基于降维算法的结构混合可靠性分析方法
2018-09-07孟广伟冯昕宇周立明李锋
孟广伟,冯昕宇,周立明,李锋
基于降维算法的结构混合可靠性分析方法
孟广伟,冯昕宇,周立明,李锋
(吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,吉林 长春,130025)
针对工程实际中同时带有模糊变量与随机变量的结构混合不确定性问题,提出1种基于降维算法的混合不确定性变量的可靠性分析模型。首先,利用模糊数学中的−截集概念,将模糊变量转变为水平截集下相应的区间变量,再借助于降维算法,将含有个随机变量的结构功能函数展开为个一维随机变量函数;将所得到的降维表达式进行泰勒展开,得到结构功能函数的上、下界表达式;运用变量转换方法将其中的随机变量转换为均值为0,方差为0.5的正态分布变量,并结合二项式展开定理、Gauss−Hermite积分方法与变量转换方法计算出结构功能函数上下界的统计矩;将所得的矩信息应用到Edgeworth级数展开式中,计算得到对应于−截集的失效概率区间,从而获得失效概率的隶属度函数。研究结果表明:本文提出的方法不仅计算精度高,而且计算量小。
结构可靠性分析;混合可靠性;降维算法;模糊变量;Edgeworth级数
结构可靠度分析是工程实践中的重点研究内容之一[1−6]。带有随机变量的失效概率计算问题是概率可靠性设计中的重点研究内容之一,带有模糊变量的失效概率计算问题同样也是模糊可靠性设计中的重点问题。