防潮密封型光纤连接器
2021-01-08张新立唐群植伍浩成黎志刚吕宏伟
张新立,唐群植,伍浩成,黎志刚,吕宏伟,汤 科
防潮密封型光纤连接器
张新立,唐群植,伍浩成,黎志刚*,吕宏伟,汤 科
中国电子科技集团公司第三十四研究所,广西 桂林 541004
针对高功率光纤激光系统中光纤对接端面产生水雾凝结的问题,分析出产生该问题最重要因素为连接器不具备防潮密封性能,对其结构装配及使用过程进行剖析,同时指出其防潮密封缺陷原因,进行技术创新与工艺改进,设计了防潮密封型光纤连接器。介绍了该新型连接器防潮密封原理及结构组成;重点对该新型光纤连接器性能进行全面测试,包括浸水试验、恒定湿热试验、在线运行应用验证等。试验结果表明,其插入损耗小于0.2 dB,防潮密封性能良好,取得较好的预期效果。
高功率光纤激光;水雾凝结;防潮密封;光纤连接器;光纤端面
1 引 言
高功率激光光纤传输与测量应用中,光纤传输功率较高,在光纤对接端面处产生热量,当激光断开后,陶瓷插芯冷却,空气中的水汽会在接续端面凝结水雾,导致光纤接续损耗增大,甚至会损伤光纤端面,影响装置运行[1-3]。当前解决光纤端面水雾凝结现象主要的办法是定期清洁光纤端面,在不改变现有设备接口结构的前提下并无理想替代方案。然而,随着高功率激光装置规模不断扩大、激光输出能量成倍提升,严重的光纤端面水雾凝结现象将对激光装置产生更大更差的影响,直接导致装置光纤线路损耗增大,系统末级输出稳定性变差,甚至损伤(烧毁)光纤端面,增加故障定位及工程维护难度。传统定期清洁端面策略在巨型高功率激光装置中已不具备可操作性,需从根本上解决连接器光纤端面水雾凝结问题。造成水雾凝结现象最重要的因素为传统光纤连接器不具备防潮密封性能,其装配过程没有密封工艺,未做防潮密封处理;在与法兰对接使用时也未做防潮密封处理工艺,导致空气中的微尘和水汽进入光纤对接的陶瓷插芯周围及端面,使连接器内部潮湿及洁净度不达标,在光传输、光测量、光传感领域带来严重后果[3-6]。在不改变光纤连接器现有结构及光学指标的前提下,对光纤连接器的结构与装配过程进行深入分析,指出其防潮密封缺陷原因,通过技术创新与工艺改进,设计并实现了一种防潮密封型光纤连接器,为解决高功率激光装置光纤端面水雾凝结问题提供了技术方案和可靠产品。这种新型防潮密封型光纤连接器概念及其特性目前尚未检索到相关报道。在前人工作基础上,除了对新型连接器防潮密封性原理与关键技术进行全面系统论述外,还给出其性能测试方法与结果。最后介绍了该连接器在高功率光纤激光系统在线运行应用情况,指出防潮密封型光纤连接器较好地解决了光纤端面水雾凝结问题。
