青鱼Viperin是一种抗病毒蛋白质
2018-09-28周旻昱
田 彧,陈 慧,周旻昱,李 俊,肖 俊,冯 浩*
(1.湖南师范大学生命科学学院省部共建淡水鱼类发育生物学国家重点实验,中国湖南长沙410081;2.中南大学湘雅二医院,中国湖南长沙410011;3.湖南农业大学生物科学技术学院,中国湖南长沙410128)
Teleost fishes possess both innate and adaptive immune systems.Innate immunity is more important for protecting them against pathogen microbes,such as viruses[1~4].The interferon(IFN)system of vertebrate provides a powerful and universal intracellular defense mechanism against viruses in both innate and adaptive immunity[5~9].After viral infection,IFNs are rapidly induced and subsequently activate a broad spectrum of interferon-regulated genes(IRGs)or interferon-stimulated genes(ISGs)[8~10].Although some IFN-inducible proteins,such as protein kinase R(PKR),the GTPase myxovirus resistance 1(Mx1),ribonuclease L(RNaseL)and IFN-stimulated protein of 15 kD(ISG15),have been functionally well characterized as antiviral effectors,the functions of most IFN-inducible proteins remain unexplored[10~12].
Viperin(virus inhibitory protein,endoplasmic reticulum-associated,IFN-inducible),also known as radical S-adenosyl methionine domain-containing protein 2(RSAD2)and cytomegalovirus-induced gene 5 protein(CIG5),was first identified as a virusand IFN-induced molecule from human cytomegalovirus(HCMV)-infected primary human foreskin cells[13~15].It is one of the few ISGs shown to have direct antiviral activity and has received increasing attention due to its ability to limit a broad range of viruses and play an emerging role in modulating innate immune signaling[16~19].
Human viperin is composed of 361 amino acids with a relative molecular mass of approximately 42 kD[12].Like human viperin,mammalian vertebrate viperin homologues are highly conserved in the primary sequence and composed of three distinct domains,which include a relatively less conserved N-terminal amphipathic α-helix required for endoplasmic reticulum(ER)localization,a central radical S-adenosylmethionine(SAM)domain containing a CxxxCxxC motif important for the formation of a[4Fee4S]cluster,and a highly conserved C-terminal region known to be critical for antiviral activity against a number of viruses[12,13].
Fish viperin was first identified in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss[20].Like its mammalian homologues,rainbow trout viperin is directly induced by viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus(VHSV)without the requirement of ongoing protein synthesis and by a rainbow trout IFN-like factor,which indicates that there exist IFN-dependent and-independent pathways for teleost viperin induction.Teleost viperin has been identified in many other species[21~28],such as zebrafish Danio rerio,red drum Sciaenops ocellatus,rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus,Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi,crucian carp Carassius auratus,tilapia Oreochromis niloticus,Atlantic cod Gadus morhua,Atlantic salmon Salmo salar,etc.Viperin of some fish species has been verified to play important roles in host cells against viral infection[20,28].
Black carp(Mylopharyngodon piceus)is among the“four famous domestic fishes”in China and is the most expensive food fish among these four domestic cyprinid fishes.However,there are few studies about the immunity of this agricultural important species.In our previous study,a type I IFN of black carp(bcIFNa)was identified as a secreted antiviral cytokine against spring viremia of carp virus(SVCV)and grass carp reovirus(GCRV)[29].At the same time,mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein(MAVS)and inhibitor of NF-κB kinase ε (IKKε)of black carp were cloned and the reporter assay showed that both proteins activated the promoter activity of zebrafish IFN and fathead minnow IFN,whose count-parts in high er vertebrates are upstream regulators of IFNs[30,31].To elucidate the mechanism of MAVS/IKKε/IFN signaling in the innate immunity of black carp,viperin of black carp(bcViperin)has been cloned and characterized in this paper,and was supposed to be an effector of MAVS/IKKε/IFN pathway.All the data generated in this paper support the conclusion that bcViperin is an antiviral protein and plays an important role in the host antiviral innate immune response against GCRV and SVCV.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Cells and plasmids
HEK293T(293T),HeLa,Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney(CIK),Epithelioma papulosum cyprini(EPC)and Mylopharyngodon piceus fin(MPF)cells were kept in the lab[32].293T and HeLa cells were cultured at 37℃;EPC,CIK and MPF cells were cultured at 25℃.All the cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10%fetal bovine serum(FBS),2 mmol/L L-glutamine,100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin.Cell transfection was done as previously described[33],in which calcium phosphate was used for 293T transfection,Lipofectamine® 2000(Invitrogen,USA)and FuGENE® 6(Roche,Switzerland)were used for HeLa and EPC cells,respectively.
