Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Viburnum tinus L.
2020-01-01YingbingHeZhikangDuanLiliLou
Yingbing He,Zhikang Duan,Lili Lou
Key Laboratory of Computational Chemistry-Based Natural Antitumor Drug Research &Development,Liaoning Province,School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract Viburnum tinus L.is a shrub native to the Mediterranean basin.Because of its sedative and antispasmodic activities,it is often used as a folk medicine in Europe.Phytochemical researches have shown that numerous chemical components,including iridoid glycosides,diterpenes,triterpenes,coumarin,flavonoids and anthocyanidins have been isolated from Viburnum tinus L..This study reviewed the chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Viburnum tinus L.to provide a reference for further researches.
Keywords:Viburnum tinus L.; chemical constituents; pharmacological activities; review
1 Introduction
ViburnumL.genus contains over 230 species,distributed in South America (Peru) and South-East Asia (Philippines,Malaysia) [1].Among them,Viburnum tinusL.is an evergreen shrub,distributed throughout the areas with Mediterranean climate in Southern Europe and North Africa [2].Some of the species,are characterized by berries,showy flowers and fragrance,that make them popular as garden or landscape plants,while others have edible fruits that can be eaten raw or used to make jam [3].A few studies have revealed the existence of multifarious chemical components,including iridoid glycosides,diterpenes,triterpenes,coumarins,flavonoids and anthocyanidins inViburnum tinusL.[3].This genus is commonly used in folk medicine for its diuretic,sedative and antispasmodic properties [4].This study reviewed the research progress on the chemical constituents of theViburnum tinusL.,together with their pharmacological activities.
2 Chemical constituents of Viburnum tinus L.
Studies have shown thatViburnum tinusL.contains a variety of chemical constituents,including terpenoids,flavonoids,coumarin,and other compounds.
2.1 Terpenoids
2.1.1 Iridoid glycosides
Studies in the twentieth century have shown thatViburnumgenus is rich in iridoid glycosides,mainly Valeriana-type iridoid with a sugar moiety at C-11 [5,6].Numerous iridoid glycosides are also found inViburnum tinusL..
In 1995,six iridoid glycosides were extracted and isolated from fresh leaves and branches ofViburnum tinusL.by Tomassini et al.[7].Their structures were elucidated by1H-NMR and13C-NMR.One of the six compounds was a known one,isolated fromViburnum suspensumLindley previously [8],while the other five,viburtinosides I-V (1-5) [7],were new.Two other iridoid glycosides,viburtinoside A (6) and B (7),along with a known compound suspensolide A (8) were obtained from air-dried leaves ofViburnum tinusL.by Marzouk et al.in 2005 [9].The structures of the eight compounds are shown in Fig.1.
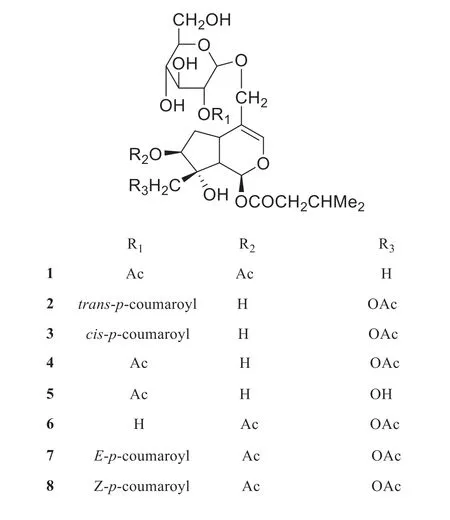
Fig.1 Structures of iridoid glycosides isolated from Viburnum tinus L.
2.1.2 Diterpenes
Vibsatins A (9) and B (10),were isolated by Gao et al.from the twigs and leaves ofViburnum tinuscv.Variegatus,a cultivated species ofViburnum tinusL.[10].The structures and absolute configurations were identified by NMR spectra,optical rotation,and X-ray diffraction experiments.These structures are shown in Fig.2.
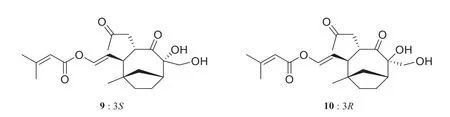
Fig.2 Structures of diterpenoid isolated from Viburnum tinus L.