2 光纤连接器结构及成型工艺
普通单模光纤连接器(简称“光纤连接器”)是光传输、测量、传感领域中光纤之间与设备之间活动连接不可或缺的器件[7-10],其防潮密封技术与工艺已经成为特种光纤连接器研究的一个重要方向。
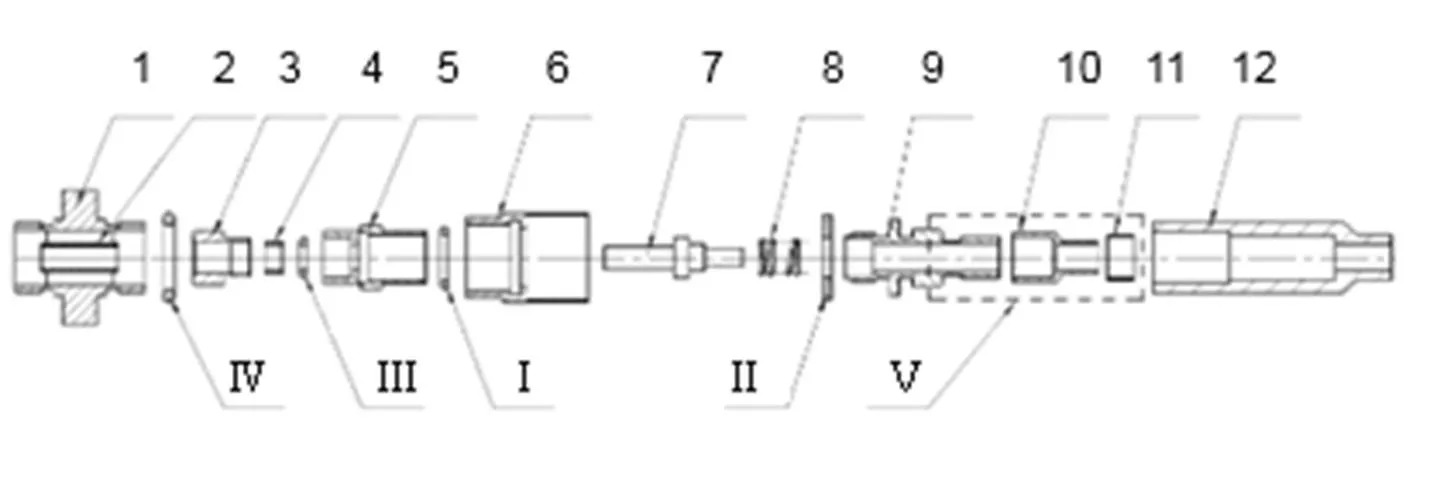
光纤连接器的结构如图1所示,其各零部件组成装配如图2所示。
图1与图2中,1为法兰,2为内陶瓷芯管,3为止推座,4为外陶瓷芯管,5为前套,6为外螺,7为陶瓷插芯,8为弹簧,9为后套,10为压紧环,11为圆环,12为尾纤套管。
其装配过程为部件4置于部件3中,整体再置于部件1中组成法兰盘;部件7向右依次套接部件8和部件9,向左依次套接部件6和部件5;部件10压紧部件9,部件11紧套部件10,部件12向左套紧,此时已套至部件9左侧第二处凹槽,构成完整光纤连接器。
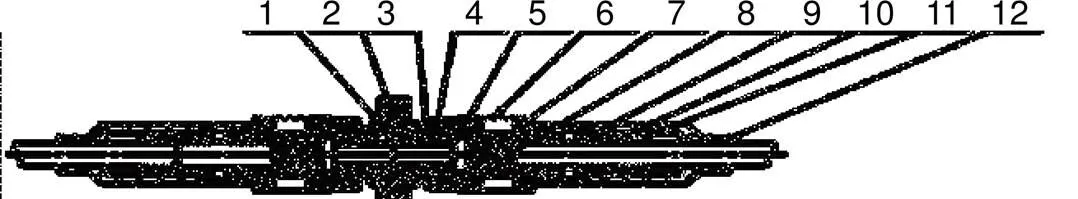
图1 传统普通单模光纤连接器结构图
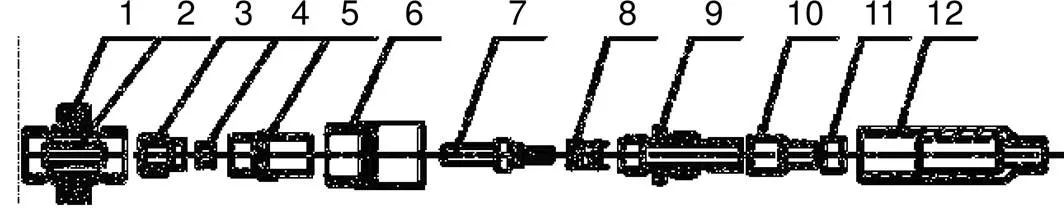
图2 传统普通单模光纤连接器装配图
3 光纤连接器防潮密封性研究
3.1 防潮密封性缺陷原因分析
按图1所示的光纤连接器,其装配与应用过程中存在以下五个方面的防潮密封性缺陷。
1) 部件5右半部分与部件6左半部分固定时,一方面为刚性接触,另一方面固定后两者之间还有1 mm的缝隙。
2) 部件9与部件6套接时,部件9中间凸起部分与部件6右端内平台为刚性接触,固定后存在缝隙。
3) 部件4、部件5和部件7套接时,一方面部件7左端外径尺寸小于部件5左端内径,另一方面部件7与部件4固定后,之间还有1 mm的缝隙。
4) 部件10压紧在部件9上,部件11压紧在部件10上,一方面这种压紧为刚性固定,其间存在缝隙,另一方面光纤外径尺寸远小于部件9与部件10的内径尺寸。
5) 部件6左侧内螺纹与部件1右侧外螺纹扭定后,一方面为刚性接触,另一方面部件1右侧外螺纹未到底,两者固定后,还有1.5 mm的缝隙。
以上均为普通单模光纤连接器成型与使用过程中存在的防潮密封性隐患、缺陷,应针对各具体隐患、缺陷进行防潮密封性技术创新与工艺改进。
3.2 防潮密封性技术创新与工艺改进
针对光纤连接器装配与使用过程中存在的防潮密封性缺陷,进行技术创新与工艺改进,其设计效果如图3所示,具体措施包括以下五个方面。
