Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody Against Clostridium perfringens α-toxin and Screening and Identification of Phage Display Technology
2020-11-03WangHongweiLiuHaixinXieZhenzhenZhangYueZhongMingandLiGuangxing
Wang Hong-wei, Liu Hai-xin, Xie Zhen-zhen, Zhang Yue, Zhong Ming, and Li Guang-xing
Key Laboratory for Laboratory Animals and Comparative Medicine of Heilongjiang Province, College of Veterinary Medicine, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
Abstract: Clostridium perfringens phospholipase C (plc), also called α-toxin, is encoded by the plc gene Clostridium perfringers.The production of α-toxin can lead to the occurrence of gas gangrene.Vaccination is considered as one of the best solutions against Clostridium infections.In this study, an anti-Cp α-toxin monoclonal antibody (mAbs) A10E5 was successfully prepared, which had better biological reactivity.Then, the phage random 12-peptide library was used to screen mAb A10E5 protein.After four rounds of screening, three peptides with high affinity to the anti-α-toxin mAbs were screened.Two 12-peptide peptide Q and peptide E with higher inhibition rate were obtained by indirect ELISA.Two polypeptides of 500 μg · mL-1 synthesized in vitro were mixed with 30 μg · mL-1 α-toxin at a concentration to treat Hela cells.Cell viability was determined by MTT assay.The results showed that both of the peptides significantly increased the survival rate of Hela cells compared with the α-toxin group, and the effect of peptide Q was more obvious.The chickens were immunized with phages expressing two different affinity polypeptides and then challenged.The results of chicken weight change, intestinal lesion score, bacterial count, and antibody titer in peripheral blood showed that the two phages expressing the polypeptides had a certain protective effect on the chickens compared with the PBS group, and peptide Q had better protection effect.In conclusion, the high affinity peptide with mAb A10E5 was screened in this study, and the protective effect of the plc polypeptide vaccine was verified by in vivo and in vitro experiments, which was of great significance for the comprehensive prevention and treatment of the disease.
Key words: Clostridium perfringens, phospholipase C, phage, peptide
Introduction
Clostridium perfringens(Cp) is a Gram-positive,spore-forming anaerobic pathogenic bacterium,which is ubiquitous in the soil, water, human beings and animal intestines, and is an important zoonotic pathogen (Odaet al., 2012; Huanget al., 2018,Siqueiraet al., 2018).It is separated from the blood vessels that produce bubbles in a corrupted body by British Welchii and Nuttad (1982), named after Welchii (Songeret al., 1996), hence, the nameClostridium welchii.Under the microscope, the length of the bacterium is about 3-5 μm, and the ends are obtuse, mostly in pairs or in piles (Denniset al., 2004).
As of 2011, 16 kinds of Cp toxins have been found,includingα,β,ε,ι,μ,λ,v,γ,δ,К,η,θand so on,α,βandεtoxins are the main pathogenic factors of the disease (Ferreiraet al., 2016).Cp is classified into five toxin types, A, B, C, D and E, through produced the four major lethal toxins and neutralization test of their antitoxins (Liet al., 2013; Karunakarnanet al., 2018;Laceyet al.., 2018).All the strains of Cp possess the gene encoding for phospholipase C (plc) and produceα-toxin.Soα-toxin are considered to be the most basic and important virulence factors (Keyburnet al., 2008;Huanget al., 2018).plc has traditionally been considered a virulence factor associated with the development of gas gangrene, food poisoning in human beings, enterotoxaemias, enteritis in domestic animals and necrotic enteritis in poultry.The essence ofα-toxin is enzyme, which is the first bacterial toxic protein that has been found to have both enzymatic and toxin properties.It is also the main exotoxin of Cp type A, which plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of Cp (Keyburnet al., 2008).This toxin consists of 370 amino acid residues comprising two domains:the N-terminal domain possessing plc activity that acts on phosphatidylcholine with reduced activity on sphingomyelin, suggesting that the active site is located in this domain and the C-terminal domain that plays a key role in mediating interactions between toxin and membrane phospholipids (Titballet al.,2010; Nayloret al., 1998).
