口腔医学专业文理科学生学习成绩Logistic回归分析
2021-09-15王春风侯晔坡徐美玉赵光叶肖婵阎青
王春风 侯晔坡 徐美玉 赵光叶 肖婵 阎青

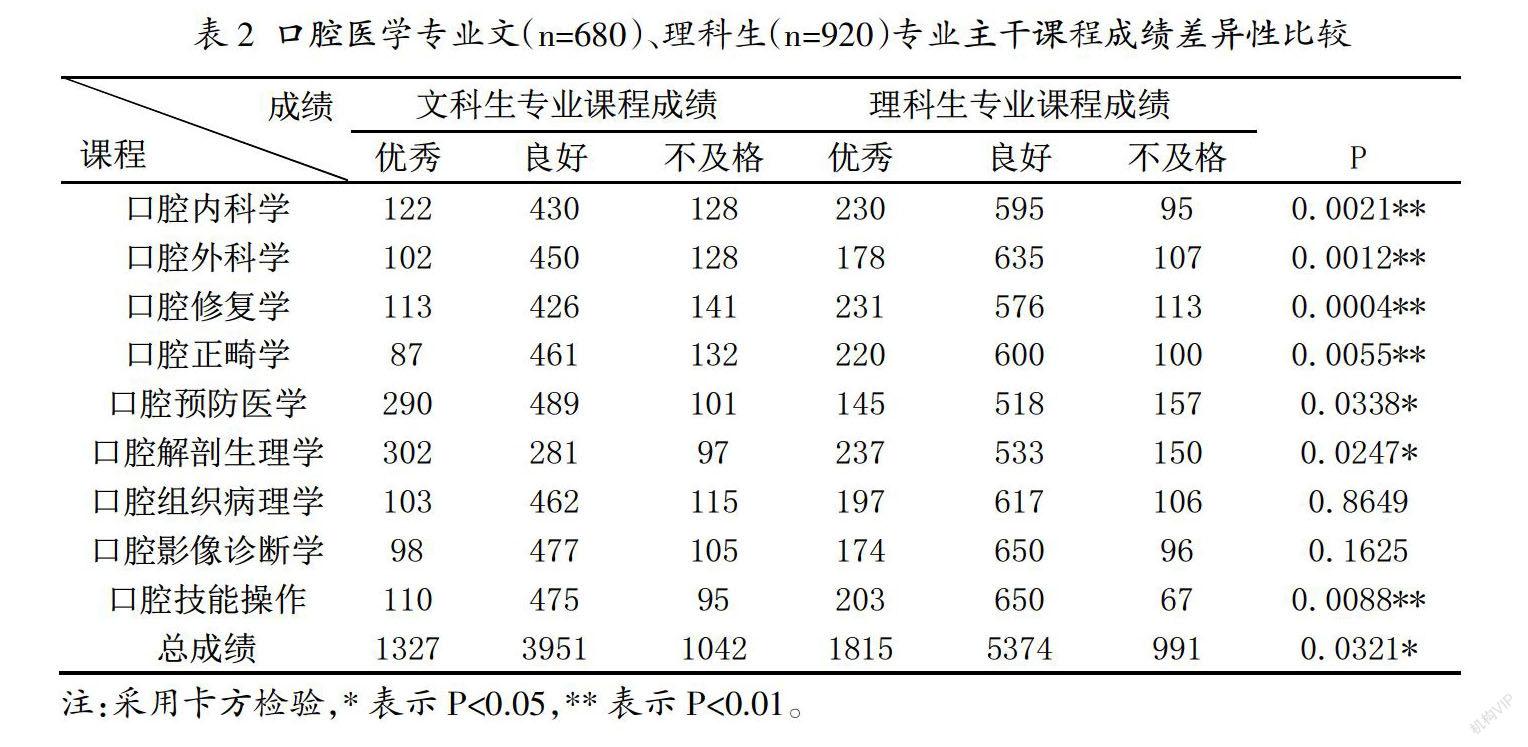

摘 要:目的:探讨口腔医学专业文理科生在校学习成绩的差异,以及自主学习能力、创新能力、沟通能力、团队协作能力、实践动手能力、应变能力与文理科生成绩的相关性,为口腔教学提供科学依据。方法:调查湖南医药学院2017-2020级1600名口腔医学专业学生,采用Logistic回归分析方法,分析自主学习能力、创新能力、沟通能力、团队协作能力、实践动手能力、应变能力对文理科生学生的影响。结果:偏记忆性的课程如口腔预防医学、口腔解剖生理学课程文科生成绩优于理科生(P<0.05),而偏实践性强的课程如口腔内科学、口腔外科学、口腔修复学、口腔正畸学、口腔实践操作课程理科生成绩明显优于文科生(P<0.01),理科生总成绩优于文科生(P<0.05)。结论:理科生由于自主学习能力和实践动手能力较强,更适合学习口腔医学专业课程。
关键词:文科生;理科生;口腔医学专业
中图分类号:G640 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2096-000X(2021)24-0065-04
Abstract: Objective: to explore the differences in study scores of arts and science students in stomatology, and the correlation between autonomous learning ability, innovation ability, communication ability, team cooperation ability, practical ability, adaptability and study scores of arts and science students in stomatology, so as to provide scientific basis for stomatology teaching. Methods: 1600 stomatological students in Hunan Medical College from 2017 to 2020 were investigated. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the influence of autonomous learning ability, innovation ability, communication ability, team cooperation ability, practical ability and adaptability on arts and science students. Results: the scores of liberal arts students were better than those of science students in the courses of partial memory, such as Oral preventive medicine, oral anatomy and physiology(P<0.05), while the scores of science students in the courses of partial practice, such as oral medicine, oral surgery, prosthodontics, orthodontics, oral practice, were significantly better than those of arts students(P<0.01), and the total scores of science students were better than those of arts students(P<0.05). Conclusion: science students are more suitable for stomatology because of their strong self-learning ability and practical ability.
Keywords: liberal arts students; science students; stomatology
自1977年恢復高考后,我国为快速培养各类专业人才在高中实行了文、理分科。近年来,由于我国大学院校的扩招,大多数医学院校各专业包括口腔等医学类专业在内为了积极拓宽招生渠道,丰富生源结构,开始文理兼收[1-2]。但是,由于我国高中阶段采用文、理分科的教育模式,文科生过早地远离化学、物理学、生物学等理科课程,理科基础相对薄弱,在步入医学院校后学习与理科有关的课程时有一定的难度,给高校文理科学生实施同班混合教学提出了更高的要求和新的挑战[3]。就口腔医学专业来说,由于口腔医学专业需要学生具有较强的理科背景和动手操作能力,文理不分科录取后,口腔教师又如何针对文理学生进行教学是当下医科院校所面临的紧迫任务[4]。为解决上述问题,本研究选取湖南医药学院2017-2020级文、理不同来源的1600名口腔医学专业学生进行回顾性研究,探索文、理科对口腔专业学生成绩的影响,为高校口腔医学专业的培养和教学改革提供理论依据,现将结果报告如下:
一、对象与方法
(一)研究对象
选取按国家统一高考政策录取的湖南医药学院2017-2020级文、理不同来源的1600名口腔医学专业学生为研究对象。
(二)研究方法和内容
