网络脆弱性及网络空间供应链安全弹性投资协调机制
2020-09-09张子健
张子健,李 傲
网络脆弱性及网络空间供应链安全弹性投资协调机制
张子健,李 傲
(重庆交通大学 经济与管理学院,重庆 400074)
网络空间供应链中企业的安全水平是受自身对网络安全的投入、网络脆弱性和相关联企业在网络安全方面的投入等多因素的影响。本研究首先讨论了分散决策下在网络脆弱性影响下,供应商和零售商成员网络安全弹性的投资策略选择,在此基础上分析了网络脆弱性、关联企业在网络安全方面的投入、对企业安全投资水平的影响。其次,在合作博弈情形下推导出供应商和零售商的最优投资策略,分析两种情形下的博弈,得出企业在非合作博弈下的网络安全投资不足。最后设计一种协调补偿机制形成网络投资不足问题,促使供应链整体的安全弹性投资水平最优。
网络空间供应链;网络脆弱性;安全弹性;协调机制
0 引言
互联网络下的供应链近些年已经变得越来越脆弱,一些引人注目的网络攻击事件瘫痪了知名大公司的供应链,揭示出黑客的进入常常是针对供应链间连接的薄弱环节。美国信息安全论坛(Information Security Forum)2013年所发布的研究报告显示,企业组织所遭遇的数据安全破坏有40%以上是来自于其供应商所形成的攻击[1]。网络犯罪者越来越意识到“这是能够进行网络攻击的有效渠道”[1]。不断增加的复杂性以及对供应链可视化要求的提升,更加恶化了这一情况。供应链的本质要求企业与其合作伙伴之间交换敏感信息,整个供应链中,零售商、供应商、第三方物流公司等对信息数据保护的能力高度不同,互联网窃贼常常会利用最薄弱的环节,即利用网络脆弱点展开攻击。而就互联网风险而言,不断增加的对互联网的依赖性导致在一个网络中的供应商数量不断增加,因此这又增加了组织间连接的数量(Dederick et al., 2008)[2],这些链接增加了网络脆弱性,为网络攻击提供了温床并且以此来进行对网络中其他部分的攻击。基于此,业界与研究者将此类由关键信息组件和服务所构成的供应链定义为“网络空间供应链(Cyber Supply Chain)”,意指整个网络空间的关键成员,包括系统终端使用者、信息供应商、系统整合商、政策制定者,这些成员在所构成的供应链组织及流程层面交互计划、建设、管理、维系并保护网络空间[3,4]。对其安全管理的专门研究领域“网络空间供应链安全(Cyber Supply Chain Security)”也正在快速形成(Boyson et al., 2009;Linton et al., 2014;Bartol,2014)[5-7],致力于通过系统终端使用者、信息供应商、系统整合商以及政策制定者共同治理和维护网络安全,实现网络空间供应链各环节的安全性和可控性。
企业必须对供应链能力进行投资以抵抗来自互联网的攻击,也即增加网络安全弹性(cyber-resilience)以应对潜在的威胁。这一并不常常被讨论的风险方向是一种“新常态”,引起信息安全、供应链管理、风险管理等领域学者们的高度关注。Amin等[6]研究表明这些自我防御方法在一定范围上是有效的,但是网络安全不仅仅是一个简单的技术问题,更是涉及多个主体间互相影响的复杂管理问题。Gordon和Loeb[8]率先利用经济学模型将信息系统的防御措施和脆弱性看作一个整体,通过两类典型的S(z,v)函数对投资水平和潜在损失进行比较,发现最优的投资水平不应超过潜在损失的36.79%。Kunreuther和Heal[9]运用博弈论研究相互关联企业的安全投资纳什均衡,分析了罚款、保险、第三方检查等外部机制对安全投资的影响。