Studies on the chemical components and biological activities of the genus of Juncus
2020-01-01JiaxinQiWanruJiangGangChenDiZhouNingLi
Jiaxin Qi,Wanru Jiang,Gang Chen,Di Zhou,Ning Li
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica; Key Laboratory of Computational Chemistry-Based Natural Antitumor Drug,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract Juncus is the largest genus of Juncaceae family,with about 240 species around the world.There are 77 species,1 variety and 10 deformations grown in China.Up to now,117 components have been identified as phenanthrenes and dihydrophenanthrenes,which are the characteristic constituents of this genus,and 48 ones have been identified as triterpenoids,glycerides,coumarins,flavonoids from this genus.The reported constituents displayed diverse bioactivities,including antiproliferative,antimicrobial,anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,anxiolytic,sedative,spasmolytic,anticholinesterase and antialgal effects.This review summarized the research progress on the chemical components and pharmacological effects of the genus of Juncus so far.
Key words:Juncus; chemical components; pharmacological activities
1 Introduction
Juncusis widely distributed in the world [1].Most of the species grow in coastal marsh lands or inlands and a few in meadows,swamps,watersides and damp environments [2].The genus ofJuncushas about 240 species globally.Among them,Juncus(J.)effusus,J.acutus,J.inflexusandJ.setchuensiswere studied systematically (Table 1).Some species are extensively used in the traditional Chinese medicine to treat numerous disorders.Medulla Junci(“Deng Xin Cao”),the dried stem pith ofJ.effususL.,is officially recorded in thePharmacopoeiaof the People’s Republic of China(2015).It is recommended for the treatment of insomnia,fidgetiness,oliguria and ulceration in the mouth or on the tongue [3].The stems ofJ.conglomeratus,J.effususandJ.inflexusare applied in the treatment of warts and other skin diseases [4,5].The seeds ofJ.rigidusare used to treat diarrhoea and diuretic disorders [6].Phytochemical research identified the major components as phenanthrenes,dihydrophenanthrenes,triterpenoids,glycerides,coumarins and flavonoids,and the critical bioactive components ofJuncusare considered to be phenanthrenes and dihydrophenanthrenes [7].These components possess a wide variety of biological activities,including antiproliferative,antimicrobial,anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,anxiolytic,sedative,spasmolytic,anticholinesterase and antialgal activities [8-11].
The present review aims to summarize the latest research on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects ofJuncus,and to provide reference for further research.
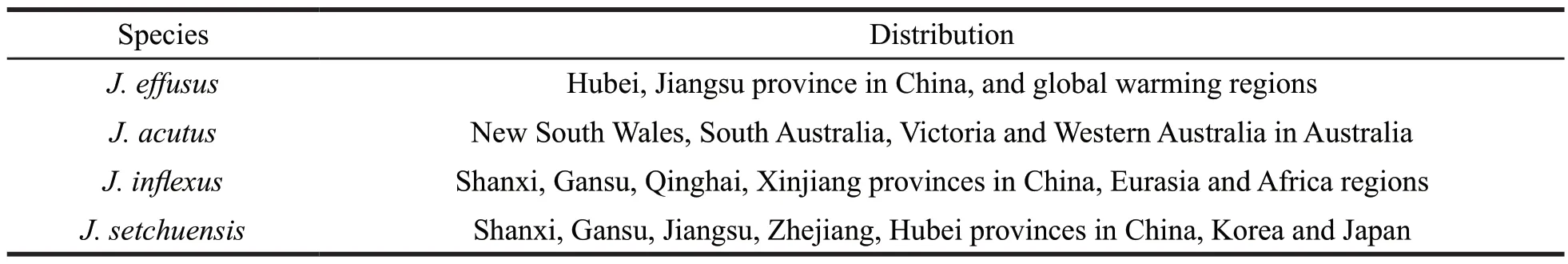
Table 1 The species and distribution of Juncus plants
2 Research on chemical components
Phenanthrenes (9,10-dihydrophenanthrenes),triterpenoids,glycerides,coumarins,flavonoids,and other components have been identified from variousJuncusgenus species,includingJ.acutus,J.atratus,J.effusus,J.inflexus,J.maritimus,J.roemerianus,J.setchuensisandJ.subulatus.
2.1 Phenanthrenes and 9,10-dihydrophenanthrenes
Totally 117 natural phenanthrenes and 9,10-dihydrophenanthrenes have been isolated fromJuncus.These compounds are mainly identified fromJ.acutus,J.effusus,J.inflexusandJ.setchuensis.
2.1.1 Dihydrophenanthrenes
The vinyl-substitute is a characteristic moiety of dihydrophenanthrenes skeleton fromJuncus.
2.1.1.1 Vinyl-substituted dihydrophenanthrenes
There are 36 vinyl-substituted dihydrophenanthrenes identified fromJuncus.These compounds were divided into three subtypes(A1-A3) based on the different positions of vinyl substituent in ring C:C-5,C-6 or C-8,respectively.Their structures are as follows(Fig.1).Detailed names and origins of 1-36 are listed in Table 2.
