Design and Experiment of four Lines Trailed Potato Fertilization Seeder
2018-10-10LvJinqingDuiHanSunHeandPengManman
Lv Jin-qing, Dui Han, Sun He, and Peng Man-man
College of Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
Abstract: In order to solve the problems which are widespread in potato seeding planter, such as lower operating efficiency,unideal performance index, higher replay rate and leakage rate and uneven spacing sowing in seeding operating, a trailed potato fertilization seeder was designed. The key components of the special structure had been got through the description of the structure and working principle of the whole machine. A crossing seed-taken technology along with the vibration component was adopted to achieve precision seeding. The results showed in the field test of the machine: all the performance indexes of the machine met the agronomic requirement of potato planting; the multiple and missing index were low; it completed the ditching, fertilizing, seeding as well as ridging in one planting process; its operation efficiency was high and the stability was good. This design of the trailed potato fertilization seeder provided a reference for the development of large traction-type potato seeding machine.
Key words: agriculture machinery, mechanization, potato planter, seed-metering device, field experiment
Introduction
The potato is called "underground apple", which has high nutritive value, has attracted wide attention to the world. At present, with the gradual advance of potato staple food strategy, potato has become the fourth major food crops in China, and its planting area has been increasing year by year, and its planting process is one of the most important links in potato production. The demand of potato planters, especially large seeding machine combined with fertilization,is increasing accordingly. Therefore, it is significant to research and design potato fertilizing and planting machine to suit Chinese potato cropping pattern, raise the mechanization level of potato planting and increase the yield and quality of potatoes in China (Du et al.,2011; Jia et al., 2010; Lv et al., 2015).
The study of potato fertilization and planting machinery started earlier abroad, such as the four lines and above potato fertilizer planter manufactured in German Grimme Company, Norway Kvemeland Company and the United States Double L Company (Jia et al.,2010). These fertilizer planters are high in automation,structure complexity and price, while the most of the farms in China are unbearable, and they are larger in size, which are not suitable for small planting areas in China. Foreign small-scale potato fertilization and planting machines are mainly produced in Italy and Japan, most of which are simple in structure, but the foreign models do not match the potato planting pattern of China. Domestic researches on potato planting machine started relatively late: 2CM-4 potato planting and fertilizing combined had developed by Harbin Agricultural Mechanization Research Institute (Li et al., 2012), which brought a spiral agitator as the fertilization device, in order to prevent fertilizer blocking; 2BSL-2 model of potato ridging planter which was simple in design but efficient in operation had developed by Agricultural University of the Inner Mongol, in addition that the requirements of soil preparation were not so high (Zhao et al., 2001).At present, some potato planters have poor seeding performance, and then the cultivation of potato suffers from the high miss and multiple index and serious damage of seed potato (Yang et al., 2015; Yang et al.,2016; Yazgi, 2007). Based on the mentioned issues above, a trail-type potato combined seed and fertilizer was designed which had higher seeding efficiency,lower index of miss and multiple and more uniform spacing sowing.
The structure of seed-metering device and other key components was designed, and field experiment was carried out to verify its performance test, which showed that this traction-type potato fertilization seeder met the operational requirements of potato planting and fertilizing. A higher quality of work equipment for precision sowing potato was provided.
Materials and Methods
Complete unit structure, operational principle and main technical parameters
