Association Study between the GATA4 Gene Polymorphism and Congenital Heart Disease in Tibetan Chinese
2019-12-03MAQiangHAOErwaYANGYingzhongLIUYongnian
MA Qiang,HAO Erwa,YANG Yingzhong,LIU Yongnian
(1.Qinghai University Medical College,Qinghai 810001,China; Research Center for High Altitude Medicine,Qinghai University,Qinghai,810001,China)
Abstract Objective Via testing whether the GATA4 gene is associated with the susceptibility to CHD(Congenital Heart Disease)in the Tibetan Chinese,providing theoretical basis for pathogenesis of CHD in Tibetan Chinese.Methods The GATA4 gene were genotyped by a ABI 3730 DNA analyzer in seventy patients with CHD and seventy matched healthy Tibetan controls.Results PCR products sequencing showed one non-synonymous mutation at codon 1129(rs3729856)of exon 6 of GATA4 gene.There was no difference in the genotypic and allelic frequencies between each group(P>0.05).Conclusions GATA4 gene rs3729856 polymorphism are not correlated with CHD in Tibetan Chinese.
Keywords:Congenital heart disease;GATA4 gene;Tibetan Chinese
1 BACKGROUND
CHD refers to a defective disease with abnormal cardiac vascular development in embryonic period[1],The incidence rate among newborns is 0.4%~1.0%[2].Its clinical manifestations mainly include ventricular septal defect,atrial septal defect and patent ductus arteriosus,tetralogy of Fallot.Studies have proved that the interaction between genetic susceptibility and environment is the cause of CHD,and its heritability is 55%~65%[3].
So far,over 40 genes associated with CHD have been identified as being contained in the human genome[4-8].Of them,GATA4 gene was one of the most significant transcription factors in the development of heart.Located on chromosome 8p22-23,GATA4 gene contains seven exons and is capable of encoding the protein that is comprised of 422 amino acids[9].In recent years,there have been reports that validate its gene mutation as having a close relation to CHD.By conducting literature review,few studies have explored the relationship that exists betweenGATA4 gene and CHD in Tibetans. In order to detect the potential relationship ofGATA4 gene with CHD,a genetic sequencing and screening was performed in CHD patients.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Subjects
During the period from 2016 to 2018,seventy Tibetan CHD patients(CHD-p)were hospitalized in Qinghai University Affiliated Hospital.In accordance with the relevant diagnostic criteria,the diagnosis of CHD was made.The control group was comprised of healthy Tibetans(CHD-c),who originated from the same region and were similar to the experimental group in respect to gender and age.In addition,they were observed to have developed neither CHD nor other plateau-induced disease(Table 1).The study involved a total of seventy Tibetan CHD patients along with seventy healthy Tibetans to match. Besides,there was no single pair of them related by blood.The research received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee at College of Medical,Qinghai University. In the mean time,formal consent was given by all the participants.
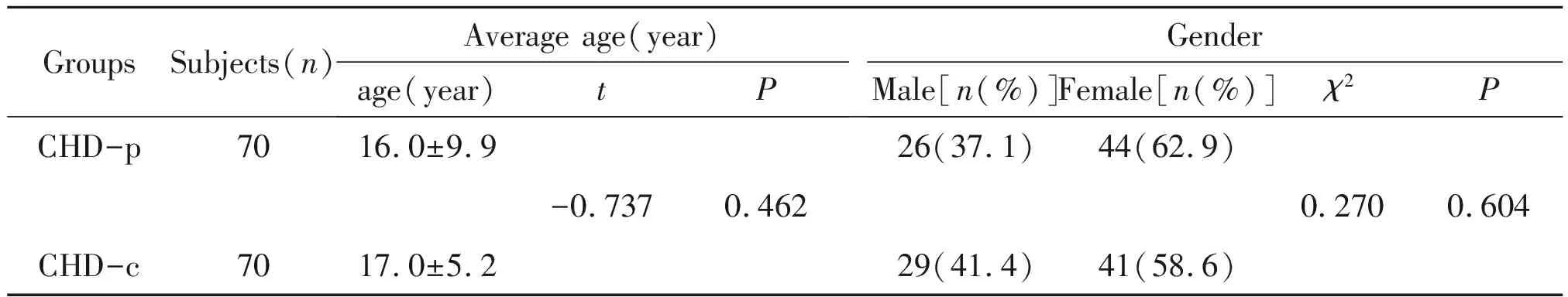
Table 1 Comparison of baseline data of two groups
CHD-p:congenital heart disease patients;CHD-c:healthy Tibetan control
2.2 Sample collection and DNA extraction
Each subject was sampled with 5 mL of venous blood,and EDTA-anticoagulation was conducted for the collected samples.Subsequently,Gentra Puregene Blood Kit(Qiagen,158389,Germany)was employed to perform genomic DNA extraction,with the standardized procedure as reference.Cryostorage at -20 ℃ was applied prior to the samples being sent for further test.