然而在工程实践中,往往仅带有单一类型变量的结构比较少,混合类型变量共同存在的情况较多。目前,已有很多方法用于求解带有随机变量和模糊变量的结构失效概率f,例如,CHAKRABORTY等[7−8]基于信息熵方法,将模糊隶属函数转换为等效概率密度函数进行可靠性分析;SMITH等[9]基于尺度变换方法,将传统概率可靠性分析理论应用于混合可靠性分析;ADDURI等[10−12]基于概率理论利用一次二阶矩法和一次二阶矩法的改进方法求解混合失效概率等。在利用上述方法计算时,信息熵法在理论上与模糊可靠度的结果存在一定偏差,且丧失了模糊性。另外,尺度变换法对模糊数类型的要求较为严格;一次二阶矩法在非线性情况下,存在迭代收敛慢甚至不收敛的情况。因此,本文作者结合降维算法和Edgeworth级数展开法[13],针对同时含有随机变量和模糊变量的混合结构,提出1种简便的计算失效概率方法:通过−截集概念将模糊变量转化为水平截集下相应的区间变量;利用降维算法,将功能函数分解为个一维随机变量函数叠加的形式;借助于泰勒展开,得到功能函数的上、下界;再结合变量转换法、Gauss-Hermite数值积分计算获得功能函数上、下界的矩信息,并将其应用到Edgeworth级数展开式中,最终计算得到结构功能函数的失效概率隶属度。
1 模糊变量λ−截集
对于同时带有随机变量和模糊变量且两者相互独立的结构,其结构功能函数可表示为
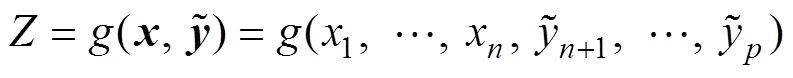
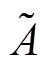


