考虑PT断线故障的同步发电机励磁控制策略
2019-10-21凡绍桂段建东孙力
凡绍桂 段建东 孙力

Abstract:To solve the problem of synchronous generator uncontrollable voltage caused by the broken of voltage sampling PT, the high dynamic quality voltage measurement and excitation control technology was proposed. When the PT broken fault occurs, the measurement system will automatic switch from threephase measurement mode to singlephase measurement mode. To adapt to frequency fluctuation and voltage distortion, the RMS value of phase voltage was obtained by using the voltage square singlephase detection technique. However, the sampling delay caused by singlephase measurement will result in poor dynamic performance when the excitation controller has fixed PID parameters. To solve this problem, a sliding mode controller with the estimation of steady state voltage drop of generator winding was proposed. With the proposed control method, the system has high steadystate accuracy and fast dynamic performance and strong robustness to generator system model. The effectiveness of the proposed redundancy voltage sampling technique and the excitation control technique is proved by a 10 kW synchronous generator system.
Keywords:excitation controller; PT breaking fault; singlephase voltage measurement; sliding mode controller
0 引 言
中、小容量内燃发电机组如柴油发电机组,燃气轮机发电机组等被广泛用在石油钻井平台、船舶供电,海岛供电等远离市电供电场合。孤岛运行的发电机组,要求其发电机励磁控制器具有高可靠性,高稳态精度,以及较快的动態性能[1-2]。
励磁控制器的电压传感器(potential transformer,PT)断线故障会导致发电机无法正常工作,严重影响孤岛发电机组可靠性。本文提出发电机电压容错测量技术,正常情况下采用三相四线制测量模式,当发生PT断线故障时自动切换至单相容错测量模式。许多学者通过构造直角坐标系来实现单相电压测量,如积分延时T/4构造直角坐标系[3]、基于反Park构造直角坐标系[4]、采用微分构造直角坐标系[5]以及采用广义二阶积分器(secondorder generalized integrator,SOGI)构造直角坐标系[6-7]等,以上构造直角坐标系的方法需要稳定的频率信号,对于并网发电系统,电网频率基本恒定,可以采用以上方法[8-9]。而对于孤岛发电系统,发电机频率波动较大,电压畸变严重,不易采用以上单相电压测量方法。本文采用电压自平方单相检测方法,该方法对频率波动及电压畸变有较大适应性。由三相测量切换至单相测量后,单相测量带来的采样延时使经典PID调节器在不改变PID参数情况下,很难达到三相测量时的控制效果,使发电机动态性能受到较大影响。为提高励磁控制器性能,很多学者对励磁控制器进行了改进,如文献[10]设计了一种同时以机端电压、有功功率、无功功率、角速度、功率角作为反馈量的线性最优励磁控制器,将发电机功角、无功功率这两个与稳定性和品质密切相关的重要参量引入控制规律,提高了并网发电机稳态性能;文献[11]将预测函数与线性多变量反馈结合组成一种复合励磁控制器,可在提高电力系统稳定性的前提下解决发电机端电压稳定问题。文献[12]提出在最优控制下,采用变增益控制策略,以保证系统小扰动稳定性。文献[13] 将预测控制与模型降阶技术相结合,以解决最优励磁控制和传统比例积分微分励磁控制无法考虑系统复杂状态和控制输入约束的问题。
以上控制策略以并网发电机为研究对象,没有考虑孤岛发电系统运行时负载扰动问题。滑模控制器具有较强的鲁棒性,被广泛应用于电动机转速控制[14]。文献[15]将滑模控制器应用在励磁系统,提出了一种非奇异终端滑模控制的调压控制策略,使发电机系统具有良好的稳态性能与优越的动态性能,不过该方法需要发电机参数较多,为工程应用带来一定的困难。本文提出一种不需要发电机精确模型的滑模控制器,该控制器对发电机绕组稳态压降进行估计,简化了负载压降模型,提高了负载条件下发电机稳态性能,将负载扰动以及三相测量切换至单相测量带来的采样延时归为扰动项,提高了励磁控制器动态性能与对发电机参数的鲁棒性能。
1 容错测量逻辑及单相测量方法
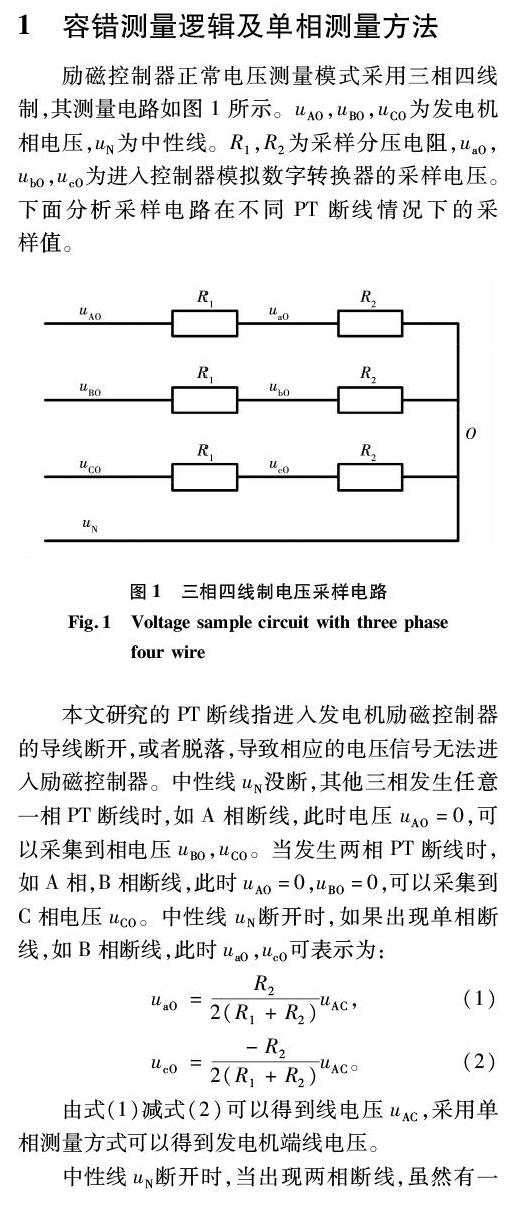
励磁控制器正常电压测量模式采用三相四线制,其测量电路如图1所示。uAO,uBO,uCO为发电机相电压,uN为中性线。R1,R2为采样分压电阻,uaO,ubO,ucO为进入控制器模拟数字转换器的采样电压。下面分析采样电路在不同PT断线情况下的采样值。
