Tanreqing injection with ambroxol hydrochloride for heart failure and pulmonary infection in senile degenerative heart disease: a randomized controlled trial
2019-10-14GuangQiangZhao
Guang-Qiang Zhao
Department of Respiratory Medicine, Sanya People's Hospital, Sanya, Hainan Province, China
Abstract
Key words: Tanreqing injection; ambroxol hydrochloride; senile; heart failure; pulmonary infection; pathogenic bacteria; cardiac function;degenerative heart disease
INTRODUCTION
Background and objective
Senile individuals may suffer from heart failure resulting from degenerative heart disease.As populations age, the incidence of heart failure is increasing.1-6Senile heart failure can lead to pulmonary infection caused by various pathogens as a result of degenerative changes of cells in cardiac tissue and declining immune function, which has adverse effects on patient survival.7,8The inflammatory factors serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein are prevalent in the body and participate in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases.9,10An appropriate drug therapy regimen is therefore required to improve cardiac function and reduce pulmonary infection in senile patients with degenerative heart disease.
Previous studies have shown that ambroxol hydrochloride can promote the removal of viscous secretions in the respira-tory tract and reduce the retention of mucus and increase expectoration, and is therefore commonly used in the treatment of respiratory tract infections.11-16The traditional Chinese medicine compoundTanreqinginjection is composed primarily ofRadix Scutellariae, bear bile powder,Flos Lonicerae, cornu caprae hircus, andFructus Forsythiae.Tanreqinginjection can clear heat, dissipate phlegm, and detoxify.Previous studies have shown that the combination of cefoperazone-sulbactam andTanreqinginjection is effective in the treatment of chronic heart failure and pulmonary infection caused by senile degenerative heart disease and can improve symptoms of infection.17,18
An online search of the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and WanFang databases for papers published from January 2017 to December 2018 using the search terms“heart failure,” “pulmonary infection,” and “treatment”identified three studies of the efficacy of different methods in the treatment of heart failure with pulmonary infection were screened (Table 1).17-19
This planned trial will evaluate the effect ofTanreqinginjection combined with ambroxol hydrochloride on pulmonary infection and cardiac function in senile patients with heart failure.
