巨泌乳素检测在女性住院精神分裂症患者中的意义
2020-12-23陈海支费小聪王振华沈晔雷礼磊赵徐东曾雷任丽华
陈海支 费小聪 王振华 沈晔 雷礼磊 赵徐东 曾雷 任丽华

[摘要] 目的 探讨巨泌乳素(MPRL)检测在女性住院精神分裂症患者中的意义。 方法 收集2018年1月-2019年6月浙江省湖州市第三人民医院精神科住院的65例精神分裂症患者,常规使用利培酮片治疗。在治疗过程中记录患者月经情况,并于治疗前、治疗后第6周末分别用发光免疫分析与酶联免疫吸附测定法检测泌乳素(PRL)和MPRL含量。应用前后自身对照研究对治疗前后PRL及MPRL含量进行比较,同时根据第6周末PRL及MPRL含量将65例患者划分为PRL正常组16例、高PRL血症组49例,将高PRL血症组再分为MPRL血症组21例、非MPRL血症组28例,并对不同组月经延迟情况进行比较。 结果 65例患者治疗后PRL及MPRL水平较治疗前明显升高,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。PRL正常组、高PRL血症组、MPRL血症组及非MPRL血症組出现的月经延迟数及发生率分别是2例(12.5%)、30例(61.2%)、5例(23.8%)及25例(89.3%)。四组月经延迟发生率两两比较,MPRL血症组与PRL正常组比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),非MPRL血症组月经延迟发生率分别高于高PRL血症组、MPRL血症组及PRL正常组,差异有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01),高PRL血症组月经延迟发生率高于MPRL血症组及PRL正常组,差异有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。 结论 利培酮所致MPRL血症可能不会导致患者月经延迟,临床上检测MPRL有利于指导高PRL血症的治疗。
[关键词] 利培酮;精神分裂症;泌乳素;巨泌乳素;月经延迟
[中图分类号] R749.3 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)10(a)-0105-04
Significance of macroprolactin detection in the female inpatients with schizophrenia
CHEN Haizhi1 FEI Xiaocong1 WANG Zhenhua1 SHEN Ye2 LEI Lilei1 ZHAO Xudong1 ZENG Lei1 REN Lihua1
1.Department of Psychiatry, the Third People′s Hospital of Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, Huzhou 313000, China; 2.Clinical Laboratory, the Third People′s Hospital of Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, Huzhou 313000, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the significance of macroprolactin (MPRL) detection in the female inpatients with schizophrenia. Methods From January 2018 to June 2019, 65 schizophrenics patients were collected in Department of Psychiatry, the Third People′s Hospital of Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province and all of them were treated with Risperidone Tablets. The menstrual situation of the patients was recorded during the treatment, and the contents of prolactin (PRL) and MPRL were measured by luminescent immunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay respectively before and at the end of the sixth weekend of the treatment. The content of PRL and MPRL were compared by self-control study before and after the treatment, at the same time, according to the content of PRL and MPRL at the end of the sixth weekend, 65 patients were divided into the normal PRL group (16 cases) and the hyperprolactinemia group (49 cases). The hyperprolactinemia group was then divided into the macroprolactinemia group (21 cases) and the non-macroprolactinemia group (28 cases), and the menstrual delay in different groups was compared. Results The levels of PRL and MPRL in 65 patients after treatment were significantly increased compared with those before treatment, and the differences were highly statistically significant (all P < 0.01). The number and incidence of menstrual delay of the normal PRL group , the hyperprolactinemia group, the macroprolactinemia group and the non-macroprolactinemia group were 2 cases (12.5%), 30 cases (61.2%), 5 cases (23.8%) and 25 cases (89.3%), respectively. The incidence of menstrual delay in four groups was compared in pairs, there was no significant difference between the macroprolactinemia group and the normal PRL group (P > 0.05), the incidence of menstrual delay in the non-macroprolactinemia group was higher than that in the hyperprolactinemia group, the macroprolactinemia group and the normal PRL group, with highly statistically significant differences (all P < 0.01). The incidence of menstrual delay in the hyperprolactinemia group was higher than that in the macroprolactinemia group and normal PRL group, with highly statistically significant differences (all P < 0.01). Conclusion Macroprolactinemia caused by Risperidone may not lead to menstrual delay. The clinical detection of macroprolactin is helpful to guide the treatment of hyperprolactinemia.
