Study on Relationship Between Differential Proteins of Bacillus cereus LBR-4 and Its Salt Tolerance Mechanism
2020-11-03TanJialiDuChuanyingWangJianNiHejiaGaoJiguoandLiHaitao
Tan Jia-li, Du Chuan-ying, Wang Jian, Ni He-jia, Gao Ji-guo, and Li Hai-tao
College of Life Sciences, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
Abstract: In order to explore the salt tolerance mechanism of Bacillus cereus LBR-4 with salinity of 14% NaCl, differential proteomic analysis of the whole protein of LBR-4 strain expressed under 14% NaCl high salinity condition and normal culture condition (1% NaCl) was studied by two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry.The isoelectric point of most detected proteins was between pH 4-7 and the molecular weight distribution was 10-70 ku.Compared with the normal culture condition, the expression level of 118 protein spots in the whole protein expression map changed significantly (accounting for 25.2% of the total protein spots).The expression level of 78 protein spots increased significantly, including 22 new protein spots that appeared under high salt stress.The expression levels of 40 protein spots decreased significantly, including 18 protein spots that disappeared under high salt stress.By mass spectrometry, six distinct differentially expressed protein spots were dihydroxy acid dehydratase, cell division protein FtsZ, iron sulfur cluster synthesis protein SufD, unknown carboxylase YngE, hypothetical acetaldehyde dehydrogenase DhaS and phenylalanine acid tRNA ligase alpha subunit.It was speculated that under high salt stress, the cells had protective measures and the secretion of intracellular compatible solutes increased.The iron and sulfur clusters involved in various physiological reactions also activated the stressful suf synthesis pathway, and the rate of cell division and reproduction was also slowed down and ensured the normal progress of physiological reactions in the cells.
Key words: Bacillus cereus LBR-4, proteomics, two-dimensional electrophoresis, protein profile, salt tolerance mechanism
Introduction
Soil is the environmental resource on which human beings depend and maintained an ecological balance.However, with the rapid development of the society,human activities have seriously affected the structure of the soil.Environmental pollution, over exploitation and irrational use make soil salinization increasingly serious (Zhaoet al., 2012).According to the results of the second national soil survey in China, the total area of saline soil in China is about 36×106hm2, accounting for 4.88% of the nationally available land area.The salinized area of cultivated land reaches 9.21×106hm2,accounting for 6.62% of China's cultivated land area,mainly distributed in northeast, northwest, north China and coastal areas (Du, 2014).Large areas of saline land cannot be cultivated normally, which seriously affects the use of land and causes huge economic losses.
Bacillusis a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped,straight or nearly straight, 0.3-2.2 μm×1.2-7.0 μm.Most of the movements, the flagella are lateral,ability to form heat-resistant endogenous cells that are exposed to the air without hindering the formation ofcells (Buchanan and Gibbens, 1984).Bacillusis one of the dominant microbial populations of soil and plant micro-ecology.It has strong anti-reverse ability and anti-bacterial, disease-preventing and yield-increasing effects.It can survive in extremely harsh environment and can also be displayed high tolerance in highsalt environment (Yang, 2012; Lüet al., 2016; Zhaoet al., 2006).Related studies have shown that the spore formation, stress resistance and disease resistance ofBacillusare related to the expression and regulation of related proteins.The proteomics technology is used to study the difference of protein expressions of salttolerant bacteria, and to further study the salt tolerance mechanism and the possible changes of physiological pathways of strains under high salt stress (Qinet al.,2018; Höperet al., 2006; Sánchezet al., 2005; Moroet al., 2015).Feng (2005) used proteomics technology to study the difference in protein expression of a strain ofBacillus sphaeroidesunder short-term high salt shock, long-term high salt stress and hypotonic shock.Li (2008) studied the changes of plasma membrane proteome of moderately halophilicBacillus.sp I121 under salt stress by proteomics method, the molecular mechanism of osmotic regulation of this strain under high salt stress was proposed.Although the use of proteomics technology to analyze the salt tolerance mechanism of salt-tolerant bacteria has been increasing in recent years, it is necessary to further explore the salt tolerance mechanism and physiological changes of strains under high salt stress (Chenet al., 2010; Duet al., 2014; Lilleyet al., 2002).Increasing the research onBacillusprotein is conducive to the development and utilization ofBacillusresources, which is of great significance for making full use of saline soil and improving the saline soil ecosystem (Yanget al., 2018;Wanget al., 2010; Zhanget al., 2006).