PARTICIPANTS/METHODS
Design
Prospective, single-center, randomized controlled clinical trial.
Setting
Sanya People’s Hospital, Sanya, China.
Investigator qualification
All physicians performing medical treatment, pathogen examination, and cardiac function evaluation in this study will have received professional medical training and will have more than 5 years of clinical experience in the Department of Respiratory Medicine.
Participants
Recruitment
Recruitment notices detailing the research content and benefits of participation will be posted on the bulletin board of Sanya People’s Hospital.Interested patients and their family members will directly contact recruiters to sign up for the trialviatelephone.After providing written informed consent and undergoing screening procedures, eligible individuals will be included in the trial.
Inclusion criteria
- Diagnosis of heart failure in accordance with the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) 2005 Guideline Update for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult
- Classification of cardiac function: New York Heart Association classes II-IV
- Men and women aged 60-75 years
- Presence of pulmonary infection
- Provision of written informed consent
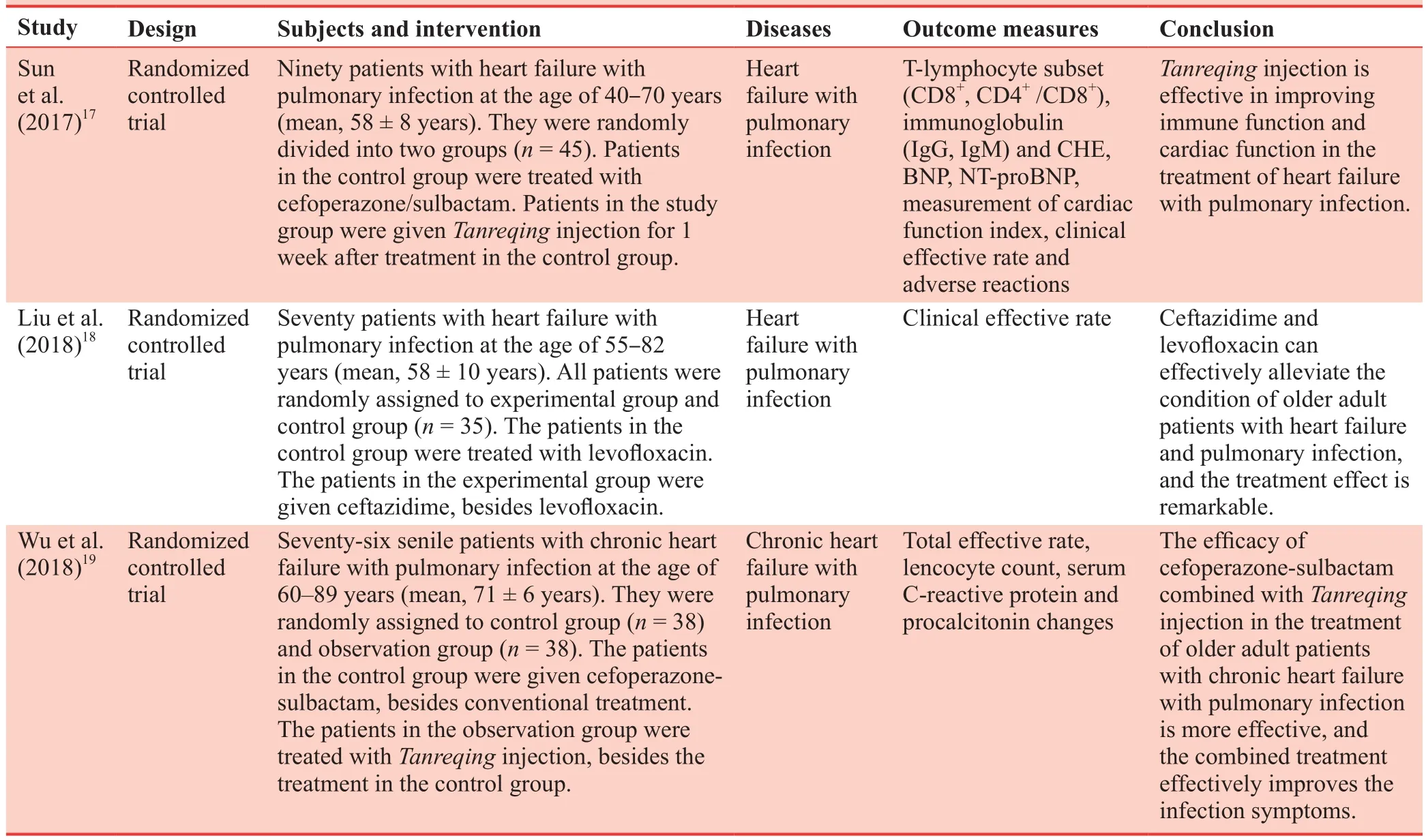
Table 1: Three Chinese most representative clinical trials addressing different methods in the treatment of heart failure combined with pulmonary infection caused by senile degenerative heart disease from 2017 to 2018
Exclusion criteria
- Presence of malignant tumors
- Severe cognitive dysfunction or abnormal kidney function
- Severe metabolic disease
Withdrawal criteria
- Incomplete clinical data
- Poor compliance or inability to complete treatment
Provision of insurance
Participants who participate in this clinical trial will be required to have inpatient medical insurance, and the majority of medical expenses during hospitalization will be paid by the insurance company in proportion to the medical insurance contract.
Interventions
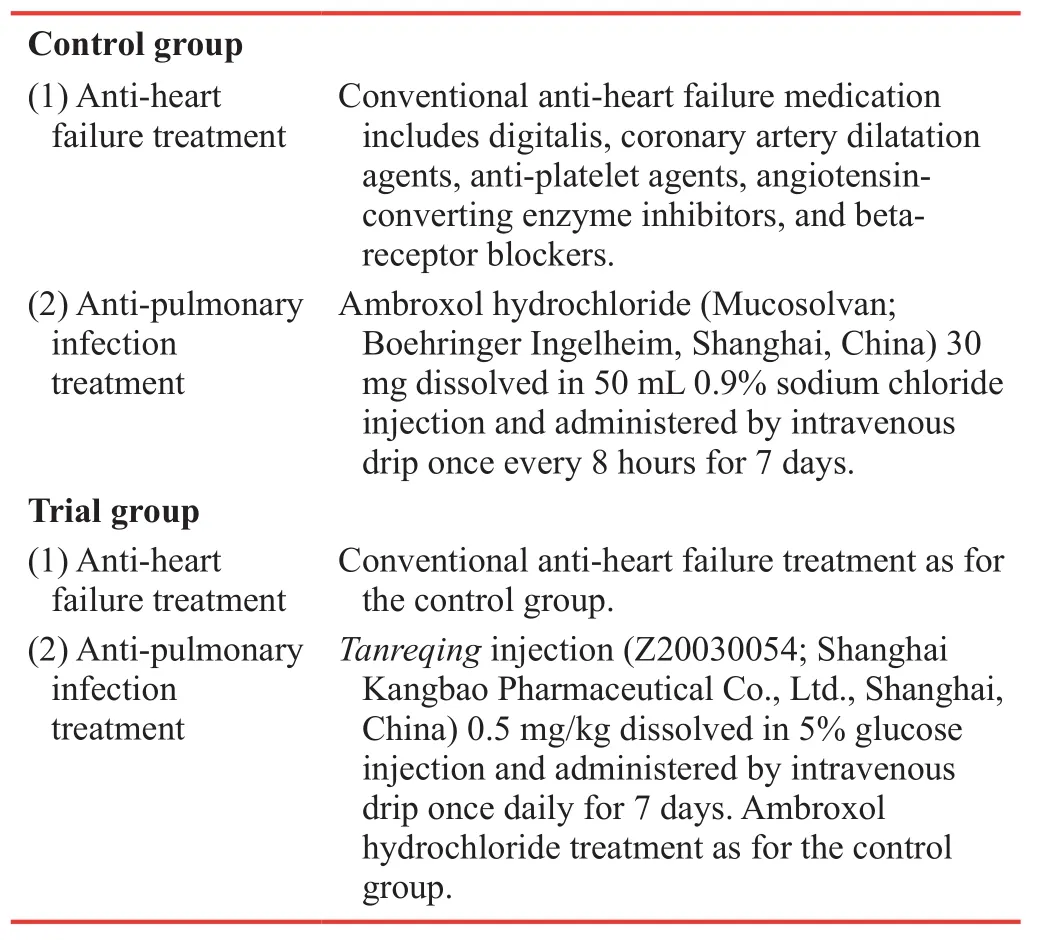
Control group(1) Anti-heart failure treatment Conventional anti-heart failure medication includes digitalis, coronary artery dilatation agents, anti-platelet agents, angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors, and betareceptor blockers.(2) Anti-pulmonary infection treatment Ambroxol hydrochloride (Mucosolvan;Boehringer Ingelheim, Shanghai, China) 30 mg dissolved in 50 mL 0.9% sodium chloride injection and administered by intravenous drip once every 8 hours for 7 days.Trial group(1) Anti-heart failure treatment Conventional anti-heart failure treatment as for the control group.