基于转录组的剑麻ARF基因家族的鉴定及表达分析
2019-12-14鹿志伟侯晓婉杨子平张燕梅李俊峰周文钊
鹿志伟 侯晓婉 杨子平 张燕梅 李俊峰 周文钊

摘 要 生长素反应因子(Auxin Response Factors, ARFs)是植物特有的多基因转录因子家族,参与植物生长发育过程的调节。本研究基于转录组数据,通过生物信息学方法鉴定剑麻ARF基因家族成员,同时对其进行相关生物信息学分析。结果表明:在剑麻中共鉴定得到15个ARF基因,并依次命名为AhARF1~15。其编码的蛋白质含有409~1011个氨基酸,分子量约为45.17~112.13 ku,等电点为5.17~9.34。亚细胞定位预测结果显示,13个AhARFs定位于细胞核,2个AhARFs定位于叶绿体。保守结构域分析结果表明,AhARFs基因家族有8个成员同时含有B3、ARF和Aux/IAA这3个相对保守的结构域,其他成员仅含有B3和ARF这2个结构域。进化树分析表明,剑麻AhARFs蛋白可分为5个亚家族。15个剑麻AhARFs基因在剑麻紫色卷叶病不同发病时期呈现不同的表达规律。本研究为进一步深入探索剑麻ARF基因家族的功能奠定了重要理論基础。
关键词 剑麻;ARF;基因家族;转录组中图分类号 S563.8 文献标识码 A
Transcriptome-wide Identification and Expression Profiling of the Auxin Response Factor (ARF) Gene Family in Agave.hybrid No.11648
LU Zhiwei1,2, HOU Xiaowan1, YANG Ziping1,2, ZHANG Yanmei1,2, LI Junfeng1,2, ZHOU Wenzhao1,2*
1. South Subtropical Crops Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, Zhanjiang, Guangdong 524091, China; 2. Zhanjiang City Key Laboratory for Tropical Crops Genetic Improvement, Zhanjiang, Guangdong 524091, China
Abstract Auxin response factors (ARFs) are plant-specific polygenic transcription factor families involved in the regulation of plant growth and development. In this study, the members of the agaveARF gene family were identified and analyzed by bioinformatics methods, based on transcriptome data. The results showed that 15ARFgenes were identified in agave and named fromAhARF1toAhARF 15in turn, its encoded protein varied from 409 to 1011 amino acid residues in length, the molecular weight ranged from 45.17 to 112.13 ku, and the isoelectric point varied from 5.17 to 9.34. Subcellular localization prediction showed that 13AhARFswere localized in the nucleus and 2AhARFswere located in the chloroplast. Conservative domain analysis results indicated that there were eight members among theAhARFsgene family which containing three relatively conserved domains, B3, ARF, and Aux/IAA. The other members contained only the two domains, B3 and ARF. Phylogenetic tree analysis indicated that the AhARFs protein could be divided into five subfamilies. The 15AhARFsgenes showed different expression patterns in different stages of agave purple leaf curl disease. This research would lay an important theoretical foundation for further study of the function of theAhARFsgene family.
