hMex-3A is associated with poor prognosis and contributes to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
2021-05-19YiFanLiuXiaoYanSunJiaKaiZhangZhiHuiWangZhiGangRnJiLiWnZhiGuoShuiJunZhang
Yi-Fan Liu ,Xiao-Yan Sun ,Jia-Kai Zhang ,Zhi-Hui Wang ,Zhi-Gang Rn ,Ji Li ,Wn-Zhi Guo ,,Shui-Jun Zhang ,,∗
a Zhengzhou Key Laboratory of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases and Organ Transplantation, Zhengzhou 450052, China
b Henan Key Laboratory of Digestive Organ Transplantation, Zhengzhou 450052, China
c Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
d Open and Key Laboratory of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery and Digestive Organ Transplantation at Henan Universities, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
e Department of Infectious Diseases, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
Keywords:Hepatocellular carcinoma hMex-3A Targeted therapy
ABSTRACT Background: HMex-3A,an RNA-binding protein,was found to be associated with tumorigenesis.However,the roles of hMex-3A in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression remained unclear.Methods: The different expression of hMex-3A between HCC tissues and non-tumor tissues was evaluated using The Cancer Genome Atlas database.Thereafter,the hMex-3A expression was evaluated in HCC tissues using Western blotting and qRT-PCR.Immunohistochemistry was performed to investigate the association between hMex-3A level and clinicopathological features including prognosis in HCC patients.In addition,we used si-hMex-3A to knockdown hMex-3A in HCC cells to test Cell Counting Kit-8,colony formation,cell migration and invasion.Results: The hMex-3A expression was significantly elevated in HCC tissues.Analysis of the clinicopathological parameters suggested that hMex-3A expression was significantly associated with pathological grade (P=0.019) and TNM stage (P=0.001) in HCC.Moreover,univariate and multivariate Coxregression analyses revealed that high hMex-3A expression (HR=1.491,95% CI:1.107–2.007;P=0.009)was an independent risk factor for overall survival in HCC patients.Finally,we confirmed that si-hMex-3A could significantly inhibit HCC cell proliferation,migration,and invasion in vitro .Conclusions: HMex-3A may contribute to the progression of HCC and might be used as a novel therapeutic target and prognostic marker in HCC.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is among the deadliest types of cancer in the world.There are approximately 840 0 0 0 new cases reported worldwide each year [1–3].The treatments for HCC include local ablation,liver resection,liver transplantation,and targeted molecular therapy [4–6].Despite advances in therapy,the 5-year overall survival (OS) of HCC remains poor and less than 30% [7,8].HCC tumorigenesis is a multistep process,including accumulation of several structural and genomic transformations,gene expression profiles,and intracellular signal pathway changes [9,10].Therefore,it is critical to understand these changes clearly and generate novel strategies for diagnosis,prognostic prediction,and discovery of therapeutic targets in HCC patients.
Posttranscriptional regulation of mRNA involves controlling eukaryotic gene expression.It is also worth mentioning that RNAbinding proteins (RBPs) regulate the fate of mRNA [11,12].The preternatural expression of RBPs affects RNA function.Eventually,this results in various diseases,including cancer.About 500 RBPs have been discovered in humans.However,only a small portion of them have been identified to have a tumor-suppressive or oncogenic role [12],including Igf2 mRNA-binding protein 1(IMP1) and insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1(IGF2BP1) [10,11,13–15 ].By binding to coding or non-coding sequences,RBPs can target specific structural components that are important for RNA processing,transportation,localization,stability,or function.However,the role of most RBPs in malignancy still needs to be elucidated.
HMex-3 proteins,which include hMex-3A to 3D,are evolutionally conserved RBPs with two K-homology (KH) RNA-binding domains (RBDs) [16].HMex-3A and hMex-3B are components of the P-small body.P-small bodies,also known as cytoplasmic treatment of small bodies,regulate the process of mRNA transcription and expression.They are mainly involved in mRNA degradation,translation inhibition,mRNA monitoring,RNA-mediated gene silencing,and other vital activities [17].Studies have shown that hMex-3A is related to ‘stemness’ via the regulation of CDX2 in human colon cancer [18,19].Furthermore,hMex-3A is highly expressed in cancers such as bladder urothelial carcinomas [20],whereas downregulation of hMex-3A using siRNA in human gastric cancer cells was shown to obviously limit cell proliferation [21].Nevertheless,the relation between hMex-3A expression and its effects on the prognosis and the direct impact of hMex-3A on HCC progression are not clear.
