高通量小粒径种子流检测装置设计与试验
2020-08-12丁幼春王凯阳杜超群刘晓东陈礼源刘伟鹏
丁幼春,王凯阳,杜超群,刘晓东,陈礼源,刘伟鹏
高通量小粒径种子流检测装置设计与试验
丁幼春,王凯阳,杜超群,刘晓东,陈礼源,刘伟鹏
(1. 华中农业大学工学院,武汉 430070; 2. 农业农村部长江中下游农业装备重点实验室,武汉 430070)
针对油菜播种过程中因农艺要求增大播量以及高速播种产生的排种频率过高而导致高通量种子流检测精度不足的问题,提出了一种将高通量种子流分流为多路低通量种子流并行检测的方法,设计了基于分流机制与薄面激光-硅光电池结合的高通量小粒径种子流检测装置。考虑高通量种子流分流均匀性与快速通过性,对分流结构进行设计,运用离散元仿真软件EDEM及台架试验对处于不同倾斜角度的分流结构分流均匀性进行分析,当分流结构倾角小于5°时,分流管排量一致性变异系数的仿真与试验结果分别不超过5.19%和8.58%。基于薄面激光照射范围与落种区域,确定了薄面激光发射模组角度、上导种管出种口内半径以及薄面激光距硅光电池距离三者之间的关系,并优选得到三参数最佳组合。对4路种子输入信号进行调理,经电容滤波、双级放大、半波整流、电压比较、单稳态触发处理,成为4路独立可供单片机捕捉的脉冲信号。高通量小粒径种子流检测装置台架试验表明:在排种频率61.68 Hz范围内,油菜种子检测准确率不低于96.1%。田间试验结果表明:在田间排种频率62.23 Hz范围内,检测准确率不低于95.7%,且试验过程中无堵塞现象发生,田间正常光照、机具振动对装置检测精度无影响。
农业机械;设计;试验;分流结构;高通量;小粒径;检测
0 引 言
油菜是中国分布最广,播种面积最大的油料作物[1],同时,随着相关生物技术改良,油菜油用、花用、菜用、蜜用、饲用等功能日益凸显[2]。油菜播种农艺要求随着播期的推迟,需要增加播量弥补出苗率的降低,另外随着播种机的作业速度提升,均需增加油菜排种器排种频率以满足播种密度需要。针对油菜等小粒径种子,当排种频率高于30 Hz时可以认为形成了高通量种子流。研究一种高通量小粒径种子流检测装置,实现油菜高频排种过程中的播量检测、漏播检测以及对实现播种智能化具有重要意义。
国外对大中粒径种子流检测技术研究较为成熟,并已实现部分播种检测装置的商业化。Kumar等[3]基于红外LED及嵌入式平台,设计了对射式种子流检测传感装置,将该装置安装于导种管之上,可对通过的小麦种子流进行实时检测。美国Precision Planting、John Deere,意大利MC ELECTRONICS公司[4-6]研制的基于声波与光电式种子流检测传感器,可对小麦、玉米、大豆等作物的排种总量、漏播率、播种面积等参数进行实时监测。上述国外播种监测装备价格昂贵,且主要配套在其各自生产的播种机具之上,对于中国播种机具兼容性较差,难以直接应用。
近年来,国内学者对播种检测装置研究日渐深入,和贤桃等[7-12]采用光电传感器,实现对玉米、小麦等作物播种作业时播量信息采集,可对播种作业质量进行实时监控。黄东岩等[13-17]通过采用压电薄膜、对射式红外检测传感器、光电传感器结合旋转编码器、变距光电传感器,能够实现对小麦、玉米、水稻等作物精量排种器排种性能的检测。周利明等[18-22]利用种子或肥料介电特性设计了基于电容信号的排种性能检测系统,能够实现玉米、水稻、棉籽或肥料的播量信息及相关颗粒含水率的在线检测,为变量播种、施肥提供参考。
油菜种子粒径小[23](0.8~2.2 mm),其通过传统大中粒径种子检测装置时产生的种子信号微弱不易被捕捉,另一方面检测盲区的存在降低了检测精度。李兆东等[24]采用对射式激光传感器,通过检测蔬菜种子排种盘型孔充种状态,开展精量排种器的漏充率与吸孔堵塞率测试。丁幼春等研制了基于压电薄膜油菜精量排种器种子流传感装置[25]和基于薄面激光-硅光电池的中小粒径种子流监测传感装置[26],在田间低通量排种状态下,检测准确率分别不低于99.1%和98.6%。在测试排种频率达62 Hz时,基于压电薄膜的种子流传感装置以及基于薄面激光-硅光电池种子流传感装置检测准确率不到85%。究其原因,在排种频率较高形成高通量种子流时,高通量种子流在传感装置内部发生碰撞、混叠概率提高,导致多粒种子同时穿越感应区概率增大,造成检测准确率降低。
为此,本文提出一种将高通量种子流分流为多路低通量种子流并行检测的思路,设计基于分流机制与薄面激光-硅光电池结合的高通量小粒径种子流检测装置,并进行性能测试。
1 工作原理
本文研究的高通量小粒径种子流检测传感装置对接于油菜精量集排器的某一行,其主要由分流结构、薄面激光发射模组、硅光电池、信号调理电路板等组成,如图1。油菜精量集排器排出的高通量种子流经过塑料导管进入到检测装置入种口,经过聚种漏斗聚集后的种子与分流锥盘碰撞,流入4支分流管中形成4支低通量种子流,4支低通量种子流独立穿越薄面激光层,因对激光的遮挡改变了照射在硅光电池表面的激光强度,继而硅光电池两端电压发生变化,对这种电压变化信号进行滤波、放大、整流、电压比较、单稳态触发等数字化处理,形成4路独立单脉冲序列,最终可成为单片机外部中断源,实现高通量种子流的计数,最后4路种子流再次汇聚由检测装置出种口排出。

1.信号调理电路板 2.电源指示灯 3.开关 4.锂电池 5.薄面激光发射模组 6.OLED显示屏 7.出种口 8.固定销 9.硅光电池卡槽 10.分流结构主体 11.装置外壳 12.入种口 10-1.聚种漏斗 10-2.分流管 10-3.上导种管 10-4.下导种管 10-5.分流锥盘 13.硅光电池 14.油菜种子
2 关键结构参数设计
