基于输出阻抗建模的并网系统低次谐波预测模型
2019-07-22王喜莲程迪王顺
王喜莲 程迪 王顺


关键词:并网逆变器;谐波交互;谐波预测;阻抗模型;谐振
DOI:10.15938/j.emc.2019.06.000
中图分类号文献标志码:A 文章编号:1007 -449X(2019)06 -0000 -00
Abstract:Aimed at harmonic prediction of gridconnected systems, a harmonic impedance modeling scheme was proposed based on output harmonic current of inverter. The gridconnected system harmonic resonance theory was analyzed for impedance modeling of singlephase LCL gridconnected inverter. The low frequency characteristic of inverter was analyzed. Further, the harmonic current of single LCL gridconnected inverter was considered to obtain the harmonic impedance model, which is in good agreement with the simulation results of circuit model. The harmonic impedance model was used for harmonic interaction analysis and harmonic prediction modeling of multiinverter gridconnected systems. An example of eight gridconnected inverters was proposed, and the resonance effect was analyzed for harmonic current and harmonic voltage over point of common coupling(PCC). This harmonic prediction model was compared with circuit model to prove its effectiveness and accuracy.
Keywords:gridconnected inverters;harmonics interactions;harmonics prediction;impedance model;resonance
0 引 言
随着新能源发电技术的进步,越来越多的并网逆变器接入到分布式发电系统中,这些并网逆变器不仅提供了谐波源,还与电网形成了分布式阻抗网络,可能产生谐振,对系统的安全和稳定造成影响。建立较为准确的并网系统谐波预测模型,既给并网操作的可行性提供了参考,也对经济合理地治理微网系统谐波有重要的指导意义。