孙薇等[10]研究只具有有限理性的投资主体,采用演化博弈论分析了企业的信息安全投资问题,得出组织策略选择的关键是投资成本的大小。常诗雨[11]用演化博弈理论对网络安全攻防进行建模,考虑加入第三方动态惩罚对攻防博弈模型的影响,结果表明加入第三方动态惩罚因素有利于整个网络的安全。吕俊杰等[12]以企业间的病毒传染为例,指出网络安全风险的一个重要特征是相互依赖性,从而影响企业间的网络安全投资决策,并提出了企业间安全的投资博弈模型,确定了多个企业进行投资的纳什均衡。潘崇霞[13]研究在投资正外部性效应和负外部性效应下两个相互关联企业以及多个相关联企业的网络安全投资博弈,根据两种情况下的差异,对企业的网络安全投资策略提出建议。Zhuang[14]研究指出在多个相互关联的企业中,缺乏战略视角企业的存在使得供应链中其他企业不愿意进行安全投资。然而,关于企业网络系统安全存在的负外部性以及如何进行协调等问题却很少引起了研究者的关注。周诚等[15]针对网络脆弱性分析理论与脆弱性评分技术进行分析,设计出一种更能反映实际情况的脆弱性评分方法,保证了脆弱点的多样性,实现对网络脆弱性的最优评分。Shetty等[16]的研究表明企业遭受黑客入侵造成损失的概率不但受企业自身安全水平的影响,企业所处的网络环境的安全水平也会对其产生影响,每个企业因为没有考虑自身策略的真实社会成本而导致投资不足,这就产生了所谓的负外部性。Bakshi等[17]研究运用讨价还价理论研究了不对称信息下供应商和零售商在供应链安全投资上的竞争合作,但是忽略了网络脆弱性对企业网络安全投资的影响。顾建强等[18]考虑存在负外部性的前提下的设计一种网络安全保险投资激励机制,以改善企业的安全水平并提高社会福利。Nagurney等[19]建立了一个关于零售商网络安全投资的博弈理论框架,考虑消费者的偏好取决于产品的需求量和整条供应链的平均安全水平,将纳什均衡条件转化为变分不等式问题,揭示均衡产品交易、安全性水准、产品价格、期望利润、零售商脆弱性、网络脆弱性之间的影响。
网络空间供应链安全水平取决于安全的最薄弱环节,不仅需要企业自身在安全技术与安全意识的提高,更需要在整个网络空间供应链中通过协同合作形成共同治理来实现,从而实现整体安全水平提升。利用网络脆弱性进行攻击形成的破坏已持续对经济与社会造成巨大负面影响,因此,供应链视角下分析网络安全弹性投资决策过程并建立合作协调机制是非常必要的。过去研究对于供应链中影响网络安全弹性的分析还比较孤立,缺少贯穿整个网络空间供应链安全弹性建设的内在关联与生成机理系统分析;同时以提升网络空间供应链整体安全保护的研究也较为缺乏,整个供应链安全风险控制的协调机制和共同治理策略需进一步深入研究。基于此,本文基于网络脆弱性,建立一个包括供应链与零售商的两层的供应链博弈理论模型,分析供应链中的网络安全弹性投资决策问题,对比分析供应链分散决策和集中决策两种情形,并在此基础上建立供应链合作协调机制,为供应链在网络安全弹性方面的建设提供决策理论依据。
1 模型
1.1 基本假设与描述
考虑一个上游供应商及下游零售商所构成的二元网络空间供应链,供应链中两个企业通过网络相互连接。外部网络攻击者可以直接或间接(即先通过入侵系统相联企业,再以此为基,通过网络系统入侵到目标企业)入侵供应链信息体系并获取经济利益。为了提高网络系统安全,需要通过安全投资来增加供应链的网络安全弹性并减少网络安全漏洞,从而降低被外部入侵概率并减少网络损失。文章假设如下:
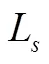