Keywords agave;ARF; gene family; transcriptome
DOI10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.10.09
生长素响应因子(auxin response factor, ARF)是一种调控生长素响应基因表达的转录因子,广泛存在于植物中,在植物生长发育过程的各个阶段中起着重要调控作用[1-2]。所有的ARF蛋白均含有一个保守的N端B3 domain,一个Auxin-resp domain(ARF)[3]。前者是DNA结合结构域,负责与靶基因结合。后者是ARF的功能结构域,能够在外界信号刺激下特异性地与靶基因启动子中的生长素响应元件--TGTCTC结合,激活或者抑制靶基因的表达,进而行使对植物生长发育的调控功能[4-5]。此外,有些ARF蛋白质C末端还含有Aux/IAA二聚化结构域,能够通过同源或异源二聚体的形成来调节ARF蛋白质的活性[6-7]。由于ARF在细胞分裂和分化、果實发育、侧根的形成、顶端优势、向性反应等诸多植物生长发育过程中起着至关重要的作用,以及高通量测序和生物信息学分析技术的飞速发展,使得越来越多植物中的ARF基因家族被鉴定出来[8],如荔枝[9]、拟南芥[10]、烟草[2]、大豆[11]、水稻[12]、番茄[13]、玉米[14]、葡萄[15]、苹果[1]、杨树[16]和香蕉[17]等植物。但是在剑麻中目前尚未发现有关ARF基因的相关报道,严重制约着剑麻中ARF基因功能的深入研究。
本研究基于前期已完成的剑麻紫色卷叶病不同发病时期转录组数据库,在转录组水平上对剑麻ARF基因家族进行鉴定与相关生物信息学分析,同时对ARF基因家族在剑麻紫色卷叶病高抗和高感植株不同发病阶段中的表达特征进行分析,初步研究ARF基因家族在植物病害应答过程中所充当的角色,为后期深入系统地研究ARF基因家族在剑麻中的功能提供前期基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
所选材料为剑麻H.11648紫色卷叶病高抗和高感植株,种植于中国热带农业科学院南亚热带作物研究所剑麻种质圃内,选择大小和长势一致的高抗和高感健康无虫植株各3株,分别统一接种粉蚧后,在0、60、90 d 3个时期(接种60 d后高感植株叶片部位开始出现紫色卷叶病病状特征)进行取样用于转录组测序分析,设置3个生物学重复。
1.2方法
1.2.1ARF基因家族鉴定 剑麻转录组数据由本课题组测序获得(相关数据未发表),共拼接组装获得66365个unigenes。利用植物转录因子数据库(http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn/)和Phytozome12基因组数据库(https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/ portal.html)下载模式植物拟南芥和水稻的ARF基因序列,将其作为探针序列,利用本地Blast软件在剑麻转录组数据中进行blast搜索比对。同时,利用关键词“auxinresponse factor”和“ARF”进行直接检索,最后除去所得全部序列中的重复序列。利用NCBI的CCD数据库对蛋白保守结构域进行鉴定,并删除不含ARF基因家族特征结构域的基因。
1.2.2 基本理化性质及保守结构域分析 利用在线软件ProtParam(http://web.expasy.org/protpara m/)对剑麻ARF蛋白序列的分子量、等电点、不稳定系数、脂肪指数和疏水性等基本的理化性质进行预测分析。利用在线软件Plant-mPLoc Server(http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/#)对剑麻ARF蛋白进行亚细胞定位预测分析。
利用在线软件MEME5.0.5(http://meme-suite. org/tools/meme)和TBtools软件对剑麻ARF家族蛋白的保守基序进行分析,基序的大数目设置为20,基序长度设置为6~200个氨基酸。运用在线软件NCBI的CCD(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi)和IBS 1.0.2软件对得到的保守基序进行功能注释,参照拟南芥和水稻的命名模式进行命名。
1.2.3 进化树分析 利用Clustal X 2.1、MEGA5.20和Evolview在线软件(http://www.evolgenius.info /evolview)对剑麻、拟南芥和水稻的所有ARF蛋白序列进行进化树构建与优化处理,其中系统发育进化树构建采用邻接法(neighbor joining,NJ),参数设置选择P-distance、pairwise deletion和Bootstrap method=1000,其他参数选择默认值。