表1中k=R2/(R1+R2),由表1可以看出,无论是否有中性线,当出现单相断线故障时,另外两相均有值,不易区分出现了哪种故障。通过观察可以发现,把剩余两相相减可以得到相应的线电压,以A相断线为例,有中性线时,B相采样与C相采样电压相减得ubc=k(uBO-uCO)=kuBC;无中性线时,B相采样与C相采样电压相减得ubc=0.5kuBC-(-0.5kuBC)=kuBC,所以当出现单相断线故障时,可以测得发电机另外两相线电压,单相断线情况下电压测量为单相线电压,定义该方式为测量方式一。有中性线时出现两相断线故障时,可以测得另外一相相电压,定义单相相电压测量为测量方式二。测量方式一与测量方式二均采用单相测量技术,只是转换为发电机相电压有效值时所乘系数不同。
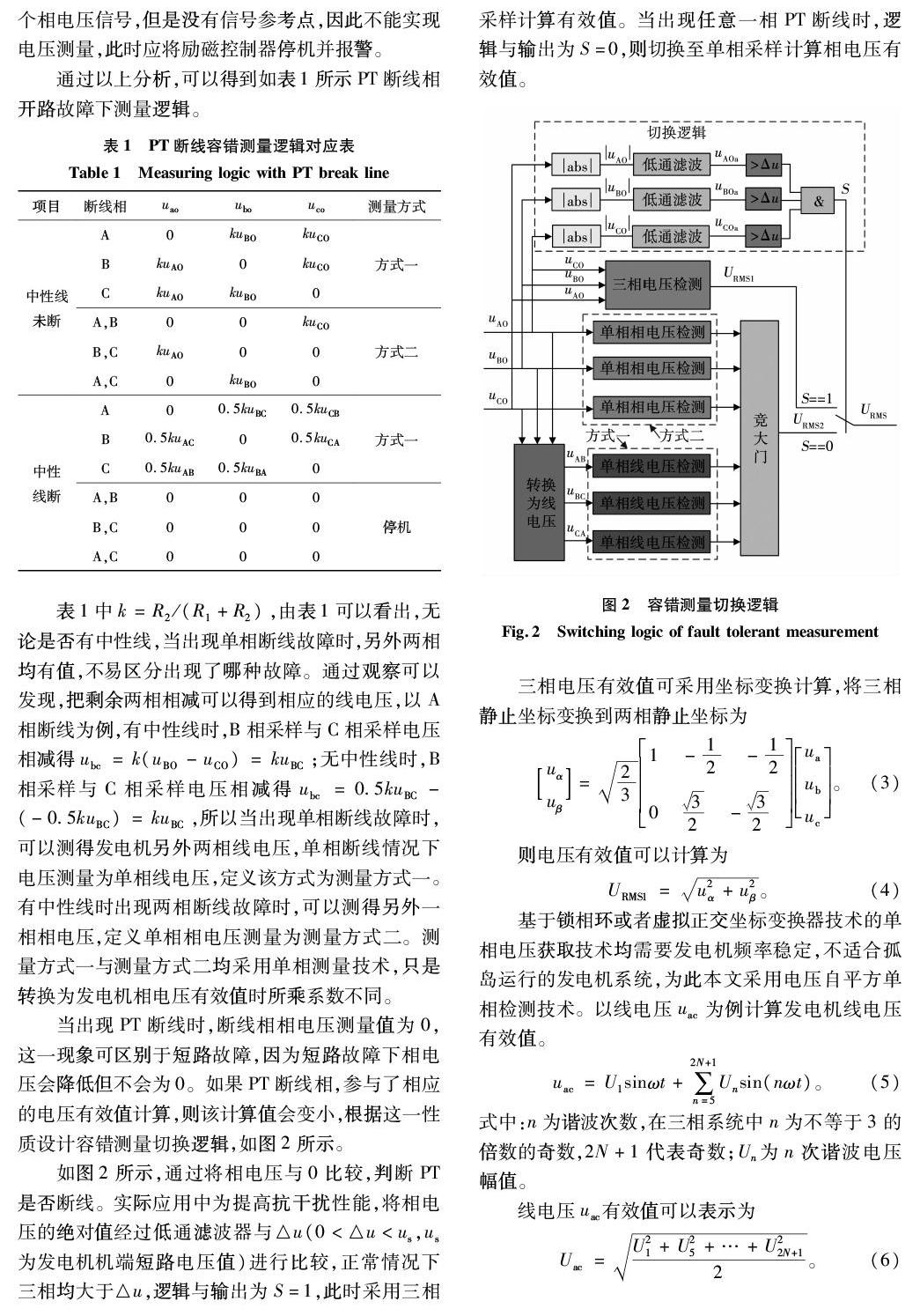
当出现PT断线时,断线相相电压测量值为0,这一现象可区别于短路故障,因为短路故障下相电压会降低但不会为0。如果PT断线相,参与了相应的电压有效值计算,则该计算值会变小,根据这一性质设计容错测量切换逻辑,如图2所示。
5 结 论
本文提出在发电机励磁控制器出现PT断线故障时,由三相测量自动切换到单相测量,实现容错测量。采用电压自平方单相检测测量方案可以在频率变化以及电压畸变情况下实现单相电压测量。单相测量中的低通滤波器带来采样延时,由三相测量切换至单相测量后,若不改变PID参数,则发电机动态性能会变差。本文提出采用具有发电机定子稳态压降估计的滑模控制器,提出的滑模控制器对系统模型参数具有较强鲁棒性,可以消除因单相采样延时带来动态性能变差的问题。文中所提容错测量方法及控制器,在10 kW发电机系统中得到验证,实验证明冗余测量方法在测量方式切换过程中发电机端电压无扰动。采用提出的滑模控制器的励磁控制器可以使系统在切换前后动态性能不变。所提容错测量方法及励磁控制器具有较强的工程实用意义。
参 考 文 献:
[1] 尚敬,年晓红,刘可安,等. 负载转矩前馈的电励磁同步电机定子磁链定向矢量控制[J].电机与控制学报,2015,19(11):25.
SHANG Jing, NIAN Xiaohong, LIU Kean, et al. Stator flux oriented vector control of excited synchronous motor based on load torque observer feedforward control [J]. Electric Machines and Control,2015,19(11):25.
[2] 杨新法,苏剑,吕志鹏,等. 微电网技术综述[J].中国电机工程学报,2014,34(1):57.
YANG Xinfa,SU Jian,L Zhipeng,et al. Overview on microgrid technology [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2014,34(1):57.