Theα-toxin is the most studied bacterial phospholipase, with its tridimensional structure and functional characterization for its domain elucidated.Therefore, two approaches for the development ofα-toxin vaccines have been suggested.One of the methods is expressing the nontoxic fragments or domains (e.g., the C-domain) of this toxin (Takagishiet al., 2015; Goossenset al., 2016).Furthermore, some studies identified many low quality clostridial vaccines in the Brazilian market, thus reinforcing the necessity of improving the available vaccines (Salvaraniet al.,2013).The use of recombinant vaccines against clostridial infections has shown interesting and effective results (Lobatoet al., 2010; Zenget al., 2011;Ferreiraet al., 2016).The mechanism of interaction between Cp and host cells needs further studies.In this study, the antibacterial activity of the specific binding peptide of the monoclonal antibody was analyzed byin vivoandin vitroexperiments using the prepared mAbs-plc in combination with the phage random peptide library technology.This study laid the foundation for the development of a new peptide epitope vaccine for Cp.
Materials and Methods
Expression and purification of recombinant proteins
Recombinant pGEX-plc bacterial solution was activated and induced to express at the final concentration of 1.0 mmol · L-1IPTG at 37℃ for 5 h.The precipitate suspension and supernatant were separately taken,mixed with an equal amount of 2×SDS loading buffer,and boiled for 10 min for SDS-PAGE analysis of the solubility of the recombinant protein.
The prepared protein sample was subjected to SDSPAGE and the color was developed in a 0.25 mol · L-1pre-cooled KCL solution.The target band was cut.The cut gel strips were washed twice with pre-cooled PBS and then crushed.These were mixed with appropriate amount of pre-cooled PBS, freeze-thaw three times in a- 40℃ refrigerator, and then centrifuged at 5 000 r · min-1for 10 min.The supernatant were carefully aspirated to obtain a purified protein solution.The purified protein solution was transferred into a dialysis bag and slowly dialyzed for 1 h in a beaker containing a reconstituted solution; it was continued to dialyze with replaced dialysis solution for 2 h; the reconstituted solution was poured and dialyzed for 2 h in TE buffer;the dialysis bag was placed in 50% PEG 8000 for concentration.
Preparation of mAbs
The purified protein pGEX-plc after purification and renaturation was fully emulsified with an equal volume of complete Freund's adjuvant.Purified pGEX-plc was then used to immunize 6-week-old female BALB/c mice by intraperitoneal injection.Immunization procedures and then generation of hybridomas were performed, according to standard methodology.Positive hybridoma cells were identified by indirect enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Determination of specificity of prepared mAbs
The crude extract of Cp naturalα-toxin protein and purified pGEX-plc recombinant protein were subjected to SDS-PAGE.The proteins were resolved on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels under reducing conditions and electro transferred onto a nitrocellulose(NC) membrane.Prepared of mAbs A10E5 was used as the primary antibodies, then HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG or HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse IgG was used as secondary antibodies.Western blot analysis was performed as described previously.The mAbs subtypes were identified using a mAbs subtype identification kit, and the titer of mAbs secreted by the positive hybridoma cell lines was determined by an indirect ELISA method.And immunofluorescence assay for surface binding ability of mAbs A10E5 Cp ATCC13124 cells [Cp (ATCC13124) was purchased from Tiancheng Technology (Shanghai, China)], the pAbs-plc prepared in the laboratory was a positive control, and sp2/0 was a negative control.The cells were fixed on a glass slide, covered with PBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin, and placed in a wet box for 1 h at room temperature.After three washes with PBS, the mAbs were added to the cells and incubated for 1 h at 37℃.After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with TRITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1 : 1 000 dilution) and TRITC-conjugated goat anti-rat for 1 h in the dark.Fluorescent signals were detected under an inverted fluorescence microscope(Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).The neutralizing activity of the mAbs againstα-toxin was examined by plc neutralization assay and erythrocyte hemolysis neutralization assay.