1.2.4 表达模式分析 利用剑麻转录组测序数据分析ARF基因的表达特征。转录组数据包括剑麻紫色卷叶病高抗和高感植株在0、60、90 d 三个不同发病时期的基因表达数据。以FPKM值表示轉录本丰度,通过对数据均一化处理,利用TBtools工具做热图。
2 结果与分析
2.1剑麻ARF基因家族的鉴定
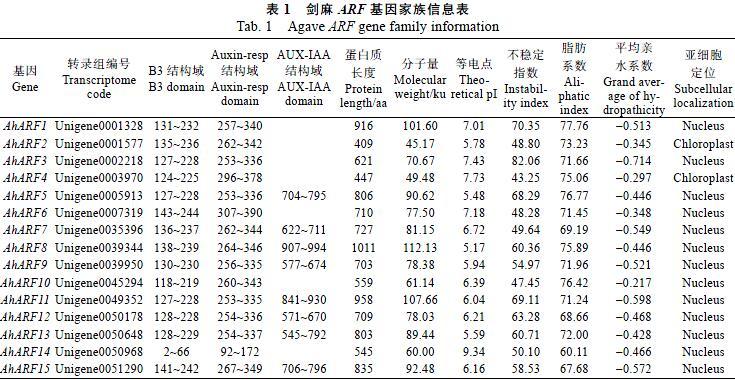
通过对转录组数据库的本地Blast文库进行检索,共获得16条ARF序列,经CCD在线数据库分析后最终获得15个含有保守结构域的ARF序列。按照基因在转录组中的ID大小为剑麻ARF编号,即AhARF1~AhARF15,见表1。从表中可以看出15个AhARF基因大小为1230~3036 bp,相应的编码氨基酸个数为409~1011个,编码蛋白质理论分子量大小为45.17~112.13 ku。编码蛋白质理论等电点大小为5.17~9.34,其中有5个大于7,平均大小为6.54,呈现弱酸性。不稳定指数均大于40,均为不稳定蛋白。平均亲水系数均小于零,说明各蛋白均为亲水性蛋白。亚细胞定位预测分析表明AhARF1和AhARF4定位于叶绿体,其他AhARFs则均定位在细胞核。
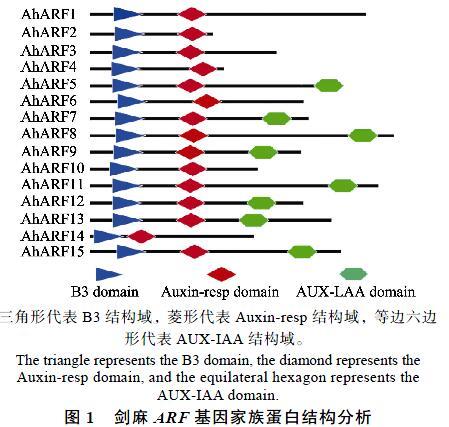
通过在线软件NCBI的CCD(https://www.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi)数据库对AhARF基因家族编码蛋白的B3、Auxin-resp和AUX-IAA保守结构域进行分析,结果表明AhARF5/7/8/9/11/12/13/15同时含有ARF家族的3个结构域,占剑麻AhARF基因家族总数的53.33%,而其他成员仅含有B3和Auxin-resp这2个结构域,相关信息见表1和图1。
2.2AhARF蛋白的保守基序分析
通过在线软件MEME和TBtools软件对AhARFs蛋白中的保守motif进行分析,结果见图2、图3。预测AhARFs基因家族中含有20个保守motif,不同ARF基因家族成员之间所包含的motif不同,按照在AhARF基因家族中出现次数进行排序,其中motif 1/6/8/9/11出现15次,motif 2/4/5/7/13/18出现14次,motif 12出现13次,motif 10/14/16出现9次,motif 3出现8次,motif 15出现4次,motif 17出现2次,motif 19/20出现1次,Motif在ARF基因家族中出现频率越高说明其越重要。
2.3ARF家族进化树分析
为充分明确剑麻ARF基因家族各成员间进化关系与生物学功能的相关性,将15个AhARF基因家族成员与模式植物水稻、拟南芥的ARF基因家族成员进行进化关系分析,构建相关进化树,结果见图4。从图4中可以看出,整个进化树共分为5个亚族,其中GroupⅠ中含有4个AhARF成员,GroupⅡ含有6个AhARF成员,GroupⅢ含有2个AhARF成员,GroupⅣ含有3个AhARF成员,而Ⅴ则没有相关AhARF成员。进化关系上归为一类的ARF基因在功能上可能较为相似,因此可以通过模式植物中已知功能的ARF基因推测剑麻中进化关系较近的AhARF基因功能。
Motif 1~20代表不同的保守氨基酸序列,每个motif中不同位置处出现的氨基酸种类越少,说明该位置处保守性越高。
Motif 1 to 20 represent different conserved amino acid sequences. The fewer amino acids species appearring at different positions in each motif, the higher the conservation at this position.
不同颜色方块代表不同的保守基序,其中OsARF1~48代表水稻ARF基因家族,AtARF 1~37代表拟南芥ARF基因家族,AhARF 1~15代表剑麻ARF基因家族。
Different color squares represent different conservative motifs.OsARF1-48represent theARFgene family inOryza sativaL.AtARF1-37represent theARFgene family inArabidopsis thaliana.AhARF1-15represent theARFgene family inAgave.hybridNo.11648.