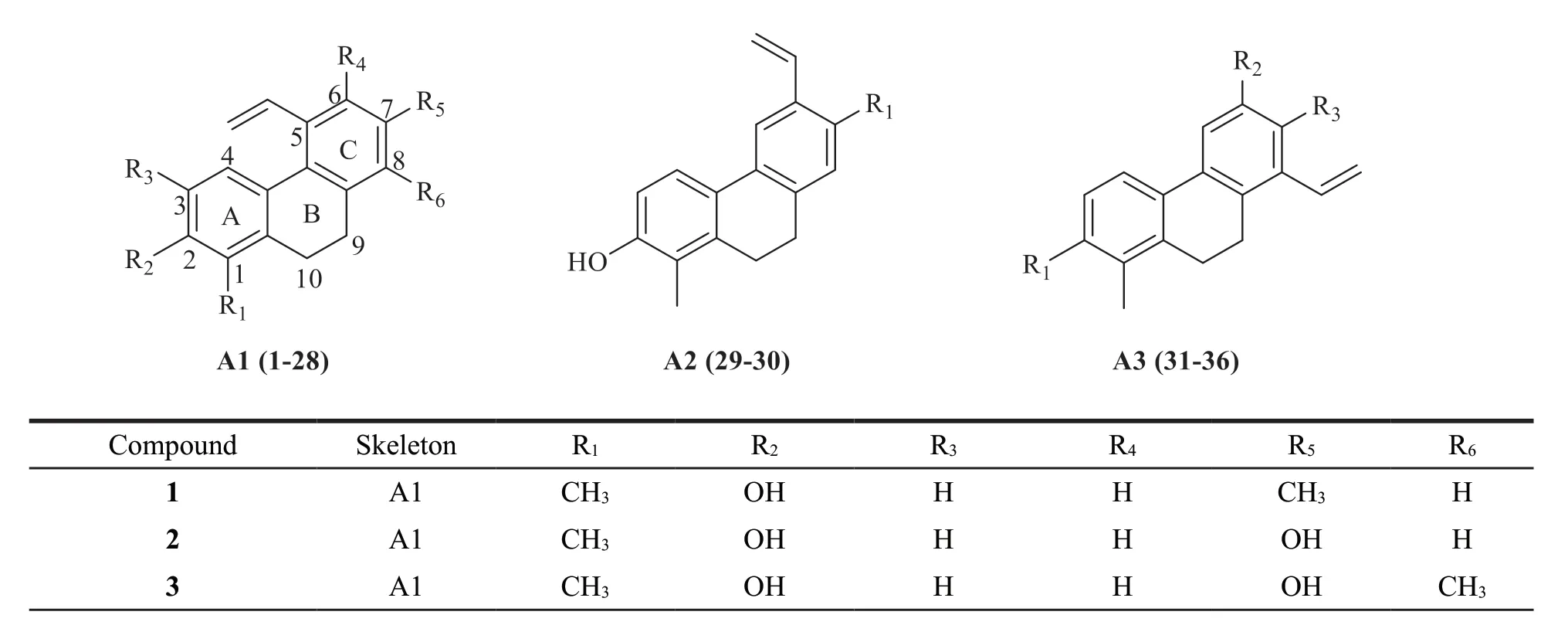
Fig.1 The structures of vinyl-substituted dihydrophenanthrenes identified from Juncus
(to be continued)
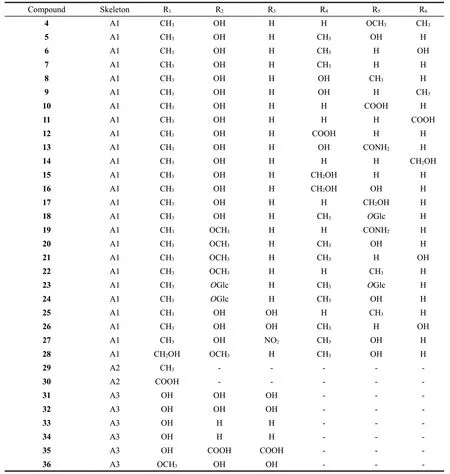
Continued fig.1
2.1.1.2 Dihydrophenanthrenes without vinyl group
27 dihydrophenanthrenes without vinyl group were identified fromJuncus.Their structures are as follows (Fig.2).Detailed names and origins of 37-63 are listed in Table 2.
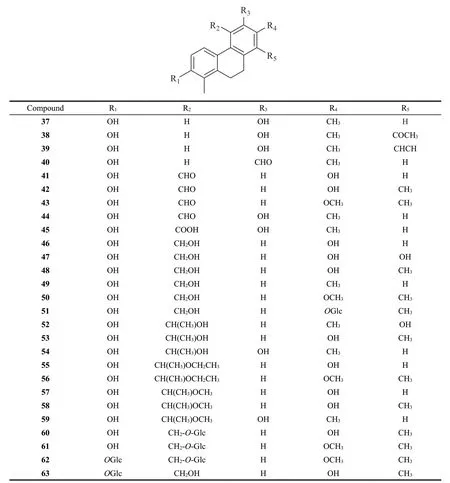
Fig.2 The structures of dihydrophenanthrenes without vinyl group identified from Juncus
2.1.1.3 Others
Other compounds with unique structures were also isolated from theJuncusgenus.In some cases,the absolute configuration of juncuenin D (64) with a hydroxyl group at C-10a was described to be (S) and chiral HPLC analysis showed a 4% enantiomeric excess resulting from theS-enantiomers.Jinflexin C (65) with a methyl and a vinyl group at C-7 and carbonyl at C-1 was isolated fromJ.inflexus.Dihydrophenanthrene 66 with a hemiacetal ring at ring C was isolated fromJ.effusus.Phenanthrenes 67 and 68 with a new six-membered ring formed by CH2-CH2groups at C-4,5 were isolated fromJ.acutus.The bridge between C-3a and C-4a was established by thesp3methine carbon (C-4)in juncutol (69),resulting in the formation of a cyclopenta[def]-phenanthrene structure fromJ.acutus.Juncuenin M (70) with an alkaloid group at C-5 of ring C was isolated fromJ.effusus.Compound 71 with a phytoxyethyl group at C-5 was isolated fromJ.acutus(Fig.3).Their detailed names and origins of 64-71 are listed in Table 2.