The present study analyzed data from The Cancer Genome Atlas(TCGA) database.We aimed to investigate the relationship between hMex-3A and HCC.
Materials and methods
TCGA database analysis
The mRNA expression and clinical datasets for 374 HCC tissues and 50 adjacent non-tumor tissues were downloaded from TCGA for prognostic analysis in HCC patients.
Patients and clinical samples collection
Specimens were obtained from 18 HCC patients who underwent liver resection without preoperative systemic therapy at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University in 2017.Among those specimens,6 pairs of HCC tissues and paraHCC tissues were used for Western blotting and the remaining 12 pairs were used for qRTPCR.All specimens were confirmed by histology and were stored at −80 °C.Paracancer tissues were within 2 cm from the tumor regions.This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital (2019-KY-21).Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Tissue microarray and immunohistochemistry
The HCC tissue microarray (HLivH180Su10) with 93 HCC tumor samples and comprehensive clinical information was obtained from Shanghai Outdo Biotech (Shanghai,China).Then we collected comprehensive clinical information of those cases.A total of 10 cases lacked relevant clinicopathologic features among all 93 cases,of which 8 cases lacked TNM data,1 case lacked tumor size data,and 1 case lacked age data.Immunohistochemistry was performed using the manufacturer’s protocol as previously described [22].Two experienced pathologists independently evaluated the score of immunohistochemistry samples on the basis of the percentage of hMex-3A positive cells and staining intensity,and the total score (intensity × percentage of staining)was calculated [23,24].The percentage of positive-staining cells:scored 1 (less than 25%),scored 2 (26% −50%),scored 3 (51% −75%),and scored 4 (76% −100%);staining intensity:no staining scored 0,weakly staining scored 1,moderately staining scored 2 and strongly staining scored 3.Sections with a total score of 0–2 were defined as negative (-);3–4 were weakly positive (+);6–8 were moderately positive (++);and score of 9 or 12 were strongly positive (+++).The total score>4 was defined as high expression and≤4 low expression [25].
Cell culture
HCC cell lines HepG2,SK-HEP-1,MHCC-97H,Hep3B,and Huh-7,and hepatocytes L02 were purchased from the Institute of Cell Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing,China).Cells were incubated in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM,Solarbio,Beijing,China) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS,Gibco,Grand Island,NY,USA) and incubated in a 5% CO 2 incubator at 37 °C.
RNA interference and cell transfection
HMex-3A knockdown in HCC cells was performed with siRNA synthesized by Genepharma (Shanghai,China).Cell transfection was done as per the previously reported procedure [26].The MHCC-97H and Hep3B cells were transfected with two different si-hMex-3A concentration (20 and 40 nmol/L) using Lipofectamine 30 0 0 reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad,CA,USA) in 6-well plates.After 48 h transfection,the cells were collected for subsequent studies.
Western blotting
Total protein was obtained from cells and 6 paired HCC tissues by lysis with RIPA buffer (Beyotime,Shanghai,China) containing PMSF (Solarbio).Homogenization of tissues was performed at 30 Hz in a TissueLyser (V4800 DHS Life Sicence,Beijing,China) for 3 × 5 min.Protein concentration was determined with a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Solarbio).Protein samples were separated using 10%SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes(Millipore,Billerica,MA,USA).The membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk for 1 h,and primary antibodies,including those against hMex-3A (1:10 0 0,ab79046;Abcam,Shanghai,China) and GAPDH (1:10 0 0,CST 5174,Beverly,MA,USA) were added and incubated overnight at 4 °C.The membranes were washed three times with 1 × TBST (10 min each),followed by a 1-h incubation with secondary antibodies (goat anti rabbit IgG-HRP,CST 7074,Beverly)diluted with 1 × TBST at 1:20 0 0.The blots were then visualized with ECL (Pierce,Shanghai,China).Protein bands were quantitated with an Odyssey infrared imaging system (LI-COR,Lincoln,NE,USA).
