Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted from Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer with graded percipitation method
2020-01-01XinyingWngYueLinJiLiuZhojunWngLinlinLiuYinglingWngJinciLu
Xinying Wng,Yue Lin,Ji Liu,Zhojun Wng,Linlin Liu,Yingling Wng,Jinci Lu,b
a.School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,PR China;
b.Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of TCM Resources Conservation and Development,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110006,PR China
Abstract Ginseng polysaccharides were extracted by water decoction from Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer (Cultivated Ginseng),named CGPS.Four polysaccharide fractions,CGPS-20,CGPS-40,CGPS-60 and CGPS-80,were precipitated at final ethanol concentrations of 20%,40%,60% and 80%,respectively.Physicochemical properties,molecular weight,monosaccharide composition and antioxidant capacity of polysaccharide fractions were all investigated.The results indicated that changing the concentration of ethanol could precipitate polysaccharides into fractions with different molecular weights,functional group composition and physicochemical properties,eventually leading to differences in antioxidant activity,which would help to find a simple,efficient,and reliable method for rapid extraction and purification of antioxidant polysaccharides from Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer.Among the four polysaccharide fractions,CGPS-80 had lower molecular weight,higher contents of uronic acid and total phenolic,and stronger scavenging ability on DPPH· and ABTS·+ radicals.
Keywords:Ginseng polysaccharides; graded ethanol precipitation; physicochemical property; antioxidant activity
1 Introduction
Panax ginsengC.A.Meyer has been used for thousands of years in China in medical and health care.Because of its great medicinal value,ginseng has always been the focus in the research of Chinese herbal medicine.P.ginsengcontains various ingredients,including ginsenosides,polysaccharides,essential oil,amino acids and peptides,nitrogen compounds,fatty acids and phenolic [1].As one of the main active components ofP.ginseng,polysaccharides have been confirmed to possess various pharmacological activities like immunoregulatory effect [2],antioxidant effect [3]and anti-tumor activity [4-6].
Water extraction and alcohol precipitation are the most common methods for extracting and purifying natural polysaccharides.Compared with other purification methods,the graded ethanol precipitation method has the characteristics of simple operation,rapid fractionation and high yields.Since polysaccharides with higher molecular weights tend to precipitate in ethanol with a lower concentration,polysaccharide fractions with different molecular sizes,structural features and activities activitiesis were obtained by gradually increasing the concentration of ethanol [7].
Oxidation is an essential process in which organisms produce energy to fuel biological processes.However,excessive production of free radicals such as reactive oxygen species (ROS)and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) will damage cellular biomolecules,resulting in coronary heart disease,carcinogenesis,atherosclerosis and other aging-related diseases [8,9].Antioxidants,as scavengers of free radicals,possess health care and disease prevention properties in both humans and animals [10].Exogenous antioxidants isolated from natural resources,such as polysaccharides,are better prophylactic and therapeutic agents than synthetic antioxidants because they are non-toxic,biocompatible and biodegradable [11].Therefore,studying the antioxidant capacity of ginseng polysaccharide may contribute to its application in the pharmaceutical field.
In the present study,ginseng polysaccharides were obtained by water decoction.Graded ethanol precipitation was used to obtain CGPS-20,CGPS-40,CGPS-60 and CGPS-80 when the final ethanol concentrations reached 20%,40%,60% and 80%respectively.The physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant capacity of the above samples were investigated to find a convenient,efficient,and reliable method for extracting and purifying antioxidant polysaccharides fromPanax ginsengC.A.Meyer.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
Cultivated ginseng (CG) was 4-6 years old and collected from Huanren (Benxi,China).The species was identified by Prof.Jincai Lu,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang,China.Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) were purchased from Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co.,Ltd.(China).1-Phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazalone (PMP)was obtained from acros organics.Monosaccharide standards including glucose (Glc),rhamnose (Rha),arabinose (Ara),galactose (Gal),xylose (Xyl)were purchased from Wako (Japan).Galacturonic acid (GalA),glucuronic acid (GlcA),and mannose(Man) were from National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (China).Molecular Weight CRM of Dextrans were purchased from Beijing Century Aoke Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.(China).1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH·) and 2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)(ABTS) radicals were purchased from Hefei Bomei Biological Technology Co.,Ltd.(China).
All other chemicals and solvents used were of analytical grade unless otherwise specified.