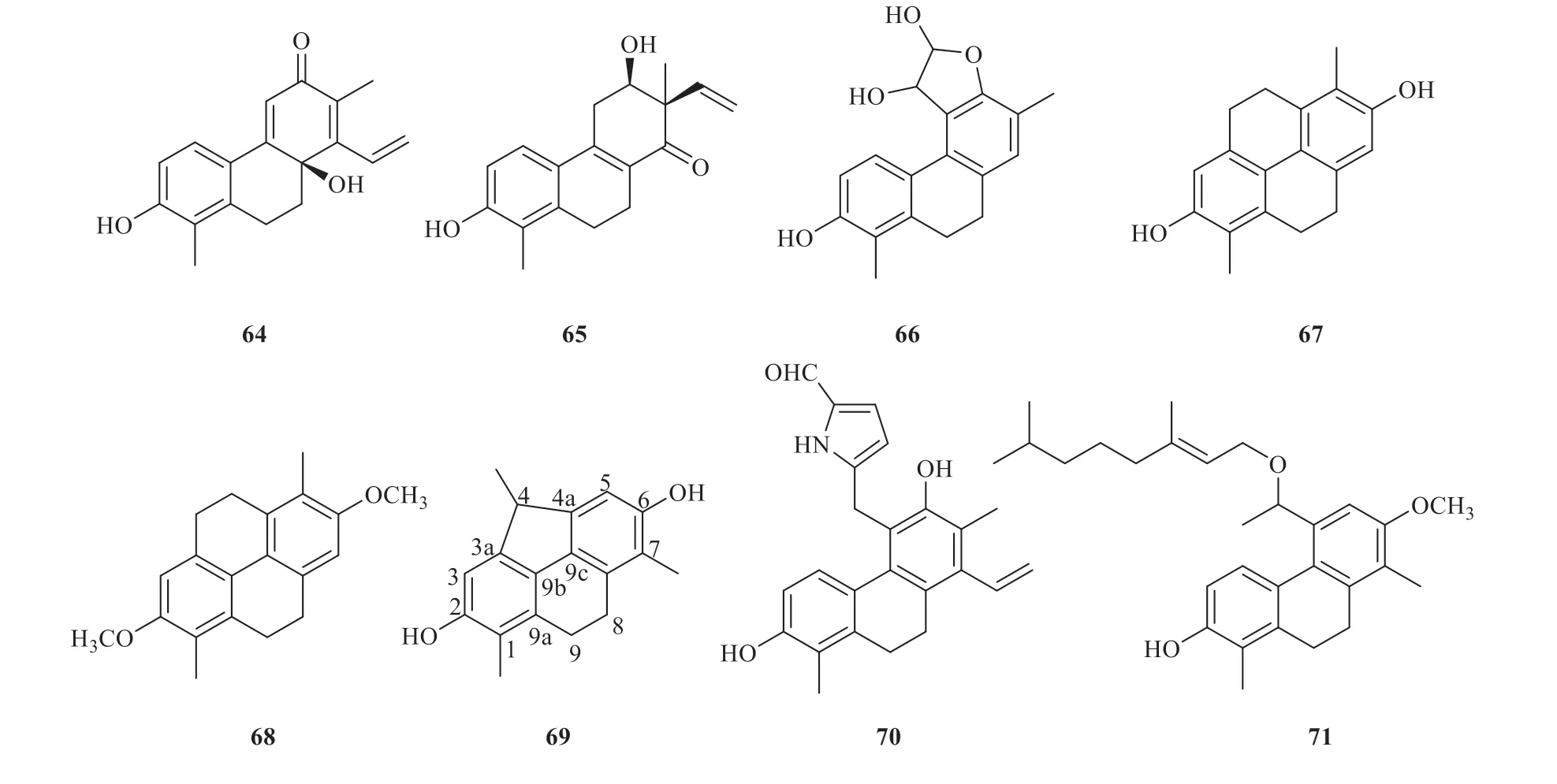
Fig.3 Other dihydrophenanthrenes identified from Juncus

Table 2 Names and origins of the dihydrophenanthrenes isolated from the Juncus genus
(to be continued)
(to be continued)
Continued table 2
2.1.2 Phenanthrenes
Vinyl group is also the characteristic substituent ofJuncusphenanthrenes and Juncaceae family.
2.1.2.1 Phenanthrenes with vinyl
14phenanthrene swithvinyl were identified fromJuncusand divided into three subtypes (B1-B3) according to the position of vinyl.Their structures are as follows (Fig.4).Detailed names and origins of 72-85 are listed in Table 3.

Fig.4 The structures of vinyl-substituted phenanthrenes identified from Juncus
2.1.2.2 Phenanthrenes without vinyl group
6 phenanthrenes without vinyl group were identified fromJuncus.Their structures are as follows (Fig.5).Detailed names and origins of 86-91 are listed in Table 3.
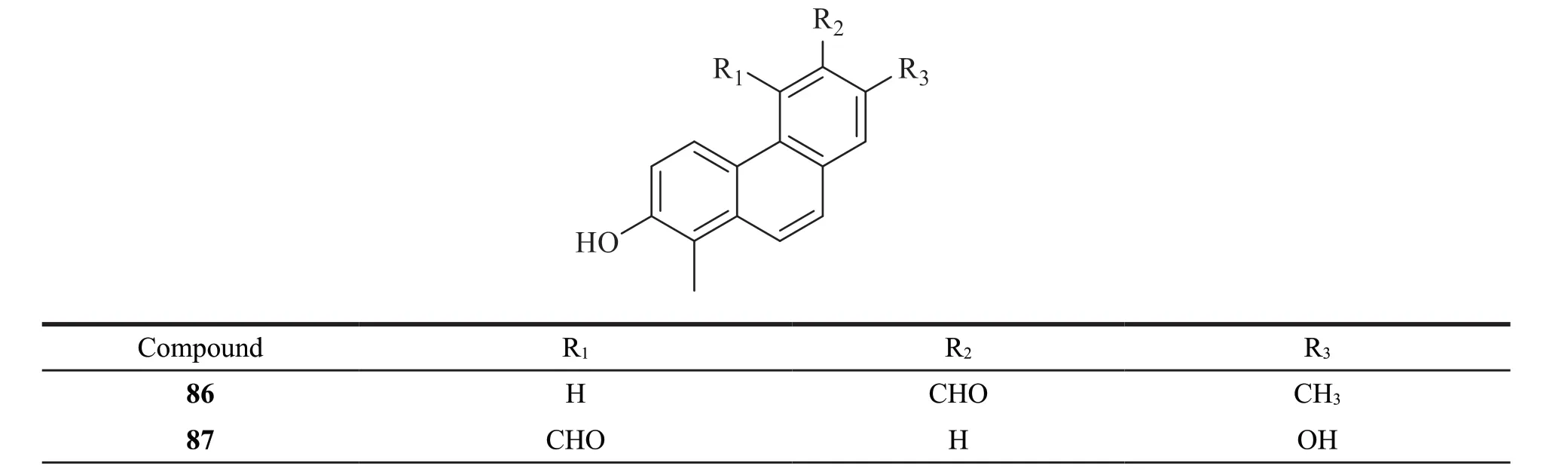
Fig.5 The structures of phenanthrenes without vinyl group identified from Juncus
(to be continued)

Continued fig.5
2.1.2.3 Others
Other phenanthrenes withunique structures were also isolated fromJuncusgenus.Dehydrojuncuenin C (92) was fromJ.setchuensis,with a six-membered lactone ring at C-1,2.Compounds 93 and 94 with more six-membered rings located at C-4,5 by CH=CH group were identified fromJ.acutus(Fig.6).Detailed names and origins of 92-94 are listed in Table 3.