1) 设置I类密封圈,为硅胶O型密封圈,其内径尺寸等于部件5后端的外径尺寸,外径尺寸等于部件6前端的内径尺寸,线径大小满足部件5与部件6连接时为过渡密封。
2) 设置II类密封圈,为硅胶O型圈平垫片,其外径尺寸等于外螺6后端的内径尺寸、内径尺寸等于后套9前端的外径尺寸,胶圈厚度满足外螺6与后套9连接时为过渡密封。
3) 设置III类密封圈,为硅胶O型密封圈,其内径尺寸等于陶瓷插芯7的前端外径尺寸,外径尺寸等于前套5前端内径尺寸,线径大小满足外陶瓷芯管4、前套5与陶瓷插芯7连接时为过渡密封。
4) 使用硅橡胶粘胶工艺,粘胶覆盖后套9后半部外表面,压紧环10和圆环11的外表面的连接缝隙处,粘胶干涸后,尾纤套管12能正常套紧。
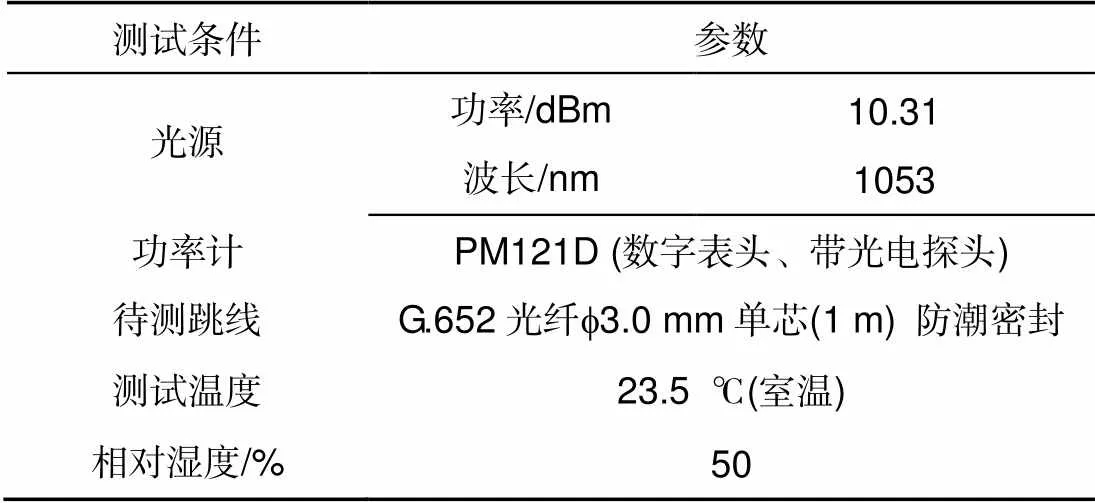
表1 测试使用仪器设备及环境条件
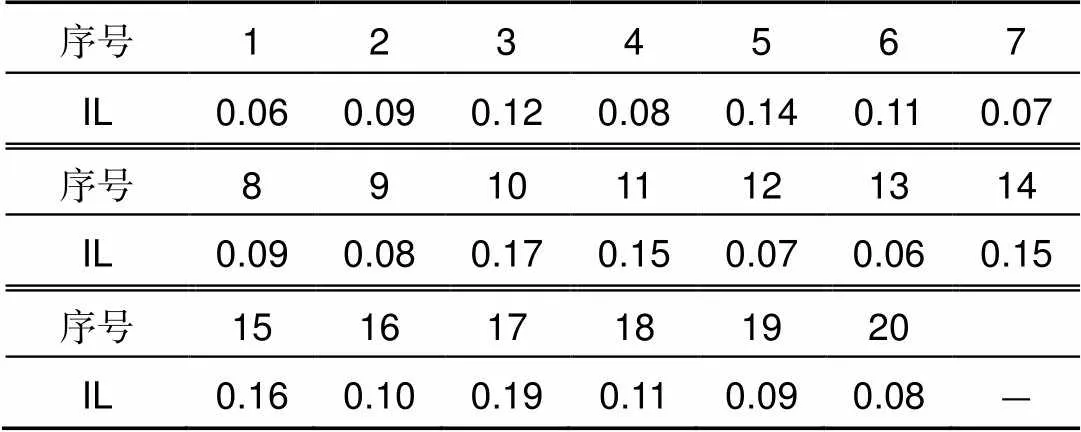
表2 防潮密封型光纤跳线IL测量结果

表3 浸水试验后跳线IL测量结果

图3 防潮密封型普通单模光纤连接器结构装配图
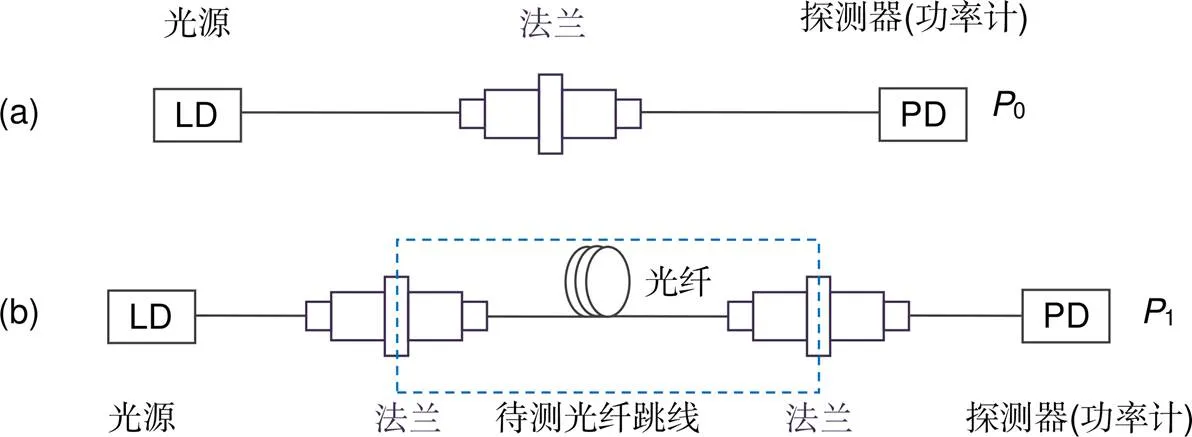
图4 防潮密封型光纤跳线插入损耗测量框图。(a) 输入光功率测量P0 (dBm);(b) 输出光功率测量P1 (dBm)
5) 设置IV类密封圈,为硅胶O型密封圈,其内径尺寸等于法兰1两侧无螺纹凹处外径尺寸,外径尺寸大于外螺6前端外径尺寸,满足法兰1、前套5与外螺6连接时为过渡密封。
4 防潮密封型连接器性能测试
4.1 光学指标测试
主要指光纤连接器插入损耗(IL)[11-12],IL测量原理如图4所示,测试所涉及实验仪器设备及环境条件如表1所示。测量对象是G.652光纤f3.0 mm单芯防潮密封型普通单模光纤跳线。
按图4对待测跳线的IL进行测量,记录跳线输入光功率0及输出光功率1,则待测跳线插入损耗IL=0-1;测量同一批次20根防潮密封型光纤跳线IL,记录相关数据如表2所示。
上述20根防潮密封型光纤跳线IL测量中,所有IL值全部小于0.2 dB,集中在0.1 dB左右,最大值为0.19 dB,符合通信行业标准YD/T1272.4-2007及YD/T2152-2010关于单模光纤跳线IL值不大于0.2 dB的规定。
4.2 密封性能测试
1) 浸水试验