Phage-display biopanning on prepared mAbs
Purified mAbs A10E5 was applied as the target and subjected to biopanning using a Ph.D.-12 Phage Display Peptide Library Kit (New England Biolabs,USA, the peptide library titer was 1.5×1013pfu · mL-1,and the host strain wasE.coliER2738.), according to the manufacturer's instructions and previous references.
Identification of genes encoding exogenous phagedisplayed peptide via sequencing
Individual phage clones were selected from the final rounds of biopanning and amplified inE.coliER2738, followed by precipitation and amplification according to the manufacturer's protocol of Ph.D.-12 Phage Display Peptide Library Kit.Deduced amino acid sequences were analyzed by post-sequencing and compared with that of plc protein using the MegAlign software program (Windows version 3.12e:DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA).
Binding activities of phages to plc mAbs A10E5
Binding activities of phage clones displaying different high-frequency peptides to their respective mAbs were determined by ELISA, according to the manufacturer's protocol and previous references.The optical density(OD490nm) was read using an ELISA plate reader.
Immunization and challenge
A total of 48 chickens of one day old were selected.When the chickens were 13 days old, the chickens were randomly divided into four groups of 12 animals each.The chickens were firstly immunized at 14 days old.Fifteen min before immunization, 0.2 mL of 25%sucrose solution was injected into the immunization site, and then 200 μL of phage mixed with an equal amount of complete adjuvant was injected into the leg muscles of the chickens.At 21 days of age, chickens were secondly immunized phage mixed with an equal amount of incomplete adjuvant in the same dose and the same manner.At 28-32 days of age, chickens were challenged with 200 μL of Cp (5×108cfu · mL-1),fasting 24 h before the challenge.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS 11.0 and GraphPad Prism 7 software (San Diego, CA).Student's test was used to analyze the experiment data from at least three separate experiments.
Results
Recombinant protein expression
The activated recombinant pGEX-plc bacterial solution and the empty vector pGEX bacterial solution were induced by IPTG, and the 0-5 h bacterial solution was induced for SDS-PAGE analysis.As shown in Fig.1,the recombinant bacterial liquid pGEX-plc showed a gradually thickened protein band as the induction time increased.At 4-5 h, the band was the thickest, and the protein expression was the largest.The position of the band was consistent with the predicted protein size(66 ku).After sonication of the cells, SDS-PAGE analysis of the supernatant and the precipitate showed that the protein expression in the precipitate was significantly higher than that in the supernatant,indicating that the recombinant protein pGEX-plc was mainly expressed in the form of inclusion bodies.

Fig.1 SDS-PAGE analysis of expressed recombinant protein of pGEX-plc
Preparation of mAbs and detection of biological activity
The mouse was immunized with the purified recombinant protein pGEX-plc as an immunogen, and the spleen cells of the immunized mice were fused with SP2/0.After screening, a hybridoma cell line stably secreting anti-plc specific antibody was obtained and named as A10E5.The mAbs secreted by the positive hybridoma cell line A10E5 was identified as subtype IgG2a by subtype (data not shown).The prepared mAb A10E5 specifically bound to its corresponding recombinant protein pGEX-plc and nativeα-toxin protein by Western blot, with specific bands at 66 and 43 ku, respectively (Fig.2A).It showed that the mAb A10E5 prepared in this experiment had good reactogenicity with recombinant protein and natural antigen.The prepared naturalα-toxin protein of Cp was used as the coating antigen, and the antibody titer of the culture supernatant of the hybridoma cells was 1 : 1 024 by indirect ELISA.The antibacterial effect of mAb A10E5 prepared in this study was analyzed by immune fluorescence assay.The results showed(Fig.2B) that the pAb-plc was able to bind to the surface of Cp.The mAb A10E5 bound to the bacterial surface and red fluorescence was observed.