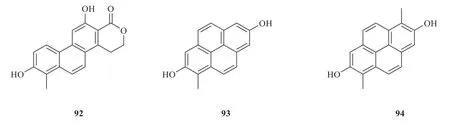
Fig.6 Other phenanthrenes identified from Juncus
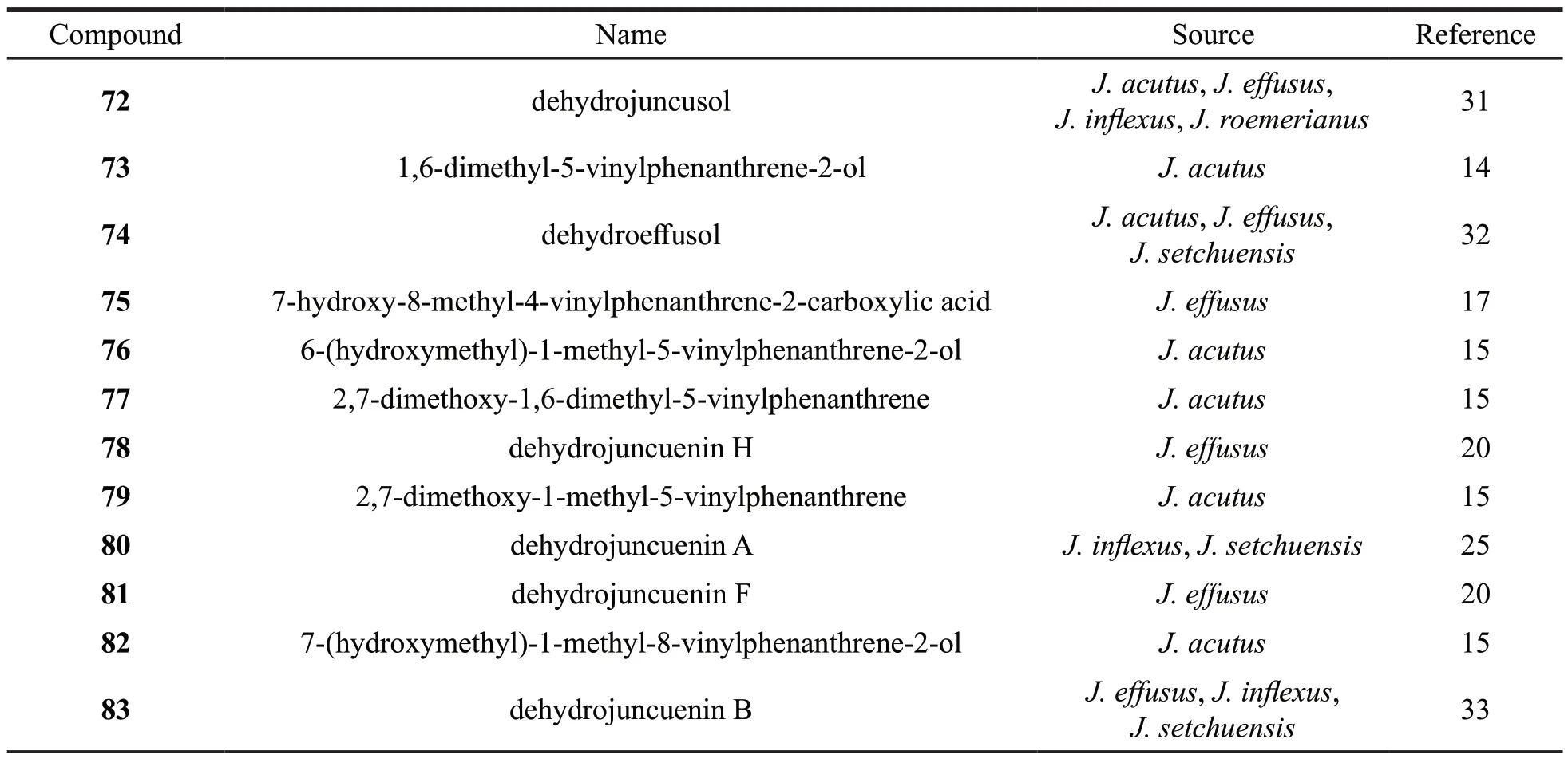
Table 3 Names and origins of the phenanthrenes isolated from the Juncus genus
(to be continued)

Continued table 3
2.1.3 Phenanthrenoid dimers
There are 23 phenanthrenoid dimers identified fromJ.acutus,J.inflexusandJ.effususso far.The dimerization pattern between two monomers could be classified into three types.The first type possesses the cage-like carbon framework with complicated stereochemistry (95-101).The second type is characterized by a single C-C' linkage between two monomers and the connection position at C-3,3',C-8,8',C-8,3',C-6,8',C-3,5' and C-7,7' linkages (102-114).The third type (115-117) are characterized by CH2or CH2-CH2linkage between two monomers fromJ.effusus(Fig.7).Detailed names and origins of 95-117 are listed in Table 4.