The objective of this study was to expore the salt tolerance mechanism and characteristics of the salttolerant strain LBR-4.Two-dimensional electrophoresis was used to separate mixed proteins, determine the isoelectric point and expression level of the protein and then perform mass spectrometry on the protein spots with obvious expression to evalute the salt tolerance mechanism and characteristics of the salt-tolerant strain LBR-4.It was speculated that the strain was under high stress in salt, in order to resist the environment of high osmotic pressure, cells had protective measures.
Materials and Methods
Experimental strains
Bacillussalt-tolerant LBR-4 had been isolated and identified in the laboratory.
Chemicals and media
Protein extraction and purification related reagents,SDS-PAGE related reagents and two-dimensional electrophoresis related reagents were purchased from Axygen Corporation.
Luria-Bertani (LB) liquid medium (g · L-1) was composed of 10 g peptone, 5 g yeast powder, 10 g NaCl,dissolved in 1 000 mL distilled water; added 1.3%agar to the solid medium, pH was adjusted to 7.0 and sterilized at 1×105Pa for 30 min.
E xtraction and purifica tion of the whole protein of strain LBR-4
The whole protein of LBR-4 strain was extracted with ultrasonic fractionation extraction following the method described by Huet al(2013).The protein sample was suspended in 10 volumes (w/v) of solution A, 1 mmol · L-1PMSF, 2 mmol · L-1EDTA and 10 mmol · L-1DTT were added to the mixture, then sonicated for1 min, 2 s/3 s, and allowed to stand at-20℃ for 2 h.Suspension was centrifuged at 4℃at 15 000 r · min-1for 15 min, the supernatant was discarded.The pellet was resuspended in 10 volumes of solution B of the sample, the operation process was the same as above and repeated the process three to four times.Removed the precipitate and vacuum dry for about 5 min to remove the organic solvent.According to the ratio of 10 mg dry powder and 200 μL protein lysate, added protein lysate and1 mmol · L-1PMSF, 2 mmol · L-1EDTA, 10 mmol · L-1DTT, sonicated for 5 min, 2 s/3 s, fully dissolved for 1 h and centrifuged at 4℃ at 15 000 r · min-1for 15 min.The supernatant was the desired protein purified samples.
Determination of protein LBR-4 protein concentration
Bovine serum albumin standard solutions 0, 0.1, 0.2,0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and 0.7 mL were mixed in sterile deionized water to 1.0 mL, respectively.Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 reagent was added, mixed evenly, determined absorbance at 595 nm and plotted the standard curve.The 0.1 mL protein samples were mixed well with 5 mL Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 reagent to determine the absorbance at 595 nm and the protein contents in the protein samples were determined by a standard curve.
SDS-PAGE analysis
The 40 μL protein samples were mixed well with 10 μL of 5×loading Buffer.The samples were placed in a boiling water bath for 5 min, centrifuged at 15 000 r · min-1for 1 min, and the supernatant was taken for electrophoresis loading.The polyacrylamide gel was prepared according to the protein electrophoresis experimental technique.The 10 μL of the protein samples were loaded, and after 80 V electrophoresis until the samples entered the separation gel, the voltage was adjusted to 120 V until the indicated Bromophenol Blue reached the bottom of the gel.After the electrophoresis was completed, the gel was taken out.The protein gel was decolorized with SI solution for 5 min, and SI solution was poured out.A small amount of SIII solution was added to SII solution, and the protein gel was stained until the protein band was clear, and washed with sterile water.Photographed by a gel imaging system.
Two-dimensional electrophoresis analysis
The samples were mixed with the appropriate amount of hydration solution and carefully added to the strip groove.The strip was placed at room temperature for 30 min, with the rubber side facing down.First put the IPG strip (3-10 of the isoelectric point range)into the strip groove, and slowly put down the strip.The 1-2 mL of cover oil was added from both ends to the middle to prevent evaporation of water and cover the strip cover.The Ettan IPGphor 3 instrument provided voltage for active hydration and high pressure focusing.Isoelectric focusing was performed at room temperature using the following procedure:30 V, 12 h; 60 V, 1 h; 150 V, 1 h; 300 V, 1 h; 600 V,1 h; 1 000 V, 1 h; 4 000 V, 1 h; 8 000 V, 10 h and 500 V,1 h (a total of 29 h).
