Role of mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles in autoimmunity:A systematic review
2020-09-18
Jing-Hua Wang,Jing-Han Yang,Clinical Medicine College,Weifang Medical University,Weifang 261000,Shandong Province,China
Xiao-Ling Liu,Department of Emergency Medicine,Yantai Shan Hospital,Yantai 264001,Shandong Province,China
Jian-Mei Sun,Department of Chemistry,School of Applied Chemistry,Food and Drug,Weifang Engineering Vocational College,Qingzhou 262500,Shandong Province,China
Dong-Hua Xu,Department of Rheumatology of the First Affiliated Hospital,Weifang Medical University,Central Laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital,Weifang 261000,Shandong Province,China
Shu-Shan Yan,Department of Gastrointestinal and Anal Diseases Surgery of the Affiliated Hospital,Weifang Medical University,Weifang 261000,Shandong Province,China
Abstract
Key words:Mesenchymal stem cells;Extracellular vesicles;Exosome;Autoimmunity;Tumor immunity;Transplantation immunity
INTRODUCTION
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a group of common multipotent progenitor cells,which can be found in bone marrow[1,2],synovium[3,4],umbilical cord[5],and adipose tissue[1,6].They are characterized by a multilineage differentiation potential and paracrine function[7].There is growing evidence that MSCs exert immunomodulatory effects through their paracrine function[8],in which multiple small molecules,including extracellular vesicles (EVs),cytokines,chemokines,growth factors,and interleukin(IL),are secreted to the extracellular microenvironment in animal models[9].Recently,numerous studies demonstrated that MSCs can be used in clinical therapy for immunomodulation and regenerative medicinein vivoandin vitro[10-12].Despite great improvements in the MSC therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases,treatment failures are still common and there is no doubt that it is imperative to carry out more studies to investigate the specific molecular mechanisms.EVs are key components of the paracrine process that play a vital role in intercellular communication by transmitting biological molecules in pathological and physiological conditions.
EV is newly identified small vesicle wrapped in lipid membranes,which is widely produced by many cells and secreted into the extracellular microenvironment.In 1967,Wolf first discovered EVs and described them as function-free platelet wastes[13].EVs can be isolated from various extracellular fluids,like blood,urine,saliva,tear,cerebrospinal fluid,milk,and so on,and various cells,including stem cells[14-18],primary cells of the immune and nervous system[19-22],and multiple cancer cell types[23-25].Their encapsulated functional molecules can be novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for many kinds of diseases,for instance,cancer,autoimmune diseases,and neurodegenerative disorders.The role of EVs in immunity and inflammation regulations has been attracting attention during the past few decades.According to diameter,EVs can be divided into three types,including apoptotic bodies,microparticles,and exosomes (Figure1)[26,27].Exosomes are the most common EVs with a diameter of 50-100 nm[28].Exosomes were first discovered in sheep reticulocytes,by electron microscopy[29].Microparticles,also called microvesicles,are submicronic vesicles with a diameter of 100-1000 nm,which are formed by budding of the cellular membrane after cell stimulation or stress,such as cell activation,apoptosis,and hypoxia.Apoptotic bodies also belong to EVs with a diameter of 50-4000 nm.They are usually released during the stage of cell apoptosis.EVs participate in the intercellular communication by delivering numerous proteins and nucleotides with biological activity,and nucleotides include microRNAs (miRNAs),long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs),mRNA,and even extra-chromosomal DNA[30,31].They play vital roles in regulating inflammation,immune response,vascular reactivity,and tissue repair[32,33].During the past few decades,MSC derived EVs (MSC-EVs) have been implicated in regulating inflammation and autoimmunity[7].It has been well established that EVs are involved in regulating autoimmune disorders by delivering a large number of bioactive molecules,including cytokines,enzymes,transcription factors,cytokines receptor antagonists,miRNAs,lncRNAs,and circRNAs[34].MSCs,as a specific group of cells,are multipotent stem cells characterized by immunomodulatory and self-renew properties[35,36].Cosenzaet al[37]have reported the important pathogenic or therapeutic role of MSC-EVs in rheumatic diseases.Therefore,we proposed that MSC-EVs can become potential biotargets for the development of novel molecular targeted drugs in autoimmune related diseases based on the above conclusions.This systematic review will provide in-depth knowledge of biogenesis and functional roles of MSC-EVs,especially exosomes,in autoimmunity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search
The key words “MSCs,” “EVs,” “exosome,” “autoimmunity,” “tumor immunity,” and“transplantation immunity” were used to retrieve relevant articles published in English from 2010 to 2020 in PubMed database.Besides,Boolean operator “AND” and“NOT” were combined admirably with those keywords to search the related articles.Reference lists from those articles were reviewed to exclude irrelevant articles.Manuscripts available were reviewed and recognized by using document management tool.All available information was obtained by skimming the abstracts of searched articles.Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
All repetitive documents were excluded,and the remainder needed to be restored for reading.Nevertheless,full text retrieval was performed due to many documents with unavailable abstract.