在分布式发电系统和大型新能源发电站中,长距离输电线和变压器导致电网阻抗不可忽略[1-2],特别是在偏远地区,此时电网为感性弱电网。谐波源和阻抗网络的存在会使并网系统发生谐波交互[3]。
文献[4]提出了基于阻抗模型的谐波分析方法,对逆变器侧和电网侧谐波进行交互分析,但其阻抗模型是在理想状态下建立的。文献[5-6]将死区效应引入到并网系统阻抗模型中对系统进行分析,提高了阻抗模型的精度。文献[7-8]将实际数字控制系统的延时引入到阻抗模型中,使并网逆变器阻抗模型更加精确。国内外学者对谐波预测方面做了大量的研究。文献[9-11]分别提出了三种针对电网公共接入点(point of common coupling,PCC)谐波电流的预测模型。预测模型建立的形式和方法均不同,但模型建立的过程都需要测量或者收集大量数据来进行分析和计算,模型的建立过程复杂、工作量大。因此,建立较为简单准确的微网系统谐波预测模型有很强的实际意义。
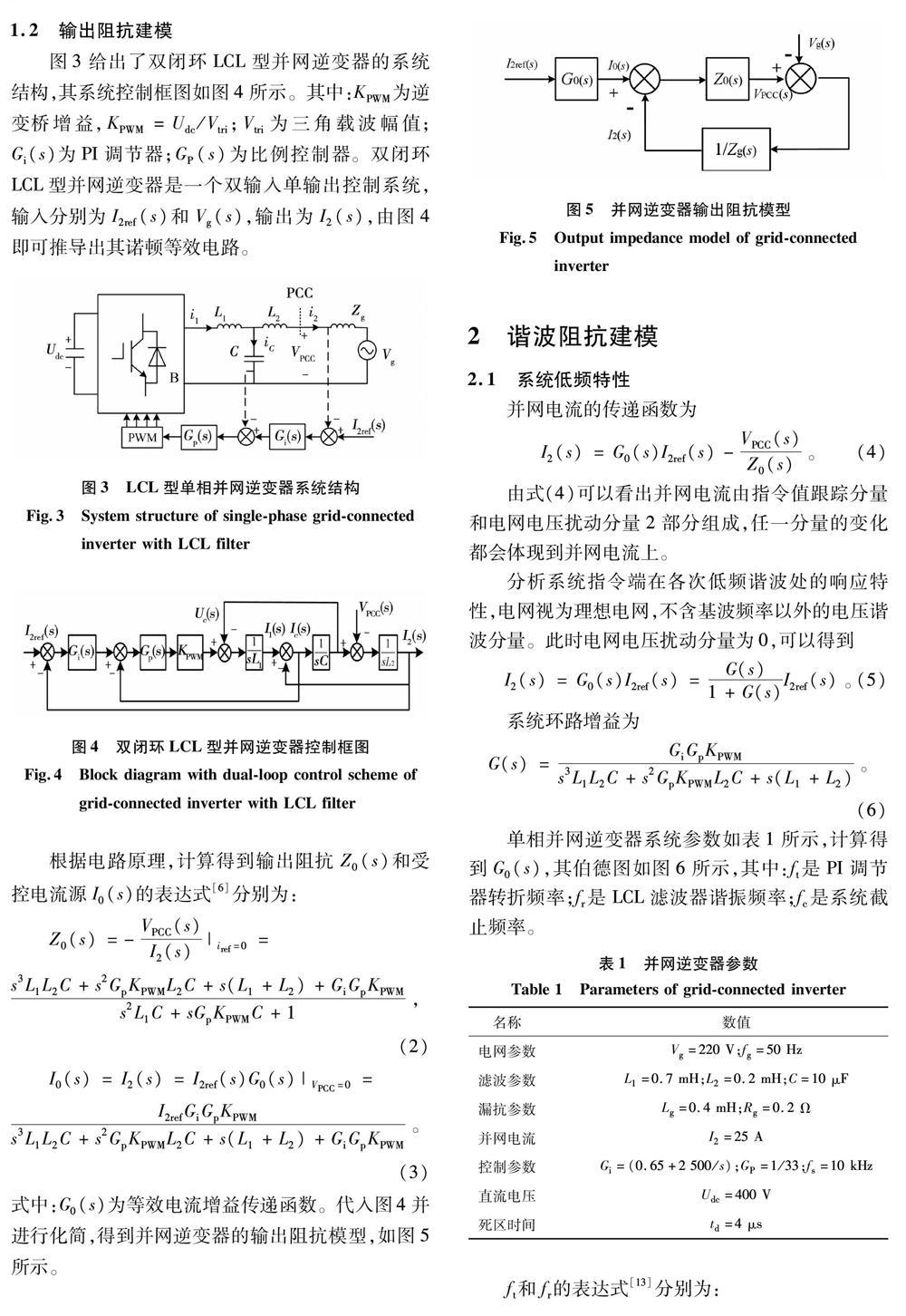
实际数字控制的并网逆变器系统包含许多非线性因素,并且有的非线性因素很难定量表达出来。为使逆变器阻抗模型更加符合实际情况,只考虑谐波结果不考虑谐波产生的过程,本文提出将逆变器实际输出谐波电流引入到模型中来,建立谐波阻抗模型。考虑到并网系统主要含有低次谐波,用谐波阻抗模型对多逆变器并网系统建模,进行谐波交互分析。以单相LCL型并网逆变器为例,推导了其阻抗模型,分析了其低频特性;在阻抗模型中引入实际谐波电流,建立多逆变器并网系统谐波预测模型,最后结合理论分析和电路仿真对模型进行了验证。
5 结 论
本文以单相并网逆变器为研究对象,分析了其低频特性,提出将并网逆变器谐波电流考虑到阻抗模型中,建立谐波阻抗模型。利用提出的谐波阻抗模型对多逆变器并网系统进行谐波交互分析,推导了多逆变器并网电流耦合矩阵,建立了多逆变器并网系统谐波预测模型,得出以下结论:
1)建立的谐波阻抗模型较好的体现了逆变器的低频特性,提高了逆变器阻抗建模的准确性。
2)多逆变器并网系统中各逆变器并网电流相互耦合,每个逆变器并网电流不仅与其自身参数有关,还与其他所有逆变器参数及电网参数有关。
3)逆变器在低频段的幅频特性为低次谐波的分析及预测提供了理论依据。谐波预测模型可以较准确、快速地定量分析系统的谐振情況,预测PCC端各次谐波电流和谐波电压的幅值及THD。
4)谐波预测模型可以较好的预测系统截止频率fc以下的低次谐波幅值,甚至可以对转折频率ft以下的各次谐波进行矢量预测。
参 考 文 献:
[1] LISERRE M, TEODORESCU R, BLAABJERG F.Stability of photovoltaic and wind turbine gridconnected inverters for a large set of grid impedance values[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2006,21(1):263.