Theα-toxin had the effect of decomposing lipoproteins in egg yolk emulsions.Therefore, the turbidity of the solution in the pores increased after the action of theα-toxin and the egg yolk emulsion,and the OD490nmvalue increased.Assuming that the antibody was capable of neutralizing the plc activity of theα-toxin, the turbidity of the solution in the well was lowered and the OD490nmvalue was decreased.The plc activity neutralization test showed that pAbplc and mAb A10E5 combined withα-toxin inhibited theα-toxin decomposition of the plc activity of the egg yolk emulsion, and reduced the turbidity of the egg yolk emulsion.The OD490nmvalues of the antiplc antibody group were significantly lower than those of theα-toxin control group (Fig.2C).The results of erythrocyte hemolysis and neutralization experiments showed that pAb-plc and mAb A10E5 had the effects of inhibitingα-toxin-dissolving red blood cells.The number of erythrocyte in the RBCs suspension was higher than that in theα-toxin control group, resulting in a significantly higher OD490nmvalue than that of theα-toxin control group.Thus, it was confirmed that the mAb A10E5 prepared in this study had the ability to neutralizeα-toxin (Fig.2C).
Screening of phage random 12-peptide library and identification of affinity
The purified mAb A10E5 was used as a targetmolecule for four-round phage screening, and the amount of coating, phage input and output in each round of screening were counted, and the output/input of each round was compared.The results are shown in the Table 1.In the case where the amount of target molecule was decreased and the input amount was constant, the phage elution amount and elution amount/input amount of each round showed an increasing trend.Therefore, after four rounds of screening, the phage was significantly enriched.
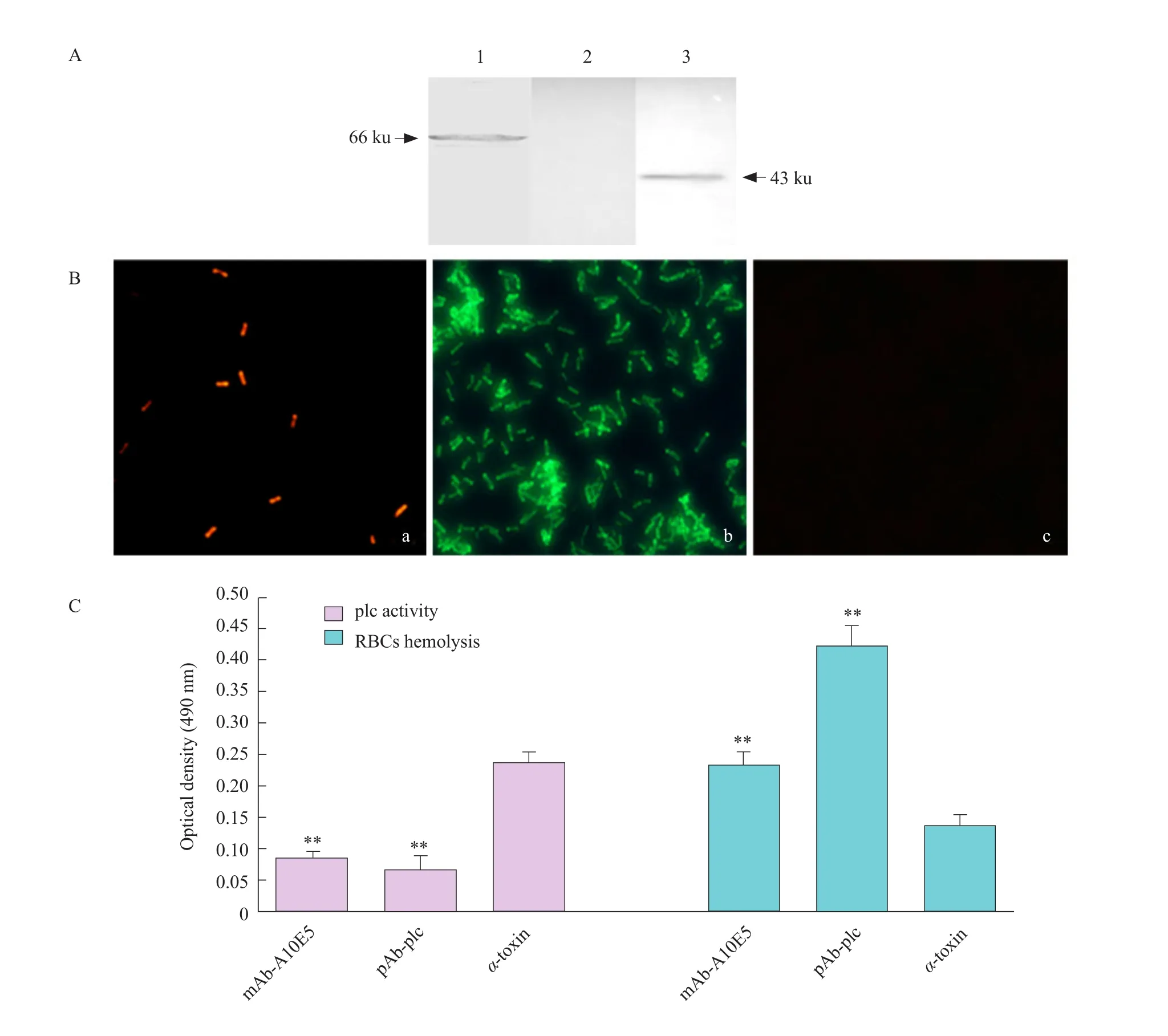
Fig.2 Identification of the biological activity of MAb A10E5

Table 1 Biopanning to purified monoclonal antibody A10E5