pcDNA5/FRT/TO(Invitrogen,USA)and pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA were kept in the lab[30].The recombinant expression vectors pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA-bcViperin and pcDNA5/FRT/TO-bcViperin-HA were constructed by cloning the open reading frame(ORF)of bcViperin fused with an HA tag at its N-terminus and C-terminus into pcDNA5/FRT/TO,respectively.
1.2 Virus produce and titration
SVCV and GCRV were kept in the lab and propagated in EPC and CIK cells,respectively,at 25℃in the presence of 2%FBS[32].Virus titers were determined by plaque assay on EPC cells separately as previously described[32].Briefly,the 10-fold serially diluted virus supernatants were added onto EPC cells and incubated for 2 h at 25℃.The supernatant was removed after incubation and DMEM containing 2%FBS and 0.75%methylcellulose(Sigma)was added.Plaques were counted at day 3 postinfection.
1.3 Semi-quantitative RT-PCR
Black carps of six months(weight 120 g)were injected intraperitoneally with GCRV(2.52×106pfu/fish),SVCV(2.43×106pfu/fish)or sterile PBS separately and cultured at 25℃.Three fishes were collect ed from each injected group(PBS,SVCV or GCRV)and were sacrificed 33 h post-injection.Total RNA was isolated from the tissues of heart,liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,muscle,skin and gills independently.The primers of bcViperin-SQ-F(45)and bc-Viperin-SQ-R(424)were used to detect bcViperin mRNA expression in the above tissues(Table 1).The semi-quantitative RT-PCR program was:94 ℃ for 5 min,then 25 cycles of 94℃/30 s,55℃/30 s and 72℃/30 s,finally extension at 72℃for 5 min.
1.4 Quantitative real-time PCR
MPF cells were seeded in 6-well plates(2×106cells/well)16 h before viral infection.After infection with SVCV or GCRV at a multiplicity of infection(MOI)of 0.01,0.1 or 1 independently,the MPF cells were harvested at different time points(0 h,2 h,8 h,24 h,48 h and 72 h),and used for RNA isolation.The relative bcViperin mRNA level in the MPF cells was examined by quantitative real-time PCR(q-PCR),in which β-actin was used as an internal reference.The primers used for q-PCR were listed in Table 1.The q-PCR program was:1 cycle of 50 ℃/2 min,1 cycle of 95℃/10 min,40 cycles of 95℃/15 s,60℃/1 min,followed by dissociation curve analysis(60~95 ℃)to verify the amplification of a single product.The threshold cycle(Ct)value was determined by using the manual setting on the 7500 Real-Time PCR System and exported into a Microsoft Excel Sheet for subsequent data analyses where the relative expression ratios of target gene in treated group versus those in control group were calculated by the 2-△△Ctmethod.
1.5 Immunoblotting
293T cells were transfected with pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA-bcViperin,pcDNA5/FRT/TO-bcViperin-HA or empty vector separately.Transfected cells were harvested 48 h post-transfection and lysed for immunoblot(IB)assay as previously described[30].Briefly,the whole cell lysates of the transfected cells or the control cells were isolated by 10%SDS-PAGE and the transferred membrane was probed with mouse monoclonal anti-HA antibody(1∶3 000;Sigma).Target proteins were visualized with BCIP/NBT Alkaline Phosphatase Color Development Kit(Sigma,USA).

Table 1 Primers used in the study
1.6 Immunofluorescence microscopy
HeLa or EPC cells were transfected with pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA-bcViperin or pcDNA5/FRT/TO-bcViperin-HA separately,and the transfected cells were fixed with 4%(V/V)paraformaldehyde 36 h posttransfection.The fixed cells were permeabilized with Triton X-100 (0.2%in PBS)and used for immunefluorescence staining as previously described[30].M-ouse monoclonal anti-HA antibody(Sigma)was pro-bed at the ratio of 1∶300 and Alexa 488-conju gated secondary antibody (Invitrogen)was probed at the ratio of 1∶1 000.Hoechst 33342(Sigma)was used to stain the nucleus.