After the first iso-point focusing was finished, the strip was taken out and the oil was dripped on the filter paper.Placed the strip in a balance tube containing the DTT balance solution, and shook for 15 min on a horizontal shaker.The strip was taken out from the balance tube containing the DTT balance solution,and the oil was dripped on the filter paper, placed in a balance tube containing the IAA balance solution,and shook horizontally for 15 min.Assembled the potting mold, filled the gel to 0.5-1 cm from the glass short plate.Saturated with n-butanol with water, and exposured to oxygen with less gel to form a flat gel surface.
After the gel was completely polymerized, poured out the n-butanol solution on the gel, and rinsed the gel surface with the gel stock solution.The balance strip was taken out and transferred to an SDS-PAGE gel to make the strip closely adhere to the SDSPAGE gel surface, and it was capped with a 0.5%low melting point agarose mixed with bromophenol blue.Removed the bubbles.After the low melting point agarose was solidified, the electrophoresis was carried out at a constant temperature of 20℃, and firstly electrophresed with 80 V and 1 W per gel for about 1 h.After the Bromophenol Blue entered the gel, it was changed to 600 V, 13 W per gel.After the Bromophenol Blue band reached the bottom of the gel (about 6 h), the electrophoresis was stopped.Coomassie Blue staining was performed.All theexperiments were conducted in triplicate.
Protein mass spectrometry
Mass spectra were analyzed using ImageMaster 7.0 software.Used the sterilized tip to dig the protein spots of interest, and the MALDI-TOF/TOF protein spectrum was identified by Beijing Liuhe Huada Gene Technology Co., Ltd.The search parameters of each protein spot were as the followings: the used enzyme was trypsin, fixed modifications were carbamidomethyl (C), variable modifications were Gln->pyro-Glu (N-term Q), Oxidation (M), mass values were monoisotopic, protein mass was unrestricted,peptide mass tolerance was±0.1 u, fragment mass tolerance was±0.1 u, max missed cleavage was 1 and the instrument type was ESI-QUAD-TOF.
Results
Two-dimensional electrophoresis analysis of strain LBR-4 under high salt stress processing of protein samples
In the process of applying two-dimensional electrophoresis to analyze differential proteomics, the preparation of protein samples directly determined the repeatability and quality of the two-dimensional electrophoresis gel image.This study referred to protein extraction method (Huet al., 2013).The whole protein of LBR-4 strain was extracted by two methods:glass bead crushing method and ultrasonic crushing step-by-step extraction method.The SDS-PAGE method was used to compare the protein extraction results.It could be seen from the electropherogram(Fig.1) that the protein bands obtained by the ultrasonication step-by-step extraction method were clearer and the bands were significantly more than those extracted by the glass bead disruption method.Therefore, the whole protein of LBR-4 strain was extracted by ultrasonication stepwise extraction method in the subsequent experiments.
In the first iso-point focusing process, the protein was precipitated by cold trichloroacetic acid (TCA)-acetone method, which could effectively remove salt ions.It also inhibited the hydrolysis of proteases and removed interfering substances, such as pigments and phenols.However, the precipitation of proteins by this method would result in the loss of some protein samples.It could be seen from the electropherogram(Fig.2) that the concentrations of the soluble sample components in the protein samples extracted by the ultrasonic stepwise extraction method were significantly higher than those of the slightly soluble and poorly soluble samples.The protein samples purified by the cold TCA-acetone method were slightly lost.