该试验全面考核光纤跳线与法兰组合的密封性能,分别将“普通跳线+普通法兰+普通跳线”和“新工艺跳线+新工艺法兰+新工艺跳线”组合体分别置于室温水中浸没,如图5所示,其中“新工艺跳线”、“新工艺法兰”均指按3.2节所述技术创新与工艺改进后的光纤跳线与法兰;试验后检测各光纤端面,其检测结果分别如图6、图7所示。
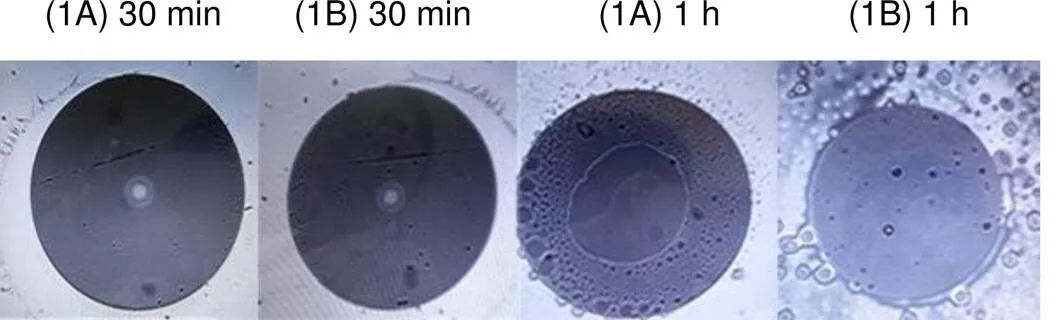
图6 普通组合体浸入水中试验后光纤端面检测结果
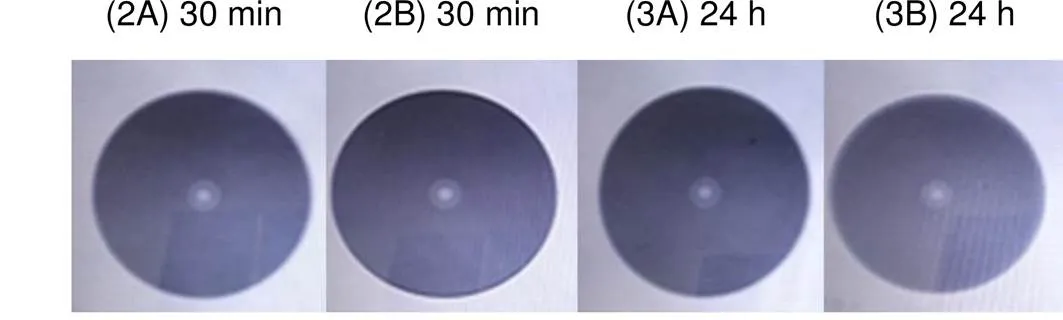
图7 新工艺组合体浸入水中试验后光纤端面检测结果
按图5(a)中对普通组合体试验,30 min后普通组合体中光纤端面已经出现明显的浸水现象,1 h后光纤端面出现严重的浸水现象,相关检测结果如图6所示,说明普通光纤跳线与法兰应用时不具备防潮密封性能。同样,按图5(b)中对新工艺组合进行试验,30 min后光纤端面没有出现浸水迹象,24 h后光纤端面也未出现明显的浸水现象,相关检测结果如图7所示,说明新工艺光纤跳线与新工艺法兰防潮防水密封性能得到显著改善。
上述各试验步骤完成后,按4.1节测量IL方法,分别测量各跳线的插入损耗,数据记录见表3。
插损测量结果表明,普通跳线与法兰对接浸水试验后,其跳线插损明显增大,即光纤端面产生水雾凝结现象后会导致光纤线路损耗变大,且水雾凝结现象越严重,光纤线路损耗越大;同步试验后,新工艺跳线插损变化不明显,维持在固有插损0.2 dB范围内。

图8 防潮密封型光纤跳线与法兰连接关系
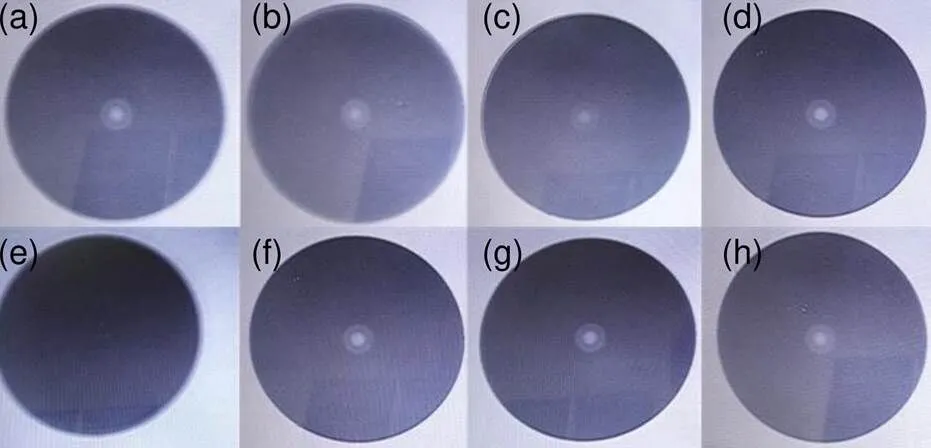
图9 新工艺组合体恒定湿热试验后光纤端面检测结果
2) 恒定湿热试验
为进一步考核新工艺组合体防潮密封性能,随机取出4根新工艺光纤跳线采用新工艺法兰依次紧固连接置于试验箱,如图8,按照GB/T2423.3-2006的要求进行恒定湿热试验,试验的严酷等级为温度(40±2) ℃、相对湿度(93±3)% RH,持续时间24 h,试验后各光纤端面检测结果如图9所示。

图5 组合体置于室温水中浸没试验。(a) 普通组合体浸没试验;(b) 新工艺组合体浸没试验
由图9中结果可知,新工艺防潮密封型光纤跳线及其法兰通过恒定湿热试验后,光纤端面洁净且无水雾凝结现象,具备良好的防潮密封性能。
4.3 在线测试
1) 拷机测试
将防潮密封型跳线按图10依次紧固连接,在实验室条件下进行拷机测试,其光源、测试跳线、具体环境参数等信息见表1,在线不间断测试60天后,检测各光纤跳线端面情况如图11所示。