(2) Anti-pulmonary infection treatment Tanreqing injection (Z20030054; Shanghai Kangbao Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shanghai,China) 0.5 mg/kg dissolved in 5% glucose injection and administered by intravenous drip once daily for 7 days.Ambroxol hydrochloride treatment as for the control group.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome measure
· Total effective rate after 7 days of treatment.The effective rate will be calculated as follows: [(number of patients with markedly effective and effective treatment response/total number of patients] × 100%.16
(1) Markedly effective: Complete resolution of the main clinical symptoms and signs.Improvement in cardiac function by more than two grades.No shadows observed in the laboratory and pulmonary X-ray examination.
(2) Effective: Significant improvement in the main clinical symptoms and signs.Improvement in cardiac function by more than one grade.Significant reduction in shadow area in the laboratory and pulmonary X-ray examination.
(3) Ineffective: No improvement in the main clinical symptoms and signs, and no improvement in cardiac function.
Secondary outcome measures
· Change from baseline in left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), left ventricular end-systolic diameter(LVESD), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and left ventricular fractional shortening (FS) after 7 days of treatment.
· Change from baseline in number of pathogenic bacteria in the lung after 7 days of treatment.Sputum cultures from the two groups will be isolated and cultured for identification in accordance with National Clinical Laboratory Regulations.Pathogenic bacteria will be identified and typed using a colorimetric VITEK-2 Compact system (bioMerieux,Marcy l'Etoile, France).The number of each pathogen will be calculated as the constituent ratio.
· Change from baseline in serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein level after 7 days of treatment.Procalcitonin is frequently used as an indicator of bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection; sepsis; or multiple organ failure.C-reactive protein agglutinates with the polysaccharide component C-polysaccharide of non-specific bacteria of Streptococcus pneumoniae and occurs in acute infection.Change in C-reactive protein level can therefore indicate a change in physiological status.
