动态监测血清降钙素原对术后重症继发性腹膜炎患者预后的影响
2019-11-22江子欣熊旭明张振辉温艺超李智博
江子欣 熊旭明 张振辉 温艺超 李智博
[摘要]目的 探讨血清降钙素原(PCT)水平及治疗后变化对重症继发性腹膜炎患者预后及生存的影响。方法 回顾性分析2016年1月~2018年1月在广州医科大学附属第二医院ICU收治的118例术后重症继发性腹膜炎患者的临床资料,以28 d存活与否分为存活组(95例)与死亡组(23例);将治疗1周后的108例存活患者分为PCT值下降≥80%组(68例)与PCT值下降<80%组(40例),选取同时期的200例未发生感染患者作为正常对照组。动态观察1、3、7 d的PCT值,总结其与危重程度及生存率之间的关系。结果 死亡組、存活组及正常对照组的初始PCT中位数分别为9.10、7.91、0.04 ng/L,三组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。7 d的PCT值ROC曲线下面积最大,取9.3 ng/L为截断点,敏感性为0.933,特异性为0.968。3、7 d的PCT值与ICU住院时间成正相关关系(P<0.05),PCT值与APACHE Ⅱ评分变化程度成正相关关系(P<0.05)。治疗1周后PCT下降≥80%组患者的月生存率显著高于PCT下降<80%组(P<0.05)。结论 动态监测血清PCT对术后重症继发性腹膜炎患者预后存在一定的评估作用。
[关键词]术后;继发性腹膜炎;动态监测;降钙素原;预后
[中图分类号] R572.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2019)9(c)-0082-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the influence of serum procalcitonin (PCT) levels and changes after treatment on the prognosis and survival of patients with severe secondary peritonitis. Methods The clinical data of 118 patients with severe secondary peritonitis after operation admitted to ICU of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University from January 2016 to January 2018 were analyzed retrospectively. According to 28-day survival or not, they were divided into the survival group (95 cases) and the death group (23 cases). One week after treatment, 108 surviving patients were divided into the PCT value decreased greater than or equal to 80% group (68 cases) and the PCT value decreased less than 80% group (40 cases). A total of 200 non-infected patients in the same period were selected as the normal control group. The PCT values of 1, 3 and 7 days were observed dynamically, and the relationship between PCT values and severity and survival rate was summarized. Results The median of initial PCT values in the death group, the survival group and the normal control group were 9.10, 7.91 and 0.04 ng/L, respectively, there was significant difference among the three groups (P<0.05). The area under the ROC curve of 7-day PCT value was the largest. The cut-off point was 9.3 ng/L, the sensitivity was 0.933, and the specificity was 0.968. There was a positive correlation between the CT value on 3 and 7 day and the length of stay in ICU (P<0.05). The change of APACHE Ⅱ score was positively correlated with CT value at 3 and 7 days (P<0.05). The monthly survival rate of the PCT value decreased greater than or equal to 80% group after one week of treatment was significantly higher than that of the PCT value decreased less than 80% group (P<0.05). Conclusion Dynamic monitoring of serum PCT can evaluate the prognosis of patients with severe secondary peritonitis after surgery.