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR
TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) was used to extract total RNA from cells and 12 paired HCC tissues.PrimeScriptTM RT reagent kit(Takara,Dalian,Japan) was used for reverse transcription (RT) to produce complementary DNA (cDNA).Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using the TB Green Master Mix kit (Takara) to detect the relative hMex-3A expression.Data were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCtmethod.
Cell proliferation assay
A CCK-8 kit (Dojindo,Kumamoto Prefecture,Japan) was used to measure HCC cell viability upon siRNA treatment.We seeded the transfected Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells in 96-well plates at 1.5 × 103cells per well for 12 h.Then,10 μL of CCK-8 solution with 90 μL medium was added to each well,and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h.A microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA) was used to quantify the absorbance at 450 nm.
Colony formation assay
A colony formation assay was utilized to determine the effect of down-regulated hMex-3A on HCC cell growth.The transfected cells were diluted and seeded in 6-well plates with 1 × 103cells per well.After incubation for 14 days,the resulting colonies were fixed,stained,imaged,and counted.
Cell migration and invasion assays
A wound-healing assay was performed to assess the migration ability of HCC cells.We plated Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells in 6-well plates.A wound was then scratched with a 20 μL sterile plastic tip after incubating for 24 h.Each scratched wound was imaged,and the wound length was measured.
A cell invasion assay was performed using Matrigel Invasion Chambers (BD Biosciences,San Diego,CA,USA).Briefly,1 × 105transfected HCC cells were seeded on Matrigel-coated transwell inserts with serum-free medium.DMEM with 10% FBS was added to the bottom chamber.After incubation for 24 h in a humidified chamber at 37 °C,the cells on the lower surface of the membrane were fixed and stained.These migrating cells were imaged and counted in five random areas at × 200 magnification.
Statistical analysis
Graphpad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software Inc.,San Diego,CA,USA)and SPSS software (version 23.0,SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA) were used to generate all graphs and analyze statistical data.Student’st-test and one-way analysis of variance were used to assess the differences between groups.APvalue<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
HMex-3A mRNA was upregulated in HCC
TCGA data were used to verify the levels of hMex-3A mRNA in HCC tissues and paired noncancerous tissues.The hMex-3A mRNA was significantly elevated in HCC tissues compared to that in the noncancerous tissues (P<0.001,Fig.1 A),and the result was consistent with the pairedt-test between 50 HCC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues (P<0.001,Fig.1 B).The fold-change in HCC tissues was 1.8 times of the adjacent noncancerous tissues.Moreover,the level of hMex-3A mRNA was significantly higher in TNM III-IV stages compared to that in TNM I-II stages (P=0.008,Fig.1 C),and the mRNA expression of hMex-3A in pathological tissues grades III-IV was higher than that in grades I-II (P<0.001,Fig.1 D).Furthermore,Kaplan–Meier analysis suggested that OS and diseasefree survival (DFS) of HCC patients with low hMex-3A expression were better than those of patients with high hMex-3A expression(P=0.007,Fig.1 E;P=0.004,Fig.1 F).
Association between hMex-3A levels and clinicopathologic parameters in HCC patients
Western blotting and qRT-PCR results demonstrated that the hMex-3A expression was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues(Fig.2).For further studies,immunohistochemistry analysis was performed by a tissue microarray analysis (Fig.3 A).Compared with paired noncancerous tissues,the expression of hMex-3A was significantly elevated in HCC tissues (Fig.3 B).Our results also showed that hMex-3A was significantly increased in HCC patients with advanced-stage TNM (III and IV) (Fig.3 C) and high pathological grades (III and IV) (Fig.3 D).HCC patients with elevated hMex-3A expression had worse OS than patients with lower hMex-3A expression (Fig.3 E).