高通量种子流一分为四,对4路低通量种子流进行并行检测,最终实现对高通量种子流计数。为保证检测装置检测准确率,应保证每一分流管内种子检测准确率较高,基于此,要求通过每一分流管内种子能快速通过且通过各分流管内种子数目差别不大。以分流均匀及快速通过为目标,对分流结构参数进行设计,包括入种口直径、聚种漏斗上端口直径、下端口直径、聚种漏斗高、分流锥盘底面直径、分流锥盘高度、分流管直径。为保证各分流管内油菜种子无盲区穿越薄面激光,对上导种管出种口尺寸、薄面激光发射模组发射角度、薄面激光距硅光电池距离参数进行确定。
2.1 分流结构设计
分流结构主要由聚种漏斗、分流锥盘、分流腔、分流管、入种口组成,如图2所示。
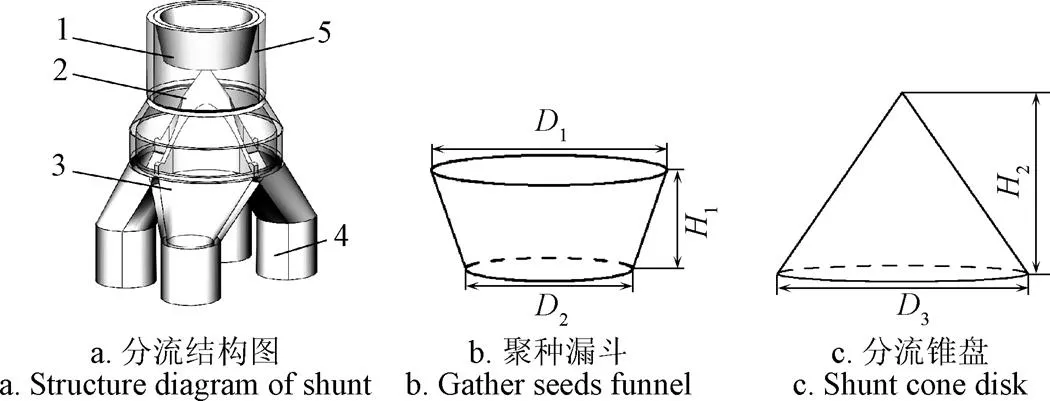
1.聚种漏斗 2.分流锥盘3.分流腔 4. 分流管 5. 入种口
1. Gather seeds funnel 2. Shunt cone disk 3. Shunt cavity 4. Shunt tube 5.Seeds entry
注:1为聚种漏斗上端口直径,mm;2为聚种漏斗下端口直径,mm;1为聚种漏斗高,mm;3为分流锥盘底面直径,mm;2为分流锥盘高度,mm。
Note:1is the diameter of the upper port of gather seeds funnel, mm;2is the diameter of the lower port of gather seeds funnel, mm;1is theheight of gather seeds funnel, mm;3is the diameter of the bottom surface of shunt cone disk, mm;2is the height of shunt cone disk, mm.
图2 分流结构示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of shunt structure
为方便将排种软管与检测装置入种口相连接,将入种口直径确定为20 mm,该尺寸可方便将排种软管套接到检测装置入种口。为保证高通量种子流进入入种口后能更好均分到4支分流管内,采取“先聚合,再分流”的设计思路,在入种口处设计聚种漏斗,聚种漏斗上端口直径1与入种口直径一致,为20 mm,为保证种子流均能与分流锥盘锥面碰撞且能较快速通过聚种漏斗,设计聚种漏斗下端口直径D为13 mm,高1为7.5 mm。为确保高通量种子流尽可能均匀进入4支分流管,且具有较好的流畅性,设计圆锥体结构作为分流结构,分流锥盘顶点与聚种漏斗下端面重合,这样可保证通过聚种漏斗汇集之后的种子流第一时间与分流锥盘发生碰撞,此时分流锥盘高度2为17.5 mm。为保证分流结构紧凑且能容纳4支分流管,设计分流锥盘底面直径3为24 mm。为使得种子在分流管不发生堵塞,设定分流管直径为10 mm。
2.2 上导种管出种口内径及薄面激光发射模组角度
为保证结构紧凑,采用一组薄面激光发射模组对应两块硅光电池,故整体装置需两组薄面激光发射模组4块硅光电池。一侧薄面激光发射模组、导种管与硅光电池安装示意图如图3a所示,另一侧安装布局同图3a一致。
为确定上导种管出种口内半径、薄面激光发射角度与薄面激光距硅光电池距离2,对图3b中的边角关系分析,得到如下方程组:


1.油菜种子 2.上导种管 3.硅光电池 4.薄面激光 5.薄面激光发射模组
1.Rapeseed 2.Upper seeds through tube 3.Silicon photocell 4.Thin surface laser 5.Thin surface laser emitting module
注:为处于同一薄面激光两上导种管轴心之间间距,mm;为薄面激光发射点;为理论上避免检测盲区出现的最小薄面激光发射模组发射角度,(°);为角度的一半,(°);2为薄面激光距硅光电池距离,mm;1为硅光电池对角线长度,14 mm;为硅光电池无感应区长度,4 mm;3、分别为对应三角形边长,mm;为避免检测盲区出现的最大上导种管出种口内径,mm。
Note:is the distance between the axes of the two upper seeds through tubes in the same thin laser, mm;is the thin surface laser emission point;is the emission angle of the smallest thin surface laser emitting module that avoids the detection of blind spots in theory, (°);is half of theangle, (°);2is the distance between the thin surface laser and the silicon photocell, mm;1is the diagonal length of the silicon photocell, 14 mm;is the length of the non-sense area of the silicon photocell, 4 mm;3,are respectively the length of the corresponding triangle side, mm;is the maximum inner diameter of the seed outlet of the upper seeds through tube to avoid detection of blind spots, mm.