· Incidence of adverse reactions after 7 days of treatment.Adverse reactions, including liver and kidney dysfunction,arrhythmia, gastrointestinal reaction, and skin allergies, will be recorded after treatment in both groups.The incidence of adverse reactions will be calculated as follows: (number of patients with adverse reactions during follow-up/total number of patients) × 100%.
The schedule for primary and secondary outcome measures is listed in Table 2.
Sample size
Based on the results of the pilot study and previous clinical experience, it is hypothesized that the total effective rates inthe control group and trial group will be 75% and 90%, respectively, after 7 days of treatment.Assuming a patient loss rate of 20%, power (1-β) = 90% andα= 0.05 (two-sided), a final effective sample size ofn= 160 per group (320 patients in total) will be calculated using PASS 11.0 software (PASS,Kaysville, UT, USA) withZtest with pooled variance.
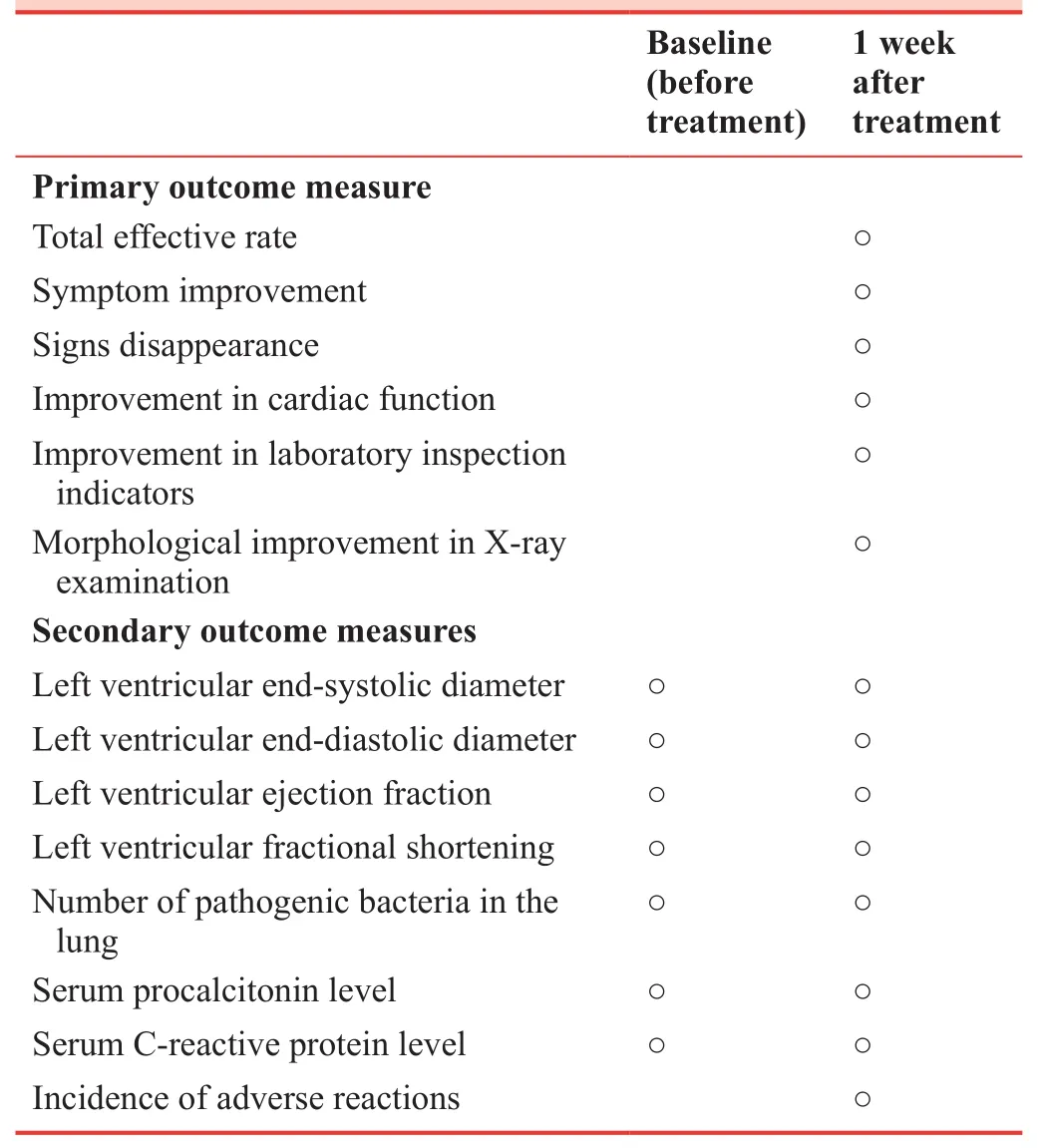
Table 2: Timing of primary and secondary outcome measures
Randomization
A random number table will be generated using SAS 9.2 statistical software (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).The patient numbering will be set to 1-320.The RANUNI function will be used to generate a random number of 0-1 for each case(1 representing the trial group and 0 representing the control group).Random numbers will be sorted using the PROC SORT function and grouped in a ratio of 1:1.The 320 patients will be randomly divided into two groups (n= 160 per group).Allocation concealment will not be performed.