Statistical analysis
This article was a systematic review and no statistical method was used in this article.
RESULTS
Initially,we retrieved 198 records for this review.Then,repetitive and irrelevant documents were excluded,and we retained ultimately 96 high-quality papers with innovative viewpoints for reference lists.The screening process of those documents is showed in Figure2.
EVs can regulate many immune and inflammatory responses by mediating intercellular communication.Moreover,MSC-EVs have been well documented toinduce multiple immune cells to mediate immune responses in innate immunity and adaptive immunity,namely,they modulate the differentiation,activation,and proliferation of immune cells,like T lymphocytes,B lymphocytes,natural killer cells(NKs),dendritic cells (DCs),and macrophages in the autoimmune system(Figure3)[38-41].
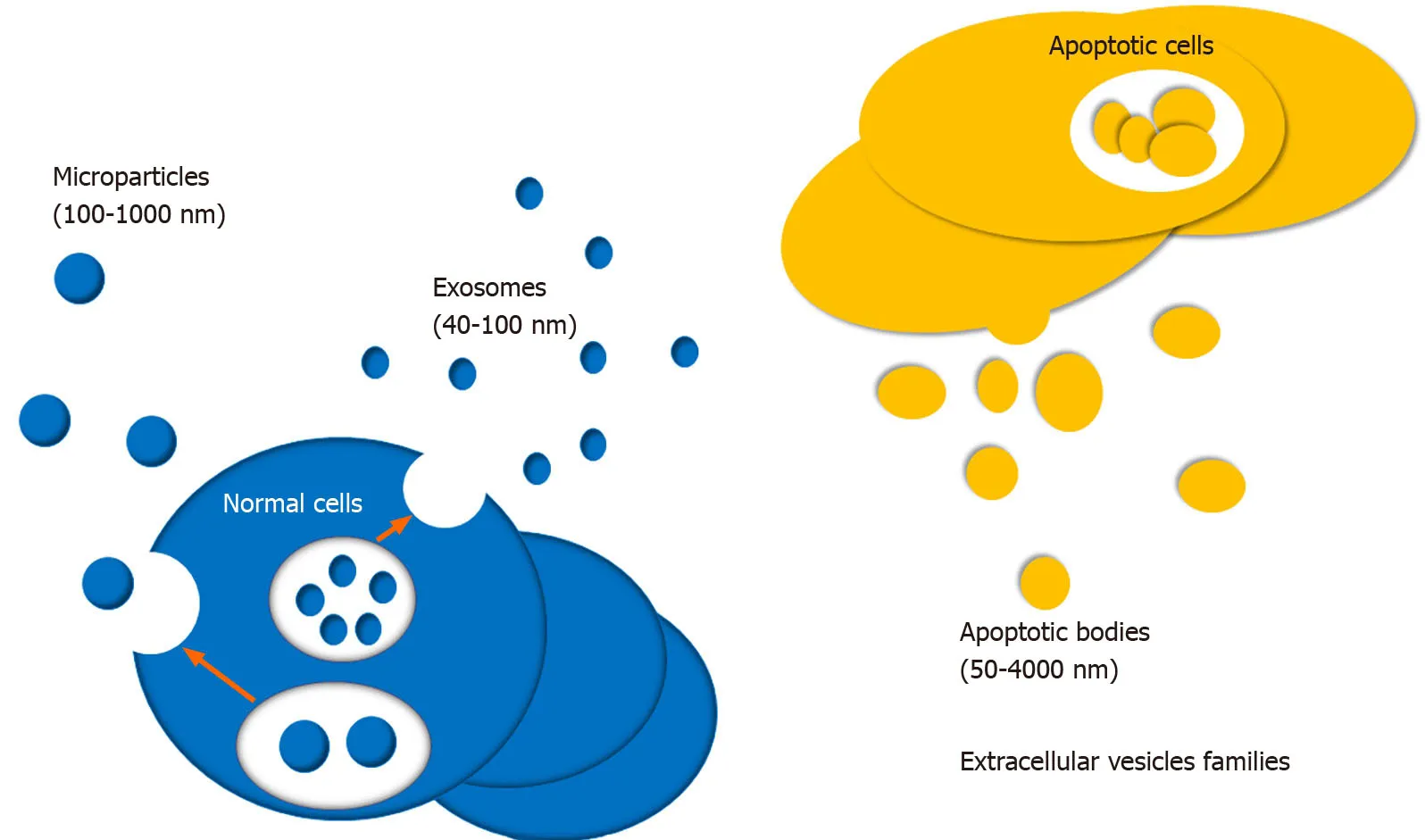
Figure1 Various kinds of extracellular vesicles.Extracellular vesicles primarily consist of exosomes,apoptotic bodies,and microparticles derived for normal cells or apoptotic cells.