[Key words] After surgery; Secondary peritonitis; Dynamic monitoring; Procalcitonin; Prognosis
继发性腹膜炎(secondary peritonitis,SP)是继发于腹内脏器疾病、腹部创伤或手术等引起的腹膜急性化脓性炎症,多属于细菌性腹膜炎,是临床上最常见的类型[1]。急性SP往往伴随严重的细菌性炎症,发病机制与细菌性炎症密切相关。Thomas-Rüddel等[2]的研究显示,腹膜炎降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)值能提示细菌感染及初步筛选细菌种类。既往研究集中于PCT在继发性腹膜中的反应及机制,对PCT判断SP患者中远期预后效能的相关研究仍需进一步完善。本研究通过回顾病例分析,以重症术后SP患者作为研究对象,评价PCT动态变化与重症SP患者中远期预后的关系。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选取2016年1月~2018年1月广州医科大学附属第二医院ICU收治的118例SP患者,均经历手术治疗,术后立即送往ICU治疗。其中包括十二指肠溃疡穿孔26例,胃溃疡穿孔28例,外伤10例,胰腺炎12例,结肠癌致肠梗阻15例,胆囊炎穿孔27例。根据28 d死亡与否将入选患者分为存活组(95例)与死亡组(23例),选取同时期的200例未发生感染患者作为正常对照组。治疗1周后将存活患者(108例)根据PCT的下降幅度分为PCT下降≥80%组与PCT下降<80%组(下降<80%或持续不降甚至升高)[3]。死亡组中,男12例,女11例;中位年龄为64岁。存活组中,男58例,女37例;中位年龄65岁。PCT值下降≥80%组共68例,男38例,女30例;中位年齡为63岁。PCT值下降<80%组共40例,男26例,女14例;中位年龄67岁。正常对照组中,男98例,女102例;中位年龄62岁。各组患者的年龄、性别等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。本研究符合医学伦理学标准,并经医院医学伦理委员会批准,所有治疗获得患者或家属的知情同意。
1.2方法
术后重症SP患者送ICU治疗当天(1 d)及治疗后第3天(3 d)、第7天(7 d)分别抽取4 ml静脉血做PCT检测,正常对照组患者于入院当天抽血做PCT检测,PCT值检测采用微量双夹心免疫发光法定量检测。
1.3观察指标及评价标准
监测治疗当天(1 d)及治疗后第3天(3 d)、第7天(7 d)的PCT值,观察其1周内的急性生理学和慢性健康状况评分系统评分(APACHE Ⅱ)变化程度、ICU住院时间、生存时间(月数)。
1.4统计学方法
采用SPSS 20.0统计学软件对数据进行分析,符合正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,多组间比较采用F检验;不符合正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用非参数检验(秩和检验)。PCT值对28 d死亡率的预测价值采用ROC曲线分析法,PCT值与患者ICU住院时间、APACHE Ⅱ评分变化程度的关系采用Pearson相关分析,绘制PCT下降≥80%组与PCT下降<80%组患者的生存曲线(K-M曲线),月生存率的比较采用Log-rank检验。
2结果
2.1各组初始PCT值的比较
死亡组、存活组及正常对照组初始PCT值的比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组的初始PCT中位数分别为9.10、7.91、0.04 ng/L,死亡组和存活组的初始PCT值均明显高于正常对照组,而死亡组初始PCT值高于存活组。
2.2 PCT值对28 d死亡率预测价值的分析