2.2 Extraction and fractionation procedure
100 g of cultivated ginseng powder was extracted with water at 100 °C for 2 h three times.The decoctions were combined and concentrated to a small volume using a rotary evaporator (N-1300,EYELA,Japan) at 55 °C under reduced pressure,and then centrifuged at 3800 rpm for 10 min.The supernatant was divided into two parts.Wherein 20% of the supernatant was added with ethanol to a final concentration of 80% to obtain ginseng total polysaccharides,named CGTPS.The other part of the supernatant was fractionated sequentially by graded precipitations to final ethanol concentrations of 20%,40%,60% and 80% (V/V),respectively,corresponding to the four subfractions assigned to CGPS-20,CGPS-40,CGPS-60 and CGPS-80.Each polysaccharide sample was prepared as shown in Fig.1.All polysaccharide precipitates were redissolved with distilled water.Samples containing starch were treated withα-amylase according to the method of Li [12]and then precipitated with three volumes of 95% ethanol (V/V).Subsequently,all samples were re-dissolved in distilled water and treated with Sevag reagent (1 :4n-butanol:chloroform,V/V) to remove protein [13].Ultimately,the polysaccharide samples were further precipitated with ethanol again and lyophilized.
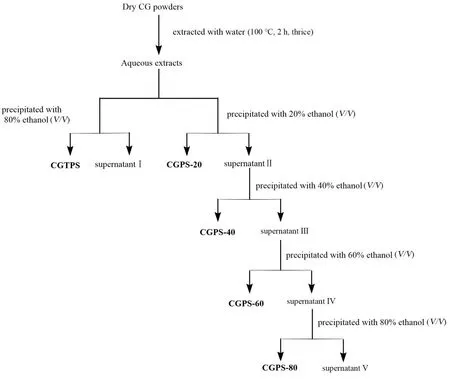
Fig.1 Extraction and fractionation procedure of polysaccharide fractions from Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer
2.3 Determination of total sugar,total phenolic,and uronic acid contents
Total sugar content (%) was determined by phenol-sulfuric acid method reported by Dubois [14]with some modifications.Glucose was used as the standard.
Total phenolic content was measured using Folin-Ciocalteau assay [15,16].The sample solution(0.9 mL) and Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (0.5 mL,2N) were mixed at room temperature for 5 min.1.5 mL Na2CO3solution (10%,W/V) was then added,and the mixture was incubated at 30 °C and kept away from light for 90 min.The absorbance of the reaction mixture was determined at 765 nm using a multimode reader.The results were expressed as gallic acid equivalent (GAE) (μg/g) dry weight of ginseng polysaccharides.
Uronic acid content was determined using the modified m-hydroxybiphenyl method [17],with glucuronic acid as the standard.
2.4 Estimation of the molecular mass
Molecular weight (Mw) was determined by high-performance gel permeation chromatography on a TSK-gel G-3000PWXL column (300 mm ×7.8 mm,TOSOH,Tokyo,Japan) coupled with a Shimadzu LC-6AD system (Tokyo,Japan).The column was eluted with 20 mM ammonium acetate solution at a flow rate of 0.7 mL/min at 40 °C and detected with a RID detector (Shimadzu).The molecular weight of polysaccharides was calculated by constructing the calibration curve of D-glucose and the dextran standards with different molecular weights (180,3620,12,600,70,800,126,000 and 496,000 Da,respectively).Samples were dissolved in mobile phase to a final concentration of 4.0 mg/mL,and an aliquot of 25μL solution was injected for analysis.The calibration curve was:lgMw=-0.5095RT+9.7135,R2=0.9935.It showed that molecular weight value had a good linear relationship with the retention time.
2.5 Analysis of monosaccharide composition
The monosaccharide composition was measured according to the previous method [18],with some modifications.Samples (5 mg) were hydrolyzed by TFA (2 M) in a sealed glass tube at 110 °C for 4 h to obtain individual monosaccharides.Methanol was added to remove the excessive TFA by co-distillation and then the dried hydrolyzed polysaccharide sample was dissolved in 1 mL of ultrapure water.Each standard monosaccharide(Glc,Man,Rha,Ara,Xyl,Gal,GlcA and GalA)or the ginseng polysaccharide sample solution(1 mL) was mixed with 0.3 M NaOH (1 mL) and 0.5 M 1-Phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazalone (PMP)-methanol solution (1 mL),respectively.The mixture was reacted at 70 °C for 60 min.At the end of the reaction,the mixture was cooled to room temperature and then neutralized with 0.3 M HCl(1 mL).The neutral solution was extracted three times with CH3Cl (2 mL) and the aqueous layer was used for HPLC analysis.All pre-column derivation products were analyzed on Shimadzu HPLC system using a Thermo ODS-2 HYPERSIL C18column(250 mm × 4.6 mm,5μm,Thermo,America)equipped with an ultraviolet (UV) detector.The column was eluted with ammonium acetate solution(0.5 M) and acetonitrile (83 :17,V/V) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min.The temperature of the column was maintained at 30 °C and the wavelength for UV detection was 245 nm.