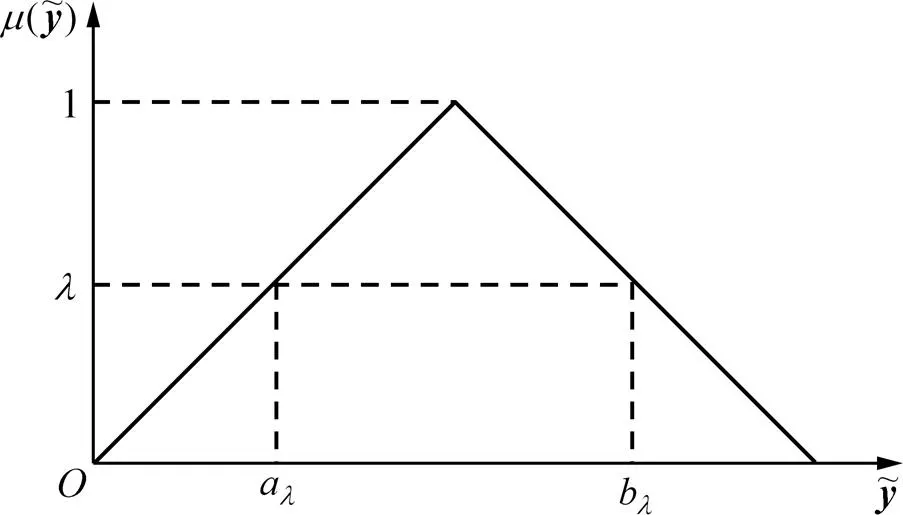
图1 模糊变量与λ−截集关系
2 降维算法
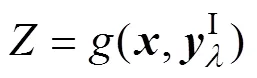
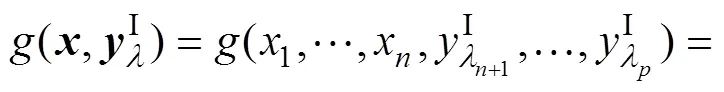
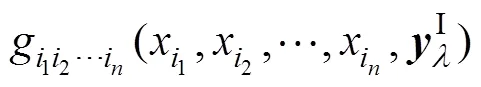
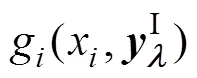

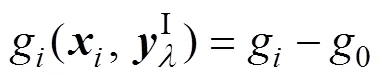
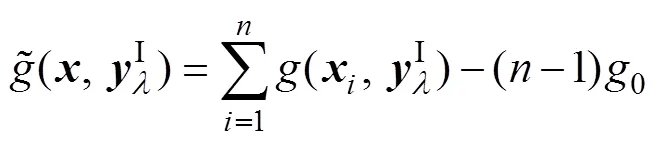

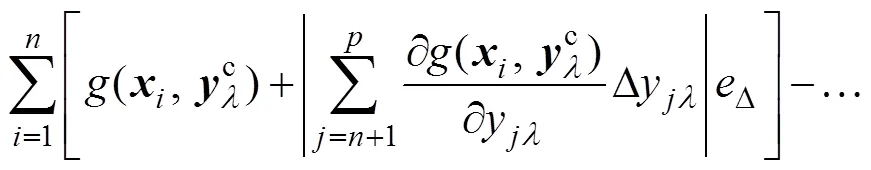

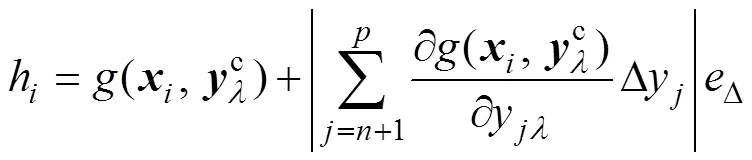
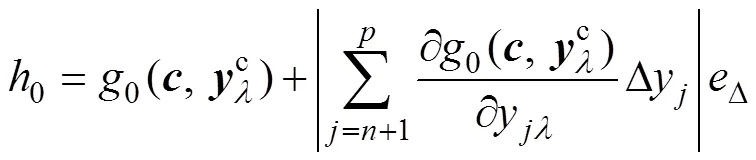
h与0的上、下界分别为
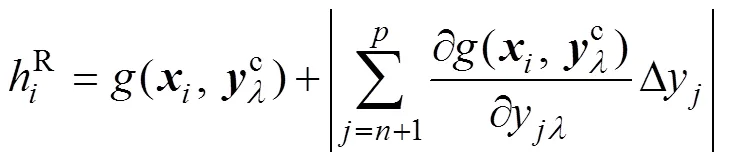

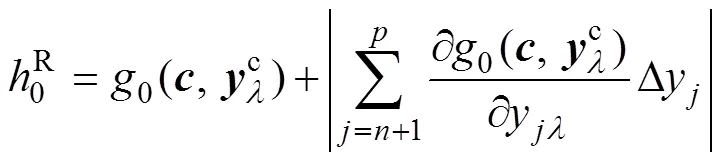


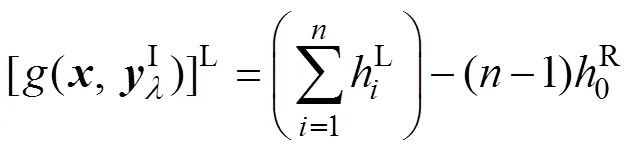
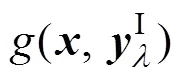
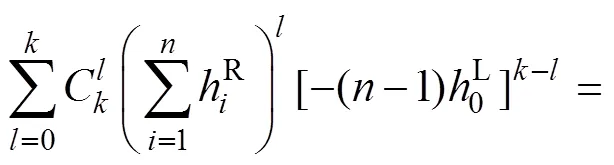