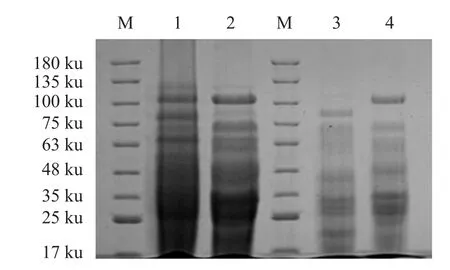
Fig.1 SDS-PAGE of the whole protein of strain LBR-4 extracted by different methods
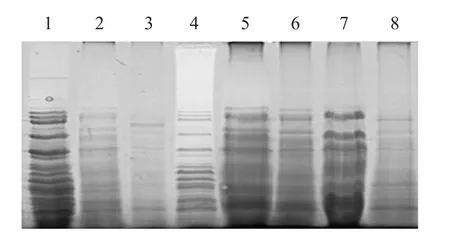
Fig.2 SDS-PAGE for protein purification by different methods
Selection of sample loading
This study compared electropherograms of protein loadings of 750, 1 000 and 1 250 μg (Fig.3).When the loading was 750 μg, there was no horizontal or vertical tailing of the protein spots, but the number of protein spots was obviously too small.When the loading was 1 000 μg, the protein spots were clear and there was no obvious tailing phenomenon.After using ImageMaster 2D Platinum 7.0 gel analysis software,statistically isolated approximately 500 protein spots;when the sample volume was 1 250 μg, the protein spots showed significant lateral tailing and covered some low-abundance protein spots.Therefore, the loading of 1 000 μg was more suitable for the twodimensional electrophoresis of the wholeBacillusprotein, and could better meet the needs of subsequent mass spectrometry analyses of protein spots.
Fig.3 Two-dimensional electrophoresis with different loadings
Image analysis of strain LBR-4 the whole protein gel
The full-protein gel image of LBR-4 strain under normal growth conditions and high salt stress was analyzed by ImageMaster 2D Platinum 7.0 analysis software (Fig.4).There were about 500 protein spots in each electropherogram.The isoelectric points of most proteins were distributed between pH 4-7 and the molecular weight distribution in the range of 10-70 ku.Compared with the 1% NaCl salt concentration, the strain LBR-4 grown in the medium containing 14%NaCl concentration showed a significant change in the expression of 118 protein spots (25.3% of the total protein spots).Among them, the expression levels of 78 protein spots increased significantly, including 22 new protein spots appearing under the high salt stress; the expression of 40 protein spots decreased significantly, including 18 protein points disappeared under the high salt stress.
Fig.4 2-DE SDS-PAGE of differentially expressed proteins
Differential protein spot mass spectrometry identification analysis
The protein spots IR1, IR2 and IR3 with significant increased in expression under the high salt stress (in which IR1 and IR3 were newly emerged protein spots)and protein spots IR4, IR5 and IR6 with significantly decreased expression under the high salt stress were selected for identification of MALDI-TOF/TOF protein profiles.Using MASCOT for peptide quality search, the isoelectric points and molecular weights of the first few proteins with the highest scores were similar to those shown on the map.It could be initially determined the unique identification result of protein point IR1-IR6.
Protein spots with significantly increased expression
Protein spot IR1: dihydroxy acid dehydratase was capable of simultaneously producing 2-ketoisovaleric acid (a precursor of leucine and valine) and 2-keto 3-methylpentanoic acid (precursor of isoleucine).Under the high salt stress, these three kinds of amino acids accumulated in the cells, which could increase the osmotic pressure of the cells, thus, maintaining the osmotic pressure balance inside and outside the cell, as shown in Table 1.The number of queries in the search parameter of protein point IR1 was 805.
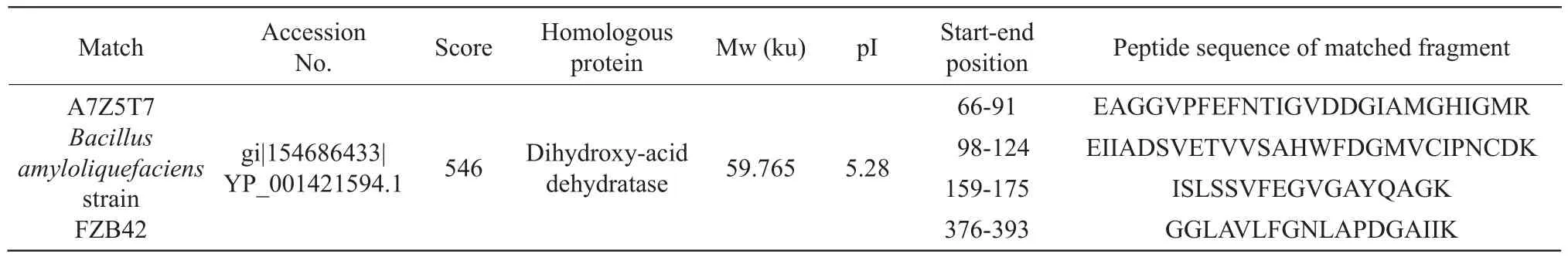
Table 1 Mass spectrometric identification results of protein spot IR1
Protein spot IR2: the cell division protein FtsZ was a microtubule-like protein ubiquitously found in prokaryotic organisms, as shown in Table 2.The number of queries in the search parameter of protein point IR2 was 856.
