早期肠内营养对重症颅脑损伤患者炎症反应和胃肠道功能的影响
2021-08-18戴竹泉嵇朝晖潘慧斌邹晓月费振海傅恺
戴竹泉 嵇朝晖 潘慧斌 邹晓月 费振海 傅恺


[關键词] 颅脑损伤;重症;早期肠内营养;炎症反应;胃肠道功能
[中图分类号] R651 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)19-0100-04
Effect of early enteral nutrition on inflammation and gastrointestinal function in patients with severe craniocerebral injury
DAI Zhuquan JI Chaohui PAN Huibin ZOU Xiaoyue FEI Zhenhai FU Kai
Department of Emergency Medicine, the First People's Hospital of Huzhou City in Zhejiang Province, Huzhou 313000, China
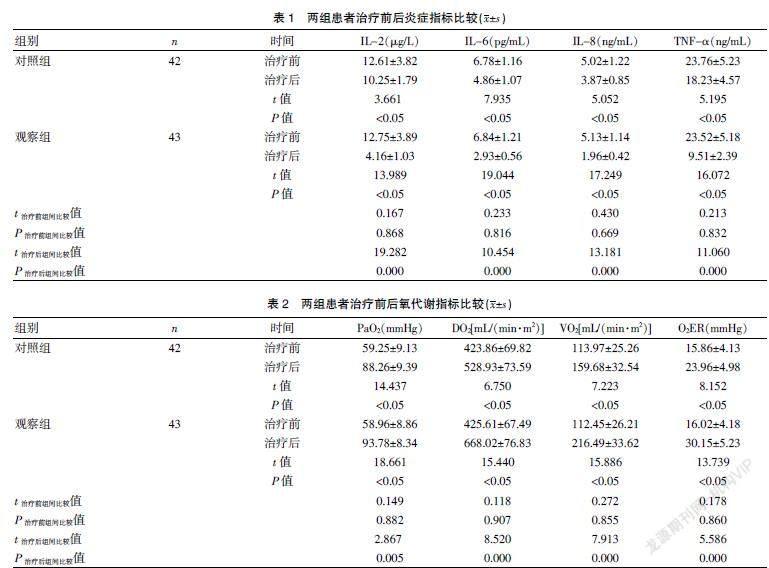
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of early enteral nutrition on inflammation and gastrointestinal function in patients with severe craniocerebral injury (SCCI). Methods A total of 85 patients with SCCI treated in our hospital from February 2017 to June 2019 were selected and divided into the control group (n=42) and the observation group (n=43)by using the random number table. The control group was received the sequential therapy of enteral and parenteral nutrition, and the observation group was received the early enteral nutrition. The inflammatory indexes and oxygen metabolism indexes of the two groups were observed before and after treatment, and the related indexes of gastrointestinal function of the two groups were compared, and the complications of the two groups were recorded at the same time. Results After treatment, the levels of interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the two groups were lower than before treatment, and those of the observation group were lower than the control group, with statistically significant difference (P<0.05). After treatment, the arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), oxygen delivery (DO2), oxygen uptake (VO2) and oxygen enhancement ratio (O2ER) were higher than those before treatment. These indicators of the observation group were higher than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The recovery time of bowel sounds, anal exhaust time and defecation time in the observation group were less than the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). The overall incidence of complications in the observation group was 9.30%, which was lower than that of (26.19%) in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Early enteral nutrition is effective in the treatment of patients with SCCI, which can reduce inflammatory reactions, improve gastrointestinal function and oxygen metabolism, and reduce complications.