2.1.3 Triterpenes
The skeletons of triterpenoids isolated fromViburnum tinusL.are all oleanane type.Two triterpenoid saponins along with oleanolic acid (11)were isolated from the leaves ofViburnum tinusL.by Marzouk et al.in 2005 [9].The structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods as 3-O-β-4C1-glucuronopyranoside-oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-4C1-glucopyranosyl ester (12) and 3-O-β-D-4C1-galactopyranosyl-(1″→2′)-O-β-D-4C1-glucuronopyranoside-oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-4C1-glucopyranosyl ester (13).These structures are shown in Fig.3.
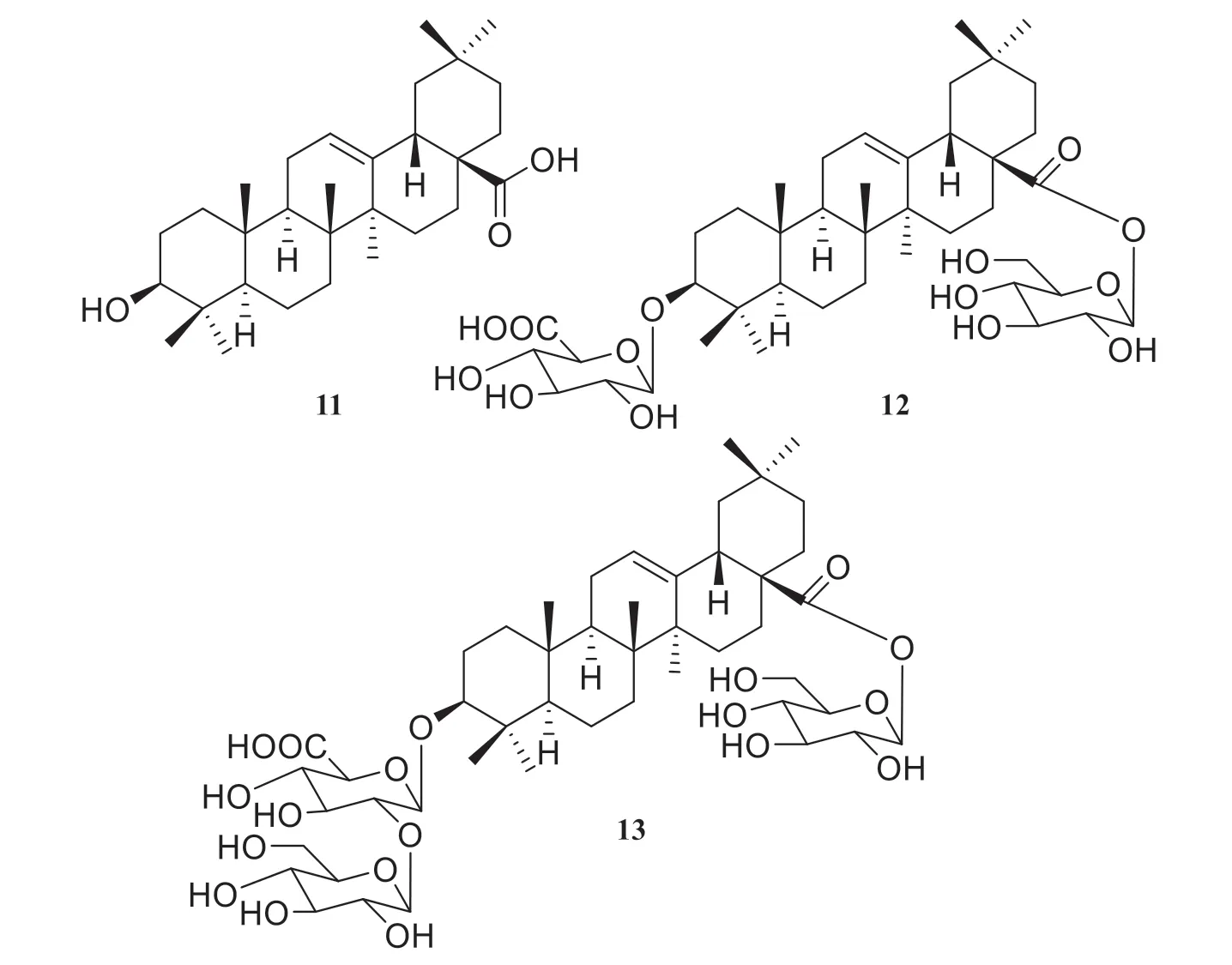
Fig.3 Structures of triterpene and triterpenoid saponins isolated from Viburnum tinus L.
