考虑产品质量差异的制造商入侵决策研究
2020-09-09张翠华李慧思
张翠华,李慧思
考虑产品质量差异的制造商入侵决策研究
张翠华,李慧思
(东北大学 工商管理学院,辽宁 沈阳 110819)
随着电子商务和物流行业的迅速发展,网络直销渠道越来越受到制造商的青睐,然而制造商入侵所引发的渠道竞争并没有得到零售商的普遍认可,大多数零售商视制造商入侵为一种威胁。本文以一个制造商和一个零售商组成的二级供应链为背景,考虑产品质量差异以及零售商具有公平敏感性,研究了制造商入侵决策以及零售商公平敏感性对供应链节点企业决策和供应链系统收益的影响。本文首先建立了制造商决策基本模型、制造商同质产品入侵模型以及制造商异质产品入侵模型,然后运用博弈理论和方法,求得制造商和零售商在Stackelberg-Nash博弈下的均衡解,最后对均衡结果进行算例仿真分析,得到相关结论。研究表明,入侵总能使制造商获益,并且异质产品入侵优于同质产品入侵;在一定条件下制造商入侵同样能使零售商获益,但零售商获益与否与其自身公平敏感性类型有关。
制造商入侵;质量差异;质量敏感;公平敏感性;Stackelberg-Nash博弈
0 引言
制造商投资建立直销渠道(例如网上商店,目录销售以及工厂折扣店等),将产品直接销售给顾客,这种现象通常被叫做入侵(encroachment)[1-2]。在经济全球化愈演愈烈的时代背景下,供应链成员间的竞争与合作关系面临一系列新的矛盾和问题,供应链成员在其生产、经营以及管理活动中,不仅要考虑与供应链其它成员的合作,还要考虑潜在入侵者对自身决策和收益的影响。随着电子商务和物流行业的迅猛发展,许多制造商在原有传统零售渠道的基础上开设了网上直销渠道,然而由于制造商入侵所引发的渠道竞争并没有得到零售商的普遍认可,大多数零售商视制造商入侵为一种威胁[2]。为了避免渠道冲突,缓解制造商和零售商之间的矛盾,维持合作关系,很多制造商被迫停止在网上直销渠道的销售,例如李维斯终止了网上直销渠道http://www.levis.com和http://www.dockers.com的销售,而将网上销售交给几个电子零售。
随着制造商入侵引发的矛盾日益凸显,学术界对制造商入侵问题的研究也逐渐兴起。Arya等[2]首先研究了制造商入侵行为对制造商利润、零售商利润以及消费者剩余的影响,同时给出了制造商入侵条件,研究表明,在一定条件下制造商入侵会使制造商、零售商以及消费者同时获益。此后学者们从不同的角度出发,对制造商入侵展开研究。Albert等[3]将产品质量水平作为决策变量建立制造商入侵模型,给出了产品最优质量水平以及制造商入侵条件;Yoon[4]研究了制造商进行R&D投资进而产生外溢效应情况下的制造商入侵问题;Li等[1,5]研究了不对称信息条件下的制造商入侵问题;Chen等[6]研究了零售商具有风险规避特性且制造商生产成本是私有信息条件下的制造商入侵问题;Li等[7]研究了零售商具有公平偏好条件下的制造商入侵问题;以上研究均是上游制造商向下游零售商进行入侵,Li和Zhou[8]则研究了制造商向上游供应商入侵问题。
现有制造商入侵问题研究大多假设产品质量为外生变量,并且当制造商选择入侵时,其在直销渠道和零售渠道销售的产品质量是同质的。产品差异化对于企业营销活动具有重要意义[9-10],而质量作为影响市场需求的重要因素,制造商在入侵时采取质量差异化战略可以缓解竞争压力。关于质量差异问题,刘家国等[11]研究了再制造产品与新产品之间存在质量差异条件下的闭环供应链价格决策;Chen等[12]研究了产品质量存在差异情形下的双渠道供应链价格和质量决策问题。
此外,现有制造商入侵问题研究大多假设供应链成员是完全理性的。而在实际经济运行中,经济主体具有一定程度的公平偏好。例如,Scheer等[13]对417家美国汽车经销商和289家荷兰汽车经销商进行研究后发现,无论是优势不公平还是劣势不公平,荷兰的汽车经销商均会对其做出反应,而美国的汽车经销商只关心劣势不公平。Huseman等[14]将个体对公平的不同偏好定义为公平敏感性,这种偏好导致个体对公平或者不公平的结果有稳定且个性化的反应。影响公平敏感性主要有两类因素:个人因素和区域文化因素[15-17]。
综上,本文区分制造商同质产品入侵和异质产品入侵两种不同情形,并且零售商具有公平敏感性,研究制造商入侵决策以及零售商公平敏感性对供应链节点企业决策和供应链系统收益的影响。与现有入侵研究相比,本文假设产品质量为内生变量,考虑产品质量差异,区分同质产品入侵和异质产品入侵两种不同情形;此外,本文将Huseman的公平敏感性理论同Fehr和Schmidt[18]的公平偏好效用损失函数共同引入到制造商入侵问题中,探讨了零售商公平敏感性对制造商入侵决策的影响。
1 问题描述与假设
本文研究的是由一个制造商和一个零售商组成的供应链系统,制造商负责生产并对产品质量进行控制。制造商不选择入侵时,将产品批发给零售商,由零售商进行销售;当制造商选择入侵时,建立直销渠道,同时通过零售渠道和直销渠道进行销售,制造商入侵情形下的供应链结构如图1所示。
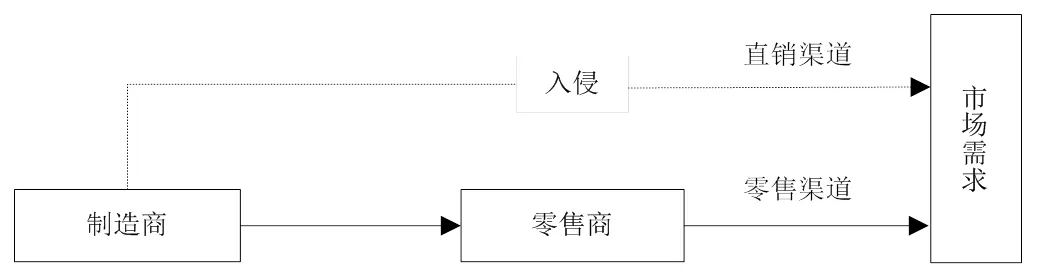
图1 制造商入侵情形下供应链结构
Figure 1 The structure of a supply chain under manufacturer encroachment
1.1 符号说明
本文所使用的相关符号说明如下:
1.2 相关假设
本文所研究的问题基于以下假设条件:
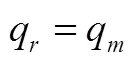