There is growing evidence that MSC-EVs serving as a type of signal molecules play major biological roles in the initiation,maintenance,and progression of multiple autoimmune related diseases,such as autoimmune diseases,cancer,and graft-versushost disease.The features of MSC-EVs immunomodulation and their therapeutic potential in autoimmune related diseases are summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
DISCUSSION
MSC-EVs and T lymphocytes
T lymphocytes are important immune cells in adaptive immunity and play a significant role in the occurrence and development of many autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.MSC derived exosomes and microparticles down-regulate T cell proliferation,and CD4+and CD8+T cell subsets decrease significantly in quantity[7].Adipose mesenchymal stem cell (AMSC) derived exosomes depress theactivity of T cells,and up-regulate IL-4,IL-10,and transforming growth factor-β and down-regulate IL-17 and interferon-γ in streptozotocin induced type-1 diabetes mellitus mice,thus deadening the progression of diseases[42].MSCs have been extensively reported to decorate the activation of CD4+T cells by some specific T cell effector cytokines or direct contact,down-regulating their immune activity and converting them to a regulatory phenotype (Treg)[43,44].Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a valuable cytokine inducing T cell activity.Research shows that MSCs express and secrete PD-1 ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2) to regulate T cell dependent immune responses by binding with PD-1[45],suggesting that MSCs possess immunosuppressive propertiesviathe modulation of T cells.AMSCs under stimulation with IFN-γ can secret a big body of exosomes to the conditioned medium,and importantly,T cells isolated from that medium are significantly inhibited in activity and proliferation[46].In a word,MSC-EVs down-regulate the activity and proliferation of T cells to inhibit T dependent autoimmune responses.
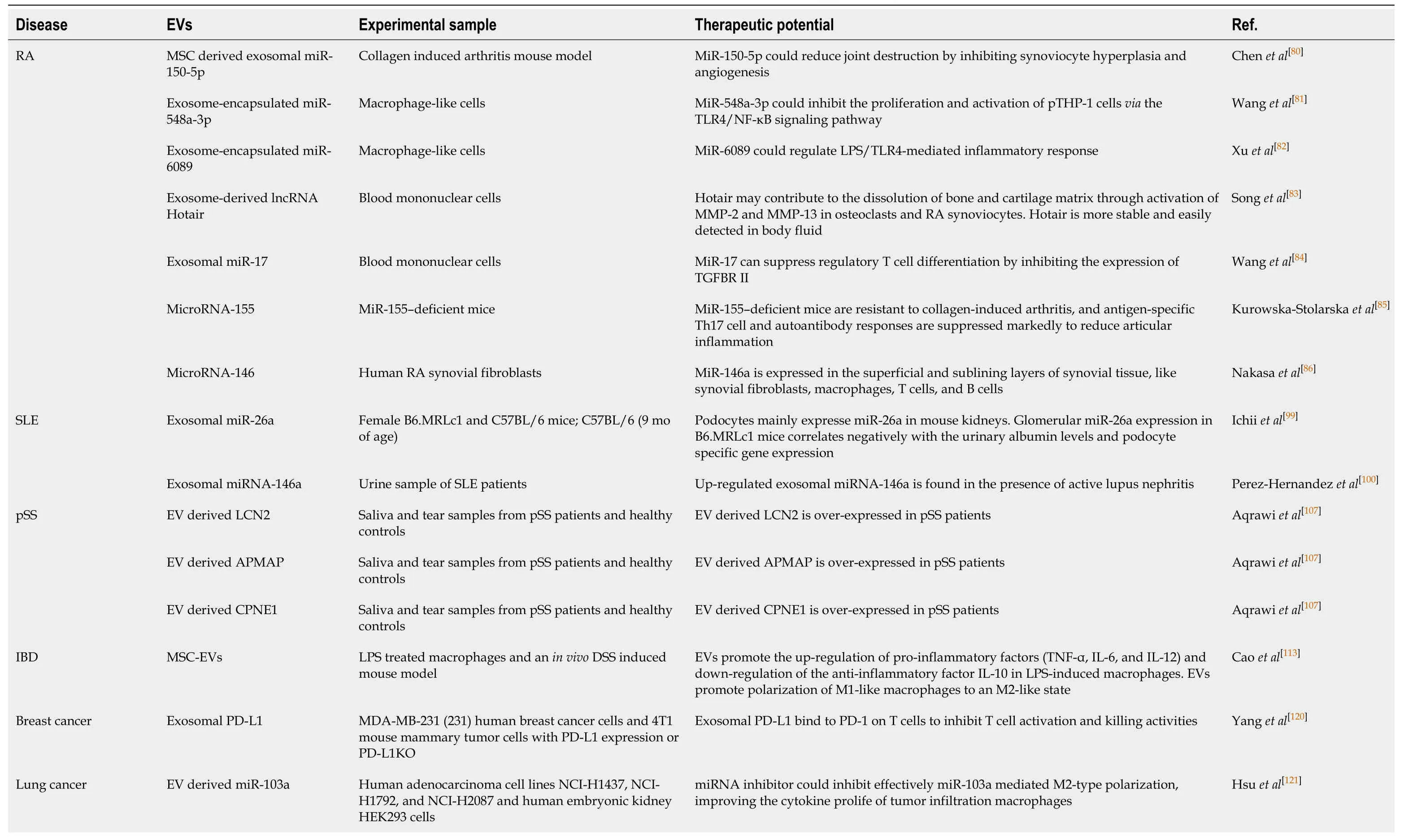
Table2 Therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles
MSC-EVs and B lymphocytes
B lymphocytes are also vital immune cells in adaptive immunity.A growing number of studies suggest that MSCs possess an immunomodulatory effect on B cells,but the molecular mechanisms involved are still mysterious[47].Nevertheless,there is little research on the role of MSC-EVs in mediating the regulatory effect of B cells on inflammatory and immune responses.Membrane vesicles derived from MSCs inhibit both B cell proliferation and differentiation in a dose-dependent fashion[48].Traggiai E and his colleagues found that MSCs positively influence the proliferation and differentiation of B cells into plasma cells secreting more immunoglobulins[47].Thus,MSCs promote downstream immune responses by mediating the conversion of B cells.Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a typical autoimmune disease characterized by constantly producing various antibodies to counter autologous cells.It is well established that B cells play a critical role in autoimmune responsesviaautoantibodies dependent mechanisms.Therefore,we infer that MSCs mediated cell conversion can boost the inflammatory progression.Therefore,MSCs can serve as a potential therapeutic tool in autoimmune diseases.
MSC-EVs and monocytes
Monocytes are secreted from bone marrow into the circulatory system and transported to target tissue,where they differentiate into mature macrophages[49].Macrophages are critical effectors and regulators of the immune system and play a central role in inflammation[50].It has been well documented that macrophages can be divided into two subpopulations:The classic M1 and the alternative M2 macrophages under microenvironmental factors.The classical M1 macrophages are induced by TLR ligands and IFN-γ and alternative M2 macrophages are induced by the immune complex IL-4/IL-13[51,52].M1 macrophages are characterized by strong microbicidal and tumoricidal activity,which can promote Th1 related inflammatory responses by releasing a range of proinflammatory cytokines,such as IL-6,IL-12,and TNF-α[53],whereas M2 macrophages with anti-inflammatory function produce less proinflammatory cytokines and more IL-10 and other anti-inflammatory factors[54].In short,both M1 and M2 macrophages contribute to the balance between destruction and repair of tissue in pathological conditions.A study suggested that after coculture of AMSCs with inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and TNF-α,a higher level of exososmes can be detected in the medium supernatant,which induce M1 differentiate to antiinflammatory M2 phenotype[55].Adipose tissue accumulating constantly in the body leads to obesity and inflammatory responses,which increase the risk of incidence of many chronic diseases,including type 2 diabetes,cardiovascular events,and part of cancers[56-58].Previous studies have revealed that the invasion of macrophages and T cells promote the formation of chronic inflammation in white adipose tissues[59,60].In high fat diet fed mice,AMSC derived exosomes promote white adipose tissue hypertrophy by inducing M2 macrophage polarization[61].A study by Némethet al[62]showed that endotoxin stimulated MSCs induce M2 macrophage polarization to release IL-10 and attenuate sepsisviathe NF-κB signal pathway in a mouse model[62].MSC-EVs induce the production of M2 macrophages with anti-inflammatory properties to restrain many relevant immune responses.