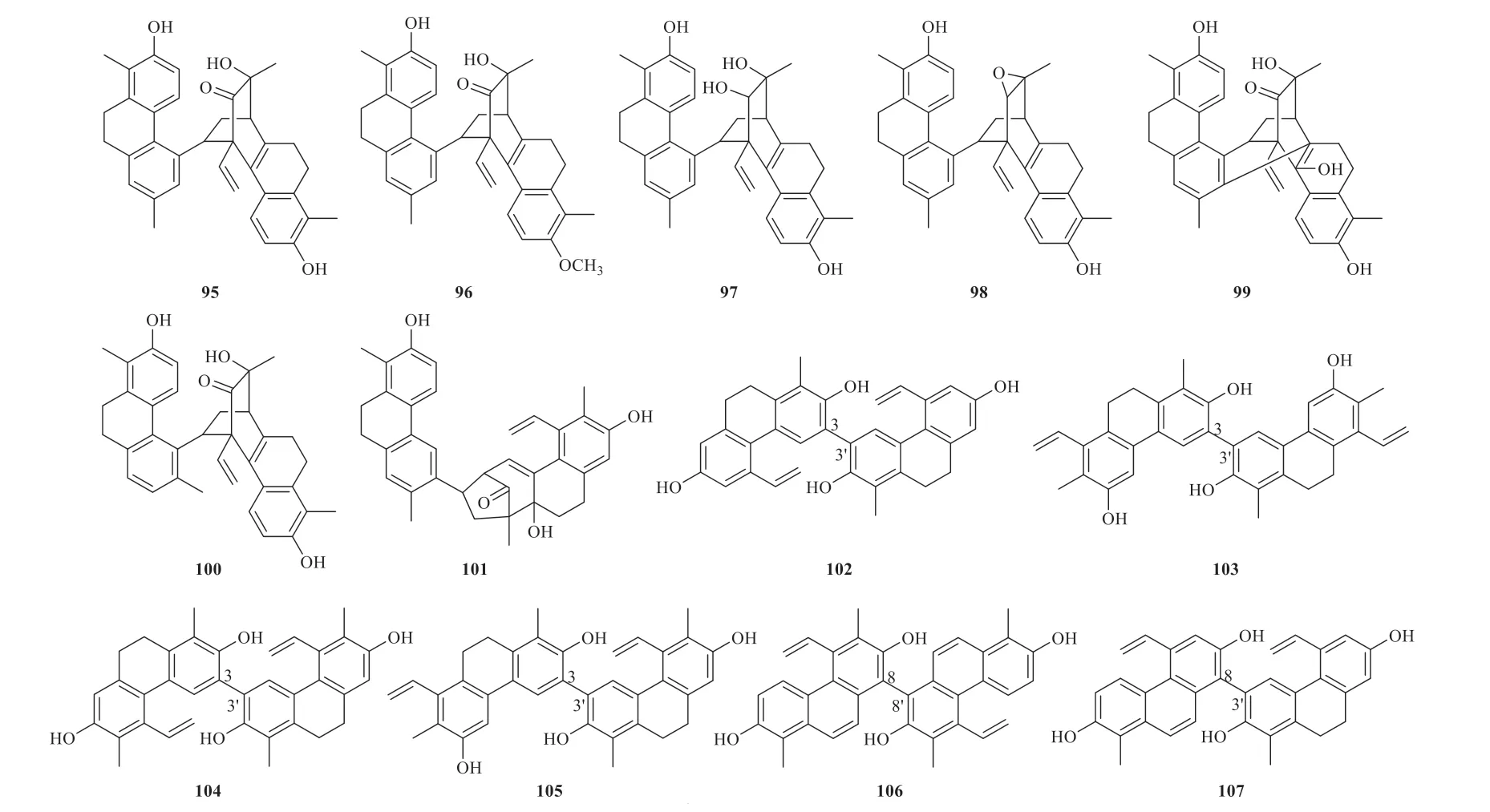
Fig.7 Phenanthrenoid dimers identified from Juncus
(to be continued)
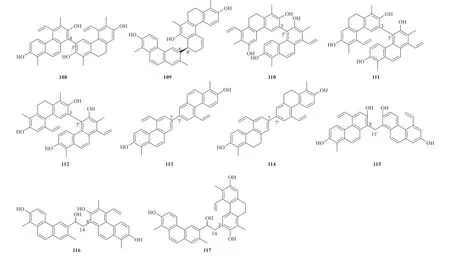
Continued fig.7

Table 4 Names and origins of the phenanthrenoid dimers isolated from the Juncus genus
(to be continued)

Continued table 4
2.2 Triterpenoids
According to published literature,16 triterpenoids were obtained fromJ.effusus,including cycloart-23Z-ene-3β,25-diol (118),3β-hydroxycycloart-25-en-24-one (119),3β-hydroxycycloartan-24-one (120),(24R)-cycloart-25-ene-3β,24-diol (121),(24S)-cycloart-25-ene-3β,24-diol(122),(24R)-24,25-epoxycycloartanol (123),(24S)-24,25-epoxycycloartanol (124),(24R)-cycloartane-3β,24,25-triol (125),(24S)-cycloartane-3β,24,25-triol (126) [41],juncoside I (127),juncoside Ⅱ(128),juncoside Ⅲ (129),juncoside Ⅳ (130),juncoside V (131),prosapogenol (132) and 3β,22Sdihydroxycycloart-24E-en-26-oic-acid (133) [42](Fig.8).