图3 薄面激光发射模组几何模型
Fig.3 Geometry model of thin surface laser emission module
对该方程组进行求解,可得、、2三者关系如下
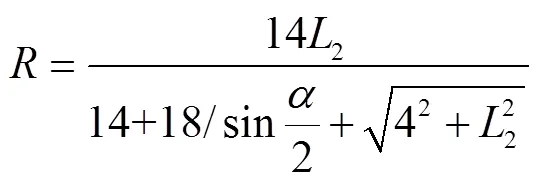
结合公式(2),绘制θ()、上导种管出种口内半径R、薄面激光距硅光电池距离L2 三者关系曲线,截取20°≤θ≤80°时的曲线如图4所示(当θ小于20°时,L2急剧变大,导致装置尺寸较大,故取θ≥20°;由于薄面激光发射模组加工工艺限制,薄面激光发射角度最大为160°,即α最大为160°,故θ最大不超过80°)。
从油菜种子在管道内的通过流畅性考虑,应保证上导种管出种口内半径尽可能大。为使得油菜种子通过上导种管出种口时不发生堵塞,应满足≥2(为油菜种子粒径,0.8≤≤2.2 mm),即最小为4.4 mm。另外,由于处于同一薄面激光的两上导种管轴心之间间距为12 mm,导管壁厚为1 mm,为防止两管道出现重叠,故上导种管出种口内半径应满足以下公式:
2(+1)≤12 (3)
由此确定取值为5 mm,此时对应为35.6°,则为71.2°,由于工艺限制(目前市场上售卖的薄面激光发射模组发射角度只有30°、60°、90°、120°等),并结合成本(发射角度越大成本越高),故选择发射角度为90°的薄面激光发射模组,此时薄面激光距硅光电池距离2=25 mm。
综上,对高通量小粒径种子流检测装置关键结构参数进行了确定,确定入种口直径20 mm,聚种漏斗上端口直径1为20 mm,下端出口直径2为13 mm,高1为7.5 mm,分流锥盘底面直径3为24 mm,高2为17.5 mm,分流管直径为10 mm,上导种管出种口内半径为5 mm,薄面激光发射模组发射角度为90°,薄面激光距硅光电池距离L为25 mm。
3 信号处理系统设计
3.1 4通道信号检测电路设计
为设计4通道信号检测电路,需对单通道种子信号进行分析,确保检测装置检测适应性。不同粒径油菜种子(0.8~2.2 mm)穿越薄面激光感应区域时,小粒径种子产生的穿越信号幅值小、历时短,大粒径种子产生的穿越信号幅值大、历时长。进行检测电路设计时,充分考虑检测电路对不同粒径种子的检测适应性。
单通道自然光条件下,薄面激光照射到硅光电池表面,会使硅光电池产生300 mV偏置电压,油菜种子通过薄面激光层时,由于对硅光电池产生遮挡,使硅光电池两端偏置电压瞬间减小,种子通过光层后,偏置电压恢复正常。通过测试得知,油菜种子下落产生的偏置电压变化范围为0.8~10 mV。为将此信号调理为单片机可处理的脉冲信号,需对该信号进行电容滤波、双级放大、半波整流、电压比较、单稳态触发处理,最终形成脉宽可控的方波信号,作为单片机中断源信号。
4路信号检测电路设计时,为确保幅值小的穿越信号能被放大至合适倍数,以最小粒径(0.8 mm)种子产生的穿越信号幅值为依据,开展电路放大环节设计,4路信号均经独立双级AD620N放大器放大至饱和,则大粒径种子信号也能满足放大要求;为确保历时长的穿越信号能被准确数字化,以最大粒径(2.2 mm)种子产生的穿越信号历时时间为依据,开展数字电路设计,充分发挥比较器LM393芯片功能,将其中两路放大信号接入同一LM393芯片,另外两路放大信号接入另一LM393芯片,通过调节接入两LM393芯片的4个504电位器阻值大小,确定比较电压;4路比较器输出的方波信号,进入2个74HC123单稳态触发器中,调节74HC123单稳态触发器外围电路参数,使得输入方波信号在单稳态触发器作用下形成可供单片机识别的脉冲信号,最大粒径种子穿越信号能被正确数字化,则也能够满足小粒径种子的正常检测,相关元件具体参数设置详见文献[26]。
与薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流检测装置的信号检测电路相比,本文研制的检测装置多出3路信号检测电路,且所有电路使用的电子元件均为常规元件,成本不会有较大增加;信号检测电路包含的滤波、放大、比较、单稳态处理等环节,相应电路都较为成熟,检测电路的检测可靠性可以保证。