Protein spot IR3: iron sulfur cluster synthetic protein SufD.Iron-sulfur clusters participated in a variety of metabolic pathways in the body, and they had excellent electron transfer functions.It could participate in the synthesis and activation of substrates, iron/sulfur storage, gene expression regulation, enzyme activity regulation, etc., as shown in Table 3.The number of queries in the search parameters of the protein spot IR3 was 716.
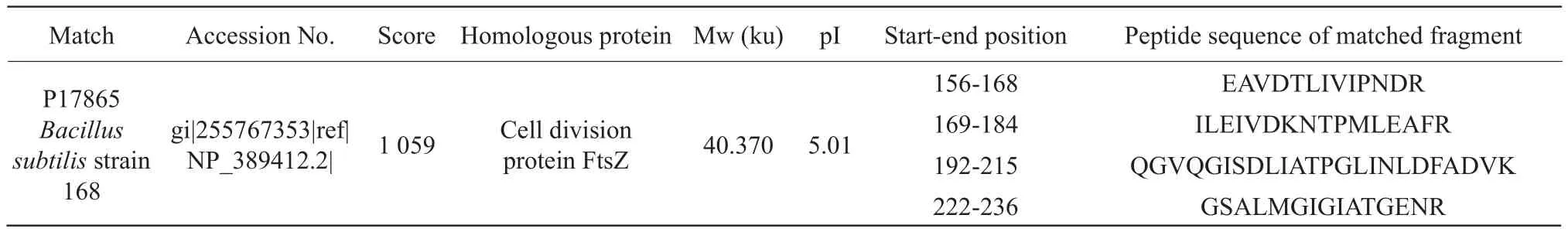
Table 2 Mass spectrometric identification results of protein point IR2
Protein spots with significantly reduced expression levels
Protein spot IR4: unknown carboxylase YngE,similar to propionyl-CoA carboxylase.Propionyl-CoA produced methylmalonyl-CoA under the action of propionyl-CoA carboxylase, and isomerized to succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutaseparticipating in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, as shown in Table 4.The number of queries in the search parameters of the protein spot IR4 was 779, and other parameters were the same as IR1.
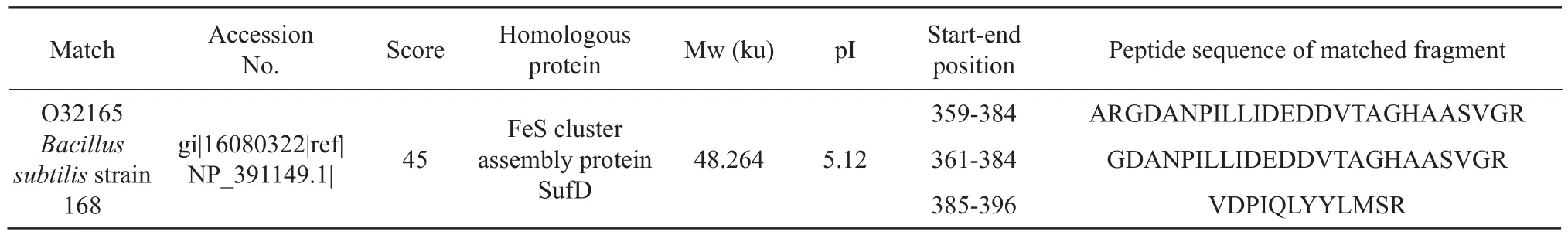
Table 3 Mass spectrometric identification results of protein point IR3
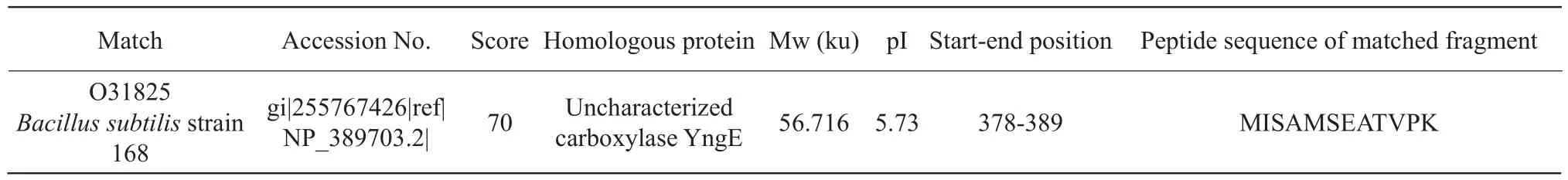
Table 4 Mass spectrometric identification results of protein point IR4
Protein spot IR5: assumed acetaldehyde dehydrogenase DhaS.Aldehyde dehydrogenase was also known as aldehyde dehydrogenase, as shown in Table 5.The number of queries in the search parameters of protein spot IR5 was 843, and other parameters were the same as IR1.