假设3. 假设消费者对产品的价格和质量敏感,并且消费者能够准确地感知产品质量水平,本文假设代表性消费者效用函数如下所示:


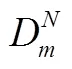
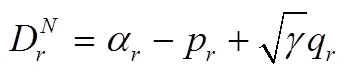
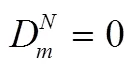
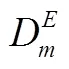


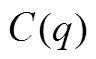
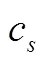

根据以上假设,得到制造商和零售商的利润如下:

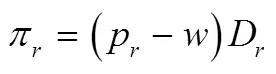
本文在Fehr和Schmidt[18]的公平偏好效用损失函数模型基础上,引入公平敏感性系数,构建零售商的效用损失函数如下:
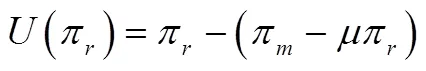
2 模型建立和求解
2.1 基本模型
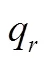
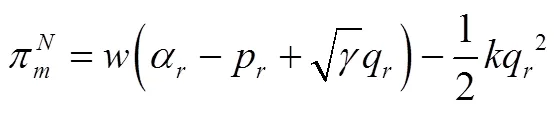
结合式(2)和式(7),得到制造商不入侵时零售商的利润如下:
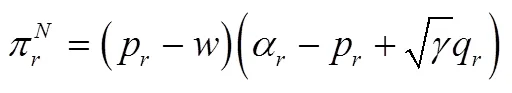
将式(9)和式(10)代入式(8),整理得到零售商存在公平敏感性时的效用如下:

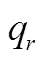


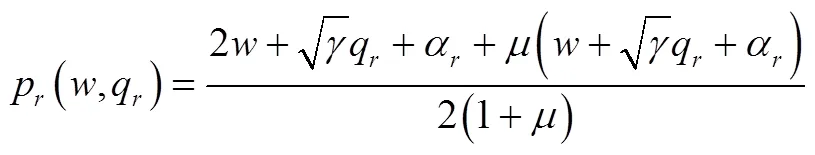
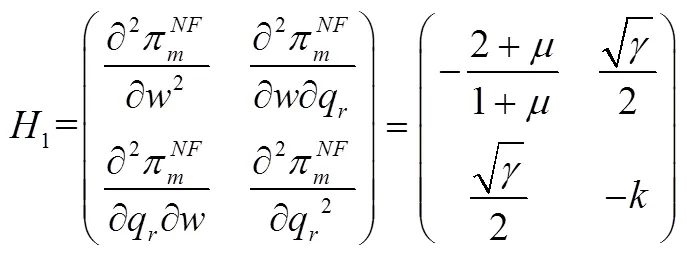
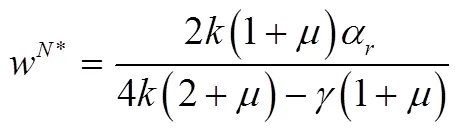

将式(13)和式(14)代入式(12)得到最优零售渠道价格:

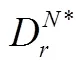
2.2 制造商同质产品入侵模型
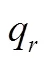

结合式(4)和式(7),得到制造商同质产品入侵时的零售商利润如下:

将式(16)和式(17)代入式(8),整理得到制造商同质产品入侵时零售商的效用如下:
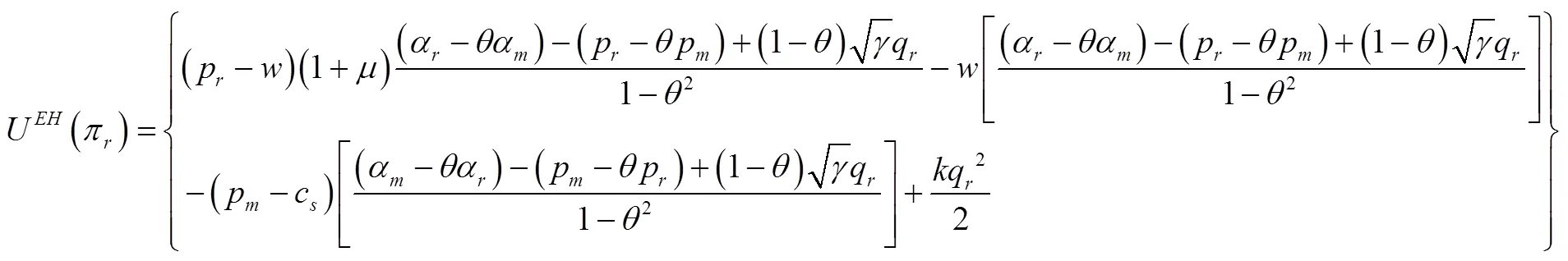
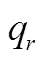


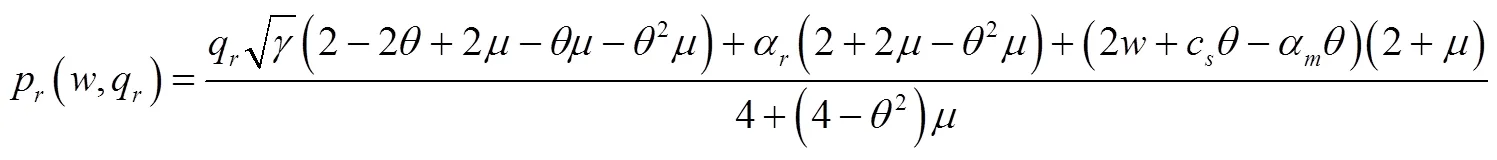




将式(21)和式(22)代入式(19)和式(20)中得到:

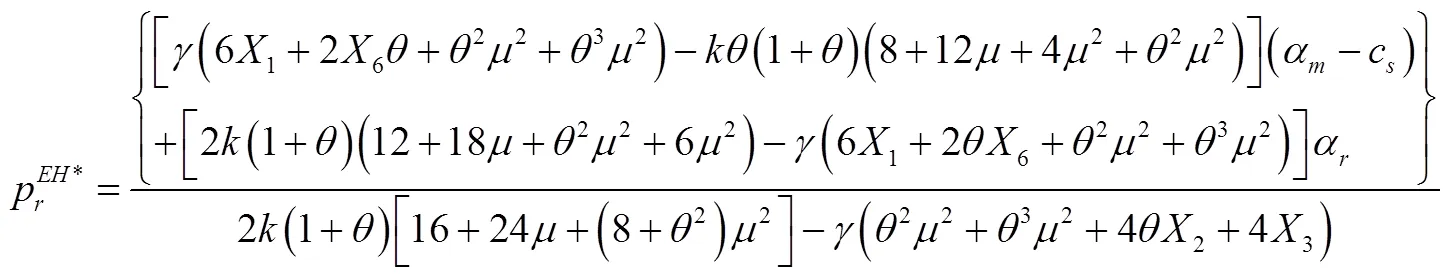
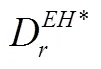
在研究制造商同质产品入侵情形时,需要保证直销渠道数量和零售渠道数量同时大于0,即需要满足以下条件:

2.3 制造商异质产品入侵模型
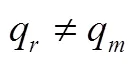

结合式(4)和(7),得到制造商异质产品入侵时零售商的利润如下:

将式(26)和式(27)代入式(8),整理后得到零售商的效用如下:
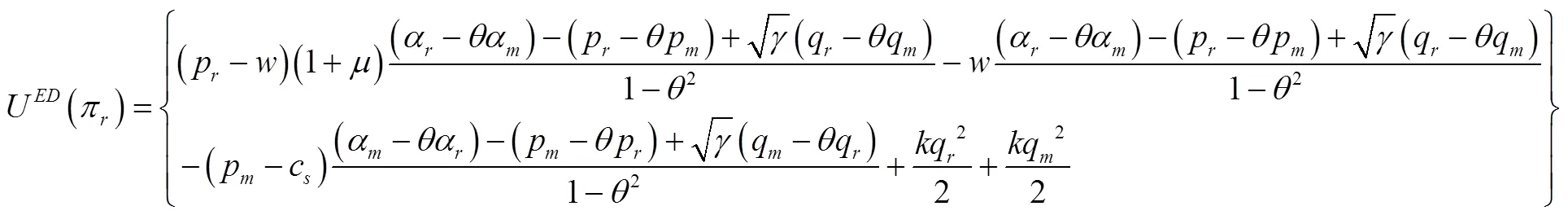




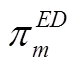
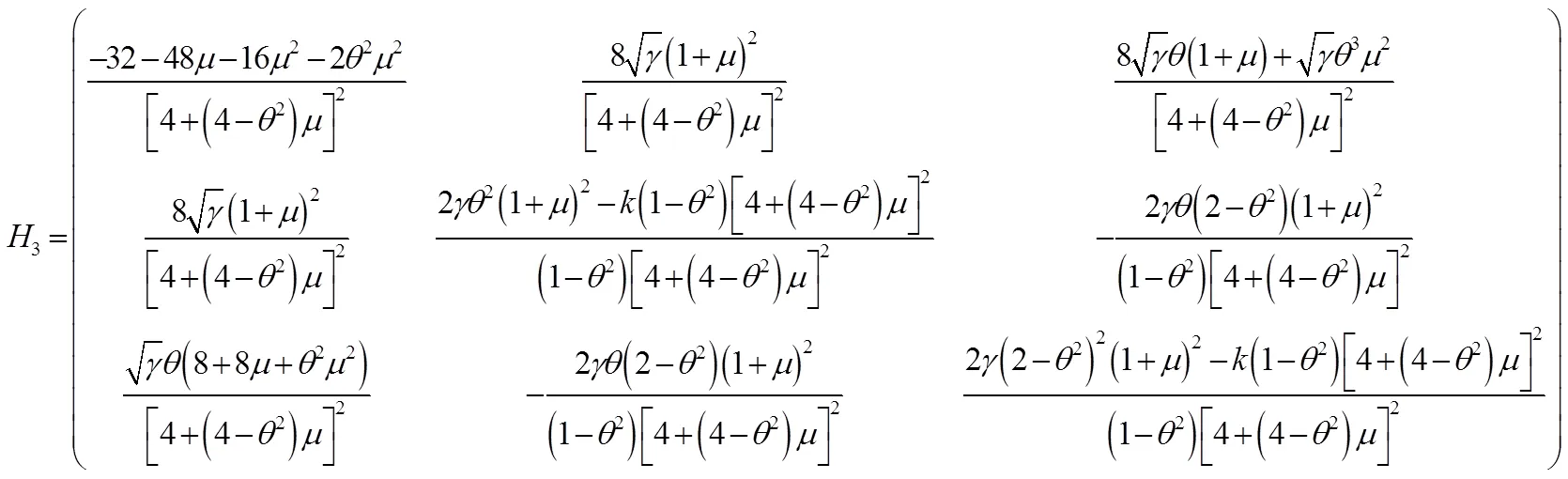
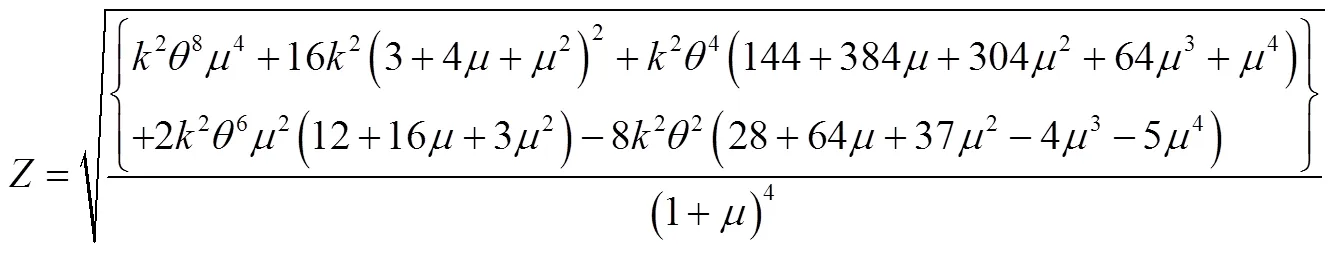
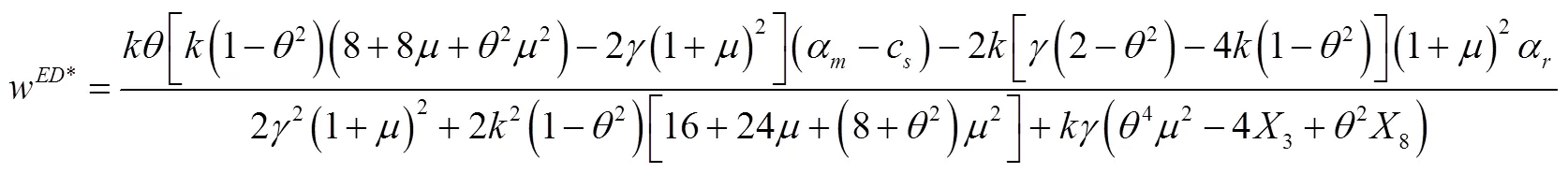
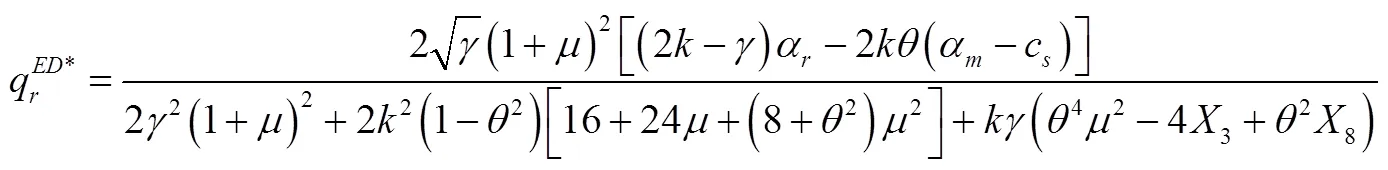
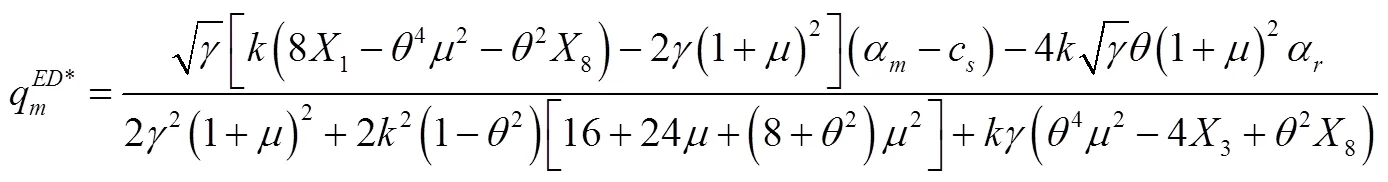
将式(31)至式(33)代入式(29)和式(30)中得到:


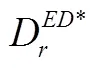
在研究制造商异质产品入侵情形时,需要保证直销渠道数量和零售渠道数量同时大于0,即需要满足以下条件:
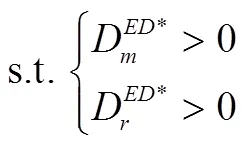
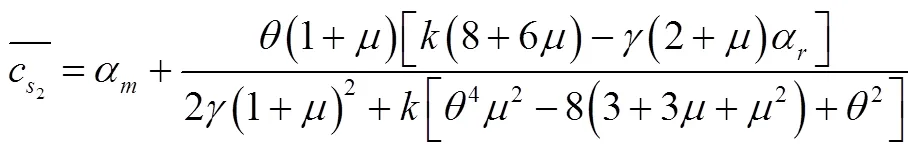
3 算例仿真与分析

(1)零售商公平敏感性对均衡结果的影响

Figure2 The relationship between the equilibrium results and the retailer's equity sensitivity coefficient
(2)直销渠道单位销售成本对制造商利润、零售商效用的影响
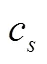
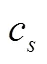
综上所述,制造商利润和零售商效用与直销渠道单位销售成本有关,当直销渠道单位销售成本在一定范围内,且零售商为特定类型时(同质产品入侵情形时自负型、自信型和自卑型;异质产品入侵情形时仅自卑型),入侵可以实现制造商和零售商利润(效用)帕累托改善。