1.2 模型
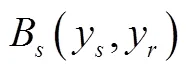

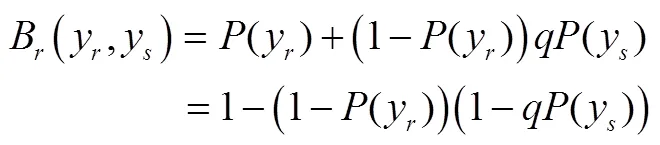


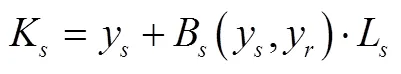

2 网络空间供应链的安全弹性投资决策
2.1 供应链分散决策
分散决策情形下,网络空间供应链中安全弹性投资决策为非合作博弈,以最大化供应商或零售商自身利益为目标。供应商与零售商在网络安全弹性投资水平上同时决策且独立确定自身企业的最优网络安全弹性投资策略,两个企业目标的是投资总成本最小化,且双方目标成本函数分别为:
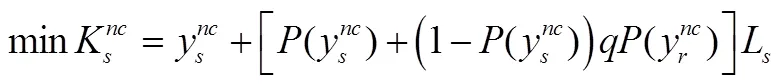

分别对式(7)和式(8)求其一阶条件为:
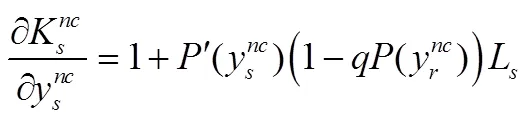



联立式(11)和式(12)求解得到:
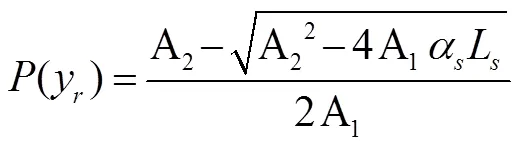

由式(13)、(14)可得:
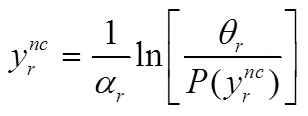

命题1揭示了网络脆弱性对供应链成员进行网络安全弹性投资激励的消极影响,即网络脆弱性越高供应链成员受到其合作伙伴信息不安全的影响越大,这又一定程度上抑制了其对自身安全弹性的投资,导致供应链中遭受损失的概率越大。值得注意的是成员增加自身网络安全弹性投资水平并不能消除其遭受间接破坏的概率,因此企业可能会降低自身的网络安全弹性投资水平,继而加剧了网络空间供应链的安全风险。这个结果类似于公共产品相关研究的“搭便车”。在信息安全背景下当两个相互关联的企业面临相同的入侵概率时,当其中一个企业选择进行安全投资,而另一个企业就会存在“搭便车”行为。

2.2 供应链集中决策
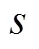
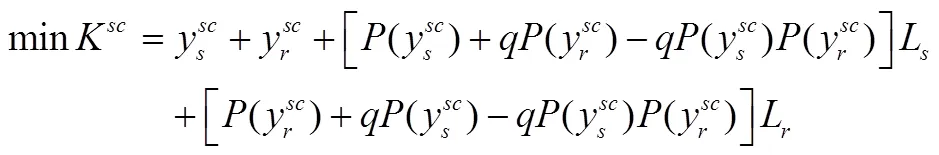
对式(17)求其一阶条件为:
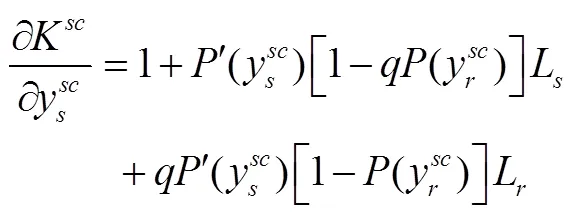



联立式(20)和式(21)求解得到:

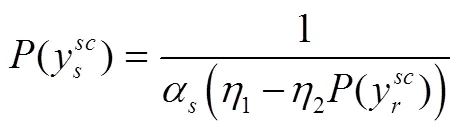
由式(22)、式(23)可得:


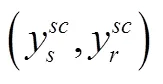
命题3 集中决策情形下,供应链成员的网络安全弹性投资水平表现为:

命题4 分散决策情形下,网络脆弱性影响下供应商和零售商对网络安全弹性的投资不足。
证明:由式(8)、式(9)可知:
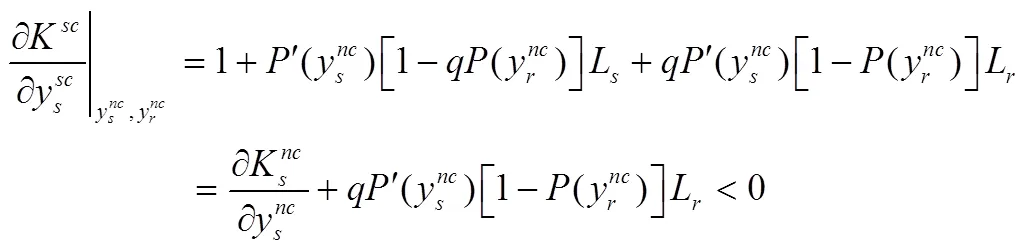
证毕。
命题4说明,在分散决策情形下,如果供应链成员供应商和零售商提高其网络安全弹性投资水平,那么遭受直接损失或间接损失的可能性就会降低,同时从供应商(零售商)的网络安全系统转而入侵零售商(供应商)的网络安全系统的概率也会降低。然而在分散决策情形下,企业在进行网络安全弹性投资时不会考虑增加投资给其他企业带来的正外部性影响,所以相对于集中决策情形,分散决策情形导致供应链中网络安全弹性投资不足。
3 合作协调机制
合作协调机制的模型描述如下:

(3)在博弈过程中零售商首先给出网络安全弹性投资策略,一旦供应商接受或拒绝这个策略,博弈马上结束。
(4)博弈过程中没有交易成本且零售商对供应商的成本函数具有完全信息。
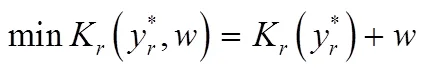
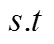

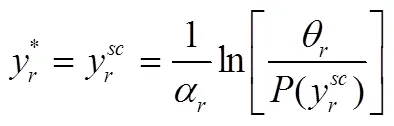


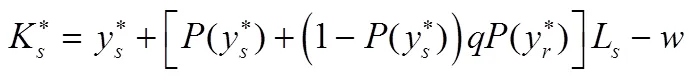


4 数值分析
现实环境下,网络空间供应链中网络脆弱性及其网络安全水平的评估与量化相对复杂,加之本文的目的是将网络脆弱性作为连续变量来分析其对供应链安全弹性投资的影响,在数据采集上存在困难。鉴于此,本文采取数值模拟方法来研究网络脆弱性对供应链企业建立网络安全性的投资决策影响。通过数值模拟,分别分析随网络脆弱性变动情况下,供应链成员网络安全弹性投资水平以及投资成本的变化情况,从而刻画网络脆弱性对供应链中企业信息安全投资决策所产生的影响。
4.1 网络脆弱性对投资水平的影响

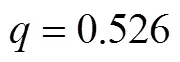

图1 网络脆弱性对供应商安全投资水平的影响
Figure 1 Impact of network vulnerability on supplier's security investment level

图2 网络脆弱性对零售商安全投资水平的影响
Figure 2 Impact of network vulnerability on retailer's security investment level
对比图1和图2可以看出合作博弈下相对于供应商来说零售商维持较高的投资水平。在非合作博弈中供应链网络脆弱性对零售商和供应商的网络安全弹性投资的影响是负面的,因为随着供应链网络脆弱性的增加,零售商和供应商进行网络安全弹性投资的边际收益是减少的,从而导致双方减少网络安全弹性投资水平。
4.2 网络脆弱性对供应链投资成本的影响

图3 网络脆弱性对供应商总成本的影响
Figure 3 Impact of network vulnerability on supplier's total cost

图4 网络脆弱性对零售商总成本的影响
Figure 4 Impact of network vulnerability on retailer's total cost



