重症急性胰腺炎不同肠内营养方式的应用
2019-09-29王颖崔静李浩田甜刘晶晶吕蔚萍
王颖 崔静 李浩 田甜 刘晶晶 吕蔚萍
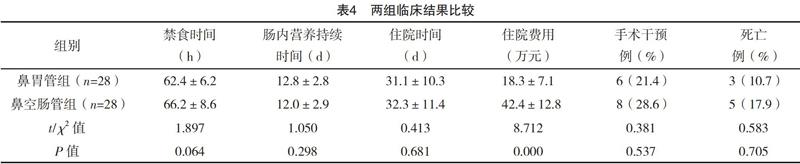


【摘要】 目的:观察经鼻胃管和经鼻空肠途径肠内营养在重症急性胰腺炎(SAP)中的应用效果及对临床预后的影响,以寻求安全有效的营养方式。方法:回顾性分析2016年9月-2018年9月本院行肠内营养支持的56例SAP患者的临床资料。根据肠内营养的不同方式分为鼻胃管组和鼻空肠管组,各28例。观察两组肠内营养治疗的相关并发症、感染并发症、器官衰竭、禁食时间、肠内营养持续时间、住院时间、住院费用、手术干预及死亡情况。结果:两组肠内营养相关并发症、感染并发症、器官衰竭发生率、禁食时间、肠内营养持续时间、住院时间、手术干预及死亡率比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),但鼻胃管组住院费用低于鼻空肠管组(P<0.05)。结论:鼻胃管与鼻空肠管肠内营养在营养相关并发症及感染并发症方面无差异,且操作方便,容易耐受,费用低廉,安全性好,具有代替鼻空肠管的可能性。
【关键词】 重症急性胰腺炎; 鼻胃管; 鼻空肠管; 肠内营养
Study on the Application of Different Enteral Nutrition Methods in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis/WANG Ying,CUI Jing,LI Hao,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2019,16(19):0-042
【Abstract】 Objective:To observe the effect of enteral nutrition through nasogastric and nasojejunal tube on severe acute pancreatitis(SAP)and its effect on clinical prognosis in order to seek safe and effective nutrition.Method:The clinical data of 56 patients with SAP who received enteral nutrition support from September 2016 to September 2018 were retrospectively analyzed.According to the different ways of enteral nutrition,they were divided into nasogastric tube group and nasojejunal tube group,28 cases in each group.The complications,infection complications,organ failure,fasting time,duration of enteral nutrition,hospitalization time,hospitalization expenses,surgical intervention and mortality of two groups were observed.Result:The enteral nutrition-related complications,infection complications,incidence of organ failure,fasting time,duration of enteral nutrition,hospitalization time,surgical intervention and mortality in two groups were compared,the differences were not statistically significant(P>0.05),but the hospitalization cost of nasogastric tube group was lower than that of nasojejunal tube group(P<0.05).Conclusion:There is no difference in nutrition-related complications and infection complications between nasogastric tube and nasojejunal tube enteral nutrition,it is easy to operate,tolerable,inexpensive and safe,and nasogastric tube has the possibility of replacing nasojejunal tube.
【Key words】 Severe acute pancreatitis; Nasogastric tube; Nasojejunal tube; Enteral nutrition
First-authors address:Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450000,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.19.010
急性胰腺炎(acute pancreatitis,AP)是一種由多种原因导致的胰酶在胰腺内被激活,继以胰腺局部炎症反应,伴或不伴有其他脏器功能改变的疾病[1]。大多数AP病情有自限性,预后良好,但20%~30% AP患者出现严重胰腺出血坏死而发展为重症急性胰腺炎(severe acute pancreatitis,SAP)[2]。在急性感染期,存在单个或多个器官功能不全,以高代谢、高分解为特点,长期的高消耗状态容易使患者出现营养不良,这时,如果让患者处于长期禁食状态,就会导致肠屏障功能受损,进而引起肠道内毒素和细菌的易位,引发一系列的胰腺及胰腺外的并发症,因此,应适当地增加营养物质的供应,以促进器官功能的恢复。有关营养支持治疗的相关研究表明,SAP患者肠内营养在感染并发症及病死率等方面明显低于全肠外营养[3-4]。总的来说,相比于肠外营养,肠内营养与人体正常生理营养方式更相符[5-6]。目前肠内营养较常用的实施方式为经鼻胃管肠内营养和鼻空肠管肠内营养两种。由于经空肠营养支持可以避免头相、胃相、十二指肠相对胰腺分泌的刺激[7],目前最常见的肠内营养的实施方式是鼻空肠管途径,但是经鼻空肠置管难度大,对操作者的技术要求较高,需要内镜及X线引导下完成,而经鼻胃管途径可在床边进行,且操作简单。两种方式在重症急性胰腺炎肠内营养上的优劣性需要更多研究证据。本研究根据实施肠内营养的不同方式分为鼻胃管组、鼻空肠组,比较肠内营养治疗的相关并发症(反流、误吸、恶心呕吐、腹痛加重、腹泻、胃潴留等)、感染并发症及器官衰竭发生率、肠内营养持续时间、住院时间、住院费用、死亡率等方面的差异。现报道
综上所述,经鼻胃管途径及鼻空肠管途径的肠内营养对SAP临床预后没有显著差异,肠内营养经鼻胃管途径是安全可行的,本研究建议,没有禁忌证的SAP患者均可进行鼻胃管途径的肠内营养。由于本研究肠内营养实施时间较晚,且具有回顾性和小样本性,需要对大样本进一步的前瞻性研究,以证实本研究的结果。
参考文献
[1]中华医学会消化病学分会胰腺疾病学组,《中华胰腺病杂志》编辑委员会,《中华消化杂志》编辑委员会,等.中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2013,上海)[J].中华胰腺病杂志,2013,13(2):73-78.