[2] 王宝忠,王志兵.基于模糊控制的光伏系统最大功率点跟踪[J].哈尔滨理工大学学报,2012,17(4):13.
WANG Baozhong, WANG Zhibing. Maximum power point tracking by using fuzzy control for photovoltaic power system[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2012,17(4):13.
[3] 谢文浩,王建赜,纪延超,等.一种LCL型并网逆变器的复合阻抗重塑方法[J].电机与控制学报,2018,22(10):35.
XIE Wenhao, WANG Jianze, JI Yanchao, et al. Composite impedance reshaping method for LCLtype gridtied inverter[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2018,22(10):35.
[4] WANG Fei, LDUARTE J, AMHENDRIX M,et al. Modeling and analysis of grid harmonic distortion impact of aggregated DG inverters[J].IEEE Transactionson Power Electronics,2011,26(3):786.
[5] XU Dezhi,Wang Fei,Ruan Yi,et al.Output impedance modeling of gridconnected inverters considering nonlinear effects[C]//Control and Modeling for Power Electronics,June 10-13,2012,Kyoto,Japan. 2012:1-7.
[6] 許德志,汪飞,毛华龙,等.多并网逆变器与电网的谐波交互建模与分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2013,33(12):64.
XU Dezhi,WANG Fei,MAO Hualong,et al.Modeling and analysis of harmonic interaction between multiple gridconnected inverters and the utility grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2013,33(12):64.
[7] 许德志,汪飞,阮毅,等.多逆变器并网系统输出阻抗建模与谐波交互[J].电机与控制学报,2014,18(2):1.
XU Dezhi,WANG Fei,RUAN Yi,et al.Output impedance modeling and harmonic interactions of multiple inverters gridconnected system[J]. Electric Machines and Control,2014,18(2):1.
[8] 张兴,余畅舟,刘芳,等.光伏并网多逆变器并联建模及谐振分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2014,34(3):336.
ZHANG Xing, YU Changzhou, LIU Fang, et al. Modeling and resonance analysis of multiparalleled gridtied inverters in PV systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(3):336.
[9] AU T M, MILANOVIC V J.Development of stochastic aggregate harmonic load model based on field measurements[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2007, 22(1):323.
[10] VASANASONG E, SPOONSER E D. The prediction of net harmonic currents produced by large numbers of residential PV inverters:Syndney Olympic Village case study[C]// 9th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power,October 1-4,2000,Orlando,USA. 2000: 116–121.
[11] YAHYAIE F, LEHN W P.Using frequency coupling matrix techniques for the analysis of harmonic interactions[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2016,31(1):112.
[12] 汪飞,冯夏云,吴春华,等.多反激式微型逆变器并网谐波交互研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2016,36(3):712.
WANG Fei, FENG Xiayun, WU Chunhua, et al. Research on grid harmonic interaction of multiple flyback microinverters[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2016,36(3):712.
[13] 鲍陈磊,阮新波,王学华,等.基于PI调节器和电容电流反馈有源阻尼的LCL型并网逆变器闭环参数设计[J].中国电机工程学报,2012,32(25):135.
BAO Chenlei, RUAN Xinbo, WANG Xuehua,et al.Design of gridconnected inverters with LCL filters based on PI regulator and capacitor current feedback active damping[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2012,32(25):135.
[14] AGORRETA J L, BORREGA M, LOPEZ J, et al.Modeling and control of Nparalleled gridconnected inverters with LCL filter coupled due to grid impedance in PV plants[J].IEEE Transactionson Power Electronics,2011,26(3):774.
[15] SUN J. Impedancebased stability criterion for gridconnected inverters[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics,2011,26(11):3075.
[16] CESPEDES M,SUN J.Impedance modeling and analysis of gridconnected voltagesource converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(3):1254.
(編辑:邱赫男)