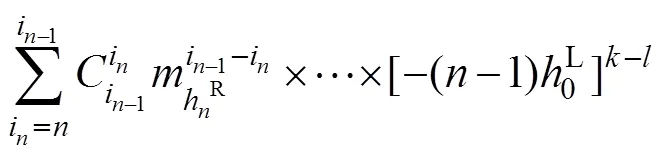
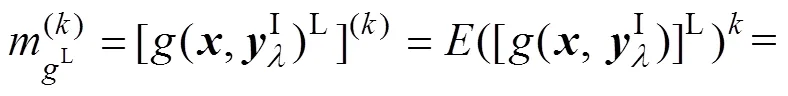
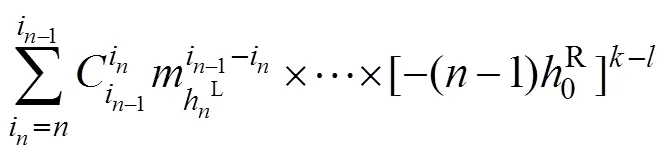

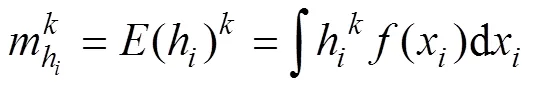
式中:(x)为随机变量x的概率密度函数。
3 变量转换
针对式(19),可运用传统的数值积分公式进行计算。计算积分的方法有很多种,其中值得提出的有快速傅里叶变换法和蒙特卡罗方法(MCS)。前者的前提条件较为严格,要求存在解析解且要求功能函数相互独立;后者是较为普遍的方法,虽然简单易行但计算量相当大,耗时较长,其工程应用范围受到了一定限制。因此,本文作者引入变量转换的方法,将相互独立的各随机变量均转换为正态分布变量(即均值为0,方差为0.5的正态分布变量)。为确保准确性,假设Z(=1,2,…,)是相互独立的,则变量转换的表达式可写为
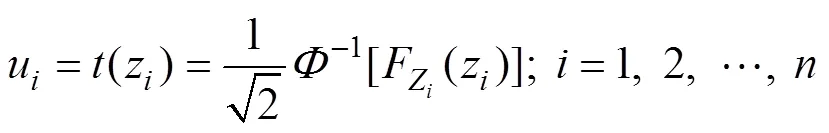
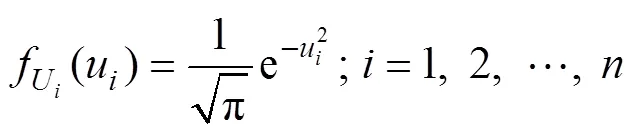
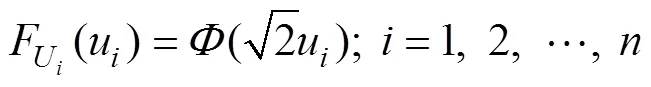
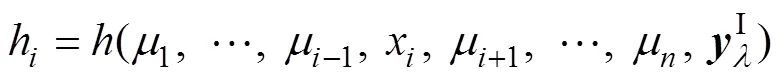
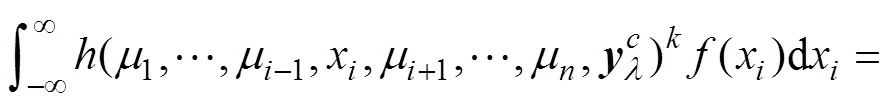