Blinding method
The assessors will be unaware of the test plan, and the blind method will be used.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Sanya People’s Hospital in October 2015 (approval No.S2015-065-03; Additional file 1).This study will be performed in strict accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association.Study protocol version is 1.0.The writing and editing of the article will be performed in accordance with the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT 2010) (Additional file 2).
Informed consent
Patients and their family members will participate in the trial voluntarily.All patients will sign the informed consent on the premise of fully understanding the treatment plan (Additional file 3).
Statistical analysis
All data will be statistically analyzed using SPSS 22.0 software(IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).Measurement data will be expressed as mean; standard deviation; median, minimum, and maximum values; and upper and lower quartiles.Count data will be expressed as number and percentage.
The results will be analyzed using a general linear model.Pre-treatment cardiac function indicators and serological indicators will be adjusted as covariates.If the condition for covariance analysis is met, the difference in cardiac function index and serological index between the two groups after 7 days of treatment will be determined by random covariance analysis after excluding the interference of each index prior to treatment.The adjusted mean and 95% confidence interval(CI) of each index will be calculated.If the cardiac function index and serological index data are non-normally distributed,the Mann-WhitneyUtest or paired Wilcoxon rank sum test will be used to compare differences between groups.The constituent ratio of number of pathogenic bacteria at baseline and after 7 days of treatment in the same group will be compared using McNemar’s test.A Pearson chi-square test will be used to compare the constituent ratio of the number of pathogenic bacteria and the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups.Factors influencing the efficacy of pulmonary infection caused by senile degenerative heart disease and heart failure(such as baseline data, dosage and type of antibiotics, and type of heart failure treatment) will be analyzed using univariate and multivariate logistic analysis.The odd ratio (OR), 95%CI, andPvalue before and after correction will be calculated in the regression model in both groups.The significance level(two-sided) will beα= 0.05.All included patients will be assigned to the per-protocol set.