2.6 FT-IR spectroscopic analysis
The dried polysaccharides samples were mixed and ground with potassium bromide,and then pressed into pellets.Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was recorded in the absorbance mode from 4000 cm-1to 400 cm-1on Shimadzu FTIR-8400s (Shimadzu Corporation,Japan).
2.7 Evaluation of antioxidant activity in virto
2.7.1 DPPH· radical scavenging capacity assays
DPPH· radical scavenging activity was measured according to the method of Hua [19]with some modifications.100μL of 0.1 mM methanolic solution of DPPH· radicals were added to 100μL of ginseng polysaccharides with different concentrations (dissolved in distilled water,0.1-5 mg/mL).After 30 min of incubation in the dark,the absorbance of the mixture was measured.Ascorbic acids (Vc) with equal concentration were used as positive control.The scavenging capacity of DPPH· radicals was measured by scavenging rate (%) using Eq.(1) as follows,where A0is the absorbance of the control group (methanol instead of the sample solution); Aiis the absorbance of the test sample mixed with DPPH· solution; and Ajis the absorbance of the sample (methanol instead of DPPH· solution).
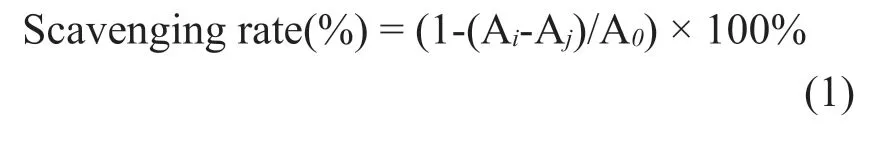
2.7.2 ABTS·+ radical cation scavenging activity assays
ABTS assay was performed according to the Katalinic’s [20]method with some modifications.10 mL of ABTS·+aqueous solution (7 mmol/L) was mixed with 10 mL of K2S2O8(2.45 mmol/L),and then incubated in the dark at the room temperature for 12-16 h.The final working solution of ABTS·+was diluted to the absorbance of 0.700 ± 0.02 at 734 nm with methanol.Diluted ABTS·+(150μL) and ginseng polysaccharide sample solutions (50μL) at different concentrations (0.1-5 mg/mL) were mixed for 10 min and the absorbance was determined at 734 nm.The ABTS·+radical cation scavenging activity was expressed as scavenging rate (%) according to the Eq.(1),where A0is the absorbance of the control group (methanol instead of the sample solution);Aiis the absorbance of the test sample mixed with ABTS·+solution; and Ajis the absorbance of the sample (methanol instead of ABTS·+solution).Ascorbic acids (Vc) with euqal concentrations were used as positive control.
2.8 Statistical analysis
All experiments of antioxidant activity were conducted in triplicate and expressed as mean ±standard deviation (SD).The data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) using GraphPad Prism 6.0 (SanDiego,CA,USA).Statistically significant differences between groups were defined asP< 0.05.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Physicochemical properties of ginseng polysaccharides
The contents of total sugar,total phenolic and uronic acid were measured and shown in Table 1.Total sugar content decreased in the following order:CGPS-20 > CGPS-40 > CGPS-60 > CGPS-80.Both phenolic and uronic acid were found in all fractions.CGPS-80 contained the most total phenolic,followed by CGPS-20.Meanwhile,CGPS-80 ranked the second in terms of uronic acid content of uronic acid,followed by CGPS-60,and CGPS-40.