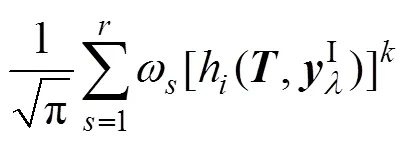
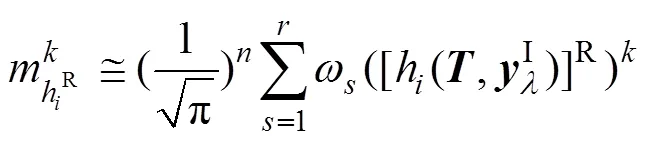
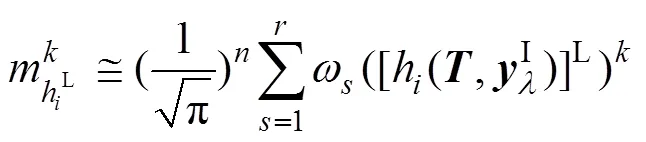
4 Edgeworth级数
计算结构失效概率的前提是具备功能函数的概率密度函数或者其联合概率密度函数表达式,但是在工程实践中,很难通过大量的数据得出精确的概率密度函数表达式。因而,可选用拟合功能函数的概率密度函数或累积分布函数的方式近似求解复杂结构的失效概率。本文选用Edgeworth级数方法进行拟合,将式(17)与式(18)计算得到的功能函数原点矩信息代入式(28)与式(29),最终将所得中心矩信息作为Edgeworth级数展开式系数,拟合结构功能函数相应的累积分布函数表达式。

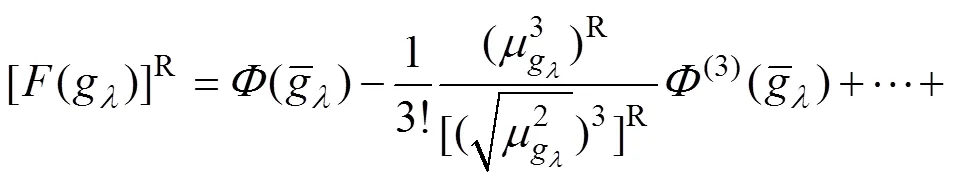

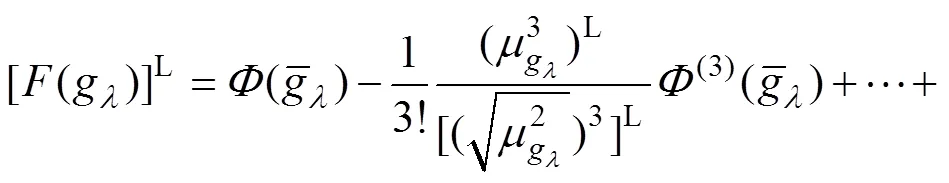
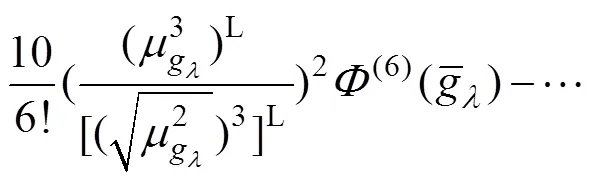

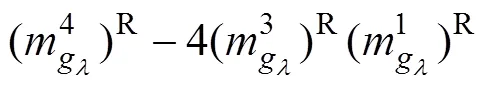
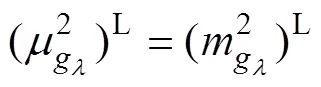
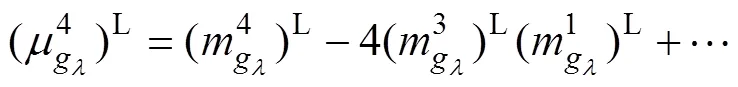
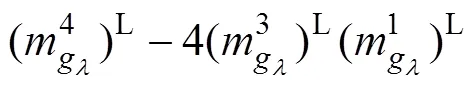
5 数值算例