Protein spot IR6: phenylalanine tRNA ligase alpha subunit, a specific enzyme that catalyzed the binding of phenylalanine to tRNA.The result is shown in Table 6.The number of queries in the search parameter of protein spot IR6 was 915, and other parameters were the same as IR1.
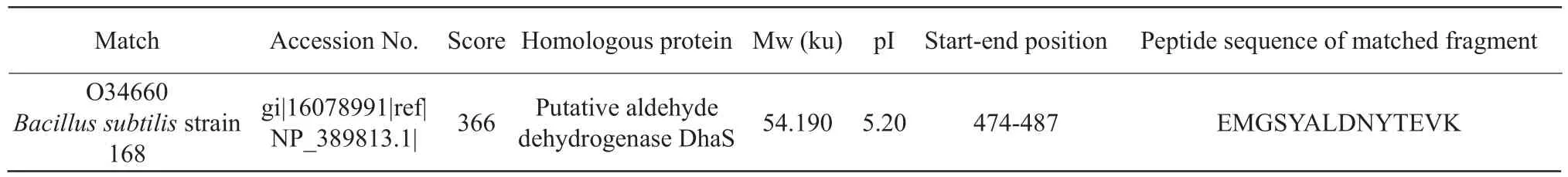
Table 5 Mass spectrometric identification results of protein point IR5

Table 6 Mass spectrometric identification results of protein point IR6
The results of protein spot mass spectrometry which was obviously up-regulated and down-regulated were analyzed.In the environment of the high salt stress, the intracellular compatible solute secretionincreased, and the iron-sulfur clusters involved in various physiological reactions activated the stresssuf synthesis pathway.The pathway maintained the balance of osmotic pressure inside and outside the cells, thus, ensuring the physiological response and function of the cells.
Discussion
According to the research on protein extraction methods (Huet al., 2013; Caoet al., 2018), the whole protein of the strain LBR-4 was extracted by glass bead crushing method, and the effect of extracting the whole protein of the strain by the improved ultrasonication step-by-step method was compared.It was found that the whole protein extracted by the ultrasonication step-by-step extraction method not only had high protein content, but also significantly had more protein bands than glass bead breaking method and less protein loss.SDS-PAGE electrophoresis was performed on the protein extracted by each step of the ultrasonic step-by-step extraction method.It was found that the protein was extracted by a single ultrasonication method and the protein was dissolved.Although the content was high, it also lost more sparingly soluble proteins and poorly soluble proteins.When the external osmotic pressure was high, the strain needed to increase the intracellular osmotic pressure to maintain balance (Yuet al., 2016).The hydrophobic protein might be more able to help the cells to remove excess water and maintain the hypertonic environment of the cells.Therefore, in the study of differential proteomics of this strain under high salt stress, the sparingly soluble proteins and the poorly soluble proteins also had important research significance (Hahneet al., 2010).The step-by-step extraction method was used to dissolve all the proteins of the strain in the lysis as much as possible, which provided more comprehensive data for the analyses of subsequent differential protein expression.