图11(a)中光纤端面出现较严重的水雾凝结现象,分析其原因,与11(a)端连接的光源输入端(in)不具备防潮密封性能,空气中水汽由(in)端进入光纤连接器组合体中,导致11(a)处光纤端面出现水雾凝结现象。而11(b)~11(g)各连接器成型及使用过程中均具备防潮密封处理,故各光纤端面检测时未出现水雾凝结现象;(h)处光纤连器成型做了防潮密封处理,但试验过程中没有与新工艺法兰防潮密封对接,是套一个防尘冒,该处理并未很好地解决防潮密封问题,如图11(h)标记处。各光纤端面检测结果显示,新型光纤跳线在成型与使用时均具备防潮密封工艺才能较好地解决光纤端面水雾凝结问题。多批次新工艺光纤跳线及其法兰多次拷机试验后均获得类似结论,验证了新工艺光纤跳线及其法兰具备良好的防潮密封性能,拷机测试结果符合预期。
2) 高功率光纤激光系统在线应用
系统全面地对新工艺光纤跳线及法兰这一创新型防潮密封型光纤连接器进行研究分析与设计实现,为高功率光纤激光系统提供了一种光纤连接器的新选择。这里介绍防潮密封型光纤连接器在资助项目(高功率光纤激光系统)的实际应用,防潮密封型光纤跳线及其法兰分别安装在设备光输入/出处进行光路级联,系统输出8束主光路(各束脉冲能量≥1.0 μJ/5 ns方波/1 Hz),其主要光学指标与高功率激光装置前端系统相同,但整体性能有较大提升,普通单模跳线、保偏光纤跳线、单偏振光纤跳线均有应用,共计100余根,其中防潮密封型光纤跳线(10根)目前针对普通单模跳线,在线运行应用90天后,随机取出若干光纤跳线进行端面检测,结果如图12所示。
图12中,12(a)~12(d)、12(e)~12(h)、12(i)~12(l)、12(m)~12(p)分别为防潮密封型普通单模光纤跳线、传统单模跳线、单模保偏跳线、单模偏振跳线端面检测结果。该结果显示,防潮密封型普通单模光纤跳线端面无水雾凝结现象,其它三种未做防潮密封处理的传统光纤跳线端面均有不同程度水雾凝结现象。
综合分析表明,这种防潮密封型光纤跳线及其法兰具备在高功率光纤激光系统中长期使用的条件,且较好地解决了光纤端面水雾凝结问题,具有良好的应用前景。

图10 防潮密封型光纤跳线拷机试验连接
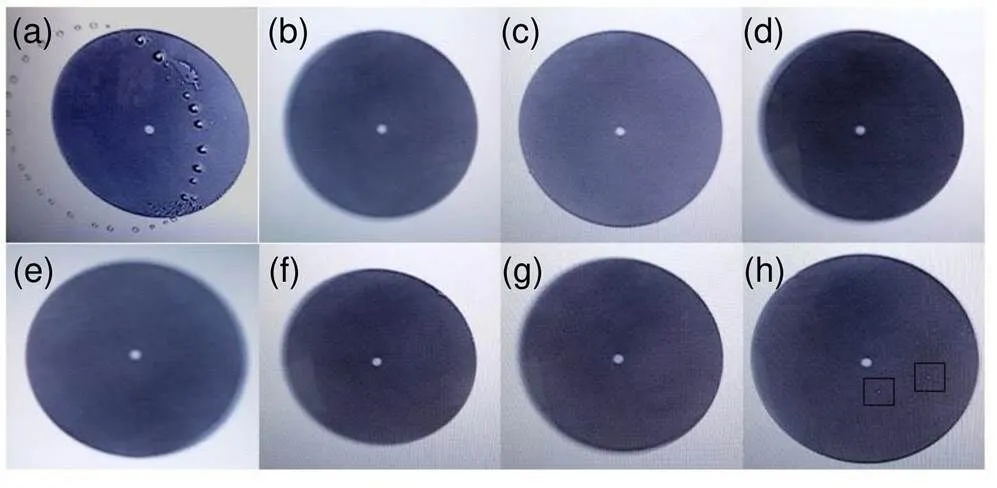
图11 新工艺组合体拷机试验后光纤端面检测结果
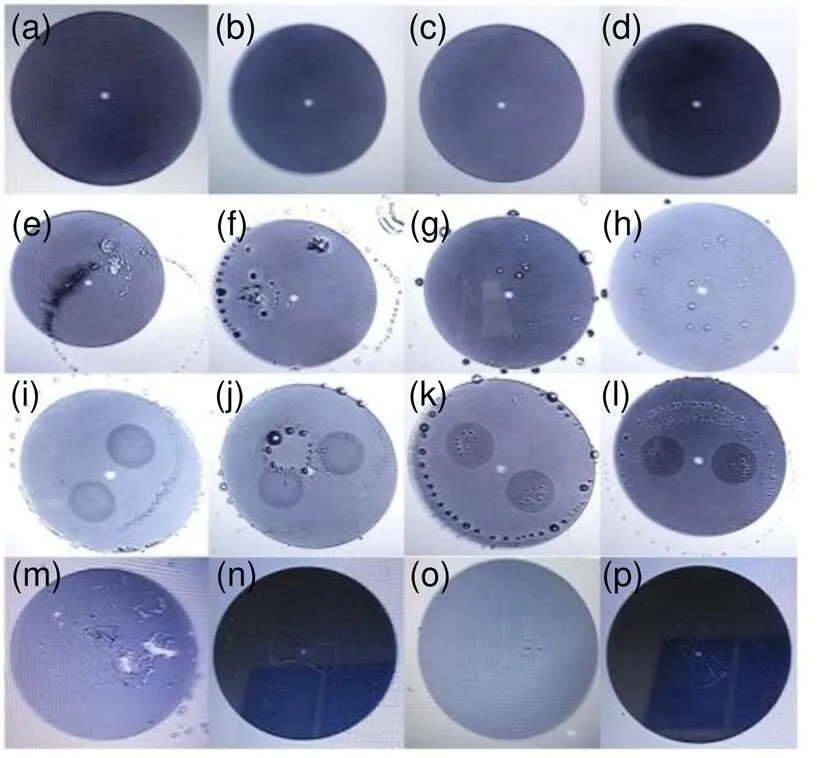
图12 在线应用90天后各类光纤端面检测结果
5 结 论