3.2 4通道信号检测流程
经调理后的4路油菜种子流信号,分别接入MSP430F149单片机的4个引脚(分别为单片机引脚P4.1、P4.2、P4.3、P4.4),4路信号作为MSP430F149单片机定时器B1捕捉中断的外部中断源,对该中断进行触发,单片机通过对四路触发信号分别计数与求和,即可获得通过各通道种子数目及种子总数目,并将相关播种信息进行实时显示。烧录到单片机中的程序包括系统初始化、中断计数程序、显示程序等。
4 装置性能检验
依据上文确定的结构参数,运用3D打印,并集成电路处理系统等获得高通量小粒径种子流检测装置。为验证高通量小粒径种子流检测装置分流均匀性,开展仿真与台架试验。
同时开展与课题组前期研制的基于薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流检测装置准确率对比试验。利用数粒仪(模拟低通量排种)与离心式集排器(可产生高通量种子流)模拟油菜不同排种状态,检验两装置在油菜低通量、高通量排种条件下的检测准确率。为进一步评估高通量小粒径种子流检测装置在实际播种时的检测效果,开展田间试验。
4.1 分流均匀性检验
油菜籽粒表面光滑、流动性较好、球形度高,可定义为球状散粒体。在仿真时将颗粒简化为硬球模型,设置其直径为2 mm,千粒质量为4.68 g,泊松比为0.25,剪切模量为1.1×107Pa,密度为680 kg/m3,接触模型选用Hert-Mindlin无滑动接触模型[27]。为便于仿真分析,将分流后的油菜种子采用4个长方体空槽进行收集,图5所示为分流结构仿真模型。

图5 分流结构仿真模型
仿真试验时,设计颗粒生成总数为2 000粒,生成时间为30 s,期间种子均匀生成。结合实际播种情况,综合考虑田间状况以及机械自身浮动作用,田间状况引起的机器倾斜角度在5°以内[28],实际播种时排种器出种口距检测装置入种口约为40 cm,建立EDEM仿真模型,如图5(仿真试验时,按照图中所示编号记录各分流管通过的种子数目)。基于此对检测装置倾斜角度为0°和5°时开展EDEM仿真试验,每个角度进行3次仿真,分析其分流均匀性,利用分流管通过的种子排量一致性变异系数表征其分流效果优劣,变异系数越小,表明分流均匀性越好。
台架试验时,采用华油杂62油菜种子作为试验材料,平均粒径0.8~2.2 mm,千粒质量4.68 g。试验所用设备主要有:离心集排式油菜精量排种器、台架、调速器、导种软管、接种杯、角度仪、秒表、高通量小粒径种子流检测装置,检测装置由3D打印技术制成,打印所用材料为工程塑料ABS。台架试验中,分别对检测装置倾斜角度为0°和5°开展台架试验,每个角度测试3次,每次排种60 s,控制排种器排种频率约为60 Hz,对4通道内种子进行计数,台架试验如图6所示,仿真与台架试验结果如表1。

1.离心集排式油菜精量排种器 2.排种器台架 3.直流电机 4.调速器 5.电位器 6.接种袋 7.高通量小粒径种子流检测装置 8.导种软管

表1 分流结构不同倾角时各分流管排量一致性仿真与台架试验结果
仿真结果表明:当分流装置倾斜角度不超过5°时,各分流管道种子排量一致性变异系数不超过5.19%,该结构具有较好分流效果。台架试验结果表明:当装置倾斜角度不超过5°时,各分流管道种子排量一致性变异系数不大于8.58%,具有较好分流均匀性,为后期精准检测高通量种子流提供了基础。
4.2 检测准确率检验
4.2.1 台架试验
台架试验材料与前文分流均匀性检验试验材料相同,均为华油杂62油菜种子,试验所用设备主要有:SLY-C微电脑自动数粒仪(浙江托普仪器有限公司)、离心集排式油菜精量排种器(下文简称排种器)、SW6234C速为测速器、电位器、台架、调速器、导种软管、接种杯、接种袋、秒表、高通量小粒径种子流检测装置、基于薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流检测装置等,试验如图7所示。