[Key words] Risperidone; Schizophrenia; Prolactin; Macroprolactin; Menstrual delay
抗精神病药物往往会引起泌乳素(PRL)水平增高,导致女性患者月经延迟,甚至闭经等一系列问题[1-3],影响患者生活质量使患者服药的依从性下降[4-5]。临床发现同样抗精神病药物,也只有67%患者出现PRL水平增高,在这些患者中并不是所有的均会出现月经延迟或者闭经[1,6-7],这可能与PRL中一种无活性的巨泌乳素(MPRL)有关[7]。为此,本课题组进行了本研究,现将结果报道如下:
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
所有病例均来自2018年1月—2019年6月浙江省湖州市第三人民医院(以下简称“我院”)住院精神分裂症患者。共收集65例女性患者,年龄18~45岁,平均(32.80±5.75)岁;婚姻状况:已婚42例,未婚23例;病程3~48个月,平均(7.0±25.0)个月;利培酮剂量2~5 mg/d,平均(3.50±0.84)mg/d。本项目获得我院医学伦理委员会审批通过,并且所有研究对象监护人签署了知情同意书。
纳入标准:①符合《精神疾病诊断与统计手册第五版》(DSM-V)[8]精神分裂症诊断标准;②阳性和阴性症状量表(PANSS)总分≥60分[9];③入院前半年内月经规律且月经周期在28~30 d之间。排除标准:①有心、肝、肾、内分泌、神经系统疾病;②无酒精依赖及其他精神活性物质滥用者;③高过敏体质者;④实验室检查指标超过正常值2倍以上且有临床意义;⑤6个月内接受抗精神病药治疗。
1.2 方法
患者入院后首日使用抗精神病药物利培酮片1 mg口服(西安杨森制药有限公司,批号:170615975),2周内依病情需加至治疗剂量(2~5 mg/d)。在住院治疗过程中记录患者月经情况,可以使用劳拉西泮片(山东信宜制药有限公司,批号:171001)0.5~1.0 mg/d,普萘洛尔片(江苏亚邦爱普森制药有限公司,批号:1801011)20~30 mg/d对睡眠障碍及心动过速分别进行处理,也可以酌情使用苯海索片及护肝药等对症支持治疗。
1.3 观察指标及检测方法
治疗前及治疗后第6周末上午7∶00分别空腹采静脉血,检测PRL及MPRL水平,血常规、血糖,肝、肾、甲状腺功能。检测PRL所用仪器为美国贝克曼库尔特有限公司生产的ACCESS型全自动微粒子化学发光免疫分析系统,所用PRL试剂盒为该公司配套的试剂盒(生产批号:07218UI00);用酶联免疫吸附测定的方法检测MPRL,MPRL试剂盒为人MPRL检测Elisa试剂盒(生产批号:E20180301A)。检验过程严格按试剂盒说明书进行操作。
1.4 分组标准
根据PRL及MPRL含量将65例患者分为四个亚组:①PRL正常组:患者血清PRL含量≤29.2 ng/mL;②高PRL血症组:患者血清PRL含量>29.2 ng/mL[1];③MPRL血症组:患者血清PRL达到高PRL血症水平且MPRL水平/总PRL水平≥30%[1];④非MPRL血症组:患者血清PRL水平达到高PRL血症但未达到MPRL血症水平。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 23.0对所得数据进行统计学分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验,计数资料采用例数和百分率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
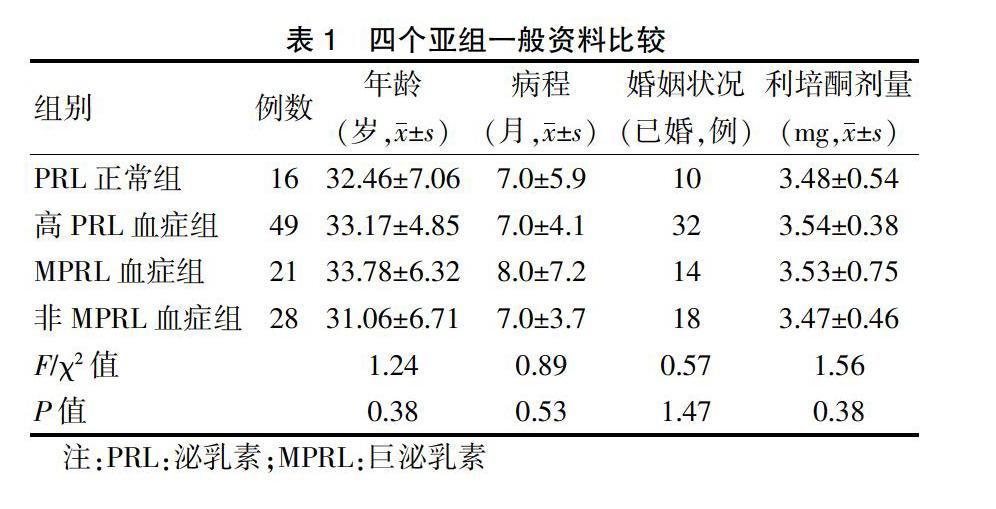
2.1 四个亚组一般资料比较
四个亚组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见表1。
2.2 治疗前后PRL及MPRL含量比较
65例患者治疗后PRL及MPRL水平较治疗前明显升高,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。见表2。
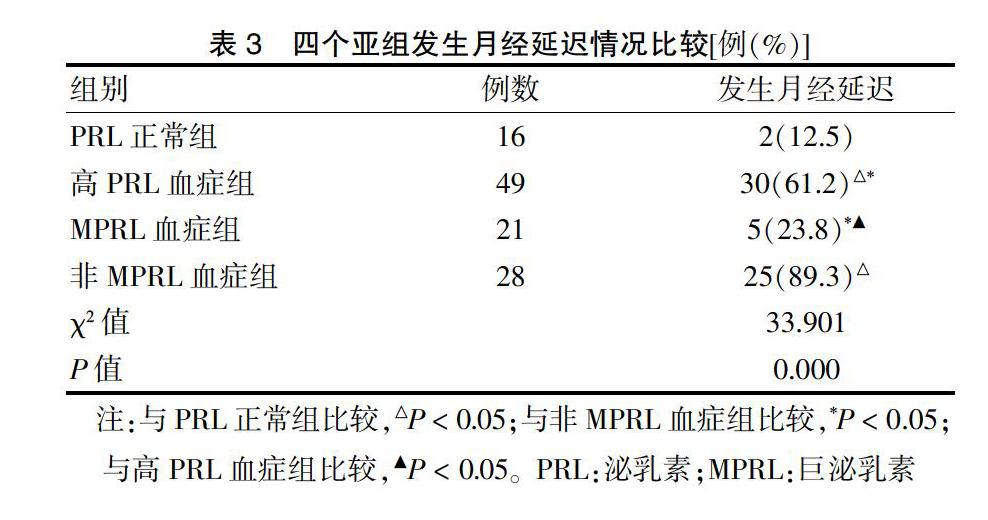