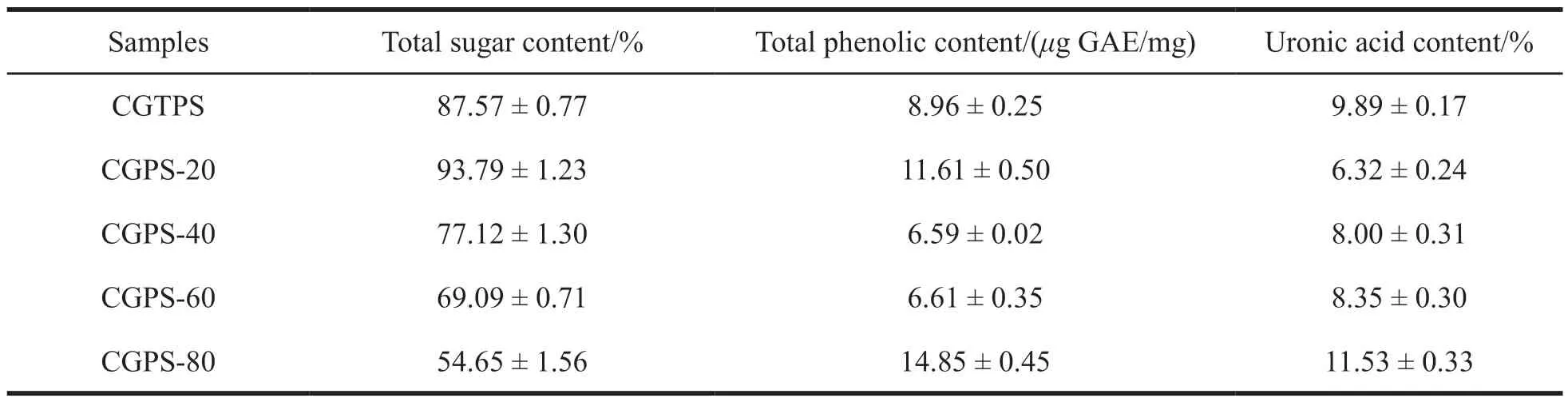
Table 1 Total sugar,total phenolic and uronic acid contents in ginseng polysaccharides
Ginseng polysaccharide fractions had wide molecular weight distribution,as displayed in Table 2.Previous study has shown that the concentration of ethanol is related to the molecular size,so polysaccharides with larger molecular size are more likely to precipitate at a lower ethanol concentration [21].However,the change in ethanol concentration did not significantly lead to the difference in molecular weight of CGPS-20-CGPS-80,which might be due to the poor solubility of polysaccharides with relatively large molecular weight,such as CGPS-20,filtered during sample processing before HPLC analysis.
The monosaccharide composition analysis of CGTPS and CGPS-20-CGPS-80 was shown in Table 2 and Fig.2.All fractions were composed of Man,Rha,GlcA,GalA,Glc,Gal,and Ara,but none of them were found to contain Xyl.HPLC analysis showed that CGTPS was mainly composed of glucose,galactose,arabinose and galacturonic acid.Other sugars,such as rhamnose,glucuronic acid and mannose,were minor components.With the increase of the ethanol concentration,the content of glucose gradually decreased.CGPS-60 contained the most galactose,followed by CGPS-80.The content of arabinose from high to low was:CGPS-80 >CGPS-60 > CGPS-40 > CGPS-20.In particular,CGPS-80 contained relatively higher contents of galacturonic acid,arabinose,and the minimum amount of glucose,which were distinctly different from the other fractions.
3.2 FT-IR spectrum analysis of CGTPS
The FI-IR analysis results of CGTPS were shown in Fig.3.The broadly stretching intense band in the region of 3400 cm-1and the small band at 2926.3 cm-1were assigned to O-H and C-H stretching vibrations.The relatively strong absorption peaks at 1630.7 cm-1and 1744.1 cm-1were due to the characteristic stretching vibration of C=O groups,which demonstrated the existence of uronic acid [22].The absorption band at 1414.7-1370.5 cm-1belonged to bending vibration of C-H bond [23].The absorptions at 1153.8 cm-1,1080.9 cm-1and 1024 cm-1indicated that a pyranose forms of sugars existed in α-configuration,and the weak bands at about 929 cm-1and 761.6 cm-1were typical D-glucose absorption bands in pyranose form.Moreover,the characteristic absorption at 849.9 cm-1was ascribed to the α-dominant configuration of the CGTPS [24,25].