1.数粒仪 2.台架 3.高通量小粒径种子流检测装置 4.基于薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流监测装置
台架试验分低通量、高通量排种检测两部分。低通量排种条件下,将高通量小粒径种子流检测装置与基于薄面激光-硅光电池的中小粒径种子流检测装置的上导种管分别与数粒仪出种口连接,利用接种杯收集由检测装置出种口落下的种子。设定数粒仪排种数量为1 000粒,通过调整数粒仪振动档位改变数粒仪落种频率,记录排种时间及检测装置显示屏上的种子数目,并对排出的种子进行人工计数,试验中调节数粒仪档位,不断增大落种频率,将屏幕上的种子数目与人工计数的种子数目进行对比,试验结果如表2。
由表2可知,高通量小粒径种子流检测装置在数粒仪模拟排种器低通量排种条件下,排种频率不超过21.54 Hz时(因数粒仪性能限制,若排种频率再增加,则数粒仪不能均匀排种),检测准确率不低于98.3%;薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流监测装置在数粒仪模拟排种器低通量排种条件下,排种频率不超过21.24 Hz时,检测准确率不低于98.1%。

表2 数粒仪低频条件下两检测装置试验结果
为测试更高排种频率下两检测装置的检测准确率,选用离心集排式油菜精量排种器[29]进行高通量排种试验,台架试验装置同图6(在测试基于薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流检测装置的检测准确率时,只需将图6中的装置7更换为基于薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流检测装置即可)。排种器工作原理为直流电机驱动其排种轴转动,带动油菜种子在内锥桶内转动,利用离心力将种子排出。台架试验中电位器为排种器供电,通过调节调速器改变排种器驱动轴转速,进而改变排种频率,为保证出种均匀,始终保持排种器内锥筒内充满种子。油菜精量联合直播机在田间实际作业时,集开沟、灭茬、旋耕、播种、施肥、覆土于一体,作业速度相对较慢,一般不超过5 km/h[30],当其工作速度为5 km/h时,根据《2018-2019年度冬油菜生产技术指导意见》计算,保证排种器每一路排种频率约为60 Hz时,才能满足油菜播种密度要求。利用测速器检测电机转速,分别设定电机转速110、120、130、140、150、160、170、180、190 r/min(经测试电机转速为190 r/min时,排种器单通道排种频率约为60 Hz,该转速下的排种频率满足油菜精量联合直播机最大排种频率要求)9个转速水平,每次试验排种60 s,每种水平测试3次,通过记录高通量小粒径种子流检测装置显示屏上的数据,同时将下落的种子由接种袋接收并人工计数,试验结果见表3。
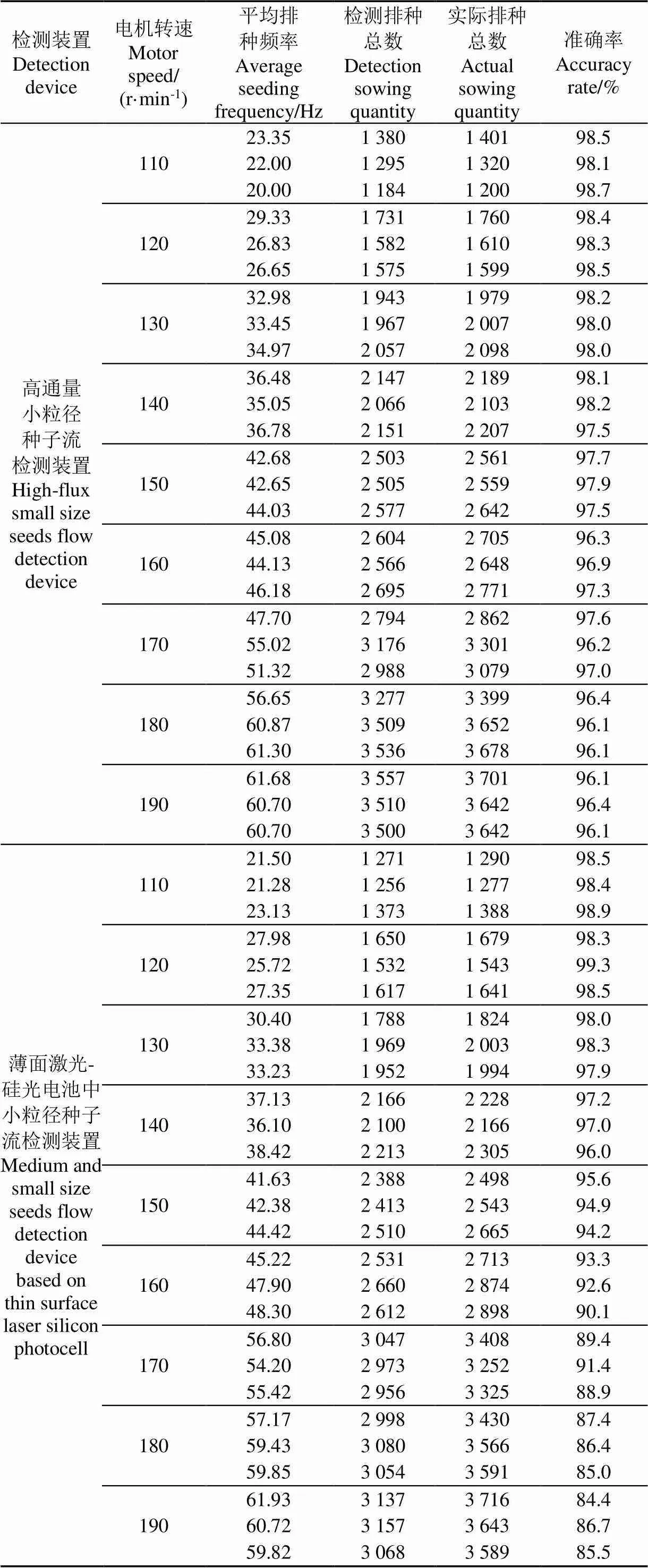
表3 排种器不同转速下检测装置试验结果
由表3可知,高通量小粒径种子流检测装置在排种器排种频率为20.00~61.68 Hz时,检测准确率不低于96.1%;基于薄面激光-硅光电池的中小粒径种子流检测装置在排种器排种频率为21.28~61.93 Hz时,检测准确率不低于84.4%。
基于薄面激光-硅光电池的中小粒径种子流检测装置在高频排种条件下检测准确率较低的原因为:种子在穿越厚度为1 mm的薄面激光感应区域时,速度约为1.1 m/s,不同粒径(0.8~2.2 mm)种子完全穿越薄面激光层所用时间范围为1.6~2.9 ms,此时会产生对应时长的信号波形,检测电路响应时间为微秒级别,能够迅速对种子信号进行处理,而油菜专用型精量直播机排出的种子流在导种管内运动时,管内气流、管壁的作用在一定程度上破环了种子的有序性,当2粒或多粒种子“同时”(相邻种子时间间隔低于1.6~2.9 ms)穿越薄面激光感应区域时,多粒种子产生的信号发生混叠,导致多粒种子被检测为1粒,且随着排种频率的增大,这种概率也会增加,造成检测准确率降低。利用高速摄影仪观察种子下落轨迹,的确存在2粒或多粒种子“同时”下落的情况。