RESULTS
Flow chart
The study flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Patients intended to be recruited into the trial
According to the previously reported admission of senile patients with degenerative heart disease (approximately 200 cases per year), it is predicted that at least 320 patients will be recruited from July 1, 2019 to August 30, 2021.
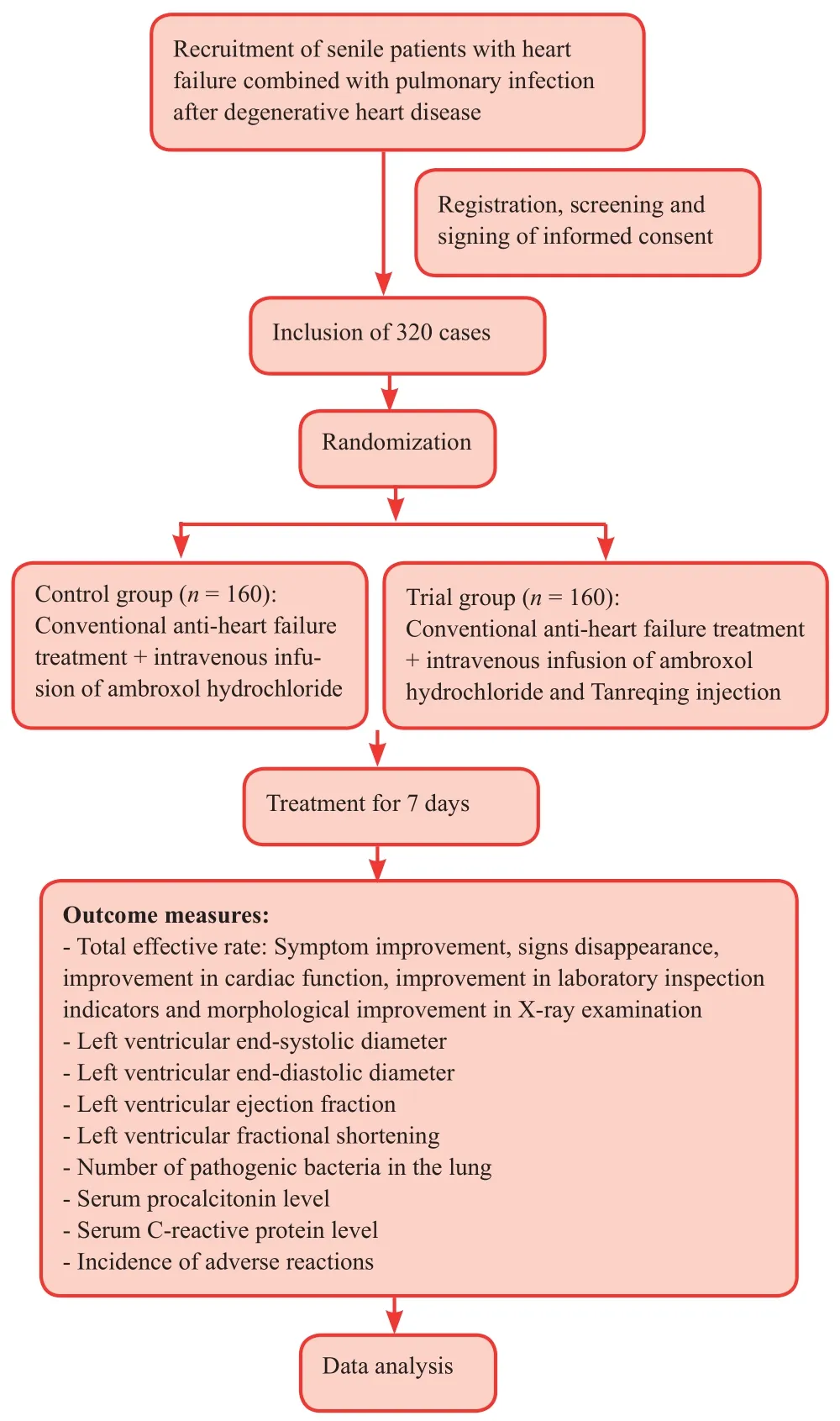
Figure 1: Trial flow chart.
Baseline requirements for prospective recruits
The patient baseline data, including age, sex, hereditary history,family history, type of combined diseases and cardiac function classification, will be recorded in detail before treatment.
Expected outcome measures
Cardiac function indicators, serological indicators, number of pathogenic bacteria, and adverse reactions during follow-up will be recorded in detail.
Expected possible adverse reactions
The main adverse reactions expected to be observed during the trial are liver and kidney dysfunction, arrhythmia, gastrointestinal reactions, and skin allergies.
Small-sample-size pilot study results
A pilot study was conducted in 120 patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection resulting from senile degenerative heart disease from May 2016 to October 2017.
Baseline data
The 120 patients were randomly divided into two groups.The control group (n= 60) comprised 32 men and 28 women aged 63-73 years (mean, 73.7 ± 10.2 years).The trial group(n= 60) comprised 31 men and 29 women aged 63-72 years(mean, 73.4 ± 10.6 years).No significant difference in age or sex was found between the two groups (P> 0.05).
Analysis of pathogenic bacteria in patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection
Gram-positive bacteria were identified as the main pathogens(53.7% in both groups).After treatment, the number of pathogenic bacteria in the trial group was markedly lower than that in the control group (11 strainsversus17 strains) (Table 3).