图5 网络脆弱性对转移支付的影响
Figure 5 Impact of network vulnerability on transfer payments

5 结语
本文基于网络脆弱性研究供应链成员在面对网络安全风险的安全弹性投资过程,分析了供应链中网络安全弹性建设的分散决策过程以及集中决策过程,并据此提出了供应链网络安全弹性投资的合作协调机制。研究结论主要包括,在分散决策情形中,零售商和供应商的网络安全弹性投资水平随着网络脆弱性的增加而降低,且在网络安全弹性投资过程两个企业的安全投资存在不足。在集中决策中,当企业遭受损失的概率大于自身遭受损失与供应链整体损失的比值时,企业处于相对不安全环境中,供应链成员的网络安全弹性投资水平随着网络脆弱性的增加而降低,当企业遭受损失的概率小于自身遭受损失与供应链整体损失的比值时,企业处于相对安全环境中,供应链成员的网络安全弹性投资水平随着网络脆弱性的增加而增加,且供应链的总网络安全弹性投资成本低于非合作博弈。在协调机制中,提出通过一个合理的转移支付补偿来激励企业在网络安全弹性建设方面的投资。未来对此问题的进一步深入研究可以考虑两个以上供应链成员在考虑网络脆弱性情形下如何实现激励机制以达到供应链总体网络安全弹性最优,或者在二元供应链基础上进一步考虑多成员之间的网络安全弹性投资博弈,设计出实现多个企业面临入侵情形下的激励协调机制。
[1] Securing the Supply Chain: Preventing your suppliers’ vulnerabilities from becoming your own[R].Information Security Forum(ISF), 2013.
[2] Cavusoglu H, Raghunathan S, Cavusoglu H. Configuration of and Interaction Between Information Security Technologies: The Case of Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems[J]. Information Systems Research, 2009, 20(2):198-217.
[3] Gao X, Zhong W, Mei S. A game-theory approach to configuration of detection software with decision errors[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2013, 119:35-43.
[4] Boyson S, Rossman H. Developing a cyber-supply chain assurance reference model [R]. Maryland: Supply Chain Management Center (SCMC), Robert H. Smith School of Business University of Maryland,2009.
[5] Linton J, Boyson S, Aje J. The challenge of cyber supply chain security to research and practice - An introduction [J]. Technovation, 34(7): 339-341.
[6] Bartol N. Cyber supply chain security practices DNA–filling in the puzzle using a diverse set of disciplines [J]. Technovation, 2014, 34 (7): 354–361.
[7] Amin S, Schwartz G A, Sastry S S. Security of interdependent and identical networked control systems[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(1): 186-192.
[8] Gordon L A, Loeb M P. The economics of information security investment[J]. Acm Transactions on Information & System Security, 2002, 5(4):438-457.
[9] Kunreuther H, Heal G. Interdependent security[J]. Journal of risk and uncertainty, 2003, 26(2-3): 231-249.
[10] 孙薇,孔祥维,何德全.信息安全投资的演化博弈分析[J]. 系统工程,2008,26(6):124-126.
Sun W, Kong X W, He D Q. Evolutionary game analysis of information security investment[J]. Systems Engineering, 2008,26(6): 124-126.
[11] 常诗雨,宋礼鹏. 基于演化博弈论的网络安全投资策略分析[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2017,38(03):611-615.
Chang S Y, Song L P. Analysis of network security investment strategy based on evolutionary game theory[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2017, 38(03):611-615.
[12] 吕俊杰,邱菀华,王元卓. 基于相互依赖性的信息安全投资博弈[J].中国管理科学,2006,14(03):7-12.
LV J J, Qiu W H, Wang Y Z. An Analysis of Games of Information Security Investment Based on Interdependent Security[J].Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2006,14(03):7-12.
[13] 潘崇霞. 相互关联性与投资外部性对网络安全投资策略的影响[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(社会科学版),2017,27(01):1-8.
Pan C X . Effects of Interconnectedness and Externality on Network Security Investment Strategy[J].Journal of Xidian University(Social Science Edition), 2017,27(01):1-8.
[14] Jun Zhuang. Impacts of Subsidized Security on Stability and Total Social Costs of Equilibrium Solutions in an N-Player Game with
Errors[J]. Engineering Economist, 2010, 55(2):131-149.
[15] 周诚, 李伟伟, 莫璇等. 一种网络安全脆弱性评估方法[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(01): 68-77.
Zhou C, Li W W, Mo X, et al. A assessment method of network security vulnerability[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2017,38(01): 68-77.
[16] Shetty N, Schwartz G, Walrand J.Can competitive insurers improve network security?[C]International Conference on Trust and Trustworthy Computing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2010: 308-322.
[17] Bakshi N, Kleindorfer P. Co-opetition and Investment for Supply- Chain Resilience[J]. Production & Operations Management, 2009, 18(6):583–603.
[18] 顾建强,梅姝娥,仲伟俊. 基于网络安全保险的信息系统安全投资激励机制[J]. 系统工程理论与实践,2015,35(4):1057-1062.
Gu J Q, Mei S E , Zhong W J. Cyber insurance as an incentive for information system security[J]. System Engineering Theory and Practice, 2015, 35(4): 1057-1062.
[19] Nagurney A, Nagurney L S, Shukla S. A supply chain game theory framework for cybersecurity investments under network vulnerability[M]. Computation, cryptography, and network security.Springer International Publishing, 2015: 381-398.
Network vulnerability and the coordination mechanism of cyber supply chain security resilience investment
ZHANG Zijian, LI Ao
(School of economics and management, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing 400074, China)