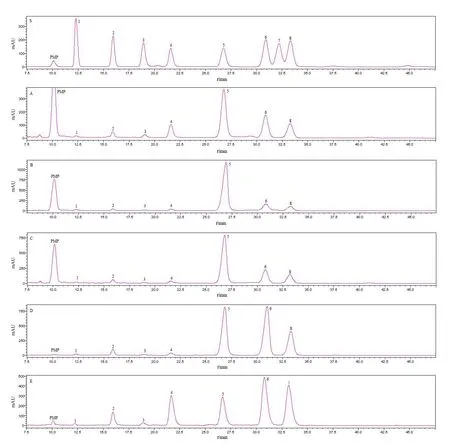
Fig.2 HPLC chromatograms of the monosaccharides derived from CGTPS,CGPS-20,CGPS-40,CGPS-60 and CGPS-80.(S) The mixed standard monosaccharides; peaks:(1) mannose,(2) rhamnose,(3) glucuronic acid,(4) galacturonic acid,(5) glucose,(6) galactose,(7) xylose,(8) arabinose; (A) CGTPS; (B) CGPS-20; (C) CGPS-40;(D) CGPS-60; (E) CGPS-80.
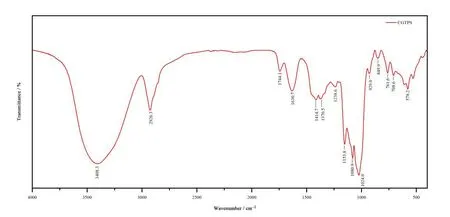
Fig.3 FT-IR spectra of CGTPS
3.3 Antioxidant activities in vitro
3.3.1 DPPH· radical scavenging activity
The scavenging capacity of polysaccharide samples on DPPH· free radicals was expressed by scavenging rate (%).The higher the scavenging rate,the stronger the antioxidant effect.As shown in Fig.4,each polysaccharide fraction showed certain scavenging activity at each concentration tested,and their activity increased with the increase of concentration within the range of 0.1-5.0 mg/mL.Difference in the antioxidant capacity of the five polysaccharide fractions was significant(P< 0.05).After graded ethanol precipitation,CGPS-80 and CGPS-20 showed stronger antioxidant activities than CGTPS.CGPS-80 was consistently found to exhibit much better scavenging DPPH·radical activity than other polysaccharides,up to 87.3% at 5 mg/mL.Wang et al.[26]summarized the latest reports on antioxidative polysaccharides and pointed out that other antioxidant substances such as pigments,flavones,peptide,protein,and polyphenol contained in polysaccharide extract,also contribute to the antioxidant activity.Besides,the activity of polysaccharides is not determined by a single factor,but by the combination of several related factors like chemical components,molecular weight,structure and conformation [27,28].Based on the physicochemical properties of polysaccharides previously determined,CGPS-80 contained higher contents of uronic acid and phenolic as well as lower molecular weight,which might be the reason for its higher DPPH· radical scavenging activity.
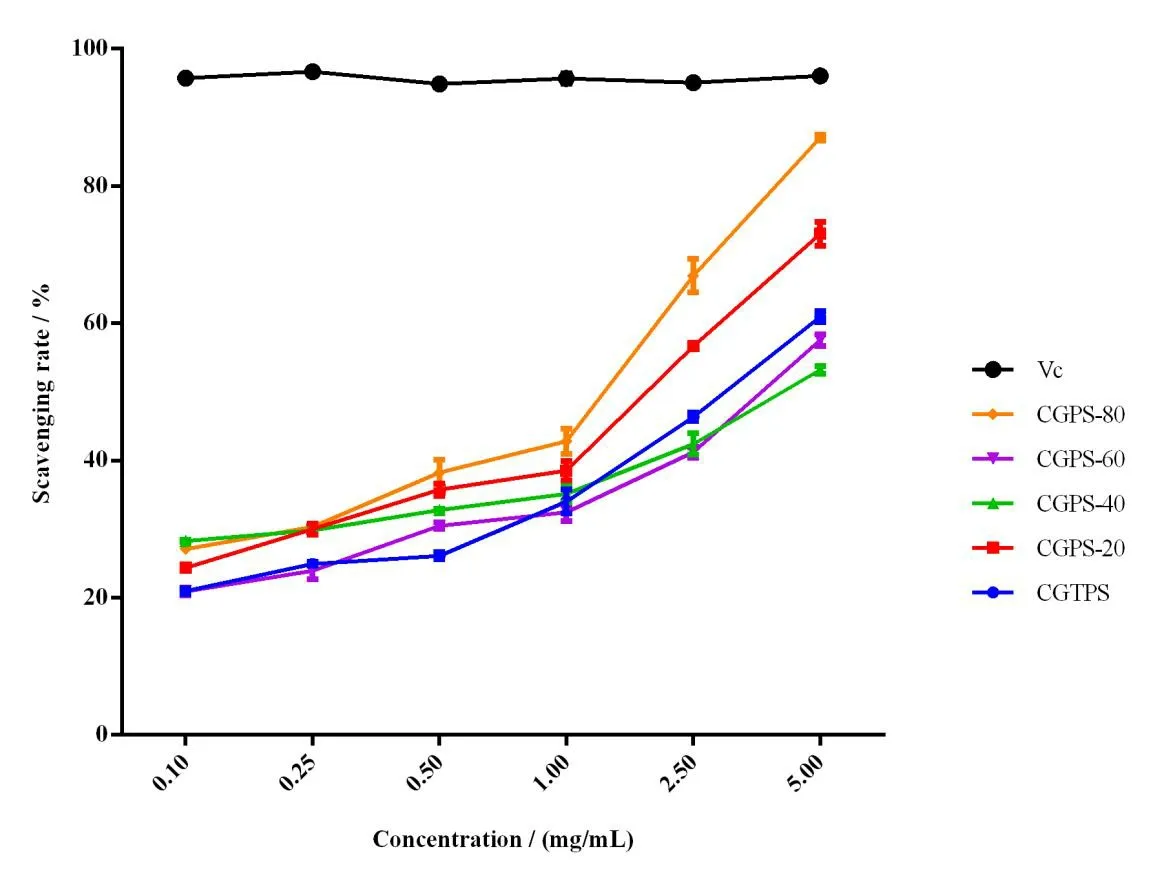
Fig.4 DPPH· radical scavenging effect of ginseng polysaccharides and Vc.Each value represents the mean ± SD (n=3,P < 0.05)
3.3.2 ABTS·+ radical cation scavenging activity