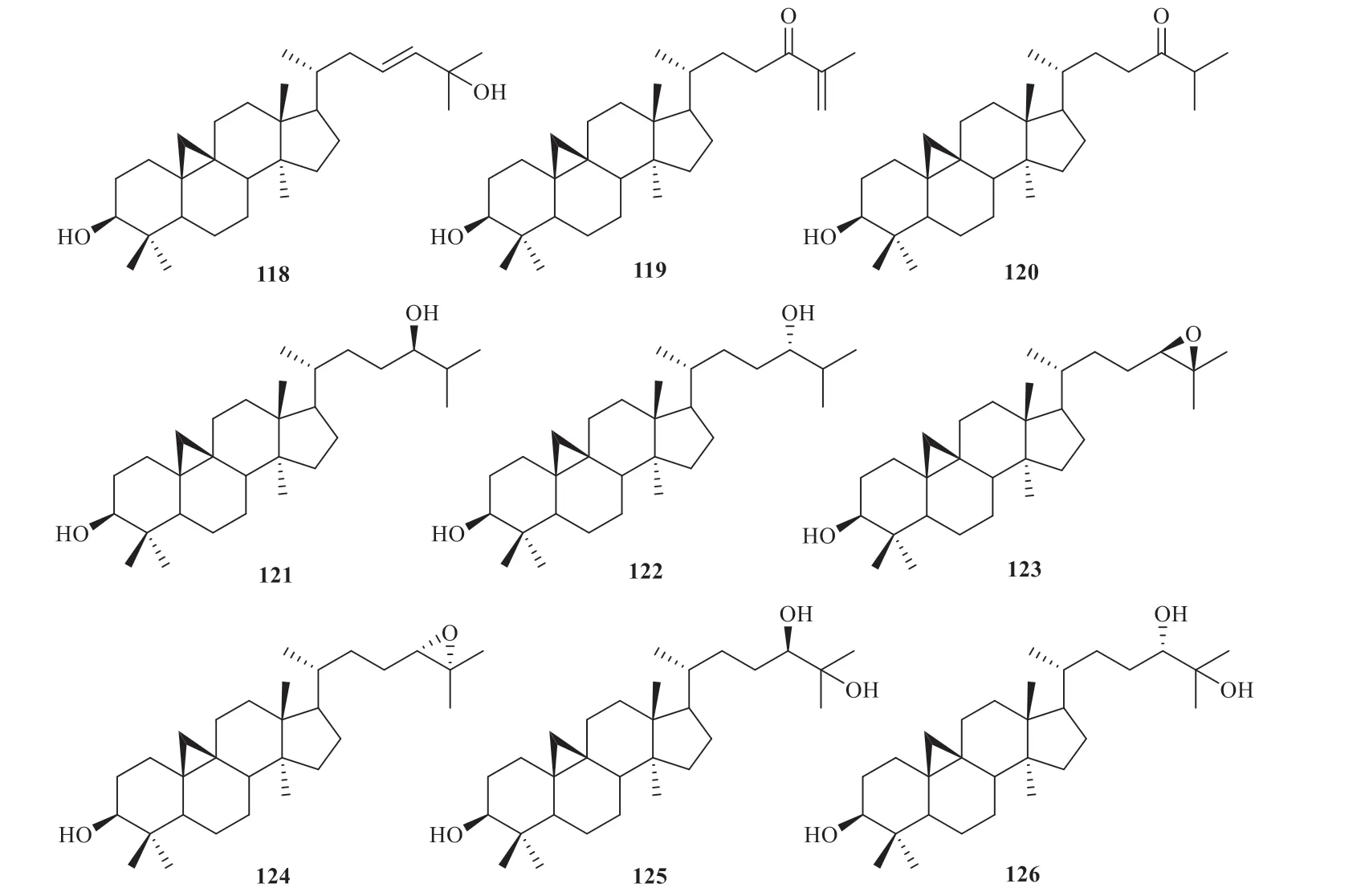
Fig.8 Triterpenoids identified from Juncus
(to be continued)

Continued fig.8
2.3 Glycerides
Glycerides are mainly fromJ.effusus.(E)-3-{[3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acryloyl]oxy}propane-1,2-diyl diacetate (134) has been isolated from the methanol extract ofJ.effusus[31].Della Greca et al.isolated eight glycerides including 2,3-isopropylidene-l-O-ρ-coumaroylglycerol(135),(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methyl (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)acrylate (136),2-O-ρ-coumaroylglycerol (137),3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propyl (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)acrylate (138),1-O-ρ-coumaroylglycerol (139),2,3-dihydroxypropyl (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)acrylate (140),2,3-dihydroxypropyl (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acrylate (141) and 1-O-furuloylglycerol (142) from the stem pith ofJ.effusus[43].In addition,one feruloylated glycoside,ethyl 5-O-trans-feruloyl-α-arabinofuranoside (143)was reported fromJ.effusus[10](Fig.9).
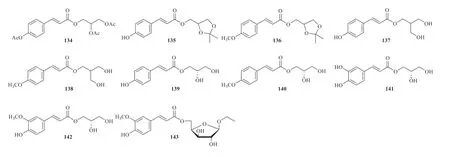
Fig.9 Glycerides identified from Juncus
2.4 Coumarins
9 coumarins have been isolated fromJuncus.Della Greca et al.isolated coumarins from the diethyl ether extract ofJ.acutus,including 7-methyl-5-vinyl-5a,8a-benzocoumarin (144),7-hydroxy-6-methyl-5-vinyl-5a,8a-benzocoumarin (145),6-hydroxymethyl-5-vinyl-5a,8a-benzocoumarin(146),7-hydroxy-8-methyl-5-vinyl-5a,8abenzocoumarin (147),7-methyl-5a,8a-benzo-[5,6-b]-furancoumarin (148),6-hydroxyl-7-methyl-5a,8a-benzocoumarin (149),and 6-hydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-7-methyl-5a,8a-benzocoumarin(150) [44].8-Methoxypsoralen (151) and angelicin(152) were isolated fromJ.effusus[45](Fig.10).