[2]王兴鹏,李兆申,袁耀宗,等.中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2013,上海)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2013,33(7):530-535.
[3] Bakker O J,Van Brunschot S,Farre A,et al.Sa1362 Timing of Enteral Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis:Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of 8 Prospective Cohorts[J].Gastroenterology,2013,144(5):S274.
[4] Seres D S,Valcarcel M,Guillaume A.Advantages of enteral nutrition over parenteral nutrition[J].Therap Adv Gastroenterol,2013,6(2):157-167.
[5] Oláh A,Romics L Jr.Enteral nutrition in acute pancreatitis:areview of the current evidence[J].World J Gastroenterol,2014,20(43):16123-16131.
[6]崔立建,阴赪宏.肠内营养对重症急性胰腺炎的治疗作用[J].中国医刊,2016,51(3):13-17.
[7]王庭槐.生理学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2015.
[8]王春友,李非,赵玉沛,等.急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2014)[J].中国实用外科杂志,2015,35(1):4-7.
[9]费改顺,贾正平.急性胰腺炎营养支持研究进展[J].西北國防医学杂志,2015,36(7):462-465.
[10]武文亚,欧阳爱云,唐小红,等.经鼻-空肠管早期肠内营养支持治疗重症急性胰腺炎的临床意义[J].临床医学,2016,36(1):50-52.
[11] Petrov M S.Gastric feeding and “gut rousing” in acute pancreatitis[J].Nutr Clin Pract,2014,29(3):287-290.
[12] OKeefe S J,Lee R B,Li J,et al.Trypsin secretion and turnover in patients with acute pancreatitis[J].Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2005,289(2):G181-G187.
[13] Boreham B,Ammori B J.A prospective evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function in patients with acute pancreatitis:correlation with extent of necrosis and pancreatic endocrine insufficiency[J].Pancreatology,2003,3(4):303-308.
[14] Petrov M S,Correia M I,Windsor J A.Nasogastric tube feeding in predicted severe acute pancreatitisA systematic review of the literature to determine safety and tolerance[J].Journal of the Pancreas,2008,9(4):440-448.
[15] Schietroma M,Pessia B,Carlei F,et al.Intestinal permeability and systemic endotoxemia in patients with acute pancreatitis[J].Ann Ital Chir,2016,87(2):138-144.
[16] Wu X M,Liao Y W,Wang H Y,et al.When toinitialize enteral nutrition in patients with severe acute pancreatitis? A retrospective review in a single institution experience(2003-2013)[J].Pancreas,2015,44(3):507-511.
[17]石慧荣,唐国都,梁志海.重症急性胰腺炎肠内营养治疗的时机[J].国际消化病杂志,2014,34(2):96-98.
[18] Guadagni S,Cengeli L,Palmeri M,et al.Early cholecystectomy for non-severe acute gallstone pancreatitis:easier said than done[J].Minerva Chir,2017,72(2):91-97.
[19] Sun J K,Li W Q,Ke L,et al.Early Enteral Nutrition Prevents Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Reduces the Severity of Severe Acute Pancreatitis Compared with Delayed Enteral Nutrition:A Prospective Pilot Study[J].World J Surg,2013,37(9):2053-2060.
[20] Van Baal M C,Van Rens M J,Geven C B,et al.Association between probiotics and enteral nutrition in an experimental acute pancreatitis model in rats[J].Pancreatology,2014,14(6):470-477.
[21]马克强,高春江,汪志强,等.早期经口进食进行肠内营养在治疗急性重症胰腺炎中的作用[J].重庆医学,2015,44(7):965-967.
