictransplanting device for potted vegetable seedlings[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2018, 11(3): 67-75.
[21] 文永双,张俊雄,张宇,等. 蔬菜穴盘苗插入顶出式取苗装置研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(22):96-104.
Wen Yongshuang, Zhang Junxiong, Zhang Yu, et al. Development of insertion and ejection type seedling taking device for vegetable plug seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(22): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王蒙蒙,宋建农,刘彩玲,等. 蔬菜移栽机曲柄摆杆式夹苗机构的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(14):49-57.
Wang Mengmeng, Song Jiannong, Liu Cailing, et al. Design and experiment of crank rocker type clamp seedlings mechanism of vegetable transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(14): 49-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张静,龙新华,韩长杰,等. 机械驱动式辣椒穴盘苗自动取投苗系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(5):20-30.
Zhang Jing, Long Xinhua, Han Changjie, et al. Design and experiment on mechanical driven automatic system of picking and throwing for chili plug seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(5): 20-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王海洋,张伟,候永瑞. 玉米钵育移栽机自动供苗装置设计及运动仿真[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(6):143-148,154.
Wang Haiyang, Zhang Wei, Hou Yongrui. The design and motion simulation of the corn pot seedling machines[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(6): 143-148, 154. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 俞高红,杜立恒,李革,等. 高速水稻钵苗移栽机送秧装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(5):39-45.
Yu Gaohong, Du Liheng, Li Ge, et al. Design and experiment of feeding-seedling device for high-speed rice pot-seedling transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(5): 39-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 李献奇,刘维维,高连兴. 摇杆滑块机构及其在农业机械上的应用研究[J]. 农业科技与装备,2014(1):20-22.
Li Xianqi, Liu Weiwei, Gao Lianxing. Rocker-slider mechanism and its application in agricultural machine[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2014(1): 20-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 韩绿化,毛罕平,缪小花,等. 基于穴盘苗力学特性的自动取苗末端执行器设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(11):260-265.
Han Lühua, Mao Hanping, Miao Xiaohua, et al. Design of automatic picking up seedling end-effector based on mechanical properties of plug seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013 44(11): 260-265. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 何吉利. 基于FluidSIM-P的涡流探伤检测台气动控制设计[J]. 机床与液压,2008,36(8):286-288.
He Jili. Pneumatic control design of eddy current testing platform based on fluidsim-p[J]. Machine Tools and Hydraulics, 2008, 36(8): 286-288. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 成大先. 机械设计手册单行本-气压传动[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2016.
[30] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. JB/T10291-2013旱地栽植机械行业标准[S]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2013.
Design and experiment of the automatic transplanter for chili plug seedlings
Han Changjie1, Xiao Liqiang1, Xu Yang1, Zhang Jing1, Li Honglei2
(1.,,830052,;2..,.,253000,)
Most of vegetable varieties have widely been applied in China at present. Transplanting plug seedlings can greatly contribute to the survival ratio of seedlings, and the resistance to disasters during the growth for better quality and yield of vegetables. However, current manual seedling fetching and transporting seedlings were commonly used in a semi-automatic transplanting machine with high cost and labor intensity. In this study, a fully automatic plug-seedling transplanting and planting machine was developed to meet the transplanting operation mode and agronomic requirements for high efficiency, where the seedlings were taken in a row to be divided, and then be dropped. The transplanting machine was mainly composed of a tray transfer, a seedling picking and dropping, a flexible chain seedling transporting, and a planting mechanism. Plug seedling transplanting was automatically realized under the cooperation of the valve control cylinder movement and mechanical transmission. The simple control system presented a novel structure to gain higher work efficiency. Furthermore, only one operator was required to place the seedling tray, indicating the labor cost-saving. A tractor was used to haul the automatic plug-seedling transplanter, where an air pump driven by a power output shaft was selected to generate the compressed air, thereby providing power for the automatic seedling picking and dropping system. The ground wheel was also utilized to drive the planting and flexible chain conveying mechanism when rotating the plug seedling. A three-dimensional design Solidworks software was used to design the specific structure after the valve control strategy was determined. Correspondingly, the movement trajectories of seedling plate putter and plug seedlings were analyzed to determine the key structure parameters of the plate-moving mechanism. A variable-step ratchet device was also characterized to confirm the size of key components. MATLAB platform was utilized to carry out the structural optimization. The force was thus determined for a seedling clamping device, together with the main component of the seedling picking and dropping mechanism. The key parameters were also determined for the cylinder of a seedling clamping device. FluidSIM software was used to simulate the pneumatic circuit system under different system parameters, further optimizing the design of a pneumatic circuit with simple structure, reliable work performance, and high efficiency. A field trial was conducted using chili seedlings with an average seedling height of 166.7 mm. Evaluation indicators were set as the success rate of seedling taking and dropping, planting frequency, coefficient of variation of plant spacing, and lodging rate. The test results showed that the average success rate of planting and dropping seedlings was 97.07%, and the planting frequency was 123 plants/min, when the working pressure was 0.4 MPa, while the operating speed of a transplanter was 1.4-1.7 km/h, and the moving parts of the machine cooperated well during working. Specifically, the lodging rate was 1.67%, and the coefficient of variation of plant spacing was 3.67%. The data was well in accordance with the machinery industry standard JB/T10291-2013 “Transplanter of dry land plant”. It verifies the rationality of plug seedlings with automatical transplanting. The finding can provide sound technical support to improve the automation level of a plug-seedling transplanter in agricultural production.
agricultural machinery; design; experiment; automatic transplanting machine; chili plug seedling; pneumatic
韩长杰,肖立强,徐阳,等. 辣椒穴盘苗自动移栽机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(13):20-29.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.13.003 http://www.tcsae.org
Han Changjie, Xiao Liqiang, Xu Yang, et al. Design and experiment of the automatic transplanter for chili plug seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(13): 20-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.13.003 http://www.tcsae.org
2021-03-11
2021-05-11
国家重点研发计划(2017YFD0700800);国家自然科学基金项目(50905153,51565059);自治区重点研发计划(2018B01001-3);自治区天山青年计划(2017Q018)
韩长杰,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事农业机械设计与智能农业装备的研究。Email:hcj_627@163.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.13.003
S223.9
A
1002-6819(2021)-13-0020-10