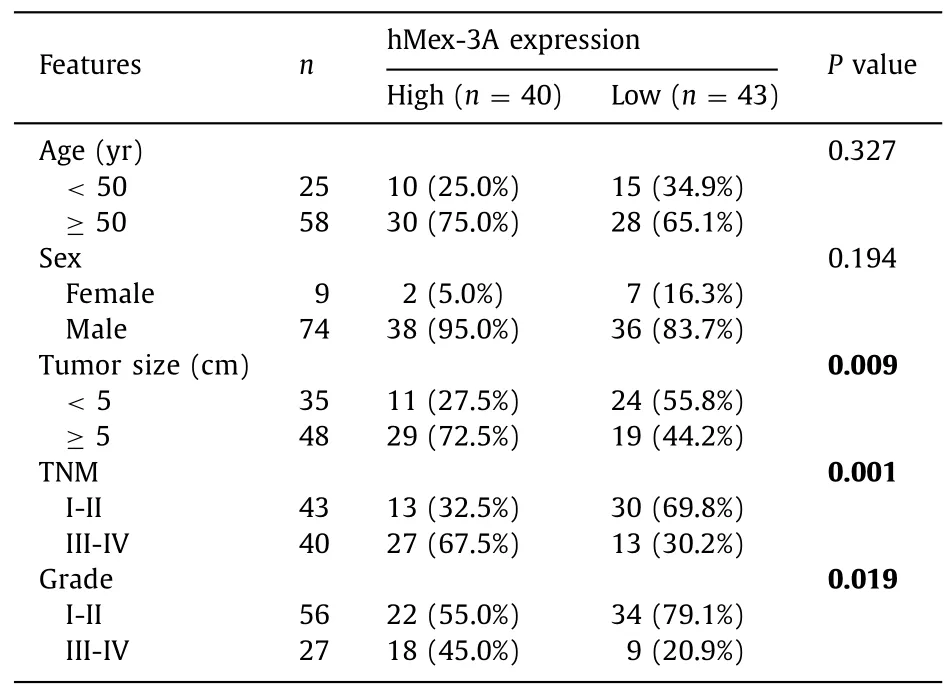
Table 1 The correlation between hMex-3A expression and clinicopathological features of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Elevated expression of hMex-3A is an independent adverse factor in HCC prognosis
Based on the above-mentioned results,we further studied the correlation between hMex-3A expression level and clinicopathologic features in HCC patients.The clinicopathological features of these HCC patients are shown in Table 1 .There were significant associations between hMex-3A levels and tumor size (P=0.009),pathological grade (P=0.019),and TNM stage (P=0.001).Univariate analysis showed that tumor size,TNM stage,and hMex-3A levels were potential factors affecting the prediction of OS in HCC(P=0.021,P<0.001 andP<0.001,respectively) (Table 2).Multivariate analysis indicated that TNM stages III-IV (HR=2.298,95%CI:1.113–4.742;P=0.024) and high hMex-3A levels (HR=1.491,95% CI:1.107–2.007;P=0.009) were independent poor factors for OS in HCC patients.In summary,these findings indicated that elevated levels of hMex-3A expression were correlated with tumor malignancy and adverse OS of patients with HCC.
Knockdown of hMex-3A inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation ability in HCC
To further study the role of hMex-3A,it was necessary to investigate whether suppression of hMex-3A could affect biological functioninvitro.HMex-3A was highly expressed in MHCC-97H and Hep3B cells (Fig.4 A);thus,we interfered with the expression of hMex-3A in these cells using siRNA.The effect of the siRNA was confirmed by Western blotting (Fig.4 B).The viability of Hep3B and MHCC-97H estimated through CCK-8 assays was significantly reduced by transfection with si-hMex-3A compared with controls(Fig.4 C).Moreover,colony formation assays showed that cells transfected with hMex-3A siRNA had significantly reduced colony formation ability (Fig.4 D).
Reduced hMex-3A expression attenuates the metastatic characteristics of HCC cells
The wound-healing assay showed that hMex-3A knockdown visibly reduced the number of migratory cells (Fig.4 E).Compared with controls,hMex-3A depleted cells revealed significantly impaired invasion capacity (Fig.4 F).These results collectively indicated that diminished hMex-3A expression suppressed cell migration and invasioninvitro.
