肿瘤合并糖尿病患者住院期间血糖控制不良原因分析和护理配合研究
2019-12-13陈秋莺
陈秋莺
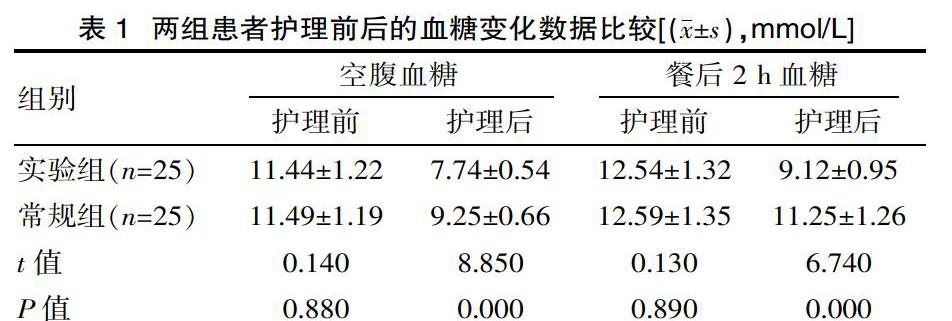
[摘要] 目的 分析并研究肿瘤合并糖尿病患者住院期间血糖控制不良原因和护理配合。方法 选取2016年3月—2019年2月来该院接受治疗的肿瘤合并糖尿病患者共计50例作为此次研究的研究对象,并按照护理方式的不同将上述50例患者平均分为两组,即实验组和常规组,每组25例患者。常规组采用一般护理方式开展护理干预工作,实验组采用针对性护理干预开展护理工作。观察并记录两组患者的血糖变化数据。结果 护理后,实验组空腹血糖为(7.74±0.54)mmol/L,餐后2 h血糖为(9.12±0.95)mmol/L;常规组空腹血糖为(9.25±0.66)mmol/L,餐后2 h血糖为(11.25±1.26)mmol/L,相比于护理前,两组患者的血糖水平均有所下降,且实验组的血糖控制效果比常规组更加显著(P<0.05)。结论 在肿瘤合并糖尿病患者住院期间,针对患者血糖控制不良的原因,开展具有针对性的护理干预,不但能够帮助患者有效控制血糖波动,还能提升化疗质量,具有积极的临床意义。
[关键词] 肿瘤;糖尿病;血糖控制;护理
[中图分类号] R47 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-4062(2019)09(b)-0170-02
[Abstract] Objective To analyze and study the causes and nursing cooperation of poor blood glucose control during hospitalization for patients with cancer and diabetes. Methods A total of 50 patients with tumors and diabetes mellitus from March 2016 to February 2019, were selected as the study subjects, and according to different nursing methods. The above 50 patients were equally divided into two groups, the experimental group and the regular group, with 25 patients in each group. The routine group used general nursing methods to carry out nursing intervention work, and the experimental group used targeted nursing interventions to carry out nursing work. Observe and record the blood glucose change data of the two groups of patients. Results After nursing, the fasting blood glucose of the experimental group was (7.74±0.54)mmol/L, and the blood glucose was (9.12±0.95)mmol/L 2 h after meal; the fasting blood glucose of the routine group was(9.25±0.66)mmol/L, and the blood glucose was 2 h after meal(11.25±1.26)mmol/L. Compared with pre-treatment, the blood glucose levels of both groups were decreased, and the blood glucose control effect of the experimental group was more significant than that of the conventional group(P<0.05). Conclusion During the hospitalization of patients with diabetes mellitus and diabetes, targeted nursing interventions for patients with poor glycemic control can not only help patients to effectively control blood glucose fluctuations, but also improve the quality of chemotherapy, which has positive clinical significance.
[Key words] Tumor; Diabetes; Glycemic control; Nursing
隨着社会经济的发展和饮食结构的转变,近几年来,我国患有肿瘤合并糖尿病的患者越来越多,已经严重威胁到了我国国民的身心健康。为了能够有效延长患者生命,在临床诊治过程中需要采取化疗的方式开展治疗活动,但是,由于患者的血糖水平容易在化疗过程中发生波动,引发酸中毒、低血糖等一些并发症,不仅会影响化疗的治疗效果,还会加速患者死亡[1]。基于此,该次研究选取2016年3月—2019年2月该院收治的50例肿瘤合并糖尿病患者作为研究对象,针对肿瘤合并糖尿病患者住院期间血糖控制不良原因进行分析,同时也探讨了研究肿瘤合并糖尿病患者住院期间血糖控制的护理方式及策略,希望能够有效控制患者血糖,提升护理服务质量。现报道如下。