The fourth round of phage eluate was diluted by 10-1-10-7.After the dilution was incubated on LB/IPTG/Xgal plates for 12 h, the plates with less than 100 plaques were selected, and 10 monoclonal phage blue spots were randomly picked for amplification.The phage pAb-M13 was used to initially detect the affinity of the selected phage monoclonal to the target molecule by ELISA.The ELISA data (Fig.3A) showed that 10 random phages selected after four rounds of screening had higher affinity with the target molecule purified mAb A10E5.

Fig.3 Screening of phage random 12-peptide library and identification of affinity
Ten phage clones positive for ELISA were selected for plc protein competition inhibition assay.The plc protein inhibited the binding of these 10 phage clones to the mAb A10E5 to varying degrees (Fig.3B).The highest inhibition rate was phage clone No.4,with an inhibition rate of 86%, followed by No.5.The results showed that the epitope formed by the positive phage screened was identical or similar to the plc epitope recognized by the mAb A10E5.Then,using+130M13 and -28M13 as the forward primers and reverse primers, the genomic DNA of 10 random phages was used as a template for PCR amplification,and specific bands of about 250 bp in length were amplified (Fig.3C).The PCR product was subjected to nucleotide sequence determination and translated into the corresponding amino acid sequence (Table 2).According to the sequencing results, two phages with higher inhibition rates were named as phage Q and phage E, respectively.

Table 2 Sequence determination results of phage clones
Peptide Q and peptide E inhibiting toxic effects of α-toxin on Hela cells
This study verified that the maximum non-toxic concentration of the two peptides was 500 μg · mL-1on Hela cells.After the cells were over a single layer, the two peptides were diluted to 500 μg · mL-1, and mixed with 30 μg · mL-1α-toxin in a ratio of 1 : 1.Then they were incubated in a thermostat for 1 h to act on Hela cells.As shown in Fig.4, the activities of peptide Q group and peptide E group cells were significantly higher than those of theα-toxin group, and the cell viability of peptide Q group was higher than that of peptide E group, but lower than that of the mock group.It indicated that the two peptides synthesizedin vitrohad strong competition withα-toxin and could inhibit the toxic effects ofα-toxin on cells.