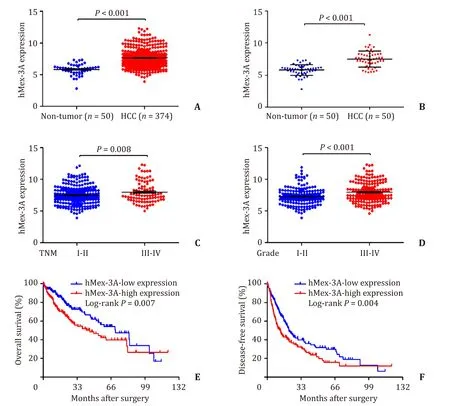
Fig.1.The expression level of hMex-3A mRNA is up-regulated in HCC tissues from TCGA data.A:hMex-3A mRNA was upregulated in 374 HCC tissues by TCGA data analysis(P < 0.001).B:hMex-3A mRNA was upregulated in corresponding 50 HCC tissues from TCGA data (P < 0.001).C and D:Comparison of the expression of hMex-3A levels in different TNM stages and pathological grades (P=0.008,P < 0.001,respectively).E and F:High expression of hMex-3A is correlated with poor OS and DFS in HCC patients(P=0.007,P=0.004,respectively).

Fig.2.Western blotting and qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of hMex-3A level in HCC tissues.A:A representative result of hMex-3A protein expression in 6 pairs of HCC tissues (T) and the non-tumor tissues (N).GAPDH was used as an internal control.B:The statistical analysis of hMex-3A mRNA levels in 12 pairs of HCC tissues and their paired non-tumor tissues (P=0.003).
Discussion
Several studies have shown that RBPs regulate the fate of mRNA [11,12,14].Most importantly,some RBPs have been found to affect the tumorigenesis [11].ThehMex-3Agene,encoding an RBP,is located at chromosomal position 1q22 [18,27].The hMex-3A protein contains two specific RNA-binding KH domains,whereas a RING finger domain located at its carboxyl terminal region may be involved in regulating protein-protein interactions [18,28,29].
Our TCGA analysis first found that hMex-3A mRNA was significantly upregulated in HCC and was associated with poor outcome.Furthermore,we showed that the hMex-3A mRNA and protein were highly expressed in HCC tissues.We also found that high hMex-3A expression in HCC showed positive correlation with TNM stage,pathological grade,and adverse prognosis through the analysis of clinicopathological data.In this regard,multivariate analysis showed that the elevated hMex-3A and TNM stage were independent poor factors for OS in HCC patients.Patients with high hMex-3A expression had significantly worse survival than those with low hMex-3A expression.Similar to our findings,Shi and Huang [20]revealed that hMex-3A was upregulated and contributed to worse OS in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma.A similar result [30]has also been reported for Wilm’s tumor.All these findings indicate that hMex-3A may play essential roles in the progression of HCC,and that it could be a prognosis predictor for HCC.

Fig.3.HMex-3A is overexpressed and associated with poor prognosis of HCC.A:Representative hMex-3A and immunohistochemical staining patterns with different staining scores by tissue microarray analysis.B:Histological scoring of hMex-3A in HCC tissues was notably improved in HCC tissues compared to that in non-tumor tissues(P=0.004).C and D:Histological scoring of hMex-3A was obviously increased in HCC patients with advanced-stage TNM (III-IV stages) and high pathological grade (III-IV grades) (P=0.031,P=0.023,respectively).E:Kaplan–Meier survival analysis between expression of hMex-3A (red,high hMex-3A expression;blue,low hMex-3A expression).HCC patients with high hMex-3A expression had markedly shorter overall survival than those with low hMex-3A expression (P=0.004).
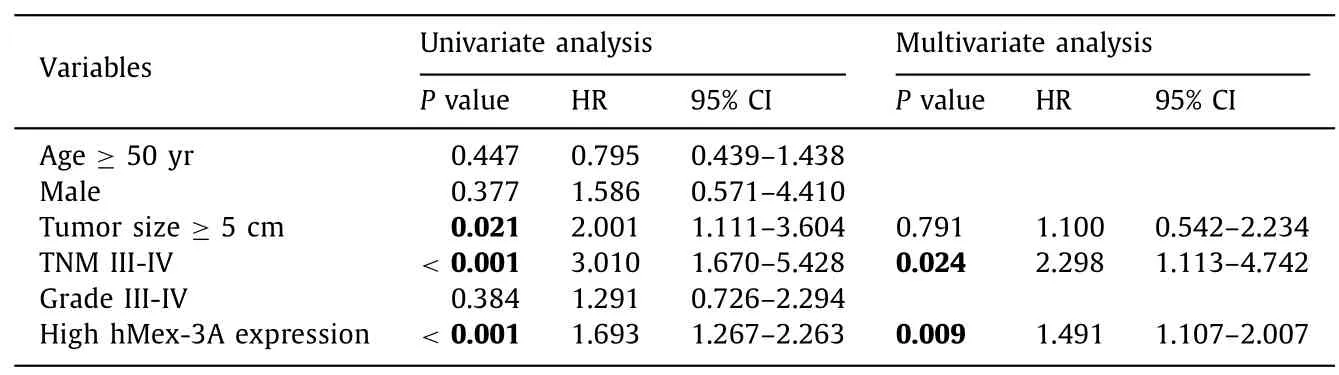
Table 2 Univariate and multivariate analysis of factors associated with overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma.