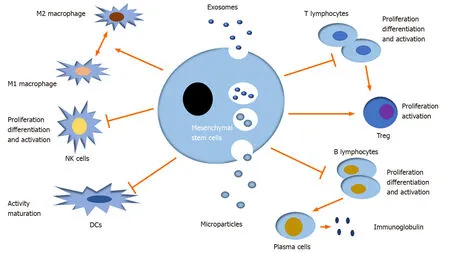
Figure3 Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles.Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) exert immunomodulatory effect on innate and adaptive immune reactions mediated by many immune cells,primarily including T lymphocytes,B lymphocytes,natural killer cells,dendritic cells,and macrophages.In brief,MSC-EVs can inhibit the proliferation,differentiation,and activation of T,B,and natural killer cells and the pathogen-presenting function of dendritic cells and macrophages.In addition,macrophage polarization can be shifted under different microenvironments in accompany with MSC-EVs.
MSC-EVs and NK cells
NK cells,a vital cell type in the innate immune system,mediate cytotoxic activity and produce certain cytokines and chemokines to mediate antigen presentation,antiviral responses,autoimmune responses,and the occurrence of various autoimmune diseases[63].A previous result showed that MSC-EVs injected into periocular tissue depress the transfer of CD161+NK cells,delay the progression of disease,and restore damaged tissue in autoimmune uveitis rat models[64,65].Decidua parietalis MSCs release IL-2 to CD69 (NK cell receptor) to stimulate IL-2 dependent NK cells and thus promote the proliferation of activated NK cells[66].Thus,decidua parietalis MSCs induce directly the activity of NK cells through IL-2 and CD69.Recent research suggested that fetal liver MSC derived exosomes carrying LAP,TGFβ,and TSP1 restrain the proliferation and activation of NK cellsviaTGFβ/Smad2/3 signaling[67].Although available data show that MSC-EVs depress the activation and proliferation of NK cells,the research on that is limited in quantity and more studies need to be carried out in the future.
MSC-EVs and DCs
DCs,important bone marrow derived APCs,present multiple antigenic peptides(major histocompatibility complex - peptide complexes) to other immune cells,like T cells,and play a key role in bridging innate to adaptive immune systems.Coculture of DCs with MSC-EVs led to down-regulated cellular surfactants and IL-10,IL-6,and IL-17 and up-regulated the number of regulatory T cells[68],and the activity and maturation of DCs are apparently restrained.Many studies suggest that these MSCEVs stimulate immature DCs to release TGF-β and PGE2,and regulate the immunocompetence of T cells in DC and T cell culture medium.Those small molecules mediate autoimmune responses with unclear mechanism.MSCs induce mature DCs to immature status with low immunogenicity and immunoregulatory property.The immature DCs express less immunomodulatory factors Ia,CD11c,CD80,CD86,and CD40,except for increased CD11[39].Overall,MSC-EVs downregulate the immune activity of DCs and T cell dependent adaptive immune responses indirectly.Nevertheless,the research on the interaction between DCs and MSC-EVs is limited,and the exact molecular mechanisms warrant further studies.
MSC-EVs and autoimmune disease
MSC-EVs have been suggested in many kinds of diseases,which can serve as promising strategies for autoimmune disease diagnosis and treatment,such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA),SLE,primary Sjgren's syndrome (pSS),systemic sclerosis,and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) due to their vital role in intercellular communications.Nevertheless,the precise molecular mechanism underlying EV regulation in autoimmunity warrants in-depth investigation.
Epidemiological survey and analysis suggest that the incidence of autoimmune diseases has been increasing year by year over the past several decades[69].Autoimmune diseases usually influence multiple organs and systems,such as the motor system,respiratory system,digestive system,and circulatory system[70].They lead to a heavy burden to public health.It is well known that some autoimmune diseases are genetically susceptible[71].Women tend to be affected by some autoimmune diseases,and approximately 90% of patients with autoimmune disease are female[72].Currently,glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive drugs are still the most frequently used non-specific therapeutic agents.That traditional therapeutic strategy causes many adverse reactions,such as opportunistic infections and metabolic abnormalities,and the development of biological molecular targeted drugs to cause slower disease progression is a priority.Accumulating data reveal the biological features of MSCs in relieving immune cell-driven systemic inflammatory responses to down-regulate immune responses,such as autoimmune diseases[73],and MSC-EVs are a significant regulator[74].The current knowledge of EVs in autoimmune diseases will be discussed in detail in the following text.