十杆桁架结构如图2所示。杆件长为=3.6 m;于节点2与节点4处施加竖直向下载荷(为外载荷,其服从均值为710 kN,变异系数为0.03的正态分布);水平方向的杆①~④面积为1m2,竖直方向的杆⑤~杆⑥面积为2m2,斜向的杆⑦~杆⑩面积为3m2(1,2,3和均为模糊变量);为材料的弹性模量,其服从均值为2.1×1011Pa,变异系数为0.01的正态分布。当在节点2处的垂直位移max不大于允许位移allow(allow=0.004 2 m)时,结构功能函数可表示为:
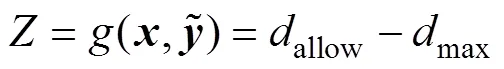
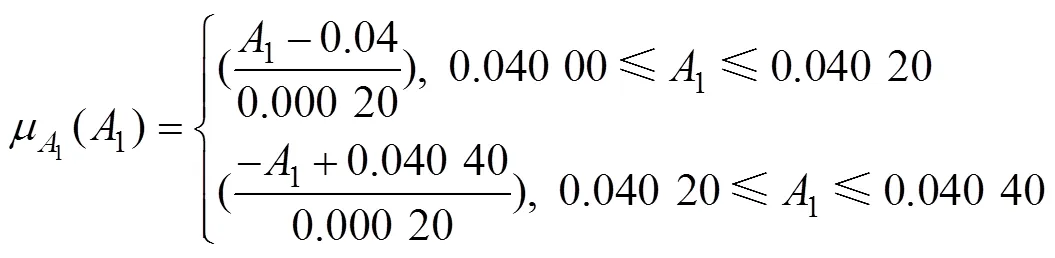
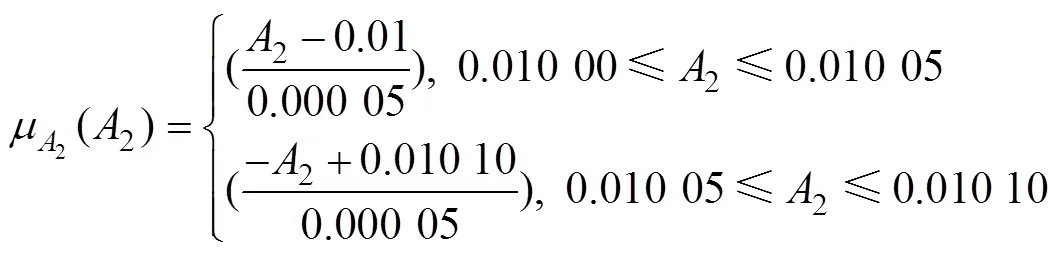
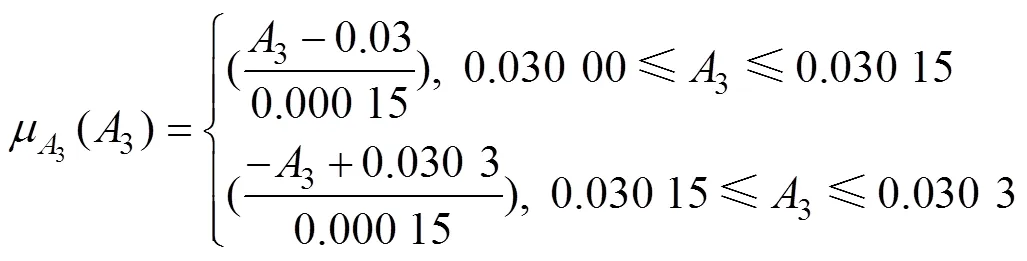
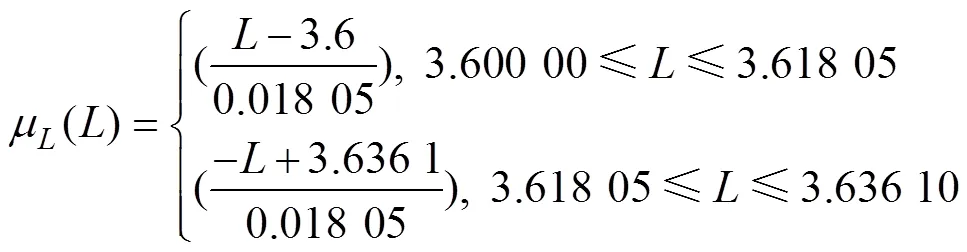
MCS方法在工程实践中被广泛认可为精确解。表1所示为本文方法与MCS方法的十杆桁架失效概率对比。图3所示为本文方法与MCS方法的失效概率−隶属度的关系。由表1和图3可知:本文方法与MCS方法计算结果非常接近。但在每个−截集处,本文方法的样本点数仅为6个,远低于MCS方法的106个,体现了本文方法的简单性和有效性。
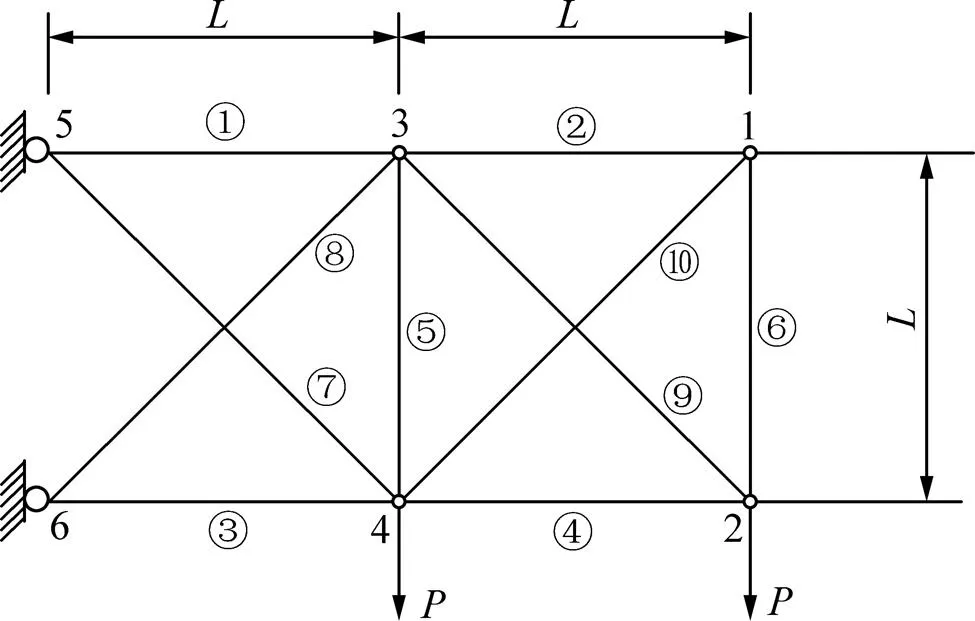
图2 平面十杆桁架结构
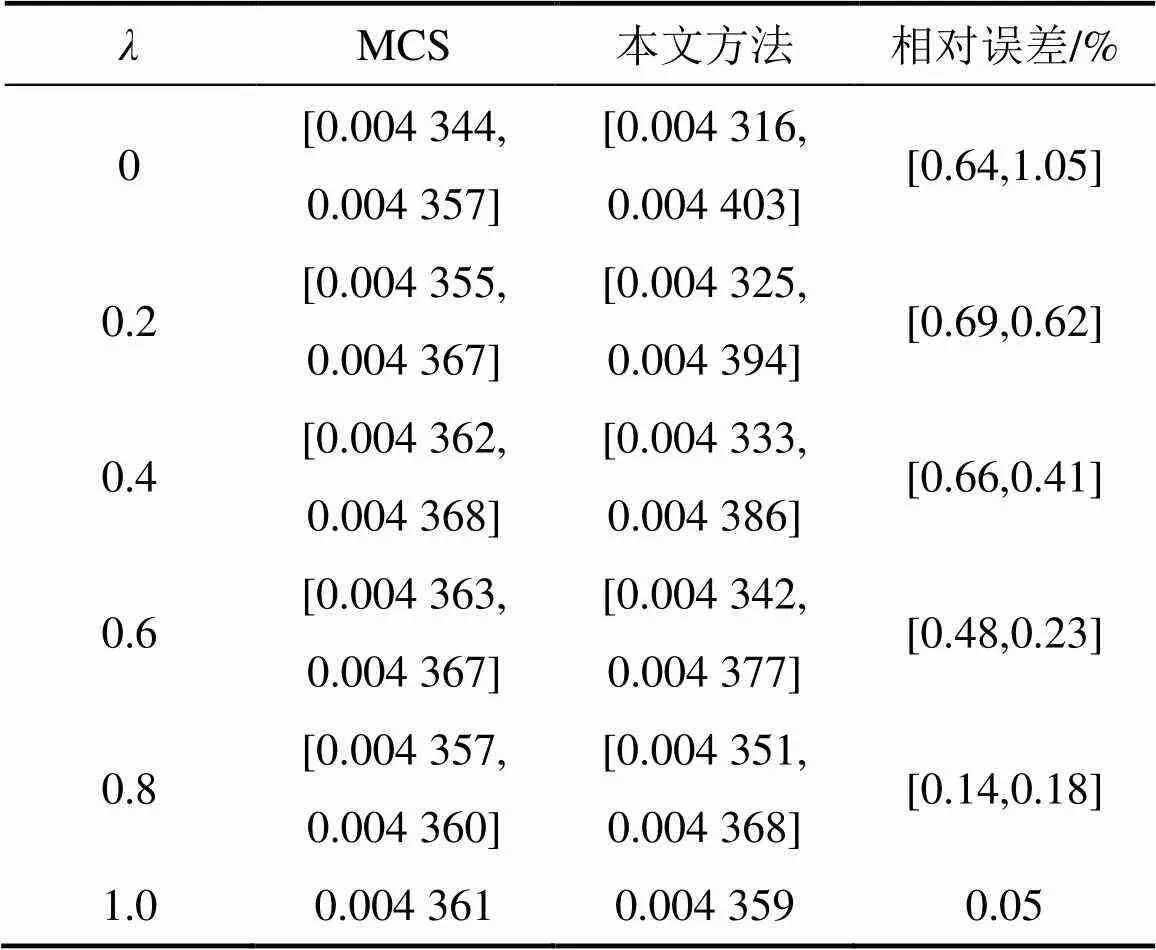