Fig.4 Peptide Q and peptide E inhibiting toxic effects of α-toxin on Hela cells
Protective effect of two phages expressing specific polypeptides on chickens after challenge
Phage Q and phage E expressing a specific polypeptide were used as vaccine to immunize chickens.When the chickens were 28 days old, the chickens were challenged.On the third day after the chickens were challenged with Cp, the PBS group began to suffer from mental fatigue, depression, wilting,loss of appetite, and insensitivity to the surrounding environment.On the 5th day, the chickens appeared to symptoms of flock together and lying.Simultaneously,symptoms of diarrhea occurred in the chickens,yellowish brown or grayish black stool had mucus and blood clots, and feathers around the anus were stained with yellow-brown feces.At the age of 14, 21, 28 and35 days of chickens, three chickens were randomly grabbed in each group and weighed them.There was no significant difference in body weight between the groups before and after immunization, but after the challenge, the body weight of chickens in the PBS group was significantly lower than other three groups(Fig.5A).On the 5th day after the challenge, the chickens in the PBS group were randomly grabbed and killed, and the intestinal lesions of the chickens were observed.

Fig.5 Protective effect of two phages expressing specific polypeptides on chickens after challenge
As shown in Fig.5B, there was a suffocation in the jejunum and ileum, a yellow chyme with bubbles in the intestine, and a bleeding point on the mucosal surface.The intestinal damage of chickens in PBS group was the heaviest, and the intestinal damage of chickens in phage Q and phage E groups was relatively mild, while there was no damage in the intestinal tract of control chickens.The intestine lesions of the chickens were scored.The results are shown in Table 3.The scores of intestinal lesions in phage Q and phage E groups were significantly higher than those in PBS group, which indicated that both phages could alleviate the intestinal damage of the chickens after the challenge.
After the chickens were orally challenged with Cp,the intestines of the chickens in each experimental group were aseptically cut out for Cp separation and counting.As shown in Fig.5B, the level of Cp detected in the intestine of the chickens of the two immunized groups was significantly lower than that of PBS group,and Cp count of the unimmunized control group was not statistically significant.The results of intestine Cp counts of chickens in each group showed that both phages expressing specific polypeptides could reduce the colonization of Cp in chicken intestine and reduce the intestinal damage of chickens.
As shown in Fig.5D, in the phage Q and phage E groups, specific serum antibody titers began to rise after the first immunization.At 35 days of age, the specific serum antibody titer reached its highest level and then began to decline.The specific serum antibody titer of phage Q group was significantly higher than that of PBS group and unimmunized control group,and the specific serum antibody titer of phage Q group was higher than that of phage E group.There was no significant difference between the unimmunized control group and PBS group, during the immunization challenge, suggesting that the two phages expressing the specific polypeptide had a protective effect on the chickens after the challenge.
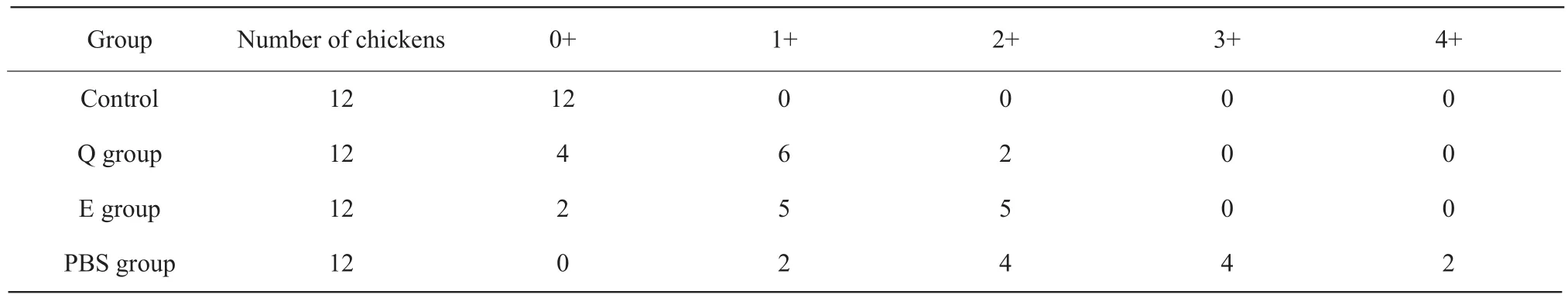
Table 3 Intestinal lesion score of chickens post-challenge
Discussion
Cp can cause avian necrotic enteritis (NE), gangrenous dermatitis (GD) and other malignant diseases, of which NE is a common disease caused by Cp that exhibits obvious pathological bacterial intestinal changes.Since its discovery in 1930, it had caused serious harm to the poultry industry (Moreiraet al., 2016; Laceyet al., 2018).In recent years, many countries and regions, such as Europe and the United States, banned the use of antibiotic growth promoters (AGPs) and other antimicrobial drugs in feeds (Castanon, 2007;Luceyet al., 2004), causing a significant increase in the incidence of this disease and seriously jeopardizing the development of the global poultry industry.