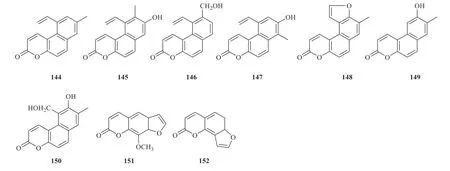
Fig.10 Coumarins identified from Juncus
2.5 Flavonoids
A number of flavonoids were also isolated and identified from theJuncusgenus.Among them,luteolin (153) and apigenin (154) were isolated fromJ.atratus[30]and luteolin 5-methyl ether(155) was from the medullae ofJ.effusus[24].Lu et al.obtained luteolin 5,3-dimethyl ether (156)from the EtOAc extract ofJ.effusus[46].Quercetin(157) and nobiletin (158) were isolated fromJ.effususby Jin et al.[47].Luteolin-7-O-β-glucoside(159) and hydnocarpin (160) were found from the CH2Cl2fraction ofrhizomes ofJ.acutusand the flavonolignan is composed of independent units of luteolin andρ-coumaryl alcohol [39](Fig.11).
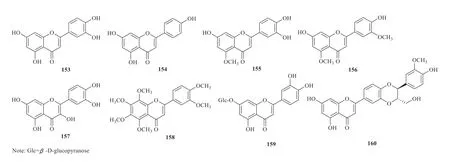
Fig.11 Flavonoids identified from Juncus
2.6 Others
Other compounds have been isolated from theJuncus genus.They are (7R,11R,E)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-ol (161),13(R)-hydroxyoctadeca-(9Z,11E,15Z)-trien-oic-acid (162) [30],4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethyl-2-nonen-4-olide (163) [24],4,4'-dihydroxy-3,3'-dimethoxybenzophenone(164) [23],and 1,7-dimethyl-6-vinyl-10,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxepine-2,8-diol (165) [48](Fig.12).
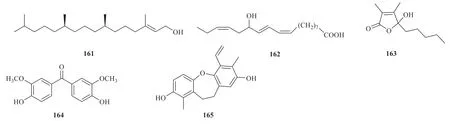
Fig.12 Other compounds identified from Juncus
3 Research on pharmacological effects
So far,research on the pharmacological activity of theJuncusgenus involved the crude extract and purified compounds.Diverse pharmacological activities,including antiproliferative,antimicrobial,anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,anxiolytic,sedative,spasmolytic,anticholinesterase and antialgal effects have been reported.
3.1 Antiproliferative activity
Over the past few years,a variety of compounds were isolated fromJ.effususandJ.atratusand tested for theirin vitrocytotoxicites against human cancer cell lines.The bioactive compounds and their IC50values are summarized in Table 5.
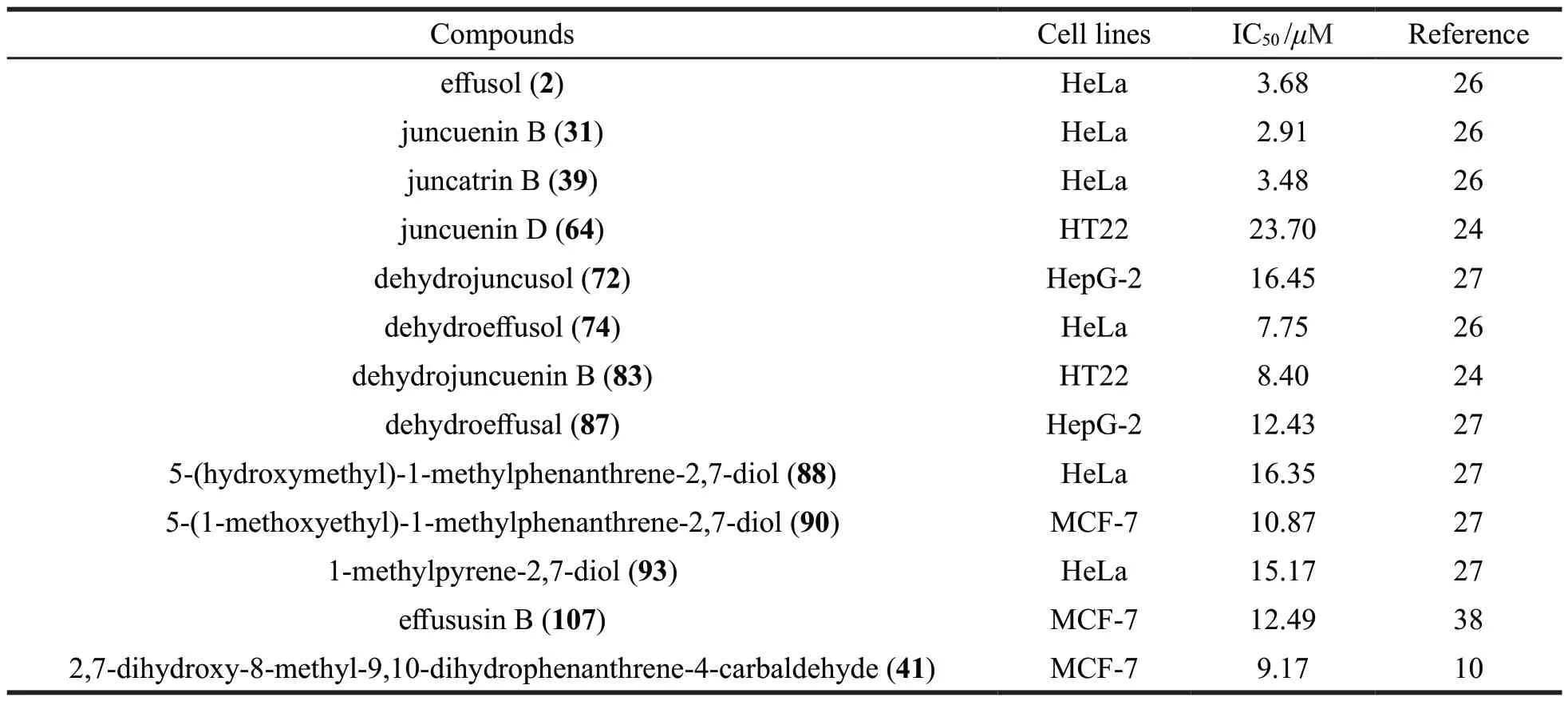
Table 5 Cytotoxicities of compounds identified from J.effusus and J.atratus against human cancer cell lines
3.2 Antimicrobial activity
Juncusol (5) and dehydroeffusol (74),from the EtOAc fraction of the methanol extract of underground parts ofJ.effusus,displayed enhanced antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus[MIC:1.6μg/mL (5),12.5μg/mL (74)][45].