综上,2种检测装置在排种频率不超过22 Hz的条件下,检测都具有较高可靠性,检测准确率不低于98.1%;在排种频率约62 Hz的高频排种条件下,高通量小粒径种子流检测装置检测准确率不低于96.1%,基于薄面激光-硅光电池的中小粒径种子流检测传感装置检测准确率不低于84.4%,高通量小粒径种子流检测装置检测准确率相较于薄面激光-硅光电池的中小粒径种子流检测传感装置检测准确率高11.7%。
4.2.2 田间试验
为考察在田间复杂工况下,振动、光照等对高通量小粒径种子流检测装置性能的影响,于2019年9月28日在华中农业大学工学院水稻地开展高通量小粒径种子流检测装置性能田间试验。
试验前首先检验光照条件对高通量小粒径种子流检测装置的影响。种箱内不放种子,利用塑料软管将检测装置入种口与排种器某一出种口连接,使播种机处于田间静止状态,打开传感装置,在太阳光照、人为打光、人为遮挡自然光条件下进行测试,测试结果表明:在田间正常光照条件下,检测装置计数始终为0,田间正常光照条件对检测装置性能无影响。进一步测试播种机在正常播种时产生的振动对检测装置检测效果的影响,种箱内不放种子,让播种机在田间以正常播种速度行驶30 m,重复3次,模拟振动测试结果表明:在播种机行驶过程中,检测装置计数始终为0,田间直播机正常作业产生的振动对检测装置性能无影响。
为保证出种均匀性,排种器内锥筒内始终应充满种子,利用塑料软管将传感装置与排种器某一出种口连接,拖拉机电瓶为排种器驱动电机供电,田间试验如图8所示。
试验中为保证与实际油菜条播播种状态一致,参照农业农村部《2018-2019年度冬油菜生产技术指导意见》,每公顷地需播种油菜6 000 g才能满足油菜播种密度要求。基于此,计算直播机每一路油菜排种频率为20、30、40、50、60 Hz时,对应拖拉机行进速度分别为1.65、2.48、3.30、4.13、4.90 km/h。在上述5种速度状态下利用调速器调整排种器转速,使得排种器排种频率为20、30、40、50、60 Hz,每种状态进行3次试验,每次试验播种距离30 m,记录检测装置检测的排种数量,并通过接种袋收集各次试验中下落的油菜种子,后期进行人工数粒,与检测装置所得结果进行对照,试验结果如表4所示。
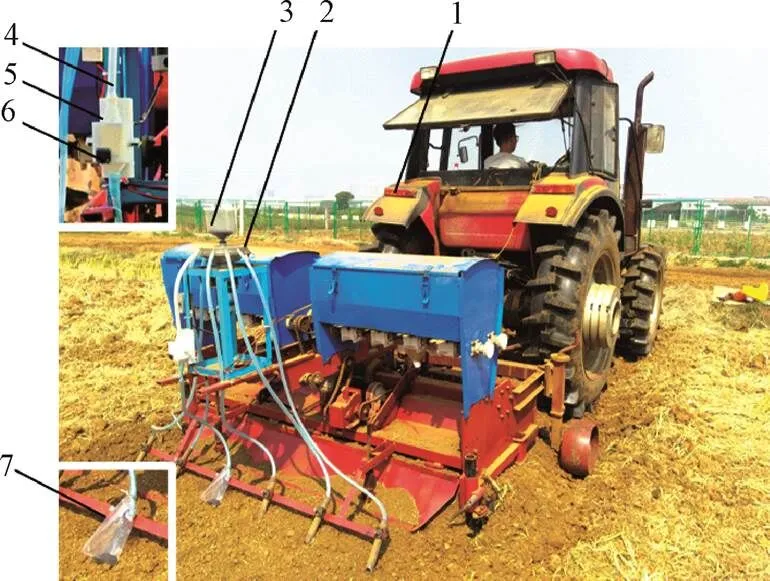

1.东方红-LX954拖拉机 2.排种器内锥筒 3.种箱 4.导种管 5.高通量小粒径种子流检测装置 6.播种检测显示屏 7.接种袋
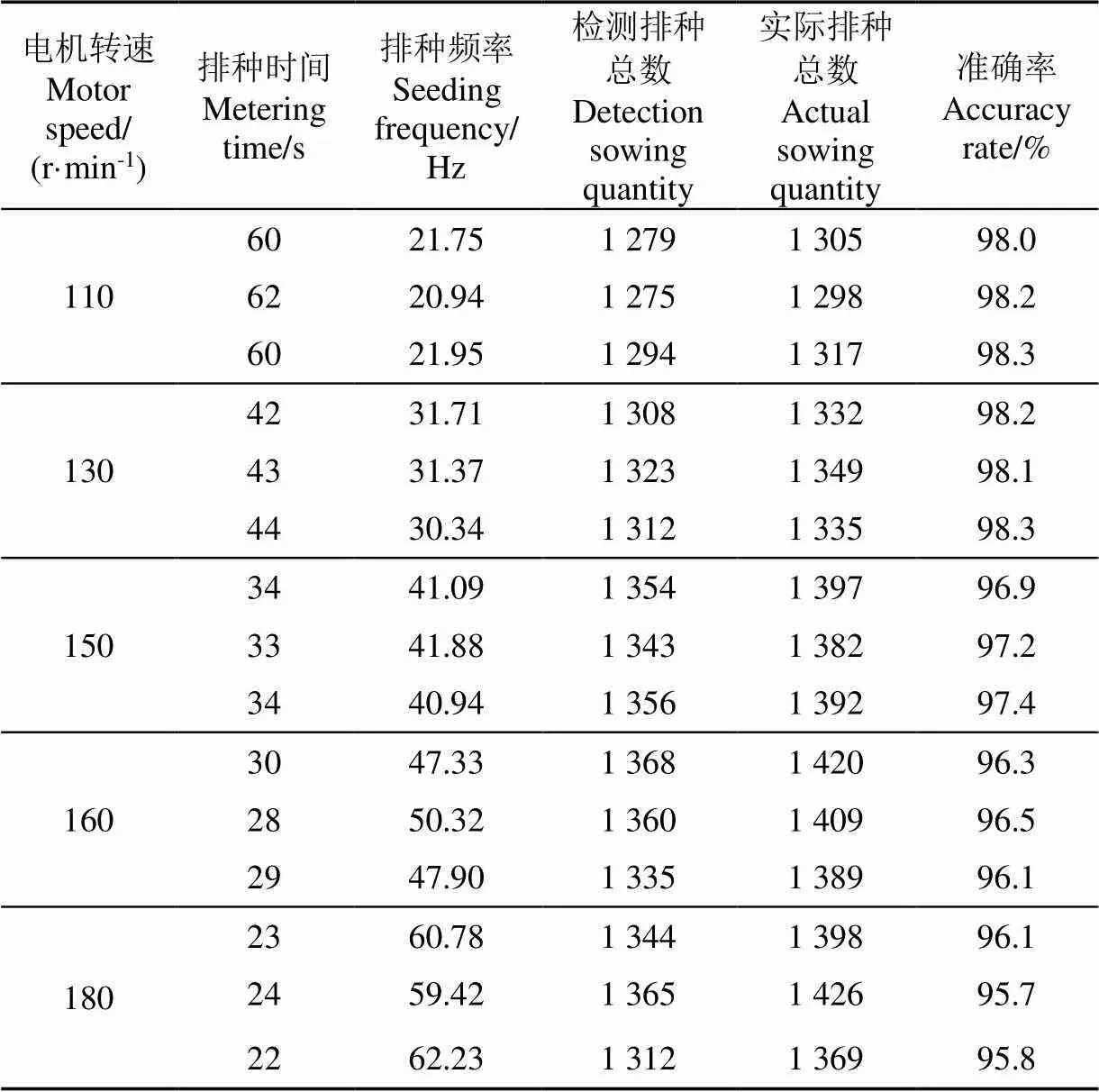
表4 检测装置田间油菜播种试验结果
由表4可知,田间试验时,高通量小粒径种子流检测装置在排种频率不超过62.23 Hz时,检测准确率不低于95.7%,且在试验中无堵塞现象发生。
5 结 论
本文设计了一种高通量小粒径种子流检测装置用于解决因农艺要求增大播量以及高速播种产生的排种频率过高而导致油菜播量检测精度不足的问题,并对高通量小粒径种子流检测装置检测准确率、抗光照干扰和抗振性进行了测试。
1)高通量小粒径种子流检测装置包括入种口、分流锥盘、分流管、薄面激光发射模组、硅光电池、出种口、信号调理电路等组成,适用于高通量排种的油菜种子流播量监测。
2)对检测装置的分流效果进行检验,结果表明,分流结构倾角小于5°时,分流管排量一致性变异系数的仿真与试验结果为分别不超过5.19%和8.58%,具有较好分流均匀性。同时在分流后的各分流管内,利用光伏效应原理,结合相应信号调理电路,实现对高通量小粒径种子流的计数。
3)高通量小粒径种子流检测传感装置台架试验表明:油菜排种频率在62 Hz范围内,油菜种子检测准确率不低于96.1%。田间试验表明:油菜籽排种频率在62.23 Hz范围内,检测准确率不低于95.7%,且在田间正常光照及机具振动状态下对检测精度无影响。
该检测装置可为未来田间高速精量播种的播量监测提供解决方案。
[1] 郭燕枝,杨雅伦,孙君茂. 我国油菜产业发展的现状及对策[J]. 农业经济,2016(7):44-46.