Figure3 The relationship between manufacturer and retailer profit (utility) and unit cost of sales in direct selling channels
4 结论
本文构建了由一个制造商和一个零售商组成的二级供应链制造商入侵模型,研究了制造商的入侵决策以及零售商公平敏感性对供应链节点企业决策和供应链系统收益的影响,得到如下结论:(1)入侵总能使制造商利润增加;在一定条件下,入侵也能使零售商获利,使双方利润(效用)实现帕累托改善;(2)异质产品入侵优于同质产品入侵,制造商开辟直销渠道并在直销渠道和零售渠道销售质量存在差异的产品能使其获得更高的利润;(3)制造商与自卑型零售商合作比与自负型零售商合作更有利,制造商与自卑型零售商合作能获得较高的利润,也比较容易实现双方利润(效用)帕累托改善,缓解入侵带来的竞争压力。
本文所构建的模型和分析得到的管理启示对相关企业具有指导意义。然而本文的研究也存在一定的不足之处,比如本文只考虑供应链成员中处于弱势地位的零售商具有公平敏感性,在未来的研究中可以考虑制造商也具有公平敏感性,研究当制造商和零售商同时具有公平敏感性时对制造商入侵决策以及供应链系统的影响。另一方面本文在模型的构建过程中,只考虑了单一制造商和单一零售商的情况,在接下来的研究中可以探讨多个制造商或者多个零售商竞争的情况,研究竞争情形下的入侵问题。
[1] Li Z, Gilbert S M, Lai G. Supplier encroachment under asymmetric information[J]. Management Science, 2014, 60(2): 449-462.
[2] Arya A, Mittendorf B, Sappington D E M. The bright side of supplier encroachment[J]. Marketing Science, 2007, 26(5): 651-659.
[3] Albert H, Long X, Nasiry J. Quality in supply chain encroachment[J]. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 2015, 18(2): 280-298.
[4] Yoon D H. Supplier encroachment and investment spillovers[J]. Production & Operations Management, 2016, 25(11): 1839-1854.
[5] Li Z, Gilbert S M, Lai G. Supplier encroachment as an enhancement or a hindrance to nonlinear pricing[J]. Production & Operations Management, 2012, 24(1): 89-109.
[6] Chen P, Li B, Jiang Y, et al. The Impact of manufacturer’s direct sales and cost information asymmetry in a dual-channel supply chain with a risk-averse retailer[J]. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 2017, 21(1): 47-70.
[7] Li T, Xie J, Zhao X, et al. On supplier encroachment with retailer’s fairness concerns[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2016, 98: 499-512.
[8] Li G, Zhou Y. Strategically decentralise when encroaching on a dominant supplier[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2016, 54(10): 2989-3005.
[9] Chung H L, Lin Y S, Hu J L. Bundling strategy and product differentiation[J]. Journal of Economics, 2013, 108(3): 207-229.
[10] Jayaswal S, Jewkes E, Ray S. Product differentiation and operations strategy in a capacitated environment[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 210(3): 716-728.
[11] 刘家国, 周学龙, 赵金楼. 基于产品质量差异的闭环供应链定价策略与协调研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2013(s2): 426-431.
Liu J G, Zhou X l, Zhao J l. Study on Price Decision and Coordination of Closed-loop Supply Chain Based on Quality Difference of Product[J] .Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2013(s2): 426-431.
[12] Chen J, Liang L, Yao D Q, et al. Price and quality decisions in dual-channel supply chains[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 259(3): 935-948.
[13] Scheer L K, Kumar N, Steenkamp J B E M. Reactions to perceived inequity in U.S. and Dutch interorganizational relationships[J]. Academy of Management Journal, 2003, 46(3): 303-316.
[14] Huseman R C, Hatfield J D, Miles E W. A new perspective on equity theory: The equity sensitivity construct[J]. Academy of Management Review, 1987, 12(2): 222-234.
[15] Miles E W, Hatfield J D, Huseman R C. Equity sensitivity and outcome importance[J]. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 2010, 15(7): 585-596.
[16] Allen R S, Takeda M, White C S. Cross-cultural equity sensitivity: A test of differences between the United States and Japan[J]. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 2005, 20(8): 641-662.
[17] Clark L A, Foote D A, Clark W R, et al. Equity sensitivity: A triadic measure and outcome/input perspectives[J]. Journal of Managerial Issues, 2010, 22(3): 286-305.
[18] Fehr E, Schmidt K M. A Theory of Fairness, Competition, and Cooperation[J].Quarterly Journal of Economics, 1999, 114(3): 817-868
[19] Cai G. Channel selection and coordination in dual-channel supply chains[J]. Journal of Retailing, 2010, 86(1): 22-36.
[20] Liu B, Cai G, Tsay A A. Advertising in asymmetric competing supply chains[J]. Production & Operations Management, 2015, 23(11): 1845-1858.
[21] Wu H, Cai G, Chen J, et al. Online manufacturer referral to heterogeneous retailers[J]. Production & Operations Management, 2015, 24(11): 1768-1782.
[22] Kaya M, Özalp Özer. Quality risk in outsourcing: Noncontractible product quality and private quality cost information[J]. Naval Research Logistics, 2009, 56(7): 669-685.
[23] Gurnani H, Erkoc M. Supply contracts in manufacturer-retailer interactions with manufacturer-quality and retailer effort-induced demand[J]. Naval Research Logistics, 2008, 55(3): 200-217.
[24] 王先甲, 张柳波, 关旭,等. 道德风险模型中代理人公平敏感性对契约影响[J]. 管理科学学报, 2016, 19(8): 21-31.