[3] 武琳,杨林,姜遠,等. 一种改进的单相整流器控制策略研究[J]. 电机与控制学报,2017,21(11):97.
WU Lin, YANG Lin, JIANG Yuan, et al. Improved control strategy of single phase rectifier[J]. Electric Machines and Control,2017,21(11):97.
[4] SAEED Golestan, MOHAMMAD Monfared. Dynamics assessment of advanced singlephase PLL structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2013,60(6):2167.
[5] GUAN Qingxin, ZHANG Yu, KANG Yong, et al. Singlephase phaselocked loop based on derivative elements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics,2017,32(6):4411.
[6] XIAO Furong, DONG Lei, LI Li, et al. A frequencyfixed SOGI based PLL for singlephase gridconnected converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics,2017,32(3):1713.
[7] CHEN Ke, AI Wu, CHEN Bing, et al. A simulation study on tracking and restructuring AC signals based on enhanced SOGIPLL[C]//2016 IEEE Power and Energy Conference at Illinois, February, 2016, Urbana, IL, USA. 2016:1-5.
[8] SAEED Golestan, MOHAMMAD Monfared, FRANCISCO D. Freijedo, et al. Design and tuning of a modified powerbased PLL for singlephase gridconnected power conditioning systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2012,27(8):3639.
[9] CHEN Xin, ZHANG Yang, WANG Shanshan, et al. Impedancephased dynamic control method for gridconnected inverters in a weak grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016,32(1):274.
[10] 罗建,任成君,冯树辉, 等. 基于线性最优控制和积分控制的励磁控制器设计[J].电力系统保护与控制,2013,41(11):134.
LUO Jian, REN Chengjun, FENG Shuhui, et al. Design of excitation controller based on linear optimal control and integral control[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013,41(11):134.
[11] 肖健梅,張科,王锡淮. 基于预测函数与线性多变量反馈控制的同步发电机励磁控制[J]. 电力自动化设备,2015,35(7):153.
XIAO Jianmei, ZHANG Ke, WANG Xihuai. Excitation control based on predictive function control and linear multivariable feedback control for synchronous generator[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015,35(7):153.
[12] 李江,李国庆,邹维,等. 固定增益与变增益最优励磁控制策略的小扰动稳定域研究[J]. 电力自动化设备,2014,34(2):97.
LI Jiang, LI Guoqing, ZOU Wei, et al. Small signal stability region of power system with fixed or variable gain optimal excitation control[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014,34(2):97.
[13] 赵洪山,兰晓明,周雪青. 基于平衡降阶模型的多机系统非线性励磁预测控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2013,33(22):61.
ZHAO Hongshan, LAN Xiaoming, ZHOU Xueqing. Nonlinear excitation prediction control of multimachine power systems based on balanced reduced model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2013,33(22):61.
[14] 高庆忠,关焕新,于子淞,等. 自适应补偿器永磁同步电机积分型连续滑模控制[J]. 电机与控制学报,2017,21(2):103.
GAO Qingzhong, GUAN Huanxin, WANG Zisong, et al. Integral continuous sliding mode control strategy with adaptive compensator for permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Electric Machines and Control,2017,21(2):103.
[15] 戴卫力,丁骏,田浩,等. 双凸极电励磁发电机系统非奇异终端滑模控制器的设计与仿真[J]. 电力自动化设备,2015,35(6):130.
DAI Weili, DING Jun, TIAN Hao, et al. Design and simulation of nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller for doubly salient electromagnetic generator system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015,35(6):130.
[16] 王良,沈善德,朱守真,等. 基于EE模型的励磁系统参数时域辨识法[J].电力系统自动化,2002,(8):25.
WANG Liang, SHEN Shande, ZHU Shouzhen, et al. A method of time domain identification based on EE model for the excitation system parameters[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2002,(8):25.
[17] 陈伯时.电力拖动自动控制系统[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2000: 67-79.
[18] 中国标准化委员会.GBT7409.3-2007同步发电机励磁系统-大、中型同步发电机励磁系统技术要求[S].北京:中国质检出版社,2014:2-4.
[19] 覃平生,刘觉民,周有庆,等. 基于80C196KC的原动机仿真系统设计[J]. 电力自动化设备,2003,23(2):41.
TAN Pingsheng, LIU Juemin, ZHOU Youqing, et al. Design of prime mover simulation system based on 80C196KC[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment,2003,23(2):41.
(编辑:刘琳琳)