MSC-EVs and RA
RA is one of the most common chronic and systemic autoimmune diseases involving multiple systems,which is characterized by the destruction of synovial joints.The representative clinical manifestations are redness,swelling,and pain of distal joints,especially small joints of hands and feet[75].Many researchers have suggested that the occurrence of RA is caused by many complex factors,such as genetic factors and environmental factors[76,77].Dysregulation of immune responses occupies a necessary position in RA.
Increasing data have revealed EVs as critical regulators in the pathogenesis of RA by delivering specific functional molecules to targeted cells.Previously,the effectiveness of MSC therapies has been elucidated in cartilage repair in both animal studies[78]and human clinical trials[79].Previous studies have revealed that EVs generated by MSCs play a critical role in protecting against cartilage destruction and enhancing cartilage regeneration.Particularly,exosomal noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs),including miRNAs and lncRNAs,have been implicated in regulating inflammation and immune response.MSC derived exosomal miR-150-5p down-regulated inflammatory responses and reduced joint destruction and vasculitis by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) and vascular endothelial growth factor in a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model,which is considered as a potential therapeutic biomarker for RA[80].We have previously demonstrated the important role of exosomeencapsulated miR-6089 and miR-548a-3p in affecting macrophage-mediated inflammatory response in RA[81,82].Exosome-derived lncRNA Hotair affected the migration of activated macrophages and significantly decreased the levels of MMP-2 and MMP-13,suggesting that it is a potential biomarker for RA[83].A study by Wanget al[84]has shown that exosomal miR-17 inhibits regulatory T cells by targeting TGFBR II in RA[84].Besides,exosomes-encapsulated miR-155 and miR-146a produced by DCs can serve as important regulators in immune response and inflammatory response in RA[85-87].It has been shown that the expression of exosomal amyloid A is positively correlated with anti-CCP antibody and CRP,suggesting a vital role of exosomal protein in predicating the disease activity of RA patients[88].Taken together,exosomal ncRNAs play critical roles in regulating immune and inflammatory cells and thus participate in the occurrence and development of RA.Nevertheless,more studies are warranted to explore the molecular mechanisms of those exosomes harboring ncRNAs in the pathogenesis of RA.
MSC-EVs and SLE
SLE is a systemic autoimmune disease with various autoantibodies,which usually affects multi-organ systems due to enhanced inflammation and complex autoimmune disorders[89,90].It has been well established that SLE is caused by the abundant activation of T and B lymphocytes,elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines,sedimentation of immune complex substance,and finally multiple organ damage,while the kidney is the most commonly involved organ in SLE and lupus nephritis(LN) is often caused[91].EVs are significant regulators in mediating cell-to-cell communications involved in inflammation and immune regulations.Mounting evidence has suggested that EV delivered nucleic acids,proteins,autoantigens,cytokines,and surface receptors can serve as significant regulators in SLE[92,93].
Microvesicles purified from SLE patients have been identified to contain higher concentrations of immunoglobulins and complements[94,95].Circulating exosomes from patients with SLE have been shown to induce a proinflammatory immune response,which is characterized by high levels of TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-6,and other inflammatory mediators[93].The study by Asamiet al[96]supports that MSCs may confer immunosuppressive effects in SLE[96].Previously published studies have elucidated that the EVs produced from MSCs,can also contribute to immunosuppressive function in SLE[97].Accordingly,EVs can be used as drug carriers because they are less immunogenic.Umbilical cord derived MSCs have been used in the treatment of SLE patients,which shows good tolerance and few adverse events associated with transplantation[98].Therefore,MSCs and MSC-EVs can effectively control the active SLE and be used as a therapeutic strategy,particularly for the treatment of refractory SLE.Ichii and the colleagues have found that exosomal miR-26a is positively associated with urinary protein level,which suggests that exosomal miR-26a in urine of LN patients can be used as a potential biomarker for predicting podocyte injury[99].In addition,Perez-Hernandezet al[100]have shown that urinary exosomal miRNA-146a is significantly up-regulated in active LN patients[100].Therefore,testing urinary exosomal miRNA can be a non-invasive method for the detection and monitoring of LN.Nevertheless,the specific molecular mechanism of EVs in regulating autoimmunity in SLE is still unclear,which warrants further investigation by more future studies.