表1 2种方法十杆桁架失效概率对比
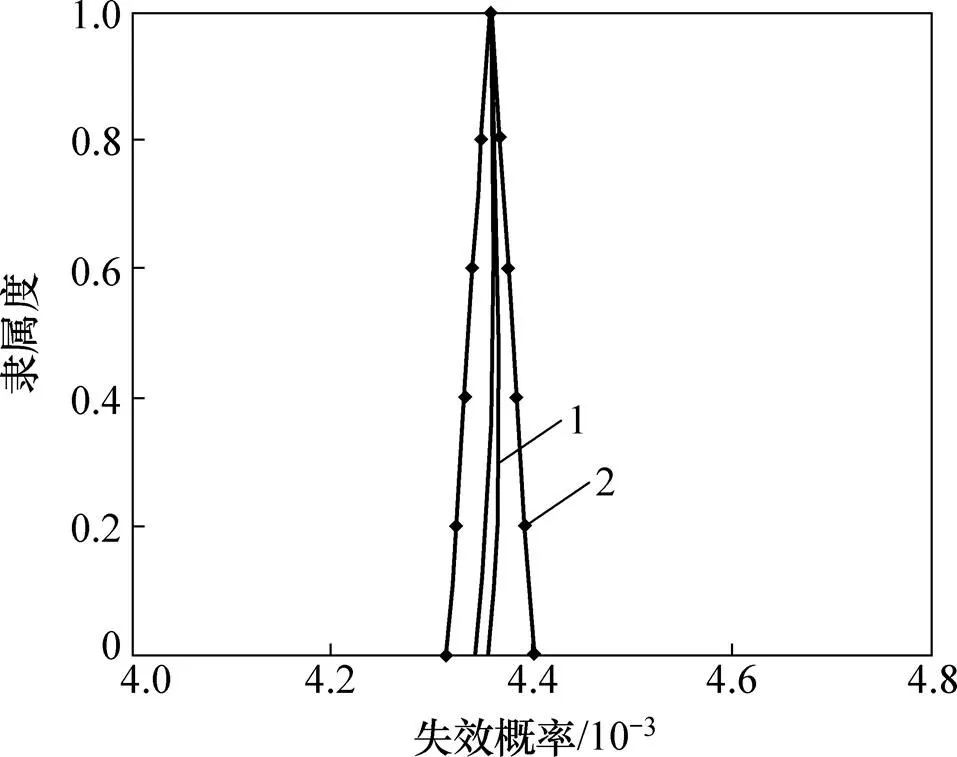
1—MCS;2—本文方法(即Edgeworth)。
6 结论
1) 提出1种针对同时带有模糊变量和随机变量不确定性问题的结构失效概率计算方法。
2) 借助于−截集概念,将模糊变量转变为水平截集下相应的区间变量,将随机模糊问题有效地转变为随机区间问题。
3) 利用降维算法建立结构功能函数的一维随机变量降维表达式,无需借助于多重积分求解结构功能函数的统计矩,无需求解结构功能函数矩阵的逆。
4) 高效且稳定地降低计算成本,有效避免了由于迭代而存在的收敛慢甚至不收敛情况的问题。
[1] 柳诗雨, 吕震宙, 员婉莹, 等. 小失效概率情况下的全局可靠性灵敏度分析的高效方法[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(9): 2766−2774. LIU Shiyu, LÜ Zhenzhou, YUAN Wanying, et al. Efficient method for global reliability sensitivity analysis with small failure probability[J]. Acta Aeronautica Et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(9): 2766−2774.