As shown in Fig.5,the ABTS·+radical cation scavenging activity of ginseng polysaccharides was evaluated and the result was similar to DPPH assay.The difference in antioxidant capacity of the five polysaccharide fractions was significantly different(P< 0.05).In short,higher ABTS·+radical cation scavenging activities is associated with greater antioxidant capacity.Among the four ginseng polysaccharides obtained by ethanol precipitation,CGPS-80 and CGPS-20 showed stronger antioxidant activities than CGTPS,and CGPS-80 showed the most significant ABTS·+radical scavenging activity,which might be due to the same reason as that for DPPH assay results.
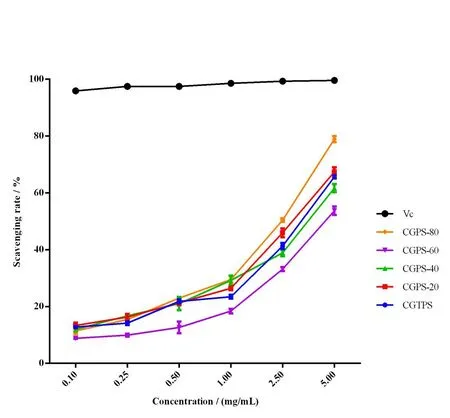
Fig.5 The percent inhibition of the ABTS·+ radical cation as a function of the concentration for ginseng polysaccharide samples and Vc.Each value represents the mean ± SD (n=3,P < 0.05)
4 Conclusions
In conclusion,four polysaccharides(CGPS-20,CGPS-40,CGPS-60 and CGPS-80)were isolated fromPanax ginsengC.A.Meyer by fractional precipitation with ethanol.Their physiochemical properties and antioxidant activities were investigated.The results showed that the four polysaccharide fractions were all heteropolysaccharides containing trace polyphenols,and their molecular weight and monosaccharide composition were significantly different.CGPS-80 exhibited the strongest antioxidant activitiesin vitro,which might be attributed to the co-action of carbohydrates,uronic acids and polyphenols.The results suggest that fractional precipitation is an effective method for preliminary purification of polysaccharides fromPanax ginsengC.A.Meyer,and CGPS-80 obtained by this method has great prospect as a non-toxic natural antioxidant.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Acknowledgements
This work was granted by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1702302)and LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program(XLYC1902119).
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- The protective effects of Gastrodia elata Bl.decoction and Gastrodin on Acrylamide-induced DNA damage in mice
- Studies on chemical constituents of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.)Swingle and their antioxidant activity
- Uncovering the potential targets of Viburnum odoratissimum for the treatment of related diseases
- Research progress on chemical constituents in Periploca forrestii and their pharmacological activities
- Studies on the chemical components and biological activities of the genus of Juncus
- Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Viburnum tinus L.