SP患者(1、3、7 d)PCT值对28 d死亡率预测价值的ROC曲线显示,ROC曲线下面积分别为0.572(95%CI为0.384~0.761)、0.867(95%CI为0.725~0.972)及0.983(95%CI为0.960~1.000)。7 d的PCT值ROC曲线下面积最大,取9.3 ng/L为截断点,敏感性为0.933,特异性为0.968(图1,封三)。
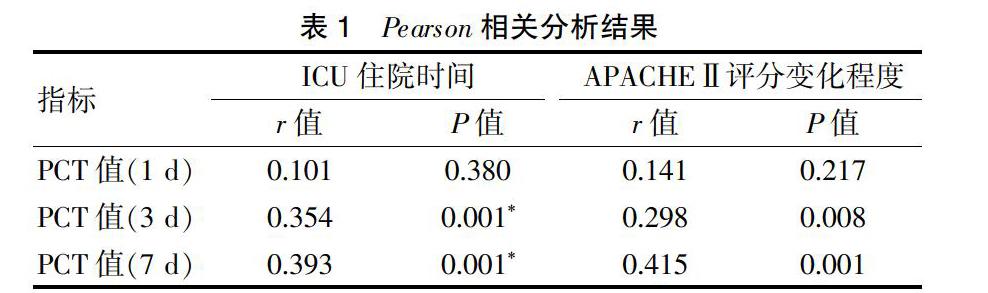
2.3 PCT值与ICU住院时间、APACHE Ⅱ评分变化程度的相关性
3、7 d的PCT值与ICU住院时间成正相关关系(P<0.05),与APACHE Ⅱ评分变化程度成正相关(P<0.05)(表1)。
2.4 PCT值变化幅度与月生存率的关系
PCT下降≥80%组患者的月生存率显著高于PCT下降<80%组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(图2,封三)。
3讨论
血清PCT是降钙素前肽物质,在细菌感染中广泛反应生成,可用于早期细菌感染诊断。SP是临床上最常见的腹膜炎,主要是由腹腔内脏器的穿孔、损伤破裂和炎症等引起,发展加重可导致感染性休克及死亡。Pupelis等[4]的研究显示,弥漫性腹膜炎患者PCT值较局灶性腹膜炎升高明显,其与SOFA评分及ICU死亡率成正相关,提示PCT值可反映腹膜炎的危重程度。Rau等[5]发现,SP患者PCT升高可预判多器官功能衰竭,其效果优于C反应蛋白(CRP)。相关研究显示,PCT在鉴别细菌感染中优于CRP、细胞因子等[6-8],两项荟萃分析[9-10]进一步肯定了其诊断价值。熊克宫等[11]的实验显示血清和腹水PCT对自发性细菌性腹膜炎的诊治有指导作用。Maruna等[12]的前瞻性研究发现,粘连和血管性肠梗阻患者PCT显著升高,提示PCT是判断SP并发严重脓毒症休克的敏感指标(敏感度为84%,特异性为91%)。Berna等[13]发现,二次缝合的剖宫产术后患者血清PCT水平明显高于对照组,提示血清PCT能够反映剖宫产术后手术部位感染的严重程度。本研究中,死亡组和存活组的初始PCT均高于对照组,且死亡组高于存活组,提示PCT值是SP术后评估患者病情危重程度的敏感指标。
Novotny等[14]研究聯合SPPCT初始值及APACHE Ⅱ评分进行分组,结果显示71%的高危组患者死于脓毒症。Miro等[15]的研究显示急性腹膜炎患者术后PCT值与48 h内的SOFA评分有正相关关系,能预测脓毒症的危重程度。本研究结果显示,术后PCT值可预测28 d死亡率,其中3 d及7 d的PCT值与ICU住院时间及7 d内的APACHE Ⅱ评分变化程度存在正相关关系,提示动态监测PCT值能反映SP的危重程度,能够一定程度地预判短期死亡率。
在SP患者中,PCT值能否作为术后使用抗生素的临床依据,目前并没有统一标准。Slieker等[3]尝试以术后3 d的PCT值指导抗生素治疗,结果提示并没有依据,死亡率并无差别。Jensen等[16]对丹麦9个多学科ICU共1200例危重病患者进行PCT值分析,结果显示PCT指导下的抗菌药物升级治疗没有提高生存率,反而导致器官功能障碍及住院时间延长。相反,Huang等[17]发现PCT指导急诊手术患者使用抗生素能显著缩短用药时间。李荣等[18]按照预定的PCT浓度截断值开始和停止抗生素的使用,结果显示,抗生素使用天数减少2.6 d。汪燕等[19]发现PCT可作为停用抗生素的参考。本研究结果显示,治疗后1周内PCT值下降≥80%组的SP患者远期生存时间延长,病死率降低,与Slieker等[3]的研究结果存在差异,可能的区别在于本实验关注PCT值变化与远期生存曲线的关系,并没有以PCT变化值作为抗生素治疗指导依据。
综上所述,SP术后1周监测PCT值对患者短期及远期预后有一定的评估作用,未来将需要大规模的前瞻性研究探讨PCT对急性腹膜炎的影响因素及预后判断效能。
[参考文献]
[1]Hartl W,Kuppinger D,Vilsmaier M.Secondary peritonitis[J].Zentralbl Chir,2011,136(1):11-17.