The potato fertilization seeder whose walking mode was traction type connected to the tractor through the traction frame. This equipment was composed of draw frame, marking device, frame assembly,seeding device, fertilizer system, disk covering shovel,drive system, ground-engaging wheel and furrowing blade etc., which had four units of seeding, which could carry out sowing and fertilizing operation simultaneously in four lines of potatoes to reduce the number of tractor into the field, shorten the planting cycle and save operation cost. The seeding and fertilizing furrow blade were separately equipped with seeding unit and fertilizer system to separate potato seed and fertilizer, otherwise the phenomenon of seed burning would happen. This equipment could accomplish many operations in one planting process,such as ditching, fertilizing, planting, ridging. The structure of the potato fertilization seeder is shown in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 Structure diagram of potato planter
The trailed potato fertilization seeder was seeding through tractor. In accordance with the tillage requirements, the hydraulic cylinder supporting the groundengaging wheel was extended to a suitable position,and the marking device on the corresponding side was laid down manually. When the tractor was forward,the fertilizer application would be furrowed at deep position side of beyond ridge. The power would be transferred from the ground-engaging wheel driving device to the fertilizer device to drive the fertilizer applicator. The seeder was provided with a fertilizing opener and a seeding opener, at the time of fertilizing opener furrowing, the fertilizer would be discharged steadily and accurately from the fertilizer box to the furrow which had already opened; meanwhile, the seeding opener would open a V-type groove where the seed potato would be sowed with accurately and quantitatively.
The structure of this trailed potato fertilization seeder could meet the agricultural technique requirement of potato fertilization and sowing, and was mainly applicable to the whole potatoes and diced potato seeding. This trailed potato fertilization seeder had the advantages of simple structure, adjustable spacing sowing, and increased the applicability of sowing machine. The main technical parameters of this trailed potato fertilization seeder had been shown(Table 1).
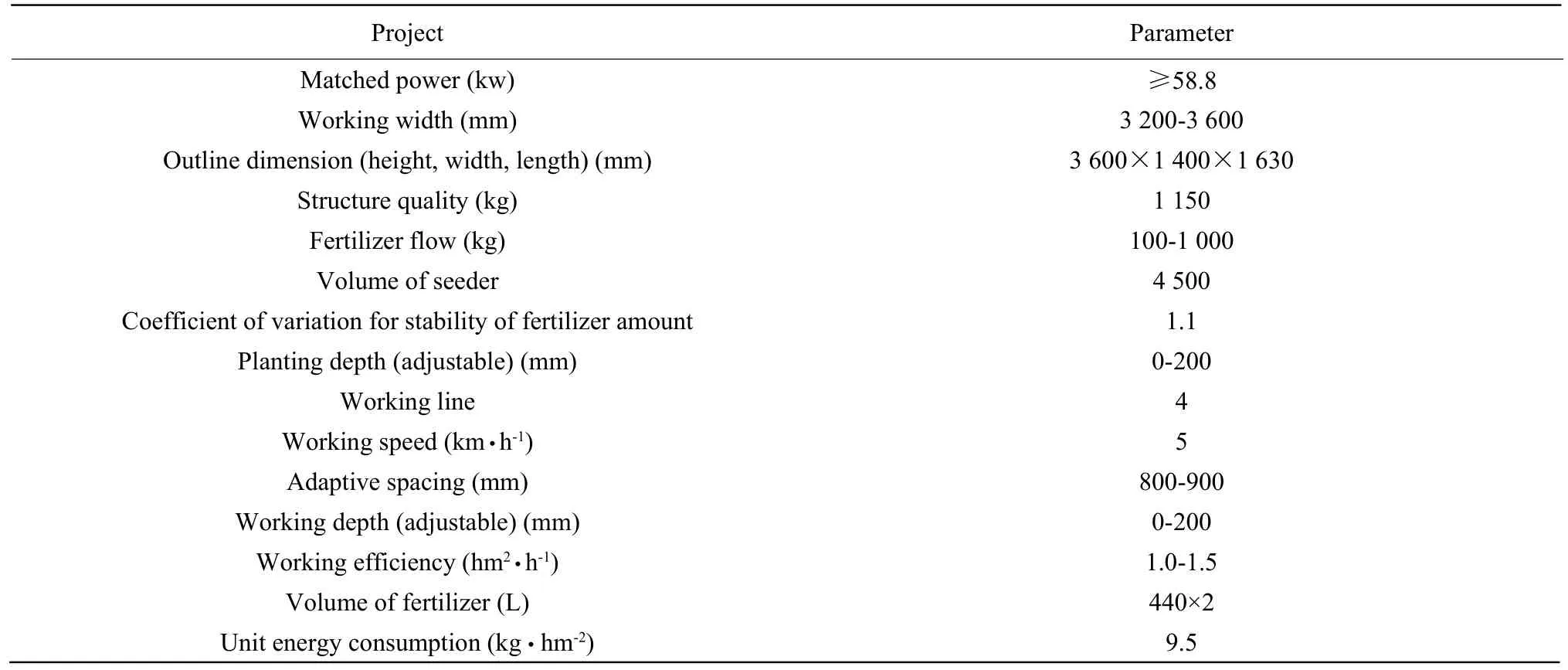
Table 1 Main technical parameters of trailed potato fertilization seeder on traction
According to the market demand of potato industry in Heilongjiang Province, the four lines trailed potato fertilization seeder innovative was designed suitable for China, which was in based of the existing mature technology "2CMF-4 suspension type potato planter"and foreign models of advanced technology. The main innovation points of the trailed potato fertilization seeder were as the followings.
(1) The machine was supported by front and rear hydraulic cylinders, the two groups of hydraulic cylinders worked together to make the machine adjust convenient to the state of transportation and operation.
(2) The clutch adopted hydraulic drive type, and solved the defects that the mechanical clutch was insensitive and inadequate.
(3) A single body profile modeling device of a sowing mechanism was combined with a profile modeling disk soil-covering device, so that the precise adjustment of the seeding depth could be realized, then the accurate seeding could be realized.
(4) The hydraulic tilting seed case and the pendulum rod seed guiding device had been designed to have anti-overhead ability and good seeding filling performance. The above innovations of the trailed potato fertilization seeder could make the regional applicability of potato planter more extensive, which had a great effect on improving the level of potato planting mechanization in China.
Main structure design
The seeding apparatus was the key component of the potato fertilization seeder (Lv et al., 2016; Wang,2015). Currently, the types of seed-metering devices used in potato were spoon-disc type, cup-belt type and needle type: the spoon disc type potato seed-metering device had lower requirement for the quality of seed potatoes, so it had wide adaptability, but its seed metering performance was poor; the needle type seed metering device had low strength and needed to be repeatedly inserted into different seed tubers, which was easy to carry pathogenic bacteria, and cause to cross infection of seed potatoes. Aiming at this problem, the cup-belt potato seed-metering device had been used and its structure has been designed, so that the seed metering performance could be better. The structure of the seedmetering device of the trailed potato fertilization seeder is shown in Fig. 2. Its front view is shown in Fig. 2(a),its lateral view is shown in Fig. 2(b).