本文针对高功率激光装置前端系统光纤连接器应用时出现水雾凝结现象,分析该现象形成原因及造成影响,对光纤连接器结构与装配工艺进行详细分解,得出其防潮密封性缺陷原因。基于此,在不改变光纤连接器原有结构与尺寸的前提下,对光纤连接器进行技术创新与工艺改进,设计并实现防潮密封型普通单模光纤连接器,对防潮密封型光纤连接器进行系列实验,其光学指标与防潮密封性能均符合预期,并在高功率光纤激光系统中进行应用,其中长期在线使用未见光纤端面水雾凝结现象,得到了较好的试验结果。当前防潮密封型普通单模光纤连接器已经在高功率激光装置前端系统中在线运行试用,试用效果较好,有望在高功率光纤激光系统中获得广泛应用。同时,对单模保/单偏光纤连接器正在进行防潮密封处理,相关验证进展顺利。
[1] Tong W J, Yang C, Liu T Q,. Progress and prospect of novel specialty fibers for fiber optic sensing[J]., 2018, 45(9): 180243.
童维军, 杨晨, 刘彤庆, 等. 光纤传感用新型特种光纤的研究进展与展望[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(9): 180243.
[2] Sun Z H, Li P, Zhao R C,. Technology of target positioning precision measurement of high power laser system[J]., 2011, 23(8): 2121–2124.
孙志红, 李平, 赵润昌, 等. 高功率激光装置打靶精度测试技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(8): 2121–2124.
[3] Zhu L, Xu S Y. Research on an OpenCV-based optical fiber end detection system[J]., 2015(1): 28–30, 38.
朱莉, 徐胜勇. 基于OpenCV的光纤端面检测系统研究[J]. 光通信研究, 2015(1): 28–30, 38.
[4] Xu Y X, Zhu R H, Chen L. Measurement of apex offsets for fiber connector end faces[J]., 2006, 12(4): 270–275.