2.2 Flavonoids and anthocyanidins
Four flavonoids,including Quercitrin(14),isoquercitrin (15),rutin (16),quercetin 3,7-diglucoside (19),along with two anthocyanidins,cyanidin 3-glucoside (17),cyanidin 3-sambubioside(18) were isolated from the fruitsofViburnumtinusL.and determined by Godeau et al.using chromatography and spectral method [11].Besides,six flavonoids,including nobiletin (20),afzelin (21),quercitrin (14),isoquercitrin (15),hyperin (22),and rutin(16) were isolated from leaves ofViburnum tinusL.by Marzouk et al.in 2005 [9].These structures are shown in Fig.4.
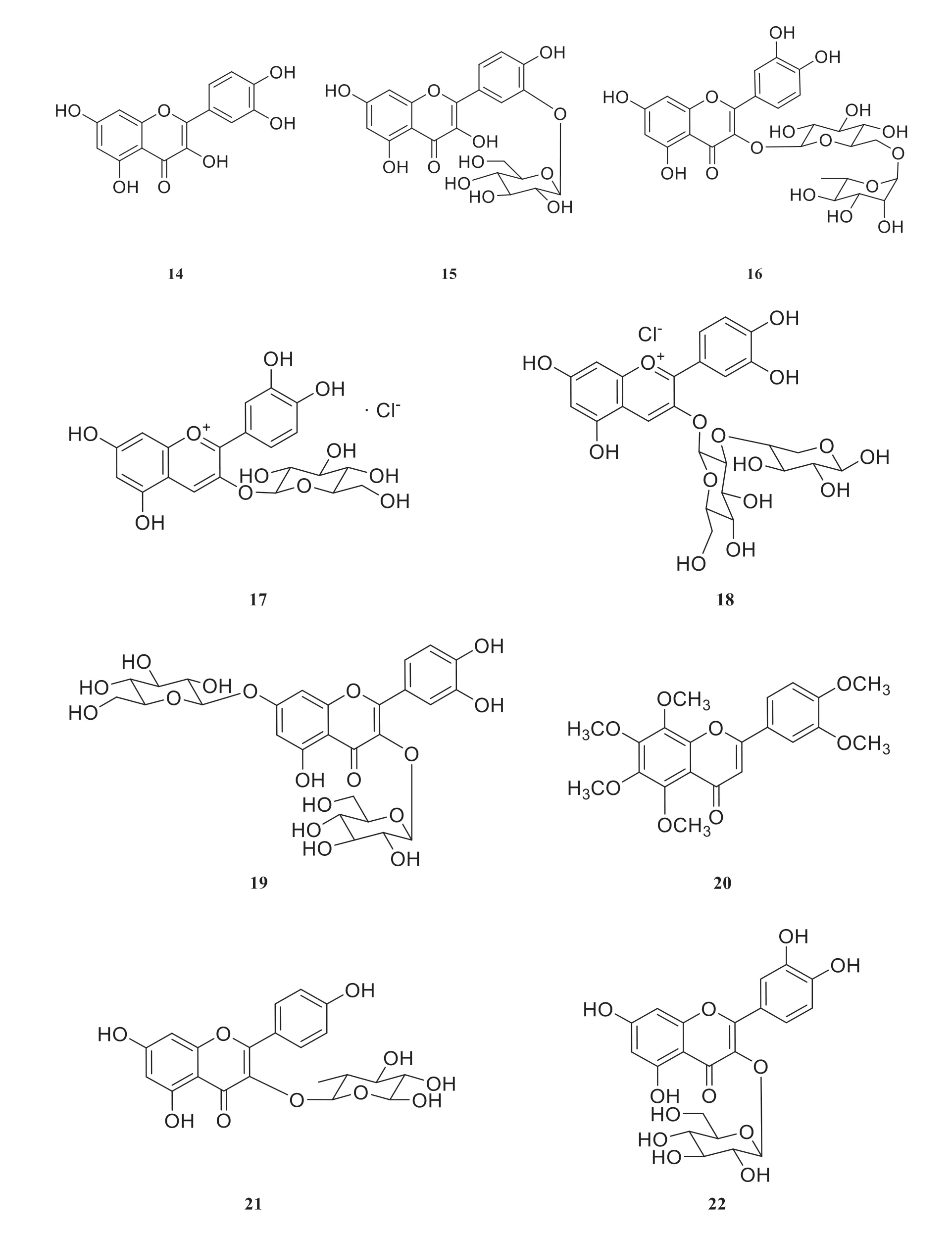
Fig.4 Structures of flavonoids and anthocyanidins isolated from Viburnum tinus L.