2.3 四个亚组发生月经延迟情况比较
四个亚组月经延迟发生率比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);MPRL血症组月经延迟发生率与PRL正常组比较,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.757;P = 0.384);非MPRL血症组月经延迟发生率分别高于高PRL血症组、MPRL血症组及PRL正常组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=6.875,P = 0.009;χ2=21.670,P = 0.000;χ2=25.321,P = 0.000);高PRL血症组月经延迟发生率高于MPRL血症组及PRL正常組,差异有统计学意义(χ2=8.231,P = 0.004;χ2=11.457,P = 0.001)。见表3。
3 讨论
PRL主要有:单体小分子泌乳素(SPRL)、大分子泌乳素(BPRL)以及MPRL分子三种[10]。1985年Jackson等人首次将以MPRL水平升高为主的高PRL血症患者称为MPRL血症[11],此类患者血液中PRL以MPRL为主,SPRL和BPRL水平正常且无明显临床症状[12]。在精神医学领域国内外对PRL研究甚广[1-3],而对PRL中的MPRL相关研究较少[13-14],这也是进行本研究的主要原因。
抗精神病药物可以导致患者出现高PRL血症从而出现泌乳或者月经延迟甚至闭经,影响患者服药的依从性[4-5]。在临床即使出现高PRL血症,也有一部分患者不会出现月经延迟或者闭经。究其原因,除个体差异外,临床现有的常规检测方法所检测的PRL实际上是总泌乳素(T-PRL)而没有区分出其中的MPRL[10]。本研究对患者PRL及MPRL进行检测,发现经过抗精神病药物治疗后患者的PRL及MPRL水平明显增高,部分患者达到高MPRL血症,这表明抗精神病药物所致高PRL血症的确有一部分患者是高MPRL血症,与其他研究结果一致[14-15]。有大量研究显示MPRL分子无实际生物学活性,不会引起PRL的垂体负反馈调节,不会导致临床症状(闭经或者泌乳)[7],但其半衰期较长且易在血流中积聚,导致MPRL血症[15-16]。这就不难解释在本研究中高PRL血症患者只有部分患者出现月经延迟。
本研究顯示,MPRL血症患者与无高PRL血症患者出现月经延迟的情况均很低,明显低于无MPRL升高的高PRL血症患者,进一步表明MPRL的确无生物活性,可能不会导致患者月经延迟,与其他研究结果一致[10-12]。这也提示在临床患者出现高PRL血症时应该进行MPRL的检测[14],以便确认是否需要对高PRL进行干预,预判高PRL血症是否会导致患者月经延迟甚至闭经,对患者进行及时准确的宣教,提高患者对治疗的依从性[4-5]。
临床对抗精神病药物所致高PRL血症,往往采用减药[13]、联合阿立哌唑[17-18]或者中医中药[19]等办法来处理,这些方法有的可能导致患者病情波动甚至复发,有的可能增加患者服药负担,降低患者对治疗的依从性。美国内分泌学会临床诊疗指南强调对于无相关临床症状的高PRL血症患者,应进一步测定MPRL水平和考虑MPRL血症的可能[20]。本研究显示高PRL血症患者有42.9%(21/49)达到MPRL血症,显然对于高PRL血症的治疗需要慎重对待,避免对这一部分患者造成不必要的影响。这也提示临床对高PRL血症患者进行必要的MPRL检测有利于避免误诊、误治[10]。
本研究提示利培酮所致MPRL血症可能不会导致患者月经延迟,临床上检测MPRL有利于指导高PRL血症的治疗。当然,本研究作为描述性研究,未设立对照、观察时间短等具有一定的局限性,下一步将克服本研究中的不足进行进一步探讨。
[参考文献]
[1] Park YM,Lee SH,Lee BH,et al. Prolactin and macroprolactin levels in psychiatric patients receiving atypical antipsychotics:A preliminary study [J]. Psychiatry Res,2016, 239:184-189.