2.3 Exons PCR and sequencing
The primers ofGATA4 gene(NG_008177.2)were designed by Primer3(version 0.4.0)to encompass each exon except exon 1(Table 2).2×Taq Plus PCR Mastermix(TIANGEN,Beijing)was utilized to amplify these exons.PCR cycles are comprised of 5 minutes of denaturation at 94 ℃,34 cycles at 94 ℃ for 45 s,60 ℃ for 45 s,and 72 ℃ for 45 s,as well as 5 minutes of elongation at 72 ℃ at last.The amplified fragments were resolved on 1.5% agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide.PCR products were bidirectionally sequenced with a ABI 3 730 DNA analyzer sourced from Shanghai Generay Biotech Co.,Ltd,before being compared with the published sequence ofGATA4 gene.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS software(version 17.0;SPSS,Inc,Chicago,IL,USA),and statistical significance was determined asP<0.05.Besides,an assessment was made of subject representativeness with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium(HWE).The allelic frequency was calculated based on the genotype frequencies in experimental and control groups,and chi-square test was further conducted to make estimation of the intergroup difference.
3 RESULTS
For both the CHD-p and CHD-c groups,no noticeable difference was observed between the two groups in respect to their gender and age,respectively. Sequencing was performed for the six exons(exon 2 to 7)of theGATA4 gene,leading to the observation of one substitutions of singe nucleotide for codon 1 129 of exon 6(Figure 1).Apart from that,no other difference was spotted.Non-synonymous mutations of A to G accounted for the variation of exon 6(specifically,AGC to GGC,p.S377G).There was pre-existing deposition of polymorphisms discovered in dbSNP with the accession number rs3729856.In comparison to the HWE obtained earlier,no deviation was spotted for the two genotype distribution(χ2=0.004,P=0.952 in CHD-p group andχ2=0.015,P=0.903 in CHD-c group).
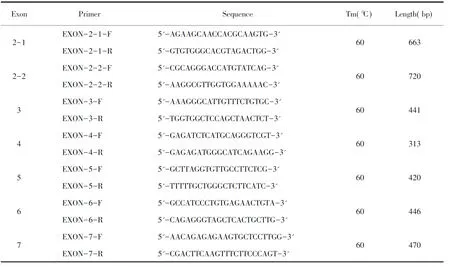
Table 2 Amplification primers for GATA4 gene exons
Tm:melting temperature
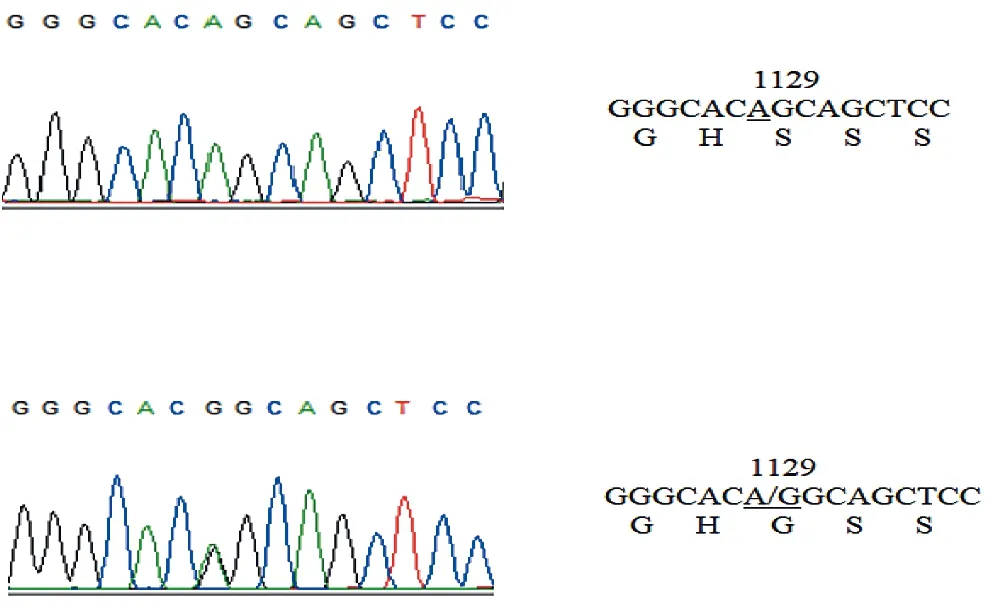
Figure 1 DNA sequencing results,partial nucleotide sequence of exon 6 in the region surrounding codon 1129(rs3729856)
According to Table 3,the rs3729856 polymorphism is discovered to bear similarity to genotypic frequency and allelic frequency between CHD-p and CHD-c groups,suggesting that there is no association with CHD risk.
4 DISCUSSION
After our study was performed,totally seventy CHD Tibetans and seventy healthy Tibetans in Chinese Qinghai-Tibet plateau were identified.The results showed that non-synonymous mutations c.1129A>G(rs3729856)of exon 6,and that there is no variations in genotype and allele frequency between the two groups.Based on the results,we concluded thatGATA4 gene polymorphism has no effect on CHD in Qinghai Tibetan Chinese.