2 Results
2.1 Molecular cloning of the cDNA of bcViperin
To study the role of viperin in the innate immunity of black carp,the cDNA of bcViperin was cloned from the spleen of this cyprinid fish.The full-length transcript of bcViperin gene consists of 1 828 nucleotides including 5′-untranslated region(UTR),co-ding sequence,3′-UTR and poly(A)tail(NCBI accession number:KX246952).The ORF of bcViperin starts at nucleotide 22 and terminates at nucleotide 1 101(Fig.1).Initial cDNA sequence ana-ly sis of bcViperin(online tools of ExPASy)predicted that bcViperin should contain 360 amino acid residues,which is composed of a relatively less conserved N-terminal amphipathic α-helix,a central radical SAM and a highly conserved C-terminal region(Fig.1 and Fig.2A).The deduced bcViperin pro-tein has a calculated relative molecular mass of 42 kD and an isoelectric point of 8.23.

Fig.1 The full-length cDNA of bcViperin
2.2 Comparison of bcViperin and other vertebrate viperins
In order to gain insight into viperin evolution,protein sequence of bcViperin was subjected to multiple alignments with viperin proteins of different species.The comparison among viperin proteins from human,mouse,chicken and black carp demonstrated that viperin is evolutionarily highly conserved(Fig.2A).Phylogenetic analysis of bcViperin and viperins of the selected species demonstrated that these homologue proteins could be divided into three groups,including mammalian,bird and fish branches(Fig.2B).bcViperin shared the highest protein se quence similarity(99%)with viperin of common carp and was clustered tightly with common carp viperin,which correlates with the closest genetic relation-ship of these two cyprinid fishes(Fig.2B).
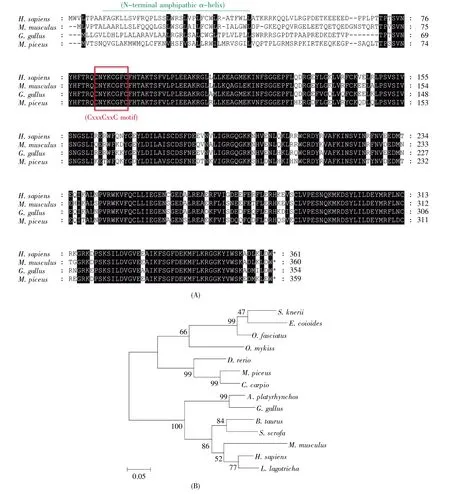
Fig.2 Comparison of vertebrate viperins
2.3 bcViperin mRNA expression in vivo
To investigate the transcription of bcViperin in the host,total RNA was extracted from the heart,liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,muscle,skin and gills of the black carp injected with GCRV,SVCV or sterile PBS(as control)separately.bcViperin transcription in these tissues was examined by semi-quanti-tative RT-PCR,in which the RT-PCR of β-actin was recruited as the endogenous control.A specific band of 453 bp was detected in all the selected tissues from the black carp injected with PBS,which demonstrated that bcViperin gene was constitutively transcribed in the heart,liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,muscle,skin and gills of this teleost(Fig.3,upper panel).The bcViperin mRNA level was increased in all the selected tissues 33 h after SVCV injection,especially in the heart,spleen,skin and gills(Fig.3,middle panel).For the GCRV group,the bcViperin mRNA level was also increased in all the selected tissues 33 h after virus injection,especially in the heart,liver,skin and gills(Fig.3,lower panel).The phenotype that bcViperin mRNA level in different tissues of black carp increased immediately after virus infection suggested that bcViperin was involved in host innate immune response initiated by pathogen invasion such as GCRV and SVCV.