Fig. 2 Structural diagram of seed-metering device
The seed metering device was mainly composed of an upper gatherer assembly, seed-metering rack,driving pulley combination, seeding guide plate,double cup staggered seeding belt, seed case and driven pulley combination. The working principle of the device was that the power was transmitted to the driving wheel rotating by chain transmission, when the seed potatoes dropped into the bottom of the seed case by gravity, the seed potatoes would be scooped on the cup of the seeding belt, the ejection pin in the middle of the seed metering would strip the seed potato in the middle of the cup, thereby multiple indexes had been reduced; when the seed potatoes were carried by the cup to the highest point of the driving wheel, the seed potatoes would fail in the back of the cup by gravity to prevent the seed of free fall; when the seed potatoes reached the seed drop point, the seed metering would complete the process of seeding.
The seed potatoes were transported from the seed cases to the soil by the seed-lifting belt, thereby, the movement state of the seed-lifting belt influenced the planting quality. The fertilization seeder was used in the structural form of top drive to prevent the belt slipping and affect the seeding accuracy.The requirements of seed-lifting belt design were enough strength; better flexibleness, un-breakable;and resistant to periodic bending deformation, etc. In view of the above design requirements, the structure of lifting belt is shown in Fig. 3.
The seed-lifting belt was a rubber belt, which had both flexibility and strength. As shown in Fig. 3(a),there were two rows of convex structure of the rubber belt, which could match with the groove in the upper pulley spoke plate, to avoid the seed-lifting belt squeezed to distortion and tilted by the seed potatoes in the seed case, during the operation, meanwhile, the convex structure could effectively reduce the slip percentage of the rubber belt and increase the operation stability and precision. The rubber belt adopted mechanical joint, which lapped both ends of hasp and fit on the seed metering device. This installation method was convenient for disassembling and installing. The structure of the cup is shown in Fig. 3(b). The circular structure is adopted on upper contact surface to make the seed potato and cup contact fully, which could prevent seed potato dropping; the structure of bend downward at the edge of cup prevented potato damage,during the cup scoop the seed potato.