MSC-EVs and pSS
pSS is a systemic autoimmune disease that is characterized by chronic lymphocyte infiltration in the exocrine glands,primarily the lacrimal and salivary glands[101,102].The primary target organs are the lacrimal and salivary glands,and dry eyes and dry mouth are often caused[103].EVs purified from saliva[104,105]and tear fluid[106,107]have been identified to be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pSS in previous studies.Those differentially expressed proteins isolated from EVs of saliva and tear fluid from patients with pSS can contribute to pSS by regulating TNF-α signaling and B cell survival,including neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin,adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein,and copine[107].The increase of platelet-derived microvesicles,soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L),and soluble P-selectin(sCD62P) in pSS patients reflects platelet activation,which can serve as disease biomarkers[108].Currently,studies on MSC-EV mediated immune responses in pSS are rare.More studies are needed to elucidate the role and underlying mechanisms of EVs in pSS.
MSC-EVs and IBD
IBD is a common digestive disease characterized by chronic,relapsing gastrointestinal tract inflammatory reactions,including two main forms,Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis[109,110].To the best of our knowledge,the pathogenic mechanisms and pathogenesis of IBD are complicated,and many factors contribute to the occurrence of this disease,like autoimmune disorder,genetics,and environment[111].Macrophages have been seen as important immune cells inducing IBD[112].Experimental studies showed that inflammatory responses are significantly restrained by inducing the production of M2 macrophages in the dextran sulphate sodium induced mouse model of colitis[113].Moreover,higher levels of immunosuppressive factors (IL-10 and TGF-β)were observed in mice treated with MSC-EVs,promoting repair and regeneration of damaged epithelial cells[113].Studies have confirmed that MSC-EVs down-regulate the production of IL-1β,NO,and IL-18 by depressing NF-κB and iNOS-driven signaling in 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid induced colitis[114,115].Therefore,MSC-EVs,as an important regulator,can suppress inflammatory responses and promote injured tissue repair.That delineates the potential of MSC-EVs as biomarkers for IBD treatment.
一多下午来谈其对于初唐文学的见解:(1)时辑类书(如艺文、北堂)之风甚盛(一多疑欧阳询及虞世南辑此两种类书,乃建成、元吉与太宗两派之竞争),而注家亦盛,如李善、章怀太子、颜师古等,故学术实盛于文学,而注家影响,实较类书为大。(2)《初学记》有事对,较初期类书更进步,对后人有所帮助。(3)声律仍沿南朝之旧,似无新贡献。(4)宫体仍盛。(5)太宗之倡议文学,影响未必佳,或受虞世南影响。(虞长四十岁,太宗书法亦从之——欧阳询则习碑与虞不同。)如无太宗,陈、张或早出。又陈蜀人,张岭南人,皆文化不多及处,乃能脱藩篱也。所论极有见。[4]
MSC-EVs and tumor immunity
Tumor immunity is critical in the processes of immune response,immune escape,and immune surveillance in cancer[116,117].Previous research findings show that EVs play an critical role in anti-tumor immune reaction and inflammatory response during carcinogenesis and cancer progression[118].In the last decade,exosomes have attracted more and more attention in cancer immunity,particularly as tumor suppressors[119].Some bioactive factors encapsulated in EVs promote immune and inflammatory responses and thus lead to tumorigenesis,while some exert immune suppressive effects by inducing Tregs and M1 polarization.
A previous study has demonstrated the specific binding capacity of exosomal PD-L1 to its receptor PD-1 to depress the anti-tumor effect of T cells in breast cancer[120].MSCs also express and release PD-L1 to regulate T cell activity,and thus both MSCs and exosomes possess immunosuppressive effect[45].Besides,it has been documented that EVs play a critical in anti-tumor immune response by regulating macrophages polarization.It has been found that EVs-delivering miR-103a contributes to lung cancer by targeting PTEN and inducing M2 polarization[121].Similarly,exosomal miR-301a-3p purified from pancreatic cancer cells was found to induce M2 macrophage polarizationviathe PTEN/PI3Kγ signaling pathway[122].Taken together,EVs,particularly MSC-EVs,exert immunomodulatory effects on cancer and mediate intercellular communications between cancer cells and immune cells through EVs harboring bioactive molecules,including proteins and ncRNAs.