[2]Thomas-Rüddel Daniel O,Bernhard P,Matthias K,et al.Influence of pathogen and focus of infection on procalcitonin values in sepsis patients with bacteremia or candidemia[J].Crit Care,2018,22(1):128.
[3]Slieker J C,Steve A,Philippe E,et al.Procalcitonin-guided antibiotics after surgery for peritonitis:a randomized controlled study[J].Gastroenterol Res Pract,2017,2017:1-6.
[4]Pupelis G,Drozdova N,Mukans M,et al.Serum procalcitonin is a sensitive marker for septic shock and mortality in secondary peritonitis[J].Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther,2014,46(4):262.
[5]Rau BM,Frigerio I,Markus WB,et al.Evaluation of procalcitonin for predicting septic multiorgan failure and overall prognosis in secondary peritonitis:a prospective,international multicenter study[J].Arch Surg,2007,142(2):134-142.
[6]Mimoz O,Edouard AR,Samii K,et al.Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein during the early posttraumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome[J].Intensive Care Med,1998,24(2):185-188.
[7]Endo S,Aikawa N,Fujishima S,et al.Usefulness of procalcitonin serum level for the discrimination of severe sepsis from sepsis:a multicenter prospective study[J].J Infect Chemother,2008,14(3):244-249.
[8]Harbarth S,Holeckova K,Froidevaus C,et al.Diagnostic value of procalcitonin,interleukin-6,and interleukin-8 in critically ill patients admitted with suspected sepsis[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2001,164(3):396-402.
[9]Simon L,Gauvin F,Amre DK,et al.Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as markers of bacterial infection:a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J].Clin Infect Dis,2004,39(2):206-217.
[10]Uzzan B,Cohen R,Nicolas P,et al.Procalcitonin as a diagnostic test for sepsis in critically ill adults and after surgery or trauma:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Crit Care Med,2006,34(7):1996-2003.
[11]熊克宫,柯坤宇,林太杰,等.血清降钙素原对自发性细菌性腹膜炎抗生素使用的指导作用[J].实用医学杂志,2015,31(23):3872-3874.
[12]Maruna P,Frasko R,Gürlich R.Plasma procalcitonin in patients with ileus.Relations to other inflammatory parameters[J].Physiol Res,2008,57(3):481.
[13]Berna AC,Begum AM,Nadiye K,et al.Serum procalcitonin levels in incisional surgical site infections requiring a secondary suture after cesarean sections[J].J Matern Fetal Neonat Med,2018,20:1-6.
[14]Novotny A,Emmanuel K,Matevossian E,et al.Use of procalcitonin for early prediction of lethal outcome of postoperative sepsis[J].Am J Surg,2007,194(1):35-39.
[15]Miro M,Del Valle GS,Agámez G,et al.Correlation between SOFA score and procalcitonin blood levels in peritonitis patients[J].Eur J Anaesthesiol,2011,28:173.
[16]Jensen JU,Hein L,Lundgren B,et al.Procalcitonin-guided interventions against infections to increase early appropriate antibiotics and improve survival in the intensive care unit:a randomized trial[J].Crit Care Med,2011,39(9):2048-2058.
[17]Huang TS,Huang SS,Shyu YC,et al.A procalcitonin-based algorithm to guide antibiotic therapy in secondary peritonitis following emergency surgery:a prospective study with propensity score matching analysis[J].PLoS One,2014, 9(3):e90539.
[18]李榮,彭开勤,朱国超,等.降钙素原指导下减少腹部外科感染抗生素使用的临床研究[J].腹部外科,2016,29(5):388-391.
[19]汪燕,严静,胡朝晖,等.降钙素原在脓毒症抗感染治疗中的应用[J].中华内科杂志,2018,57(6):464.
(收稿日期:2019-04-28 本文编辑:祁海文)