CHD stems from embryonic period[10],and severe symptoms will have impact on the normal life of patients.Across the globe,in each year,as many as 1.35 million neonates suffer from CHD,which affects 0.4%~1% of live births,with the live birth prevalence estimated to be 0.93% in Asia[11],and 0.25% on average in China[12].
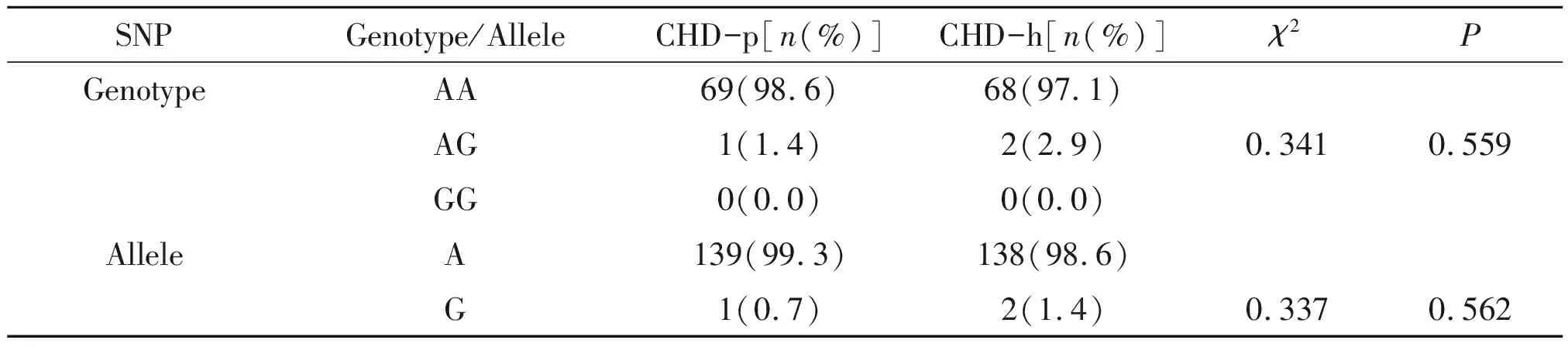
Table 3 Genotypic distributions and allelic frequencies of rs3729856 in two groups
CHD-p:Tibetan CHD patients,CHD-c:healthy Tibetan control
As revealed by recent studies[13],the high altitude environment has been identified as in association with the high incidence rate of CHD.Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,which is over 4 000 m above the sea level on average,is ranked the highest and largest plateau around the world.In the early stage,Wu[14]published the epidemiological research results of CHDs in the plateau,which revealed the discovery that the total prevalence in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau reached 1.15%,noticeably higher than in the plain areas(0.13%~0.35%).As claimed by Chen[15],who conducted a survey of 25 185 Tibetan children living in Yushu and Guoluo areas(average altitude 4200 meters)in Qinghai Province,the total prevalence rate of CHD was observed to be0.874% in the two areas.In plateau,strong hypoxia is known as the most significant influencing factor,which has an enormous effect on the population[16].Despite this,the pathogenesis of CHD remains inconclusive.
GATA4 gene is especially crucial among more than 40 genes related to CHD that have been discovered.GATA4 gene,the heart related genes,performs a critical part in cardiac precursor cell differentiation,cardiac cyclization,atrioventricular partition and conduction system maintenance[17].GATA4 gene mutation is capable of triggering a variety of heart diseases,such as atrial septal defect,ventricular septal defect,tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary stenosis[2].Previously,there were plenty of studies performed onGATA4 gene.Kathleen Gajewski[18]studied by Drosophila identified that the defects ofGATA4 gene have a potential to result in malformations in the early stages of heart development.Jiang’s study[19]by researching chicks found thatGATA4 gene is capable of regulating early embryonic cardiac morphogenesis,which are clearly correlated to embryonic folding or the migration of primordia to shape a primitive tube.Garg V[20,21]was the first to make discovery that humanGATA4 gene mutation is capable of causing CHD after carrying out the study on two congenital heart disease families.All the research results have indicated the significance ofGATA4 gene to heart development.Therefore,a full understanding of the structure and functions ofGATA4 gene is extremely crucial to conducting the study of CHD.It will provide a solid theoretical basis for the early diagnosis and effective treatment of congenital heart disease.
Tibetans have excellent adaptivity to the plateau environment.However,the incidence rate of CHD is notably higher than plain areas.Besides high altitude factors,there are suspected to be some genetic factors,such asGATA4 gene.However,there remains limited research conducted into this gene in Tibetans,for which we chose to focus on the relationship betweenGATA4 gene and Tibetans,which is despite no correlation was discovered.Therefore,there is supposed to be other pathogenesis and further research is necessary.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Our study shows thatGATA4 gene rs3729856 polymorphisms is not correlated with CHD in Tibetan Chinese.
6 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work were supported by Science and Technology Support Program of Qinghai(2015-SF-124),and the Qinghai Thousand Talents Program,the 2nd round of “Qinghai 135 high-level talents training project”.