Guo Yanzhi, Yang Yalun, Sun Junmao. The current situation and countermeasures of rapeseed industry development in China[J]. Agricultural Economy, 2016(7): 44-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张哲,殷艳,刘芳,等. 我国油菜多功能开发利用现状及发展对策[J]. 中国油料作物学报,2018,40(5):14-19.
Zhang Zhe, Yin Yan, Liu Fang, et al. Current situation and development countermeasures of Chinese rapeseed multifunctional development and utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2018, 40(5): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Kumar R , Raheman H. An embedded system for detecting seed flow in the delivery tube of a seed drill[C]// International Conference on Advances in Chemical. 2015.
[4] Precision Planting .WaveVision[EB/OL]_ (2014-07-15) [2019-11-08]. https://www.precisionplanting.com/Products/ product/wavevision
[5] John D. Monitoring and documentation [EB/OL]. (2015-08-04) [2019-11-08]. http://www.deere.com/en_US/ parts/parts_by_industry/ag/seeding/monitoring/monitoring. Page
[6] MC Electronics. Sistema full semina [EB/OL].(2018-04-11) [2019-11-08]. https://www.mcelettronica.it/it/prodotti/semina/semina-di-precisione/full-semina_272c28.html
[7] 和贤桃,郝永亮,赵东岳,等. 玉米精量排种器排种质量自动检测仪设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(10):19-27.
He Xiantao, Hao Yongliang, Zhao Dongyue, et al. Design and experiment of testing instrument for maize precision seed meter’s performance detection[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(10): 19-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 纪超,陈学庚,陈金成,等.玉米免耕精量播种机排种质量监测系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(8):1-6.
Ji Chao, Chen Xuegeng, Chen Jincheng, et al. Monitoring system for working performance of no-tillage corn precision seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(8): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 朱瑞祥,葛世强,翟长远,等. 大籽粒作物漏播自补种装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(21):1-8.
Zhu Ruixiang, Ge Shiqiang, Zhai Changyuan, et al. Design and experiment of automatic reseeding device for miss-seeding of crops with large grain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(21): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] Lu Caiyun, Fu Weiqiang, Zhao Chunjiang, et al. Design and experiment on real-time monitoring system of wheat seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017,33(2): 32-40.
卢彩云,付卫强,赵春江,等. 小麦播种实时监控系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(2):32-40. (in English with Chinese abstract)
[11] 赵淑红,周勇,刘宏俊,等. 玉米勺式排种器变速补种系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(12):38-44.
Zhao Shuhong, Zhou Yong, Liu Hongjun, et al. Design of reseed shift speed System of scoop-type metering device of corn[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2016,47(12): 38-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张继成,陈海涛,欧阳斌林,等. 基于光敏传感器的精密播种机监测装置[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版,2013,53(2):265-268,273.
Zhang Jichen, Chen Haitao, Ouyang Binlin, et al. Monitoring system for precision seeders based on a photosensitive sensor[J]. Tsinghua Univ (Sci & Tech), 2013, 53(2): 265-268, 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 黄东岩,贾洪雷,祁悦,等. 基于聚偏二氟乙烯压电薄膜的播种机排种监测系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(23):15-22.
Huang Dongyan, Jia Honglei, Qi Yue, et al. Seeding monitor system for planter based on polyvinylidence fluoride piezoelectric film[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(23): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 孙伟,王关平,吴建民. 勺链式马铃薯排种器漏播检测与补种系统的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(11):8-15.
Sun Wei, Wang Guanping, Wu Jianmin. Design and experiment on loss sowing testing and compensation system of spoon-chain potato metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(11): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 车宇,伟利国,刘婞韬,等. 免耕播种机播种质量红外监测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(增刊1):11-16. Che Yu, Wei Liguo, Liu Xingtao, et al. Design and experiment of seeding quality infrared monitoring system for no-tillage seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(Supp.1): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 贾洪雷,路云,齐江涛,等. 光电传感器结合旋转编码器检测气吸式排种器吸种性能[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(19):28-39.
Jia Honglei, Lu Yun, Qi Jiangtao, et al. Detecting seed suction performance of air suction feeder by photoelectric sensor combined with rotary encoder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(19): 28-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 赵立新,张增辉,王成义,等. 基于变距光电传感器的小麦精播施肥一体机监测系统设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(13):27-34.
Zhao Lixin, Zhang Zenghui, Wang Chengyi, et al. Design of monitoring system for wheat precision seeding-fertilizing machine based on variable distance photoelectric sensor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(13):27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 周利明,王书茂,张小超,等. 基于电容信号的玉米播种机排种性能监测系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(13):16-21.
Zhou Liming, Wang Shumao, Zhang Xiaochao, et al. Seed monitoring system for corn planter based on capacitance signal[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(13): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 周利明,马明,苑严伟,等. 基于电容法的施肥量检测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(24):44-51. Zhou Liming, Ma Ming, Yuan Yanwei, et al. Design and test of fertilizer mass monitoring system based on capacitance method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(24): 44-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 周利明,李树君,张小超,等. 基于电容法的棉管籽棉质量流量检测[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(6):47-52.
Zhou Liming, Li Shujun, Zhang Xiaochao, et al. Detection of seedcotton mass flow based on capacitance approach[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(6): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 陈建国,李彦明,覃程锦,等. 小麦播种量电容法检测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(18):51-58.
Chen Jianguo, Li Yanming, Qin Chengjin, et al. Design and test of capacitive detection system for wheat seeding quantity[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(18): 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘志壮,吕贵勇. 基于电容法的稻谷含水率检测[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(7):179-182.