Fig.3 Tissue-specific mRNA expression of bcViperin
2.4 bcViperin mRNA expression ex vivo
To further characterize elaborated bcViperin mRNA expression profile during host innate immune response,MPF cells were infected with SVCV or GCRV at different MOIs and harvested for q-PCR at different time points post-infection.In general,bcViperin mRNA level in MPF cells increased after SVCV infection at all MOIs(Fig.4).The highest relative bcViperin mRNA expression level in MPF cells after infection was up to 673 times(MOI=0.1,72 h)as much as that before viral infection(Fig.4A).The bcViperin mRNA level in MPF cells increased obviously from 2 h post-infection at 0.1 MOI;however,the mRNA level was enhanced enormously from 48 h post-infection at 0.01 MOI or 1 MOI(Fig.4B).In the groups of GCRV infection,the mRNA level of bcViperin in MPF cells increased after virus infection at all MOIs(Fig.5).The highest relative bc-Viperin mRNA expression level in host cells after GCRV infection was up to 232 times(MOI=1,48 h)as much as that before viral infection(Fig.5A).In 0.01 MOI group,bcViperin mRNA level increased slowly until 72 h after viral infection,however,the mRNA level increased sharply from 24 h post-infection in 0.1 MOI group and increased fiercely from 8 h in 1 MOI group(Fig.5B).The q-PCR data suggested that the bcViperin mRNA level elevation in MPF cells after GCRV infection was correlated with the viral input—the higher the MOI,the earlier the bcViperin mRNA level would be elevated.
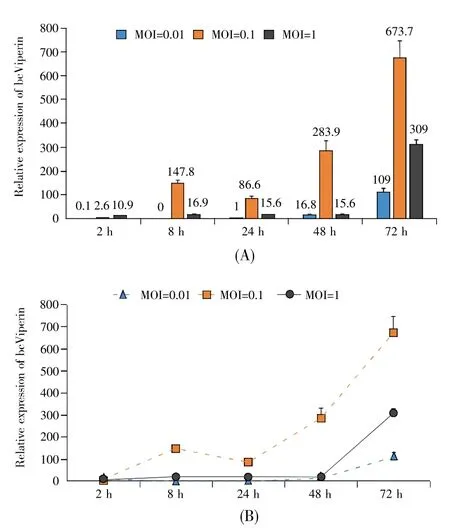
Fig.4 SVCV activated bcViperin mRNA transcription in MPF cells

Fig.5 GCRV activated bcViperin mRNA transcription in MPF cells
2.5 Protein expression of bcViperin
293T cells were transfected with pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA-bcViperin or pcDNA5/FRT/TO-bcViperin-HA separately to investigate the protein expression of bcViperin.A major band of around 42 kD,which was not found in the whole cell lysate of the empty vector-transfected 293T cells through immunoblot(IB)assay,was detected in those of viperin plasmidtransfected cells(Fig.6).The IB analysis,in which mouse anti-HA antibody was used to detect the exogenous bcViperin,showed clearly that the protein expression level of bcViperin-HA in 293T cells was obviously higher than that of HA-bcViperin(Fig.6).There were 2~3 weaker bands(heavier than the major band)were detected in the sample of HA-bcViperin and similar bands were found in the sample of bc-Viperin-HA,which suggested this teleost protein was modified post-translation.The smear smaller than the major band was found in the sample of bcViperin-HA,and it might be the degraded exogenous bc-Viperin-HA in 293T cells(Fig.6).
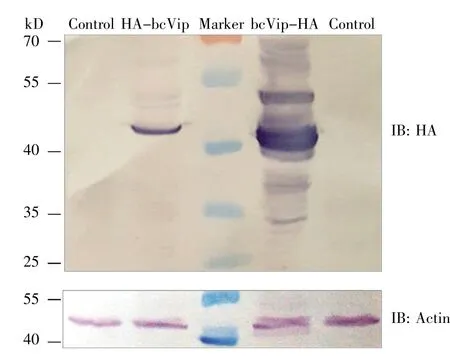
Fig.6 Protein expression of bcViperin
2.6 Intracellular location of bcViperin
Viperin is majorly a cytosolic protein and localizes on the endoplasmic reticulum(ER)and Golgi apparatus in most conditions[12].It is transported to lipid-enriched compartments called lipid droplets and harbors an amphipathic α-helix domain at its N-terminus and functions by anchoring on a lipid layer via this domain[13].In this study,both EPC and HeLa cells were transfected with pcDNA5/FRT/TOHA-bcViperin or pcDNA5/FRT/TO-bcViperin-HA separately and used for immunofluorescence staining to investigate the intracellular location of this protein.The IF data of both EPC and HeLa cells showed clearly that bcViperin expression region(green)tightly surrounded the nucleus(blue),which verified that bcViperin was a cytosolic protein(Fig.7 and Fig.8).Viperin proteins of rodents(mouse and rat)accumulated in distinct dots,which were in close proximity to promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies(PML-NBs)[15].The protein of bcViperin was presented as obvious dots in human cells,and this was similar to rodent viperin proteins(Fig.8).However,this phenotype was not seen in bcViperin-transfected EPC cells(Fig.7),which implied that fish should possess different mechanism to“arrange”this mammalian viperin homologue.