Effusol (2),existing in the rhizomes ofJ.maritimus,was proved to show antimicrobial activity against the pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici(MIC:19μg/mL,IC50:9.98μg/mL) [49].
It is reported that juncusol (5),jinflexin B (28),juncuenin D (64) and dehydrojuncuenin B (83),which were fromJ.inflexus,showed antimicrobial activity against MRSA [MIC:12.5μg/mL (5),100μg/mL(28),12.5μg/mL (64),25μg/mL (83)][22].
3.3 Anti-inflammatory activity
Ma et al.found a variety of compounds in the crude extract of medullae ofJ.effusus.These compounds exhibited inhibitory effects on NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells.Effusol (2),8-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthren-2-ol (14),5-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol (46),dehydroeffusol(74),dehydroeffusal (87),5-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methylphenanthrene-2,7-diol (88),and 1-methylpyrene-2,7-diol (93) and the mixture of 2,7-dihydroxy-1,8-dimethyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (3) and juncusol (5) showed strong inhibitory effects on NO production in LPSactivated RAW 264.7 cells with the IC50values ranging from 10.50 to 16.30μM [27].
Effususin B (104),identified fromJ.effusus,also showed strong inhibitory effects on NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells (IC50:7.42μM) [38].
Juncutol (69),existing inJ.acutus,exhibited inhibitory effects of iNOS protein expression (11.2%)in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells at 10.0μM [16].
3.4 Antioxidant activity
Using an ABTS radical cation decolorization assay,Behery et al.isolated 8,8'-bidehydrojuncusol(106) and luteolin (153) fromJ.acutus.The compounds showed strong antioxidant activity,and the diphenanthrene possessed free radical scavenging activity (85.2% and 90.7%).This effect was comparable to that of the positive control ascorbic acid (88.7%) [39].
Dehydroeffusol (74) fromJ.effususdisplayed 11.3% penetration rate into the erythrocyte membrane,and the erythrocyte membrane affected the antioxidant activity.Dehydroeffusol (74) had a high ROS scavenging effect and a strong antioxidant activity (OSC50:1.70μM) [11].
3.5 Anxiolytic and sedative activities
Anxiolytic activity of effusol (2) and juncusol(5) fromJ.effusus,were evaluated in mice[OT=58.8s,OE=6.6 (2),and OT=75.5s,OE=7.8 (5),respectively]at 5 mg/kg [17].
Dehydrojuncuenin H (78) and juncusin(109),which were from the medullae ofJ.effusus,exhibited anxiolytic properties in mice [OT=102.8s,OE=8.4 (78),and OT=83.6s and OE=8.0 (109),respectively][32].
3.6 Spasmolytic activity
Dehydroeffusol (74),which was isolated from the aerial parts ofJ.effusus,slightly and briefly enhanced contractions in a concentration-dependent manner.However,it inhibited contractions induced by KCl (100 mM),(±)-Bay-K8644 (5μM),pilocarpine (90μM),and histamine (100μM).To summarize,dehydroeffusol (74) could be a potential agent to treat spasms [50].
3.7 Anticholinesterase activity
Juncunol (1),from the leaves and roots extracts ofJ.acutus,J.maritimusandJ.inflexus,exhibited better inhibitory activities butyrylcholinesterase(BuChE,IC50:758μM) than acetylcholinesterase(AChE,IC50: 940μM) [51].
3.8 Antialgal activity
7-methoxy-1,8-dimethyl-5-vinyl-9,1 0-dihydrophenanthren-2-o l (4),juncusol (5),7-methoxy-3,8-dimethyl-4-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthren-1-ol (21)and 5-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1,7-dimethyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,6-diol (54) were isolated fromJ.effusus andJ.acutus,which were found againstRaphidocelis subcapitata(syn.Selenastrum capricornutum) [IC50:28.0μM(4),19.9μM (5),11.1μM (21),16.8μM (54)][14,29,30,35,52].
4 Conclusions
Many plants fromJuncusgenus,have been widely used as traditional herbal medicines worldwide for centuries.According to the recent studies,the genusJuncushas a wide range of medicinal value.To ensure the medication safety and reliability,it is urgent to study pharmacodynamics material basis and pharmacokinetics ofJuncus.Phenanthrenes and dihydrophenanthrenes are the characteristic components ofJuncus.These compounds possess many biological activities,in particular antiproliferative,antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities.Therefore,phytochemical investigation of otherJuncusspecies and further pharmacological studies of the identified compounds would be significant for the development of their pharmacological potential.Since dihydrophenanthrenes have potential antiinflammatory activity and the vinyl-substitutes are a characteristic moiety of dihydrophenanthrenes,systematic study and activity evaluation of dihydrophenanthrenes would be the promising area to explore in further study ofJuncus.The information collected and reviewed here provides resources for further pharmacological and phytochemical studies ofJuncus.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.81872768,81673323,U1903122),Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1807118),and Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (2018)
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- Contribution Regulations for Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines
- Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Viburnum tinus L.
- Research progress on chemical constituents in Periploca forrestii and their pharmacological activities
- Uncovering the potential targets of Viburnum odoratissimum for the treatment of related diseases
- Studies on chemical constituents of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.)Swingle and their antioxidant activity
- Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted from Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer with graded percipitation method