2.3 Other compounds
In addition to the above compounds,other compounds have been isolated fromViburnum tinusL..They are 2,6-di-C-methyl-dinicotinic acid 3,5-diethyl ester (23) [9],coumarin diglucoside scopoletin 7-O-β-D-sophoroside (24) [9],and 4-Methyl-7-formylcyclopenta(c)pyran (25) [12].Besides,an endophytic fungus,internal strain No.8984,was isolated from the leaves ofViburnum tinusL..A new phenolic ester depsitinuside (26) and two known steroids,ergosterol (27) and (22E,24S)-24-methyl-5-α-cholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5,6β-triol(28) were isolated from the cultured extract of the nonsporulating endophytic fungus [13].These structures are shown in Fig.5.
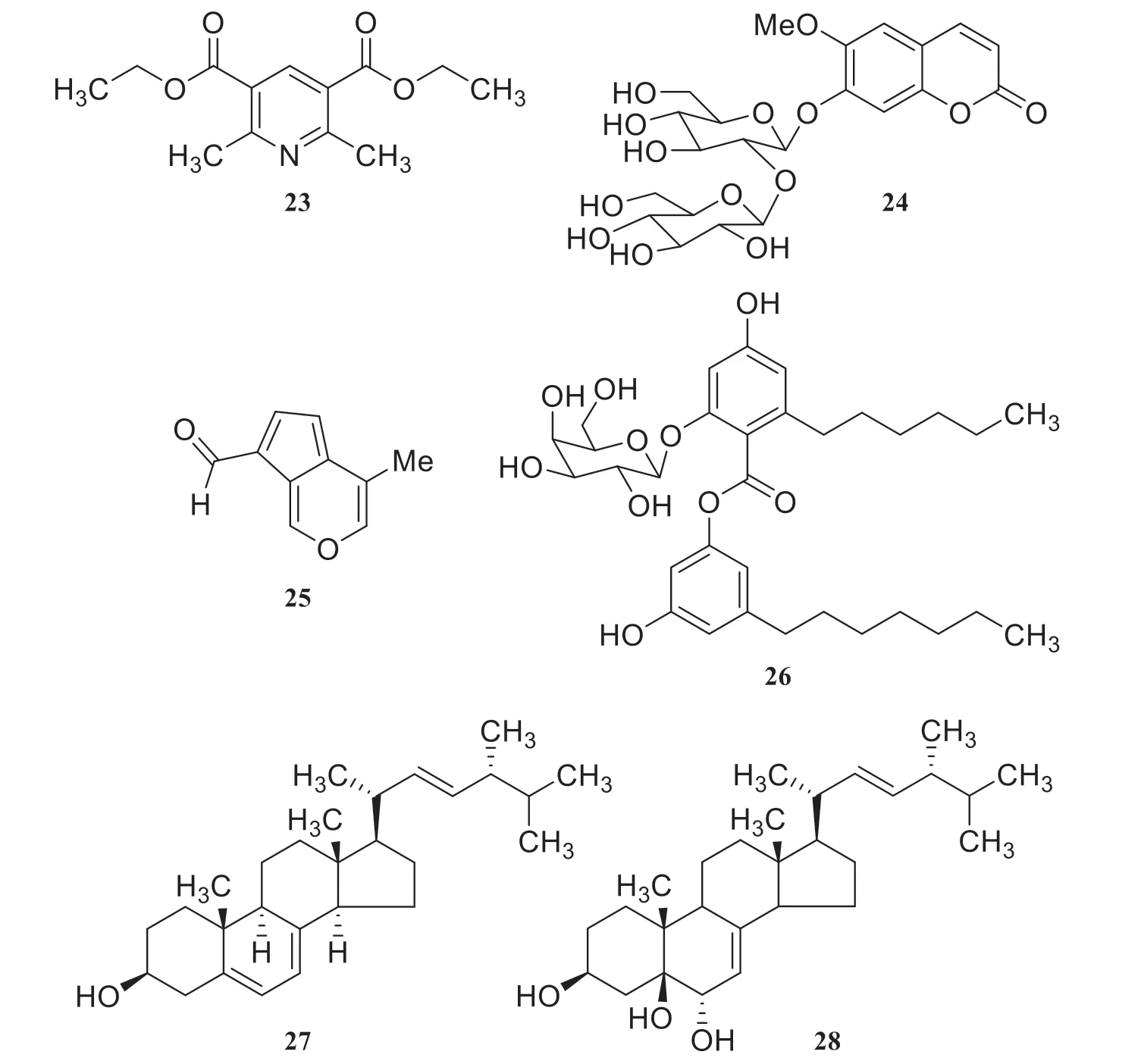
Fig.5 Other compounds isolated from Viburnum tinus L.
3 Pharmacological activities of Viburnum tinus L.
3.1 Sedative and antispasmodic activity
Cometa et al.evaluated the sedative and antispasmodic activities of the total extract ofViburnum tinusL.and its major compounds Valeriana-type iridoids (1-3) by evaluated on spontaneous locomotor activity on isolated rabbit jejunum and in mice [14].The study showed that the spontaneous activity of Valeriana-type iridoids was reduced in mice,and that viburtinoside I (1) was more effective than viburtinosides II/III (2,3).In addition,Valeriana-type iridoids also had spasmolytic effectsin vitro,and viburtinosides II/III (2,3) were more effective than viburtinoside I (1).
3.2 Hepatoprotective activity
The study of Mohamed et al.revealed that 50 mg/kg ofViburnum tinusL.extracts could significantly reduce serum lipid peroxide or nitric oxide levels,and had a significant hepatoprotection effect which was proved by the improvement of ALT and AST values in mice with CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity [9].
3.3 Other activities