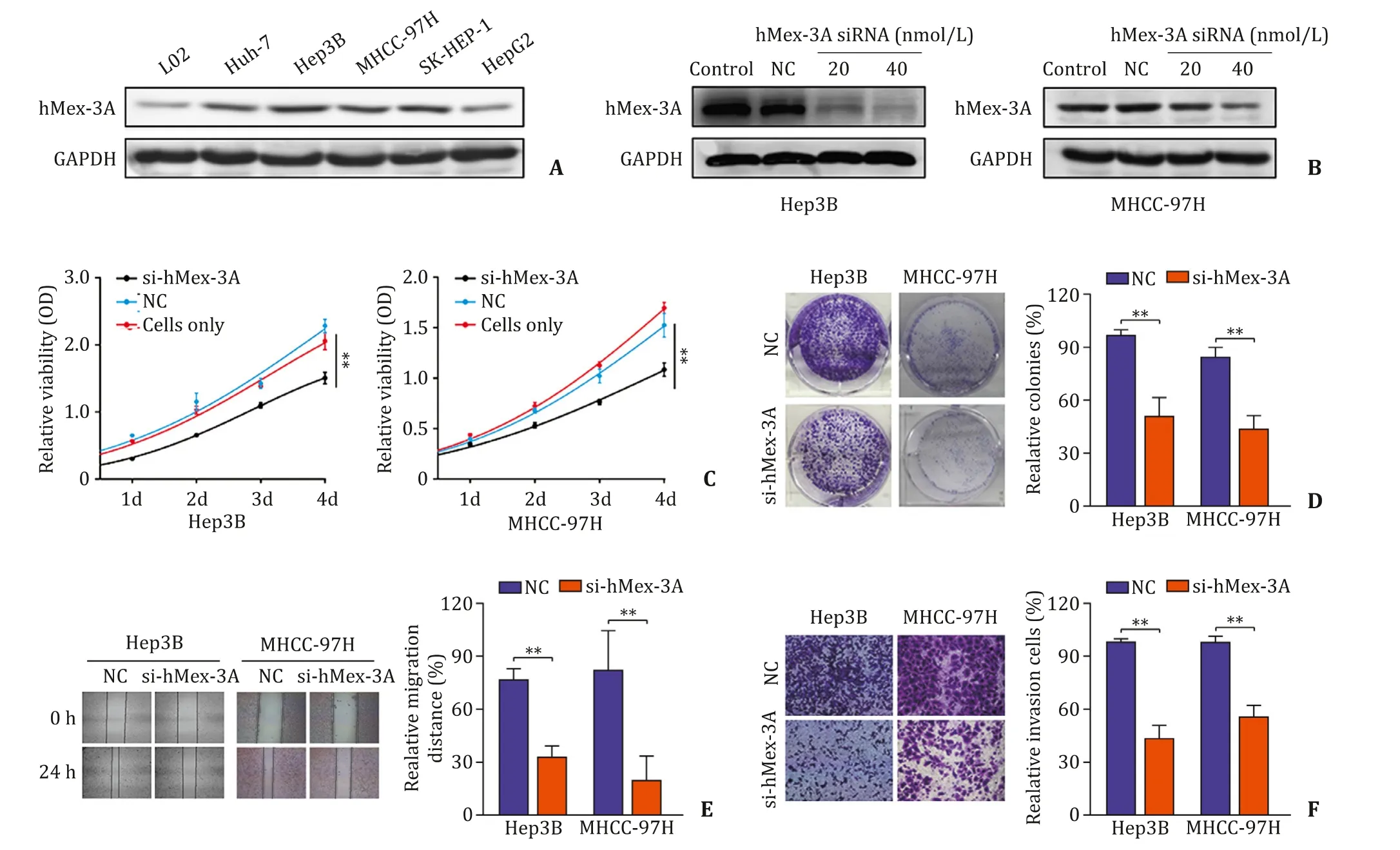
Fig.4.Downregulation of hMex-3A attenuates cell proliferation,colony formation and cell metastatic properties in HCC cells.A:The hMex-3A protein levels in different HCC cells.B:Dose-dependent si-hMex-3A downregulated the expression of hMex-3A in Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells.C:CCK-8 assay was used to confirme that hMex-3A knockdown suppresses proliferation of Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells.D:The colony formation capacity of Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells after transfection was decreased by colony formation assays.E:hMex-3A silencing caused a remarkable suppression of cell migration in Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells using wound-healing assay.F:The invasiveness of Hep3B and MHCC-97H cells after transfection was significantly suppressed according to cell invasion assay.NC:negative control.∗∗P < 0.01.