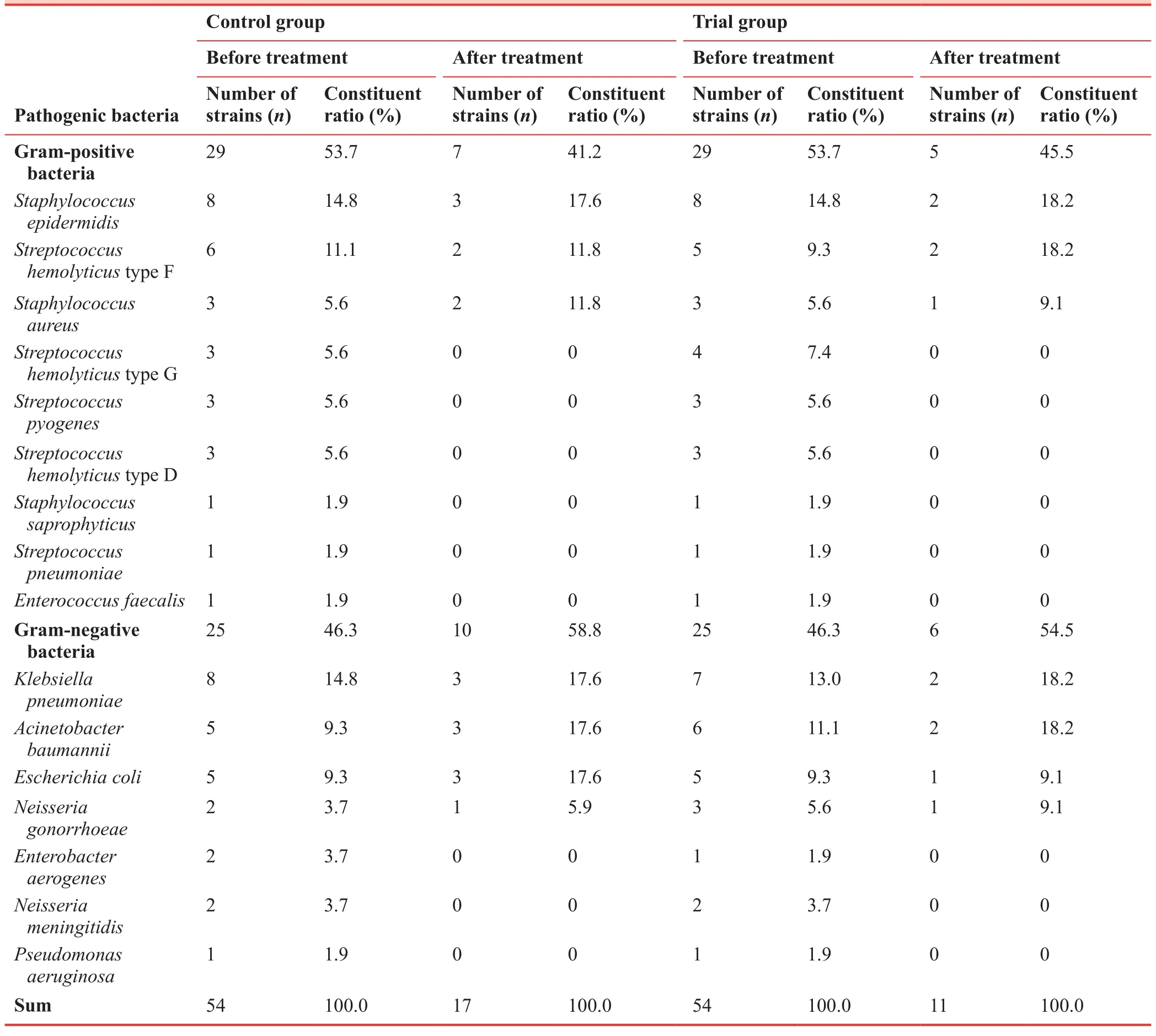
Table 3: Analysis of pathogenic bacteria in senile patients with heart failure combined with pulmonary infection
Effect of Tanreqing injection combined with ambroxol hydrochloride on cardiac function
LVEDD, LVESD, and LVEF were significantly decreased while FS was significantly increased after treatment in both groups (P< 0.05).The changes were more significant in the trial group than in the control group (P< 0.05; Table 4).
Effect of Tanreqing injection combined with ambroxol hydrochloride on serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels
Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels were significantly decreased in both groups after treatment (P< 0.05).However, the reduction was more significant in the trial group than in the control group (P< 0.05; Table 5).
Adverse events and harms
Adverse reactions during follow-up will be recorded in detail.If serious adverse reactions occur, the investigators will report the details, including the date and type of occurrence and the measures taken to treat the adverse events, to the trial leader and the ethics committee within 24 hours.No adverse events occurred in both groups during 7 days of treatment in our small-sample-size pilot study.Adverse event record form(Chinese) is shown in Additional file 4.
DISCUSSION
Study limitations
This is a single-site study design.The result indicators may be insufficient, and allocation concealment and blinded evaluation of the treatment groups cannot be achieved.Due to hospital conditions, patients themselves must know the information of drug use.Long-term follow-up data will not be collected.These limitations may affect the reliability of the results, meaning that future clinical studies may be required.
Generalizability
This trial will be conducted in a larger sample size based on a smaller pilot study.The results will provide a reference for the treatment of heart failure and pulmonary infection caused by senile degenerative heart disease.