MSC-EVs and transplantation immunity
Kidney transplantation is the current preferred treatment for end stage renal disease.However,the long-term survival rate of the transplanted kidney is still low because the transplanted recipients often suffer from acute or chronic rejection for a long period of time[123],which finally leads to graft-versus-host disease.Biopsy is still the gold standard for the diagnosis of rejection of kidney transplantation[124,125],but it is risky and traumatic.EVs in urine can be a potential biomarker for monitoring kidney transplant rejection[126].T cells infiltrate the renal tubule during acute inflammatory response,which is a major cause for transplanted renal damage.MSC-EVs possess potential of inhibition of T cell activity and proliferation and thus EVs tend to gather in damaged renal tissues and are more likely to enter the urine.Consequently,using urine for detecting rejection of kidney transplantation is more likely to operate and promising.In addition,a previous report has showed that MSC derived exosomes provide a novel and effective clinical treatment for graft-versus-host disease[127].Nonetheless,the role of MSC-EVs in transplantation immunity needs to be further investigated in the future.
Conclusions and prospects
MSC-EVs are a hot topic in current molecular biology.Accumulated data have implicated their immunomodulatory effects on many immune cells,including T cells,B cells,macrophages,NK cells,and DCs.Increasing studies have confirmed that MSCEVs can serve as regulators in the pathogenesis of autoimmune related diseases.In particular,MSC-EVs and the encapsulated bioactive molecules are potential targets for the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune disease,cancer,and other diseases.MSCEVs can serve as new medicines in the suppression of inflammatory responses.Increasing experimental results show that application of MSC-EVs can effectively inhibit immune reactions and promote the survival and regeneration of injured cells.However,there is still a long way for investigating the therapeutic strategy for autoimmunity related diseases based on MSC-EVs.More in-depth research is warranted in the future,particularly regarding the molecular mechanism of MSC-EVs in autoimmunity.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been reported to possess immune regulatory effects in innate and adaptive immune reactions.MSCs can mediate intercellular communications by releasing extracellular vesicles (EVs),which deliver functional molecules to targeted cells.MSC derived EVs (MSC-EVs) confer altering effects on many immune cells,including T lymphocytes,B lymphocytes,natural killer cells,dendritic cells,and macrophages.A large number of studies have suggested that MSCEVs participate in regulating autoimmunity related diseases.This characteristic of MSC-EVs makes them be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmunity related diseases.
Research motivation
This article describes and focuses on the identification,characteristics,immunomodulatory function,and underlying mechanism of MSC-EVs in autoimmunity related diseases.Understanding the immunomodulation effects of MSC-EVs better will help us to investigate the pathogenesis of diseases and develop novel targeted medicines.
Research objectives
The immune modulation of MSC-EVs play a key role in disease initiation,maintenance,and progression.This article provides a new direction for us to understand the precise mechanisms of action of autoimmunity related diseases,which will promote the improvement of therapeutic regimen.
Research methods
Research results
A large number of articles were retrieved and their abstracts were skimmed.When analyzing the publications,we found that it has been well documented that MSC-EVs have the ability to induce multiple immune cells,like T lymphocytes,B lymphocytes,natural killer cells,dendritic cells,and macrophages,to regulate immune responses in innate immunity and adaptive immunity.Many validated EVs-delivered molecules have been identified as key biomarkers,such as proteins,lipids,and nucleotides.Some EVs-encapsulated functional molecules can serve as promising therapeutic targets particularly for autoimmune disease.
Research conclusions
MSC-EVs play an important part in the differentiation,activation,and proliferation of immune cells,and they may become potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmunity related diseases.
Research perspectives
MSC-EVs can serve as regulators in the pathogenesis of autoimmune related diseases.In particular,MSC-EVs and the encapsulated bioactive molecules are potential targets for the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune disease,cancer,and other diseases.However,there is still a long way for investigating the therapeutic strategy for autoimmunity related diseases based on MSC-EVs.More in-depth research is warranted in the future,particularly regarding the molecular mechanism of MSC-EVs in autoimmunity
杂志排行
World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Mesenchymal stromal cells as potential immunomodulatory players in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection
- Practical choice for robust and efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells
- Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer's disease
- Exosomes derived from stem cells as an emerging therapeutic strategy for intervertebral disc degeneration
- Off-the-shelf mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord tissue can significantly improve symptoms in COVID-19 patients:An analysis of evidential relations
- Human embryonic stem cells as an in vitro model for studying developmental origins of type 2 diabetes