As far as we know,this is the first study to explore the role of hMex-3A in HCC progression.siRNA has been used as a valid and mature tool to explore gene function by decreasing the target gene expression.For further investigation of hMex-3A biological function in HCC progression,we performed siRNA transfection to knockdown hMex-3A expression in HCC cells.The results suggested that decreased expression of hMex-3A resulted in the inhibition of HCC cell growth and metastasis which indicated that hMex-3A has a tumor progressive effect.Similarly,gastric cancer cells transfected with hMex-3A siRNA showed a decrease in the proliferation and migratory ability [21].Based on the above results,hMex-3A can be considered a promising target for therapeutic intervention.
HMex-3A is an RNA-binding phosphoprotein which mainly accumulates in the cytoplasm.It functions by shuttling between the cytoplasm and the nucleus.HMex-3A has been shown to downregulate the intestinal transcription factor CDX2.Through binding determinant present in CDX2 mRNA 3 ′ untranslated region,it contributes to intestinal carcinogenesis [19].It is worth mentioning that hMex-3B,a fancy element of the P-small body,can also enhance the invasion of gastric cancer cells.Xue et al.reported that HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) induced Runx3 degradation through hMex-3B binding to Runx3 [31].The family of hMex-3 proteins (hMex-3A-D) was found to have E3 ubiquitin ligase activity,facilitating degradation of mRNA for embryonic development and carcinogenesis [32,33].We speculate that hMex-3A may facilitate the progression of HCC by degrading bound transcription factors.However,this requires further verification.
In conclusion,our study provided novel insights into HCC progression.We confirm that hMex-3A is upregulated in HCC tissues which contributes to poor prognosis and disease progression.Further,si-hMex-3A impairs the proliferative and migratory abilities of HCC cells.Overall,this study may accelerate the assessment of hMex-3A as a prognostic determinant or a therapeutic target for HCC.
Acknowledgment
None.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Yi-Fan Liu:Conceptualization,Investigation,Methodology,Project administration,Writing -original draft,Writing -review&editing.Xiao-Yan Sun:Formal analysis,Resources,Validation.Jia-Kai Zhang:Formal analysis,Investigation.Zhi-Hui Wang:Software,Validation.Zhi-Gang Ren:Investigation,Resources.Jie Li:Supervision,Validation.Wen-Zhi Guo:Investigation,Resources.Shui-Jun Zhang:Conceptualization,Funding acquisition,Project administration,Writing -review &editing.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Medical Science and Technology Program of Henan Province (SBGJ2018002),Basic Research Project of Henan Science and Technology Department (142300410221),National S&T Major Project of China(2018ZX10301201-008),and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC20 0 050 0).
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2019-KY-21).
Competing interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
杂志排行
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- Practice of precision surgery in primary liver cancer
- Reporting of longitudinal pancreatojejunostomy with partial pancreatic head resection (the Frey procedure) for chronic pancreatitis:A systematic review
- Hepatobiliary&Pancreatic Diseases International
- Presentation and surgical management of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is effective in patients with chronic portal vein thrombosis and variceal bleeding
- Long-term follow-up of HCV patients with sustained virological response after treatment with pegylated interferon plus ribavirin