Rationale
The results from the pilot study showed that Gram-positive bacteria were the main pathogenic bacteria in the study population.The number of pathogenic bacteria in the trial group markedly decreased after treatment.LVEDD, LVESD, and LVEF were also decreased, while FS was markedly increased.Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels were diminished after treatment in both trial and control groups, although the changes were more pronounced in the trial group than in the control group.These findings indicate thatTanreqinginjection combined with ambroxol hydrochloride markedly improves cardiac function and reduces infection by pulmonary pathogens in senile patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection caused by degenerative heart disease.
DATA AUTHENTICITY MANAGEMENT
Data collection
All data from senile patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection caused by degenerative heart disease will be collectedviaWeChat, telephone follow-up, or hospital visit and will be entered into case report forms.Data quality will be closely monitored during the trial.Patients who discontinue the study or are lost to follow-up will be replaced.
Data management
Data will be entered into electronic case report forms using double-data entry and a two-pass verification method.Allelectronic data will be stored confidentially and will be accessible only using a password.

Table 4: Effect of Tanreqing injection and ambroxol hydrochloride on improving cardiac function in older adult patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection
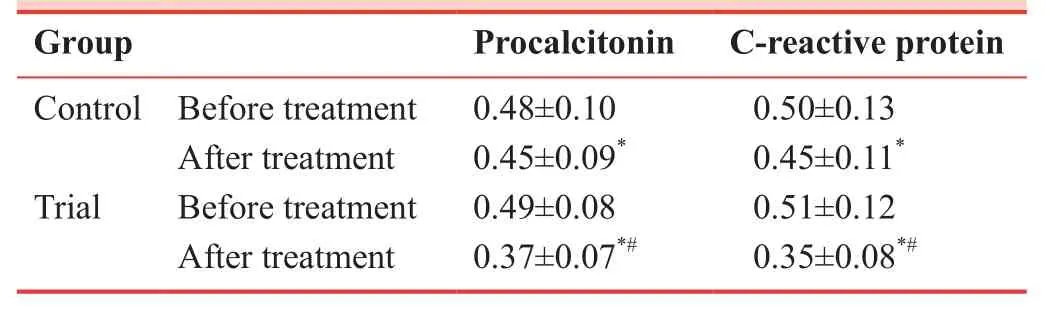
Table 5: Effects of Tanreqing injection and ambroxol hydrochloride on relative optical density ratio (/β-actin)of serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein
Data quality control
Data supervisors will visit the research center regularly to verify the case report forms against the source patient data to ensure that the collected data are true, complete, and accurate.
Modification of research plan
Participating researchers may not modify the content of the protocol during the trial without the permission of the research leader.
Audits
Regular monitoring will take place during enrollment to ensure that enrolled patients meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria,the experimental procedures have been carried out in accordance with the study protocol, and the study data are complete.
Confidentiality
The participating center and study researchers will ensure the authenticity and confidentiality of all patient data.
Result release
Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
TRIAL STATUS
Registration time: April 29, 2019
Recruitment time: July 1, 2019-August 30, 2021
Study completed:December 30, 2021
Trial status: Completing study design.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Hospital Ethics Approval (Chinese).
Additional file 2: CONSORT checklist.
Additional file 3: Informed Consent Form (Chinese).
Additional file 4: Adverse event record form (Chinese).
Author contributions
GQZ designed the study, wrote the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Financial support
None.
Institutional review board statement
This study will be performed in strict accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association.This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Sanya People’s Hospital in October 2015 (approval No.S2015-065-03).
Declaration of patient consent
The author certifies that all appropriate patient consent forms will be obtained.In the forms, the patients will give their consent for their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal.The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity.
Reporting statement
This study followed the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials(CONSORT) statement.
Biostatistics statement
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by the biostatistician of Sanya People’s Hospital in China.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by all authors before publication.
Data sharing statement
Individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article, after deidentification (text, tables, figures, and appendices).Data will be available immediately following publication, with no end date.Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
杂志排行
Clinical Trials in Degenerative Diseases的其它文章
- Relationship between low vitamin D status and extra-skeletal diseases: a systematic review on effects of prophylaxis with vitamin D
- Hemodynamic responses of patients with stable coronary artery disease to a comedy film: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- Clinical progress of cell therapy in treating age-related macular degeneration
- Role of trace mineral in periodontal health: a review
- CTDD call for papers