Enterprise network security level under the Internet depends not only on its network security investment but also on many other factors such as the supply chain network vulnerability and the investment in network security. In the cyber supply chain, the network data protection ability of suppliers, retailers, and third-party logistics companies are profoundly different, and internet hackers often use the weakest link as the network attacking vulnerable point. Key members in the whole cyberspace need to plan, construct, manage, and maintain interactively in the supply chain organization and process level against attacks from the Internet.
This paper considers a binary cyber supply chain consisting of an upstream supplier and a downstream retailer. The two enterprises in the supply chain connect through the Internet. The network hacker can compromise the supply chain system directly. Alternatively, the network hackers can invade the enterprise associated with the supply chain. Hackers can also indirectly invade the information system of the supply chain through the network system and gain economic benefits from the targeted enterprises. It is necessary to increase cybersecurity resilience and reduce cyber vulnerability in the supply chain through security investment to improve cybersecurity. As a result, the probability of external intrusion and reduce network loss can be reduced. In this context, this paper discusses the decentralized decision-making and centralized decision-making processes of the supply chain under the influence of cyber vulnerability. It establishes the coordination mechanism in the supply chain.
Our proposed model assumes that once the information system of the supply chain is damaged, the supplier and the retailer will afford certain losses, and that will come from direct losses and indirect losses, respectively. The probability of direct loss of supplier or retailer depends on their investment level of cybersecurity resilience, and the probability function is a second-order differentiable convex function. The function shows that the probability of direct loss decreases with the increase of cybersecurity investment, but its effect is marginal decrease. As for the indirect loss, the model assumes that the probability of the indirect invasion to the supplier or retailer is constant. The constant is the vulnerability of the network location of the supplier or retailer. On this basis, the expected cost function of suppliers and retailers is established in the case of the cybersecurity resilience investment of each member.
In the first part, the decentralized model discusses the choice of investment strategies for the cybersecurity resilience of the supplier and the retailer in the case of decentralized decision-making of supply chains. With decentralized decision-making, the decision of security resilience investment in the cyber supply chain is a non-cooperative game to maximize the interests of the supplier or the retailer itself. Based on this, it analyzes the influence of network vulnerability on the input of supply chain members and their affiliated enterprises in network security. The result shows that the level of cybersecurity resilience investment of the supplier and the retailer decreases with the cyber vulnerability and increases with each other in the supply chain.
In the second part, the centralized model discusses the investment decision-making process of the cybersecurity resilience of the supplier and the retailer under centralized decision-making. With centralized decision making, the supplier and the retailer can coordinate their investment level to improve the security investment level and optimize the overall cybersecurity investment of the supply chain.
In the third part, the comparative analysis compares the decentralized decision and centralized decision in the supply chain. It then establishes the transfer payment mechanism among the members of the supply chain to realize the coordination of the supply chain with the investment of security resilience,solving the double marginal effect of cybersecurity investment in the supply chain.
Finally, The numerical simulation analyzes the influence of cyber vulnerability on the investment decision of the supplier and the retailer. It respectively analyzes cases along with the change of cyber vulnerability, how the cybersecurity resilience investment levels and the investment cost change, as so to describe the influence of cyber vulnerability to security investment decisions in the supply chain.
Cyber supply chain(CSC); Network vulnerability; Security resilience; Coordination mechanism
2018-02-21
2018-06-25
Supported by the National Social Sciences Foundation of China(17BGL177)
F273
A
1004-6062(2020)05-0130-007
10.13587/j.cnki.jieem.2020.05.014
2018-02-21
2018-06-25
国家社会科学基金资助项目(17BGL177)
张子健(1976-),男,湖北荆州人;重庆交通大学经济与管理学院教授;研究方向:供应链管理,风险管理。
中文编辑:杜 健;英文编辑:Charlie C. Chen