[5] Fu Y J, Zou W D, Xiao H R,. The research of measuring technology for fiber connector endface[J]., 2005, 26(3): 70–71.
伏燕军, 邹文栋, 肖慧荣, 等. 光纤连接器端面检测技术的研究[J]. 激光杂志, 2005, 26(3): 70–71.
[6] Huang H, Sun B, Zeng S K,. Typical application environmental conditions and failure mechanisms analysis of fiber optic connectors[J]., 2012, 32(2): 32–39.
黄欢, 孙博, 曾声奎, 等. 光纤连接器的应用环境条件和失效机理分析[J]. 机电元件, 2012, 32(2): 32–39.
[7] Li H Q. Recent trend of military optical fiber connector technology[J]., 2015, 39(3): 21–23.
李华强. 军用光纤连接器技术近期发展动向[J]. 光通信技术, 2015, 39(3): 21–23.
[8] Duan J A, Liu D F, Zhong J. Influences of polishing on return loss of optical fiber connectors[J]., 2005, 12(3): 320–323.
[9] Huang B. Handling and operation rules of optical fiber connectors[J]., 2011, 29(5): 48–52.
黄蓓. 光纤连接器使用操作规范探讨[J]. 电子产品可靠性与环境试验, 2011, 29(5): 48–52.
[10] Horwitz D. COTS fiber optic connectors for harsh environments[C]//, Baltimore, 2000: 3.
[11] Liu J W, He X D. Endface treatment technology in fabrication of fiber optic connector[J]., 2007(3): 22–25.