不同颜色代表不同聚类家族。不同的形状表示不同的物种,五角星代表来自水稻的ARF蛋白,正方形代表来自拟南芥的ARF蛋白,圆形代表来自剑麻的ARF蛋白。
Different colors represent different cluster families. Different shapes represent different species, the star represents the ARF protein from rice,the square represents the ARF protein from Arabidopsis and the circle represents the ARF protein from agave.
2.4剑麻ARF基因家族表达分析
根据已完成的剑麻紫色卷叶病高抗和高感植株的RNA-Seq数据库(相关数据未发表),找出筛选出的15个AhARF基因相应的RPKM值,经均一化处理后,利用TBtools进行HeatMap热图制作,结果见图5。从图5可以看出,15个AhARF基因在高抗和高感植株中均有表达,但不同基因间有其独特的表达模式,同时也有其表达共性,如粉蚧接种处理0 d时,大多数AhARF基因在高抗和高感植株中均呈现上调表达,随着处理后时间的延长,多数基因均呈现下调表达趋势。此外,随着粉蚧接种处理后时间的延长,AhARF13/14基因在剑麻紫色卷叶病高抗植株中呈现先上调后下调的表达趋势,AhARF10基因则在高感植株中呈现一直上调的表达趋势,推测这3个基因可能直接或者间接的参与剑麻紫色卷叶病抗性的调节。
3 讨论
当前,随着高通量测序和生物信息学技术的迅猛发展,越来越多植物ARF基因家族相继被鉴定出来,ARF基因家族鉴定方式主要包括全基因组学水平的鉴定和转录组学水平的鉴定这2种方式[8]。基于全基因组学水平的鉴定方式,分别从拟南芥[10]、烟草[2]、大豆[11]、水稻[12]、番茄[13]、葡萄[15]、蘋果[1]、杨树[16]、桃[18]、铁皮石斛[19]等植物中鉴定得到了23、50、51、25、21、19、29、39、18、14个ARF基因。而基于转录组学水平的鉴定方式,分别从荔枝、黄芩、水仙等植物中鉴定得到了21、24、21个ARF基因。本研究通过转录组学水平的鉴定方式,从剑麻中鉴定得到了15个ARF基因家族。通过蛋白质保守结构域预测,结果发现除AhARF9和AhARF14外,其他AhARFs蛋白B3 domain均由102个氨基酸组成,这与水仙、柑橘的研究结果相似[8-20]。Tiwari等[21]和Ulmasov等[22]研究发现,B3 domain与AUX-IAA domain之间的非保守区域如果富含甘氨酸(G)、丝氨酸(S)、亮氨酸(L)和脯氨酸(P)残基则为转录抑制子,如果富含谷氨酰胺(Q)、丝氨酸(S)和亮氨酸(L)残基则为转录激活子。本研究中发现剑麻AhARF蛋白中有8个AhARF蛋白同时含有B3 domain与AUX-IAA domain结构域,其中AhARF 5/8/11/13富含Q、S、L,推测其为转录激活子,而AhARF 7/9/12/15则
红色系列和绿色系列圆点代表其对应基因相对表达量分别为正值和负值。圆点越大其对应基因相对表达量的绝对值越大。相反,圆点越小其对应基因相对表达量的绝对值越小。在列标题中,F代表高感植株;R代表高抗植株;0、60、90 d分别代表粉蚧接种后0、60、90 d。在行标题中,AhARF1~15分表代表不同剑麻ARF基因。
The red series and the green series dot represent the relative expression levels of the corresponding genes are positive and negative, respectively. The larger the dot, the larger the absolute value of the its corresponding gene relative expression levels. Conversely, the smaller the dot, the smaller the absolute value of its corresponding gene relative expression levels. In the column title, F represents disease-susceptible plant; R represents disease-resistant plant; 0 d, 60 d, 90 d represent 0 day, 60 day, 90 days after inoculated with mealybug.In the row title,AhARF1–15represent different agave ARFgenes.