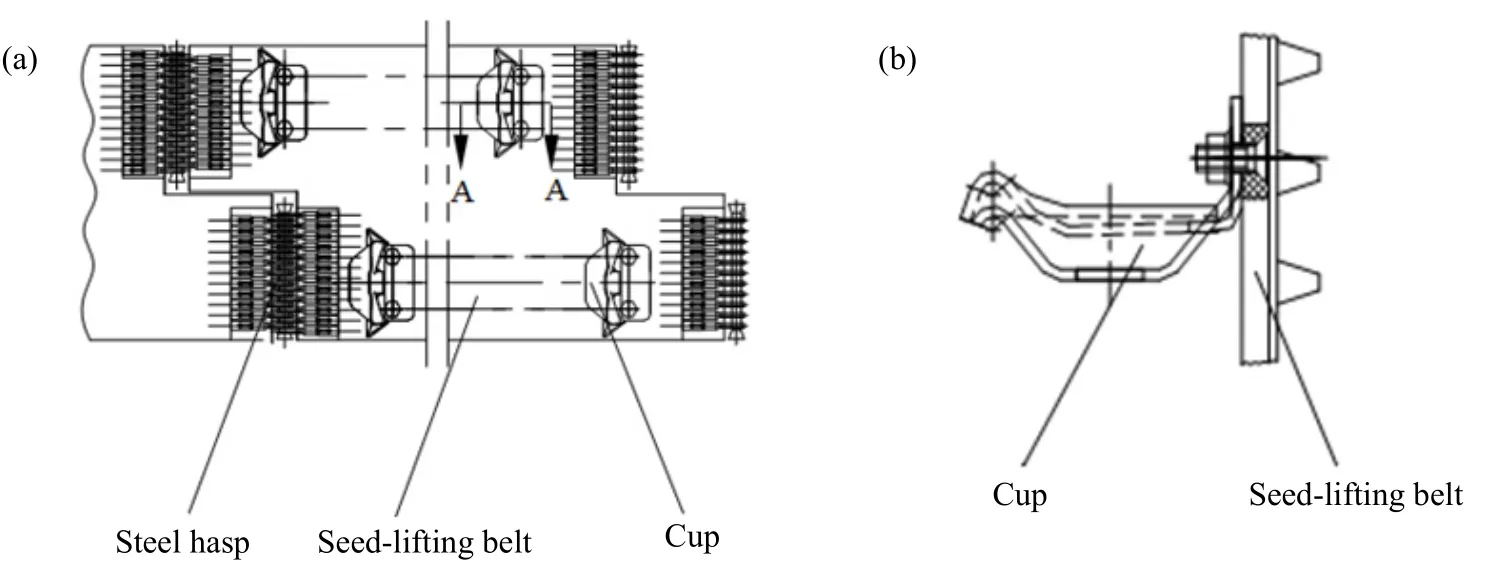
Fig. 3 Structural diagram of seed-lifting belt
Field experiment
The field experiment of the trailed potato fertilization seeder was carried out at KeShan Farm in Heilongjiang Province in September, 2016. The soil preparation had been completed before the experiment, and before the experiment the physical parameters of the soil was tested as the followings: the experimental land was ordinary black soil, the soil hardness was 63.2 kPa and soil moisture content was 17%. The physical parameters of seed potatoes were measured before the experiment: the physical size of seed potato was 45.5 mm×36.3 mm×25.1 mm, the shape of seed potato was ellipsoid, the average mass was 21.5 g and the shape index was 207. The wheeled tractor with the power of 58.8 Kw was used, and the forward speed was 5 Km · h-1. The field operation of the machine is shown in Fig. 4 (a) and experimental model is shown in Fig. 4(b).
In order to verify whether the operation performance of the trailed potato fertilization seeder could meet potato planting operation requirements, a field experiment was built according to (GB/T 6242-2006 and NY/T 1415-2007) The field fertilization and sowing experiments were carried out on smooth cultivated land, and the evaluation indexes were coefficient of variation in eligible seed potato spacing, multipleseeding index, miss-seeding index and qualified index of seed tuber spacing.
In the course of the experiments, miss-seeding referred that a position should be planted, but actually not, at the time of statistical calculation, when the measured spacing of seed tubers was greater than 1.5 times the theoretical spacing, it was considered as the miss-seeding. Multiple-seeding referred that a position should be planted one seed potato, but actually planted two or more, at the time of statistical calculation the measured spacing of seed potatoes no more than 0.5 time theoretical spacing was considered to be multiple-seeding. The coefficient of variation referred to the percentage of actual spacing deviation from the standard spacing. During the operation, the spacing between adjacent seed after the end of each group experiment was measured and denoted as X,all recorded X values were distributed among both sides of Xref, Xrefreferred to the theoretical seeding distance set at the time of experiment, the distribution interval was 0.1 Xref, and at this time, different sections could be obtained at around Xref: [0.9Xref, Xref], [Xref,1.1Xref], etc. The variables for each section were set as:

Where, xiwas the median of section.

Fig. 4 Experimental model and field experiment
According to the formula (2), frequency division interval shown in drawing the corresponding frequency meter, frequency meter referred to each section of the value Xiand frequency ni, the frequency distribution histogram took Xias abscissa, and the relative frequency Fi=ni/N was ordinate. N was the total numbers of seed potatoes measured in the experiment.

Converted the formula (2) to the relationship shown as below:

Then:

By the formulas (1)-(4), the number of multiple seed, the number of qualified seed, the number of miss seed, the number of interval and the qualified average distance were as the followings:
Number of multiple seed:

Number of miss seed:

Number of qualified seed:

Number of interval:

Average eligible distance:

Where, Xi∈{>0.5–≤1.5}.
Then, the corresponding test index was calculated as followings:
Qualified index:

Multiple-seeding index:

Miss-seeding index:

Coefficient of variation in qualified seed:

Where, Xi∈{>0.5–≤1.5}.
Results and Discussion
All the indexes met the operational requirements of potato planting Table 2. Meanwhile, the equipment commendably completed the ditching, sowing, fertilization, soil covering, ridging and other operations.The trailed potato fertilization seeder had the high operation efficiency, the simple structure and work stability.
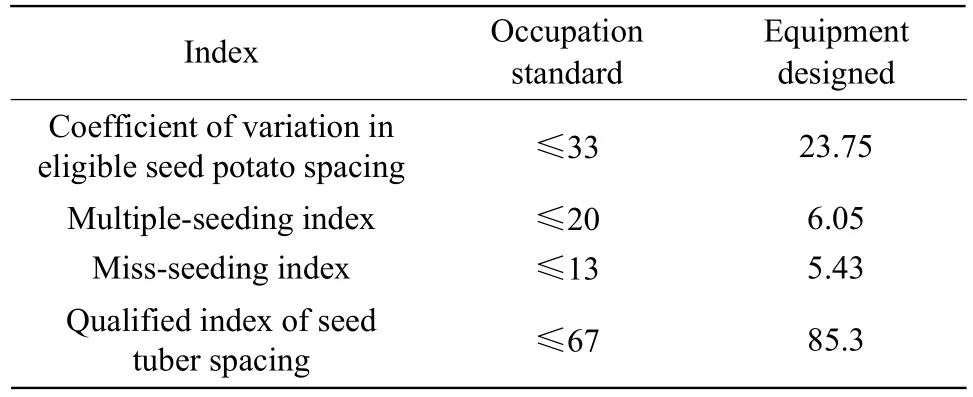
Table 2 Test results
Conclusions
(1) The trailed potato fertilization seeder was compact and reasonable structural in design. Furrowing, sowing,fertilization, covering and ridging could be completed in one operation, which was stable and efficient.(2) The mode of double cup staggered picking seed with the technology of vibration had been adopted in this seed-metering device, which was beneficial to improve seeding precision and quality. Changed the speed of the conveyor to adjust sowing spacing to increase the adaptability of the equipment. (3) The field experiments showed that coefficient of variation in eligible seed potato spacing, multiple-seeding index,miss-seeding index and qualified index of seed tuber spacing met the operational requirements of potato planting, and the operation performance was better.
In order to solve the problems of high multipleseeding and miss-seeding index of existing potato planter, the trailed potato fertilization seeder had been designed, the coefficient of variation in eligible seed potato spacing, multiple-seeding index and missseeding index had been reduced and the qualified index of seed tuber had been increased. It provided a reference for the development of potato planter.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Mapping and Candidate Gene Screening of Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus Resistant Gene ty-5
- Mowing Height and Mowing Frequency Interactions on Turf Performance of Kentucky Bluegrass
- Molecular Cloning and Expression Analysis of AcFT3 in Allium cepa
- Screening of Actinomycetes from Medicinal Plant Rhizosphere Soils for Industrial Enzymes and Antimicrobial Activity
- Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Glycine soja Roots Under Salinity and Alkalinity Stresses Using RNA-seq
- A Novel Bacillus thuringiensis Cry57 Protein Domain Swap In fluence on Insecticidal Activity