α-toxin is an important virulence factor for the pathogenicity of Cp infection, and it is also the primary target for the preparation of Cp vaccine and establishment of detection methods.In this study,pGEX-PLC protein was used as immunogen to prepare mAb againstα-toxin, and a hybridoma cell lineA10E5 with high efficiency and stable secretion of anti-α-toxin mAb was screened.The mAb of this strain was identified as belonging to the IgG2a subtype, and the antibody titer was 1 : 1 024.The mAb was identified that it specifically bound to the naturalα-toxin of Cp by Western blot, and both IFA andin vitroneutralization experiments showed that the mAb had good reactogenicity.
Using phage screening methods and peptide binding and competition assays can identify potential epitopes on plc proteins and help to understand the structure of antigen and antigen-antibody interactions, which is of great significance for the development of vaccines and diagnostic reagents.Antigenic epitopes could be divided into linear epitopes and conformational epitopes.A linear epitope was a few amino acids of a primary structure adjacent to each other on an antigen;a conformational epitope was a discontinuous primary structure on the antigen (Castanon, 2007; Dibneret al.,2005).Peptide synthesis and protein degradation methods can be used to determine linear epitopes,but fail to determine conformational epitopes.Most epitopes are conformational epitopes.In the phage display library, a random fragment of the short peptide is inserted into the N-terminus of the filamentous phage protein PIII, which has been successfully used to screen for epitopes recognized by antibodies or other ligand proteins.Using this technique, not only the linear epitopes could be screened, but also the potential conformational epitopes could be screened(Malhotraet al., 2009).In the competition inhibition experiment of peptides and toxins, peptide Q and peptide E inhibited the toxic effects ofα-toxin on Hela cells.It was speculated that the polypeptide had a structure similar to the epitope of the plc protein, the polypeptide contacted a part of the cell surface receptor after contacting the cell, thereby blocking a part of the action ofα-toxin on the cells.Animal experiments also showed that the phage Q and phage E which expressed specific polypeptides were screened and had good immune protection on chickens.
Conclusions
In this study, mAb A10E5 was prepared as a targeting molecular, Q and E were screened by phage random peptide library technology.The antibacterial activity of the peptide specifically binding to the monoclonal antibody was analyzed byin vivoandin vitroexperiments, respectively.The identification of the active site of the main pathogenic factorα-toxin of Cp had an important role in studying the interaction mechanism with the host cell.Currently, there was no report on the identification of Cpα-toxin monoclonal antibody ligand by phage random peptide library technology.To some extent, this study had perfected the research field of the interaction mechanism between Cpα-toxin and host cells; at the same time, it laid a foundation for the development of new peptide epitope vaccines and provided reference data for the prevention of Cp.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Effects of Drought Stress and Re-watering on Osmotic Adjustment Ability and Yield of Soybean
- Winter Hardiness Physiological Response with Dehydration in Winter Wheat
- Effects of Constant High Temperature on Survival, Development and Reproduction of Aphis glycines Matsumura
- Fine Genetic Mapping of Dwarf Trait in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)Using a RIL Population
- Evolution of Heavy Metal Speciation During a Large-scale Sewage Sludge Composting
- Generation of a Canine-origin Neutralizing scFv Against Canine Parvovirus