The findings obtained in the study by Yilmaz et al,revealed that the branch-EtOAc and fruit-MeOH extracts ofViburnum tinusL.had significant cholinesterase inhibitory effects,and the fruit-MeOH extract showed the greatest TYRO inhibitory effect [3].Moreover,significant antioxidant activity was observed in most extracts.
El-Khayat et al.reported thatViburnum tinusL.extract showed strong activity againstBiomphalaria alexandrinasnails [15].The sub-letal concentration,½LC5(5.5 ppm),of this extract caused a considerable decrease in the survival rate and infection rate ofSchistosoma mansonimiracidia infected snails.
4 Conclusion
Viburnum tinusL.is often used as a folk medicine in Europe because of its sedative and antispasmodic activities.Phytochemical investigations have revealed that the chemical constituents ofViburnum tinusL.include iridoid glycosides,diterpenes,triterpenes,flavonoids and anthocyanidins,coumarin,and other compounds.Existing research has shown that the extracts ofViburnum tinusL.have some pharmacological activities and biological activities,including sedative and antispasmodic,hepatoprotective,cholinesterase inhibitory,antioxidant and molluscicidal activities.In this paper,chemical constituents and pharmacological activities ofViburnum tinusL.were summarized,aiming to provide reference for further development and research.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- Contribution Regulations for Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines
- Studies on the chemical components and biological activities of the genus of Juncus
- Research progress on chemical constituents in Periploca forrestii and their pharmacological activities
- Uncovering the potential targets of Viburnum odoratissimum for the treatment of related diseases
- Studies on chemical constituents of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.)Swingle and their antioxidant activity
- Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted from Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer with graded percipitation method