刘君文, 何兴道. 光纤连接器制作中的端面处理技术[J]. 光纤与电缆及其应用技术, 2007(3): 22–25.
[12] Li H Q, Huang Y Y, Li T H,. Research on the inserting loss of fiber connector with high power[J]., 2010, 34(2): 46–48.
李华强, 黄媛媛, 李太华, 等. 大功率光纤连接器插损测试技术研究[J]. 光通信技术, 2010, 34(2): 46–48.
Moisture-proof seal optical fiber connector
Zhang Xinli, Tang Qunzhi, Wu Haocheng, Li Zhigang*, Lv Hongwei, Tang Ke
No. 34 Research Institute, CETC, Guilin, Guangxi 541004, China
Structure of moisture-proof seal fiber connector
Overview:In the application of high-power laser optical fiber transmission and measurement, the transmission power of optical fiber is higher. With the laser disconnected, the ceramic insert core is cooled, and the water vapor in the air will condense at the end face of the connector. It will increase the fiber splicing loss and even damage the fiber end face. It is necessary to fundamentally solve the problem of water mist condensation on the end face of the connector. The most important factor of water mist condensation is that the traditional optical fiber connector does not have moisture-proof sealing performance. This paper analyzes the structure assembly and use process of the connector, and points out five defects of the moisture-proof seal. Specifically, there is no sealing process or moisture-proof sealing treatment in the assembly process. In addition, when the connector is used for the butt joint with flange, no moisture-proof sealing process has been carried out. It causes the dust and water vapor in the air to enter the surrounding and end face of the ceramic insert core. So, the internal humidity and cleanliness of the connector are not up to standard, which brings serious consequences to the field of optical transmission and optical measurement. Through technological innovation and process improvement, a new moisture-proof seal fiber connector is designed and completed without changing the original structure and size of the optical fiber connector. The principle and structure of the moisture-proof seal of the new connector are introduced. The main performances of the new connector are tested comprehensively, including the main optical performance test, immersion test, constant damp heat test, and online application test. The experimental results show that the new connector has better moisture-proof seal with IL less than 0.2 dB. After immersion test, the insertion loss index of the connector also meets the expected requirements. The main optical parameters meet the application requirements. The new moisture-proof sealing connector solves the problem of water mist condensation on the end face of the connector, and can be used in high power fiber laser system for a mid-long term, that will have good prospects. In the next step, we will continue to innovate and introduce this innovative technology and improved process into the single polarization fiber connector and the polarization-maintaining fiber connector. We will design and complete the moisture-proof sealing single-polarization optical fiber connector and moisture-proof sealing polarization-maintaining fiber connector to meet the new application requirements of the fiber laser system.
Citation: Zhang X L, Tang Q Z, Wu H C,Moisture-proof seal optical fiber connector[J]., 2020, 47(12): 200067
* E-mail: jx_lizhigang@163.com
Moisture-proof seal optical fiber connector
Zhang Xinli, Tang Qunzhi, Wu Haocheng, Li Zhigang*, Lv Hongwei, Tang Ke
No.34 Research Institute, CETC, Guilin, Guangxi 541004, China
Aiming at the problem of water mist condensation on the fiber end face in a high-power fiber laser system, the most important factor causing this problem is that the traditional optical fiber connector does not have the moisture-proof sealing performance. The connector structure assembly and use process are analyzed in-depth, and the causes of the moisture-proof seal defects are pointed out. Through technological innovation and process improvement, a moisture-proof seal fiber connector is designed and completed. The principle and structure of the moisture-proof seal of the new connector are introduced. The main performances of the new connector are tested comprehensively, including immersion test, constant damp heat test, online application test. The experimental results show that the new connector has a better moisture-proof seal with IL less than 0.2 dB.
high power fiber laser; water mist condensation; moisture-proof seal; fiber connector; fiber end face
Guangxi Innovation Driven Development Project (Major Science and Technology Projects: GuiKe AA18118032)
10.12086/oee.2020.200067
TN29
A
张新立,唐群植,伍浩成,等. 防潮密封型光纤连接器[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(12): 200067
: Zhang X L, Tang Q Z, Wu H C,Moisture-proof seal optical fiber connector[J]., 2020, 47(12): 200067
2020-03-02;
2020-07-22
广西创新驱动发展专项(科技重大专项)资助项目(桂科AA18118032)
张新立(1983-),男,硕士,工程师,主要从事光电子技术与光纤器件及其应用研究、高对比度激光脉冲产生、激光相位调制处理与检测、系统集成及产品研发等方面的研究。E-mail:13557030573@163.com
黎志刚(1985-),男,硕士,工程师,主要从事光电子技术与光纤无源器件研究及其应用、激光脉冲光源、激光功率能量检测等方面的研究。E-mail:jx_lizhigang@163.com