Wang X J, Zhang L B, Guan X, et al.Impact caused by agents’ equity sensitivity in the moral risk model[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2016, 19(8): 21-31.
Research on manufacturers encroachment decision-making considering quality difference of products
ZHANG Cuihua, LI Huisi
(School of Business and Administration, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China)
Competition between retail channels has existed for a long time. This competition is regarded as a positive economic force. However, competition in the form of manufacturer encroachment has not been widely accepted by retailers. Most retailers consider manufacturer encroachment as more of a threat. In order to avoid direct conflicts with retailers, many manufacturers have terminated their sales in direct sales channels. From this perspective, it is necessary to study the issue of manufacturer encroachment, whether manufacturers should encroach, and what impact manufacturer encroachment has on the supply chain system.
This paper considers two types of manufacturer encroachment, that of homogeneous products and that of heterogeneous products, where retailers have equity sensitivity. This paper also studies the optimal encroachment decisions of manufacturers and the impact of the equity sensitivity of retailers on the decision-making of supply chain members and the revenue of supply chain system. In comparison to existing research, this paper assumes that product quality is an endogenous variable, and based on this assumption proposes two different scenarios: homogeneous product encroachment and heterogeneous product encroachment. In addition, this paper introduces equity sensitivity theory into the issue of manufacturer encroachment and discusses the impact of the equity sensitivity of retailers on product quality, product wholesale price, retail channel price, direct sales channel price, retailer utility, and manufacturer profit.
In this paper, a two-layer chain consisting of a manufacturer and a retailer is used as an example. First, models of non-encroachment by manufacturers, homogeneous product encroachment by manufacturers, and heterogeneous product encroachment by manufacturers are established. Then, game theory and related analytical methods are applied to the above models, and the equilibrium solution of the Stackelberg-Nash game theory for the manufacturer and the retailer is obtained. Finally, an example simulation analysis is performed on the equilibrium result to obtain relevant conclusions.
The research results show that: (1) Encroachment will always increase the profit of the manufacturer; (2) The profit of the manufacturer and the utility of the retailer are related to the unit sales cost of the direct sales channel. When the unit sales cost of the direct sales channel is within a certain range, and the retailer is of a specific type (conceited, self-confident, or inferior in the case of encroachment of homogeneous products, or inferior in the case of encroachment of heterogeneous products), encroachment can achieve a Pareto improvement in profits (utility) of manufacturers and retailers; (3) Heterogeneous product encroachment is more effective than homogeneous product encroachment. Manufacturers open up direct sales channels and sell products with different qualities in the direct sales and retail channels to generate more profit; (4) Co-operation between manufacturers and inferior retailers is more profitable compared to co-operation between manufacturers and conceited retailers. Manufacturers will co-operate with inferior retailers to obtain higher profits, and it is easier to achieve a Pareto improvement in the profit (utility) of both parties, alleviating competitive pressure brought about by encroachment.
The model constructed in this paper and the management insights obtained from its analysis have guiding significance for related enterprises, but this research also has certain shortcomings. Future steps should include exploring the impact of the equity sensitivity of manufacturers and retailers on the decision-making process of manufacturer encroachment and the revenue of the supply chain system; encroachment in scenarios of competition between multiple manufacturers or multiple retailers should also be studied.
Manufacturers encroachment; Quality difference; Quality sensitive; Equity sensitivity; Stackelberg-Nash game
2018-01-25
2018-05-12
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (71371043, 71771044)
F274
A
1004-6062(2020)04-0161-010
10.13587/j.cnki.jieem.2020.04.018
2018-01-25
2018-05-12
国家自然科学基金资助项目(71371043、71771044)
张翠华(1971—),女,辽宁沈阳人;东北大学工商管理学院教授,博士;主要从事供应链质量控制研究。
中文编辑:杜 健;英文编辑:Boping Yan