富含G、S、L、P,推测其为转录抑制子。结合剑麻AhARF和拟南芥、水稻的进化树分析结果,AhARF 5/8/11/13均分布在Group II中,而AhARF 7/9/12/15均分布在Group I,进一步验证了该推测,与Tiwari等[21]和Ulmasov 等[22]的研究结果相吻合。
本研究基于转录组学水平的鉴定方式从剑麻中筛选获得15个ARF基因,并对其进行相关生物信息学和表达特征分析,为深入研究ARF基因家族在剑麻中的相关功能奠定了坚实的基础。
参考文献
[1] 李慧峰, 冉 昆, 何 平, 等. 苹果生长素响应因子(ARF)基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(7): 1045-1054.
[2] 孙亭亭, 张 磊, 陈 乐, 等. 普通烟草ARF基因家族序列的鉴定与表达分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2016, 17(1): 162-168.
[3] 李洪有, 霍冬敖, 蔡 芳, 等. 荞麦ARF基因家族的鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(1): 7-13.
[4] Li S B, Xie Z Z, Hu C G,et al. A review of auxin response factors (ARFs) in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 47.
[5] Guilfoyle T J, Hagen G. Auxin response factors[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2007, 10(5): 453-460.
[6] 郭宝健, 李 赢, 袁泽宸, 等. 大麦ARF基因家族的全基因组分析[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2016, 36(11): 1426-1432.
[7] 杨 舟, 呂 可, 吕 珊, 等. 百子莲2个ARF基因与2个Aux/IAA基因的全长克隆与序列分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(1): 86-97.
[8] 李全超, 刘 洋, 肖瑶宇, 等. 基于转录组的‘黄花2号水仙ARF 基因家族分析[J].应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(3): 687-694.
[9] 董 晨, 魏永赞, 王 弋, 等. 基于转录组的荔枝ARF基因家族的鉴定及表达分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(8): 1485-1491.
[10] Okushima Y, Overvoorde P J, Arima K,et al. Functional genomic analysis of the AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR gene family members inArabidopsis thaliana: unique and overlapping functions of ARF7 and ARF19[J]. The Plant Cell, 2005, 17(2): 444-463.
[11] Chien V H, Dung T L, Nishiyama R,et al. The auxin response factor transcription factor family in soybean: genome-wide identification and expression analyses during development and water stress[J]. DNA Research, 2013, 20(5): 511-524.
[12] Wang D, Pei K, Fu Y,et al. Genome-wide analysis of the auxin response factors (ARF) gene family in rice (Oryzasativa) [J]. Gene, 2007, 394(1-2): 13-24.
[13] Wu J, Wang F, Cheng L,et al. Identification, isolation and expression analysis of auxin response factor (ARF) genes inSolanum lycopersicum[J]. Plant Cell Report, 2011, 30(11): 2059-2073.
[14] Xing H, Pudake R N, Guo G,et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of auxin response factor (ARF) gene family in maize[J]. BMC Genomics, 2011, 12(1): 178.
[15] Wan S, Li W, Zhu Y,et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of the auxin response factor gene family inVitis vinifera[J]. Plant Cell Report, 2014, 33(8): 1365-1375.
[16] Kalluri U C, Difazio S P, Brunner A M,et al. Genome-wide analysis of Aux/IAA and ARFgene families in Populus trichocarpa[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2007, 7: 59.
[17] Hu W, Jiao Z, Hou X,et al. The auxin response factor gene family in banana: genome-wide identification and expression analyses during development, ripening, and abiotic stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 742.
[18] Li H, Ran K, Sun Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of peach auxin response factor gene families [J]. Journal of Plant Biochemistry Biotechnology, 2016, 25(4): 349-357.
[19] Chen Z, Yuan Y, Fu D,et al. Identification and expression profiling of the auxin response factors inDendrobium officinaleunder abiotic stresses[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(5): 927.
[20] 李斯貝. 柑橘生长素响应因子ARF基因家族的表达分析及功能验证[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2016.
[21] Tiwari S B, Hagen G, Guilfoyle T. The roles of auxin response factor domains in auxin-responsive transcription[J]. The Plant Cell, 2003, 15(2): 533-543.
[22] Ulmasov T, Hagen G, Guilfoyle T J. Activation and repression of transcription by auxin-response factors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 1999, 96(10): 5844-5849.