The protein spot IR1 was a new protein spot under the high salt stress, the identification result was dihydroxy acid dehydratase.In related researches, the external hyperosmotic environment would increase the contents of compatible solutes in organisms (Liu,2002; Zhaoet al., 2007).It was characterized by a sharp increase in proline content, which made the intracellular and extracellular osmotic pressure balance(Huaet al., 2010).The 2-ketoisovalerate and 2-keto 3-methylpentanoic acid produced by the dihydroxy acid dehydratase were precursors of leucine, valine and isoleucine, respectively.Under the high salt stress, the contents of leucine, proline and isoleucine increased in different degrees except for the accumulation of proline in the organism.It was speculated that under high salt stress, the strain accumulated a large amount of compatible solutes in the body to balance the highpermeability environment and increased the expression of related enzymes, dihydroxy acid dehydratase was one of them.The protein spot IR2 was a protein spot with up-regulated expression under high salt stress and it was identified as cell division protein FtsZ.In this study, the expression of cell division protein FtsZ increased significantly.FtsZ only had<20%amino acid similarity to tubulin in eukaryotes, but had a very high structural similarity and function of GTPase (Nogaleset al., 1998).In the study of opaque stress of Arthrobacter, it was found that high salt stress promoted the decrease of FtsZ polymerization in wild-type Arthrobacter (Chen, 2011).In the present study, the expression level of the cell division protein FtsZ increased significantly.It was speculated that the strain increased the expression of FtsZ protein under high salt stress, but the FtsZ protein could not be polymerized correctly, which affected the cell division and reproduction.The protein spot IR3 was a new protein spot under high salt stress and was identified as the iron-sulfur cluster synthetic protein SufD.Iron-sulfur clusters were involved in a variety of biosynthetic and metabolic pathways.At least three iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis systems had been discovered (Wanget al., 2012).Among them,the SUF system was first discovered inE.coliand theSUFgene was expressed under the stress conditions,such as iron deficiency (Outtenet al., 2004) and oxidative stress (Loiseauet al., 2005).The protein spot IR4 was a protein spot with a significant downregulation of expression under the high salt stress.The identification result was an unknown carboxylase YngE, which acted similarly to propionyl-CoA carboxylase (Poetteret al., 2008) and participated in the tricarboxylic acid cycle.Under the high salt stress,the tricarboxylic acid cycle would be inhibited and the expression of related enzymes involved in the Krebs cycle would be significantly down-regulated.The protein spot IR5 was a protein spot whose expression level was down-regulated under high salt stress.The result was a hypothetical acetaldehyde dehydrogenase DhaS, which was a kind of NAD(P)+-dependent oxidoreductase and could catalyze the conversion of aldehydes with corresponding acids.The protein spot IR6 was a protein spot with down-regulated expression under high salt stress.The identification result was phenylalanine tRNA ligaseαsubunit.The expression of phenylalanine tRNA ligase significantly decreased under the high salt stress, but its specific principle needed further researches.
Conclusions
The salt tolerance mechanism ofBacillussalttolerant bacteria played an important role in improving agricultural production and improving the ecological environment and had broad application prospects.In this study, the protein spots whose expression levels changed significantly were counted and the specific protein spots were identified by MALDI TOF/TOF MS.According to the results of mass spectrometry of each protein point, it was speculated that the strain was under the high stress in salt, in order to resist the environment of high osmotic pressure, cells had protective measures.The secretion of intracellular compatible solute increased and the iron-sulfur clusters involved in various physiological reactions also activated the stressful suf synthesis pathway to ensure normal physiological response of the cells.At the same time, because the cells were stimulated by excessive salt concentrations, their tricarboxylic acid cycle was inhibited and the rate of cell division and reproduction was also slowed down.Preliminary study of the salt tolerance mechanism of this strain would provide basic information for the study ofBacillussalt-resistant proteomics and provide detailed data for the study of salt tolerance mechanism ofBacillus.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Effects of Drought Stress and Re-watering on Osmotic Adjustment Ability and Yield of Soybean
- Winter Hardiness Physiological Response with Dehydration in Winter Wheat
- Effects of Constant High Temperature on Survival, Development and Reproduction of Aphis glycines Matsumura
- Fine Genetic Mapping of Dwarf Trait in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)Using a RIL Population
- Evolution of Heavy Metal Speciation During a Large-scale Sewage Sludge Composting
- Generation of a Canine-origin Neutralizing scFv Against Canine Parvovirus