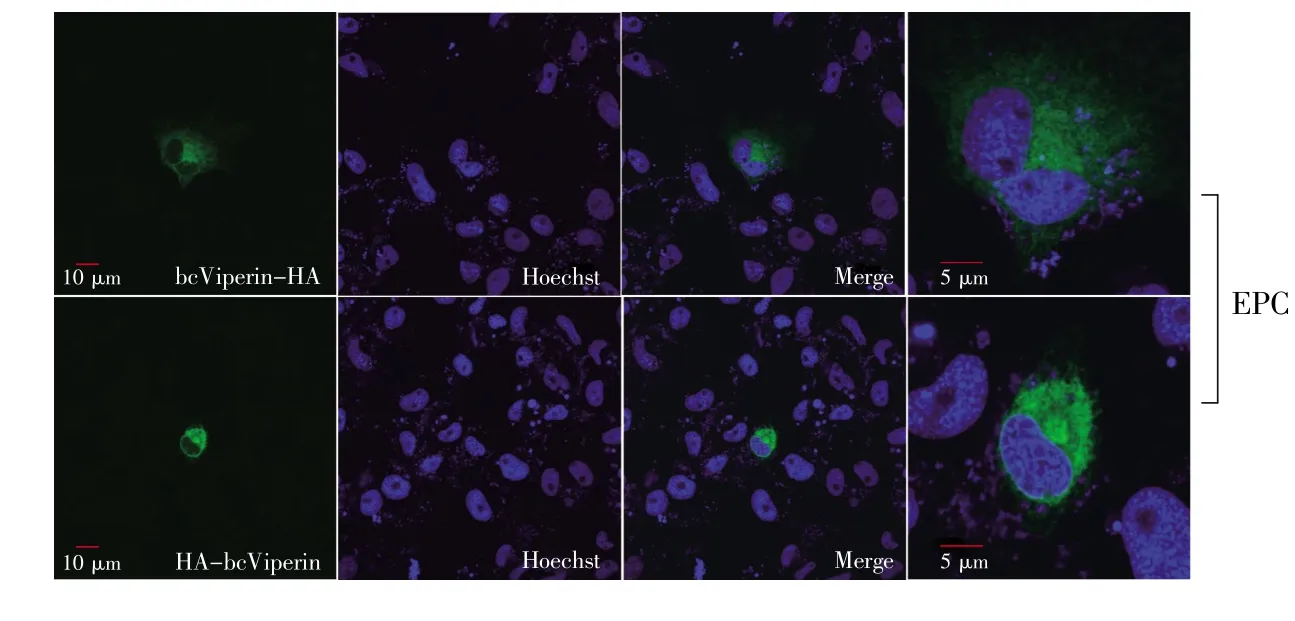
Fig.7 Intracellular localization of bcViperin in EPC cells
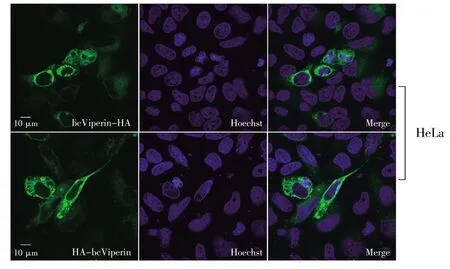
Fig.8 Intracellular localization of bcViperin in HeLa cells
2.7 bcViperin is an antiviral protein
Viperin has been shown to be active against a wide range of DNA and RNA viruses in fish and higher vertebrates[34].To investigate the role of bcViperin in the host innate immunity,EPC cells were transfected with pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA-bcViperin or the empty vector separately 24 h before virus infection.For SVCV infection at all MOIs(0.1,0.01 and 0.001),viral titers in the supernatant media of the EPC cells over-expressing bcViperin were obviously lower than those in the empty vector-transfected EPC cells,which demonstrated that exogenous bcViperin inhibited SVCV replication in EPC cells effectively(Fig.9A).The plaque assay data of GCRV group were similar to those of SVCV group,demonstrating that bcViperin also suppressed GCRV replication in EPC cells effectively(Fig.9B).The plaque assay data demonstrated that bcViperin is an antiviral protein against both SVCV and GCRV.