Liu Zhizhuang, Lv Guiyong. Mositure Content Detection of paddy rice based on capacitance approach[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(7): 179-182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 丁幼春,王雪玲,廖庆喜,等. 油菜籽漏播螺管式补种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(22):16-24.
Ding Youchun, Wang Xueling, Liao Qingxi, et al. Design and experiment on spiral-tube reseeding device for loss sowing of rapeseed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(22): 16-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李兆东,孙誉宁,杨文超,等. 光束阻断式小粒蔬菜种子漏充与堵孔同步检测系统研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(8):119-126.
Li Zhaodong, Sun Yuning, Yang Wenchao, et al. Design of synchronous detection system of missing filling seeds and suction hole blocking based on beam blocking for small vegetable grains[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(8): 119-126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 丁幼春,杨军强,朱凯,等. 油菜精量排种器种子流传感装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):29-36.
Ding Youchun, Yang Junqiang, Zhu Kai, et al. Design and experiment on seed flow sensing deVice for rapeseed precision metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 29-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 丁幼春,朱凯,王凯阳,等. 薄面激光-硅光电池中小粒径种子流监测装置研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(8):20-28.
Ding Youchun, Zhu Kai, Wang Kaiyang, et al. Development of monitoring device for medium and small size seed flow based on thin surface laser- silicon photocell[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(8): 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 廖庆喜,张朋玲,廖宜涛,等. 基于 EDEM 的离心式排种器排种性能数值模拟[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(2):109-114. Liao Qingxi, Zhang Pengling, Liao Yitao, et al. Numerical simulation on seeding performance of centrifugal rape-seed metering device based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(2): 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 刘晓东,丁幼春,舒彩霞,等. 螺旋扰动锥体离心式排肥器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(2):40-49.
Liu Xiaodong, Ding Youchun, Shu Caixia , et al. Design and experiment of spiral disturbance cone centrifugal fertilizer apparatus[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(2): 40-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张宁. 离心集排式油菜精量排种器的设计及试验研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2012.
Zhang Ning. Design and Experiment Research on Centralized Centrifugal Precision Metering Device for Rapeseed[D]. Wuhan: Hua Zhong Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 田波平,廖庆喜,黄海东,等. 2BFQ-6型油菜精量联合直播机的设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2008(10):211-213.
Tian Boping, Liao Qingxi, Huang Haidong, et al. Design of 2BFQ-6 precision seeder for rapeseed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008(10): 211-213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Design and experiment of high-flux small-size seed flow detection device
Ding Youchun, Wang Kaiyang, Du Chaoqun, Liu Xiaodong, Chen Liyuan, Liu Weipeng
(1.,,430070,;2.,,430070,)
Rapeseed is the most widely distributed and grown oil crop in China. At the same time, with the improvement of related biotechnology, the variety of rapeseed functions has become increasingly prominent. According to the agronomic requirements for rapeseed, with the delay of the sowing date, it is necessary to increase the sowing amount to make up for the decrease of the emergence rate. In addition, as the operation speed of the planter increasing, the rapeseed seeder seeding frequency is needed to increase to meet the seeding density. For small size seeds such as rapeseed, when the sowing frequency is higher than 30 Hz, it can be considered that a high-flux seeds flow. It is great significance to research a kind of high-flux and small size seeds flow detection device to realize the detection of seeds quantities and missing seeds during high-frequency sowing of rapeseed. Because the rapeseed has a small size (0.8-2.2 mm), the seed signal generated by the conventional large and medium size detection device is weak and difficult to be captured. On the other hand, the existence of blind spots in detection has reduced the detection accuracy. In the text, when the sowing frequency reaches 62 Hz, the detection accuracy of the seeds flow detection device based on thin piezoelectric film and the seeds flow detection device based on thin-surface laser silicon photocell developed by the research team in the early stage was less than 85%. The reason is that when a high-flux seeds flow is formed at a high sowing frequency, the high-flux seeds flow will collide and increase the probability of aliasing inside the detection device, resulting in an increased probability of multiple seeds passing through the sensing zone at the same time, and detection accuracy is reduced. Aiming at the problem of insufficient precision of high-flux seeds flow detection due to agronomic requirements during the sowing of rapeseed and the high seeding frequency caused by high speed sowing,a method for parallel detection of high-flux seeds flow into multiple low-flux seeds flow was proposed, then the high-flux small size seeds flow detection device based on a combination of a shunt mechanism and a thin surface laser silicon photocell was designed.Considering the uniformity and fast passage of the high-flux seeds flow, the shunt structure was designed. Discrete element simulation software EDEM and bench test were used to verify the seeding uniformity when the shunt tube tilt angles. When the inclination angle of the shunt structure was less than 5°, simulation and bench test results of the consistency of the displacement each shunt tube at different inclination angles did not exceed 5.19% and 8.58% respectively. Combining the thin face laser and the seeding area, determine the relationship between the thin face laser emitting module angle, the inner radius of upper seeds through tube, and the distance of the thin face laser to the silicon photocell, comprehensive device cost and volume optimization to get the best combination of three parameters. Bench test of high-flux small size seeds flow detection device showed that within the seeding frequency range of 61.68 Hz, the accuracy of rapeseed detection was not less than 96.1%.The field test results showed that the detection accuracy rate was not less than 95.7% when the field seeding frequency was not more than 62.23 Hz, and no blocking phenomenon occured during the test.Normal light in the field and machine vibration had no effects on the detection accuracy of the device.
argicultural machinery; design; experiments;shunt structure; high-flux; small size; detection
丁幼春,王凯阳,杜超群,等. 高通量小粒径种子流检测装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(13):20-28.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.13.003 http://www.tcsae.org
Ding Youchun, Wang Kaiyang, Du Chaoqun, et al. Design and experiment of high-flux small-size seed flow detection device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(13): 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.13.003 http://www.tcsae.org
2020-01-07
2020-06-19
国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFD0200600、2016YFD0200606)
丁幼春,教授,博士生导师,主要从事油菜机械化生产智能化技术与装备研究。Email:kingbug163@163.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.13.003
S223.2+5
A
1002-6819(2020)-13-0020-09
