丙基硫氧嘧啶与甲巯咪唑治疗妊娠合并甲亢的效果及对母婴结局的影响
2019-08-19张昌凤周雪梅官葵花
张昌凤 周雪梅 官葵花
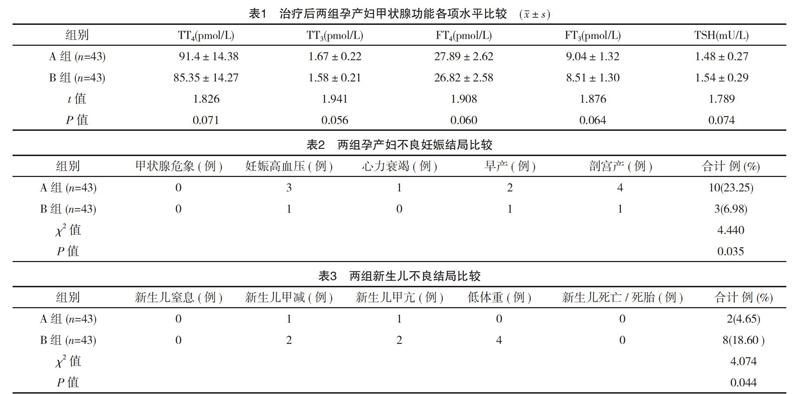
【摘要】 目的:研究丙基硫氧嘧啶(PTU)与甲巯咪唑(MMI)治疗妊娠合并甲亢的效果及对母婴结局的影响。方法:选取2015年1月-2018年1月笔者所在医院收治的妊娠合并甲亢患者86例作为研究对象,运用随机数表法将所有研究对象随机分成A组和B组,每组43例。A组确诊后口服PTU治疗,B组确诊后服用MMI治疗,观察两组病情变化,统计分析两组母婴结局。结果:治疗后,两组患者甲状腺功能各项指标(TT4、TT3、FT4、FT3、TSH)对比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,A组孕产妇不良妊娠结局发生率(23.25%)明显高于B组(6.98%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),A组新生儿不良结局发生率(4.65%)明显低于B组(18.60%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论: PTU和MMI治疗妊娠合并甲亢均取得良好治疗效果,很大程度上优化了孕妇甲状腺功能,改善母婴结局。但PTU对孕产妇产生的不良影响更大,MMI对胎儿发育影响较大,但两种药物大多数为轻微不良反应。综合衡量,MMI可作为优先治疗妊娠合并甲亢的药物,值得临床借鉴。
【关键词】 甲巯咪唑; 妊娠; 甲亢; 母婴结局
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.15.018 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2019)15-00-03
【Abstract】 Objective:To study the effect of Propylthiouracil(PTU) and Methimazole(MMI) on pregnant women with hyperthyroidism and their maternal and infant outcomes.Method:A total of 86 pregnancy complicated with hyperthyroidism were selected from January 2015 to January 2018.All the subjects were randomly divided into group A and group B with 43 cases in each group.The patients in group A were treated with PTU orally and the patients in group B were treated with MMI after diagnosis.The changes of the two groups were observed,and the outcomes of mothers and infants in two groups were analyzed statistically.Result:After treatment,there was no significant difference in thyroid function indexes(TT4,TT3,FT4,FT3,TSH) between the two groups(P>005).The incidence of adverse pregnancy outcome was 23.25%,significantly higher than 6.98% in group B (P<0.05).The incidence of adverse outcome in group A was 4.65%,significantly lower than 18.60% in group B(P<0.05).Conclusion:PTU and MMI in the treatment of pregnancy with hyperthyroidism achieved good results,greatly optimized the thyroid function of pregnant women,improve maternal and infant outcomes.But the negative impact of PTU on pregnant women is even greater,and the influence of the MMI on the development of the fetus is large,but the two drugs are mostly mild bad reaction.Comprehensive measurement,MMI can be used as a priority treatment of pregnancy with hyperthyroidism drugs,worthy of clinical reference.
【Key words】 Methimazole; Pregnancy; Hyperthyroidism; Maternal and infant outcome
正常水平的甲狀腺功能是胎儿神经、智力发育的重要条件,甲亢是指多种原因导致甲状腺激素分泌过多引起的甲状腺功能亢进[1]。妊娠合并甲亢属于高危妊娠的一种,其包括了妊娠之前已确诊甲亢及妊娠期并发甲亢者[2]。有资料指出,妊娠合并甲亢的发病率为0.1%~0.2%[3],该病若未经系统有效治疗,很有可能引起多种不良母婴结局,例如孕妇妊娠高血压、甲状腺危象、心力衰竭,以及胎儿畸形、流产、早产、低体重等不良母婴结局,对孕产妇及新生儿的健康造成了严重的威胁[4],目前临床上对于妊娠合并甲亢首选治疗方式为抗甲状腺药物治疗,有研究指出PTU、MMI作为两种常用的抗甲状腺药物,治疗效果显著,均能够有效减少妊娠期并发症,降低胎儿损害,但有关这两种药物孰优孰劣颇具争议[5]。所以,本研究主要观察了PTU与MMI治疗妊娠合并甲亢的效果及对母婴结局的影响,研究结果报告如下。