3 Discussion
Viperin genes exist in the genomes of most vertebrates,such as fish,mouse and human.Viperin proteins are a key component of the antiviral state in a variety of cell types induced by different stimulators,which include IFNs,DNA and RNA viruses,viral mimic polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid(polyI:C)and polysaccharides[13,35].Black carp is one of the most important cultured species in China.Its viperin(bcViperin)has been cloned and characterized in this paper.The full-length cDNA of bcViperin consists of 1 828 nucleotides and the predicted protein contains 360 amino acid residues(Fig.1).The amino acid number of bcViperin is similar to those of chicken,mouse and human,and the amino acid sequences of viperin proteins from all these species are highly conserved(Fig.2),which implies that the antiviral function of viperin is conserved in these vertebrates.

Fig.9 EPC cells over-expressing bcViperin showed enhanced antiviral ability against SVCV and GCRV
Human viperin has been reported to inhibit a broad spectrum of DNA and RNA viruses,which include HCMV,HCV,WNV,dengue virus,Sindbisvi-rus,influenza A virus,Sendai virus,VSV and HIV-1[12,36].Although there exist clear evidences that viperin has antiviral activity against a diverse group of pathogens,it is emerging that this protein may also contribute to host immune signaling.For instance,human viperin can modulate TLR7 and TLR9 recognition of viral nucleic acids in pDCs to promote type I IFN production[34].It has been reported that HCMV“hijacks”viperin as a proviral host factor to increase viral entry[13].As to fish viperin,rainbow trout viperin has been showed to function against VHSV,the mRNA level of red drum Sciaenops ocellatus viperin increases in response to the invasion of different bacterial pathogens,and rock bream O-plegnathus fasciatus viperin is induced by megalocytivirus infection[20].Our study demonstrated that bcViperine increased in host after SVCV and GCRV infections(Figs.3~5),and the plaque assay data demonstrated that bcViperin functioned in the fish cell line as an antiviral protein against both SVCV and GCRV(Fig.9).
The deduced bcViperin protein has a calculated relative molecular mass of 42 kD,which correlates with the relative molecular mass of the major band in the IB analysis(Fig.6).However,there were 2~3 weaker bands(heavier than the major band)that were detected in the sample of bcViperin,which suggested this teleost protein was modified post-translation(Fig.6).The asparagine residues 119(NFS)and 155(NGS)of bcViperin are located in the conserved N-linked glycosylation motif(N-X-S/T),which suggests that this fish viperin homologue is a glycoprotein[29].There are few reports about the glycosylation of viperin proteins,so the glycosidase digestion assay will be recruited next step in this lab to determine whether bcViperin is attached with glycan chains or not.
Viperin proteins are ISGs-encoding proteins that exist in most eukaryotic cells,however,their functions were not identified overall and the antiviral test of viperin proteins demonstrated variable results among species[20].Therefore,assessment of the antiviral activity of putative viperin from each species is of interest.In this paper,EPC cells over-expressing bcViperin showed impaired cytopathogenic effect(CPE)triggered by either SVCV or GCRV infection and viral titers in the supernatant media of these EPC cells were obviously lower than those of the controls,which demonstrated that bcViperin is an antiviral protein against both SVCV and GCRV(Fig.9).Whole cell lysates of 293T cells transfected with pcDNA5/FRT/TO-HA-bcViperin,pcDNA5/FRT/TO-bcViperin-HA and the empty vector were made separately 48 h post-transfection and were pre-cultured with virus before viral infection according to other study,which aimed to test the antiviral ability of bcViperin.However,the virus pretreated with bcViperin-containing whole cell lysate showed the similar replication ability in EPC cells to that pretreated with the whole cell lysate control(data not shown),which might result from the interferences of numerous factors in the whole cell lysate,such as human cytokines.We are still working on the induced expression and purification of bcViperin protein in prokaryotic cells so as to elucidate its antiviral mechanism against GCRV and SVCV.
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(81471963),Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate(CX2017B185).