[2] Sherazi NA,Baig MZ,Khan AH. Frequency of Macroprolactin in Hyperprolactinemia [J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak,2018,28(2):93-97.
[3] Wong A,Eloy JA,Couldwell WT,et al. Update on prolactinomas.Part 1:Clinical manifestations and diagnostic challenges [J]. J Clin Neurosci,2015,22(10):1562-1567.
[4] Ajmal A,Joffe H,Nacbtigall LB. Psychotropic-induced hyper-prolactinemia:a clinical review [J]. Psychosomatics,2014,55(1):29-36.
[5] 李晓玲,赵长江,罗庆新,等.抗精神病药物对泌乳素的影响和不同分子量泌乳素与临床症状的关系[J].神经疾病与精神卫生,2015(4):398-399,402.
[6] Melmed S,Casanueva FF,Hoffman AR,et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperprolactinemia:An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline [J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2011,96(2):273-288.
[7] Gibney J,Smith TP,Mckenna TJ. Clinical relevance of macroprolactin [J]. Clin Endocrinol(Oxf),2005,62(6):633-643.
[8] American psychiatric association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders [M]. 5th. Washington DC:American Psychiatric association,2012:99-105.
[9] 中华医学会精神科分会.中国精神障碍分类与诊断标准[M].3版.济南:山东科学技术出版社,2001:83-90.
[10] Saleem M,Martin H,Coates P. Prolactin Biology and Laboratory Measurement:An Update on Physiology and Current Analytical Issues [J]. Clin Biochem Rev,2018, 39(1):3-16.
[11] De Hert M,Detraux J,Peuskens J. Second-generation and newly approved antipsychotics,serum prolactin levels and sexual dysfunctions:a critical literature review [J]. Expert Opin Drug Saf,2014,13(5):605-624.
[12] Bai Z,Wang G,Cai S,et al. Efficacy,acceptability and tolerability of 8 atypical antipsychotics in Chinese patients with acute schizophrenia:A network meta-analysis [J]. Schizophr Res,2017,18(5):73-79.
[13] 陶晶,李清伟.抗精神病药物所在高泌乳素血症相关研究进展[J].中华全科医师杂志,2018,17(4):329-331.
[14] Kasum M,Ore?觢kovi■ S,■ehi■ E,et al. Laboratory and clinical significance of macroprolactinemia in women with hyperprolactinemia [J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol,2017, 56(6):719-724.
[15] Hattori N,Aisaka K,Shimatsu A. A possible cause of the variable detectability of macroprolactin by different immunoassay systems [J]. Clin Chem Lab Med,2016,54(4):603-608.
[16] Hattori N,Ishihara T,Saiki Y,et al. Macroprolactinaemia in patients with hyperprolactinaemia:composition of macroprolactin and stability during long-term follow-up [J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf),2010,73(6):792-797.
[17] Meng M,Li W,Zhang S,et a1. Using aripiprazole to reduce antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia: meta-analysis of currently available randomized controlled trials [J]. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry,2015,27(1):4-17.
[18] Robinson DG,Gallego JA,John M,et al. A Randomized Comparison of Aripiprazole and Risperidone for the Acute Treatment of First-Episode Schizophrenia and Related Disorders:3-Month Outcomes [J]. Schizophr Bull, 2015, 41(6):1227-1236.
[19] 劉海军,孙玉涛,董晓柳.柴胡加龙骨牡蛎汤治疗抗精神病药物致高PRL血症临床疗效[J].医学综述,2017, 23(3):605-608.
[20] Samson SL,Hamrahian AH,Ezzat S,et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists, american college of endocrinology disease state clinical review: clinical relevance of macroprolactin in the absence or presence of true hyperprolactinemia [J]. Endocr Pract,2015,21(12):1427-1435.
(收稿日期:2020-01-22)