[2] 孙文彩, 杨自春, 李军. 含随机-区间耦合变量的结构可靠性分析方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(4): 44−48. SUN Wencai, YANG Zichun, LI Jun. Reliability analysis for structures with random-interval coupling variables[J]. Huazhong University of Science & Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(4): 44−48.
[3] 郑灿赫, 孟广伟, 李锋, 等. 一种基于 SAPSO-DE 混合算法的结构非概率可靠性优化设计[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(5): 1628−1634. JONG Chanhyok, MENG Guangwei, LI Feng, et al. Structural non-probabilistic reliability optimization design based on a SAPSO-DE hybrid algorithm[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2015, 46(5): 1628−1634.
[4] MOJSILOVIĆ N, STEWART M G. Probability and structural reliability assessment of mortar joint thickness in load-bearing masonry walls[J]. Structural Safety, 2015, 52: 209−218.
[5] 韩志杰, 王璋奇. 基于区间有限元的吊梁非概率可靠性研究及敏感性分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(5): 1746−1742. HAN Zhijie, WANG Zhangqi. Non-probabilistic reliability research and sensitivity analysis of hanging beam based on interval finite element method[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(5): 1746−1742.
[6] 李少宏, 陈建军. 一种新的改进响应面法的结构可靠性计算方法[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(5): 1837−1841. LI Shaohong, CHEN Jianjun. A new improved response surface method for structural reliability computing[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(5): 1837−1841.
[7] CHAKRABORTY S, SAM P C. Probabilistic safety analysis of structures under hybrid uncertainty[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 70(4): 405−422.
[8] 谭巍, 李冬, 樊照远, 等. 基于模糊信息熵的航空发动机性能评估和可靠性分析[J]. 航空发动机, 2011, 37(5): 45−48. TAN Wei, LI Dong, FAN Zhaoyuan, et al. Aeroengine performance synthetic estimation and reliability analysis based on fuzzy information entropy[J]. Aeroengine, 2011, 37(5): 45−48.
[9] SMITH S A, KRISHNAMURTHY T, MASON B H. Optimized vertex method and hybrid reliability[C]//Americal Institute of Aerospace and Astronautics: AIAA-2002-1645. 43rd AIAA/ ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures: Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Denver, Colorado, USA: American Institute of Aerospace and Astronautics Inc, 2002: 22−25.
[10] ADDURI P, PENMETSA R, GRANDHI R. Membership function development for reliability analysis with mixed uncertain variables[C]//American Institute of Aerospace and Astronautics: AIAA-2005-2072. 46th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/ AHS/ASC Structures: Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference: Texas, USA: American Institute of Aerospace and Astronautics Inc, 2005: 18−21.
[11] ZHAO Yangang G, ONO T. Moment methods for structural reliability[J]. Structural Safety, 2001, 23(1): 47−75.
[12] 董玉革, 赵征权. 模糊可靠性分析的一次二阶矩法[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 28(9): 980−984. DONG Yuge, ZHAO Zhengquan. Fuzzy reliability analysis based on the FOSM method[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2005, 28(9): 980−984.
[13] KONG Chunyang, SUN Zhigang, NIU Xuming, et al. Moment methods for C/SiC woven composite components reliability and sensitivity analysis[J]. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2014, 21(1): 121−128.
[14] LI Guijie, LU Zhenzhou, XU Jia. A fuzzy reliability approach for structures based on the probability perspective[J]. Structural Safety, 2015, 54: 10−18.
[15] DAI Hongzhe, ZHANG Hao, WANG Wei. A Multiwavelet neural network-based response surface method for structural reliability analysis[J]. Computer-aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2015, 30(2): 151−162.
[16] CHATTERJEE S, SINGH J B, ROY A. A structure-based software reliability allocation using fuzzy analytic hierarchy process[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2015, 46(3): 513−525.
[17] PERIÇARO G A, SANTOS S R, RIBEIRO A A, et al. HLRF-BFGS optimization algorithm for structural reliability[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(7): 2025−2035.
[18] RAHMAN S, XU Heqin. A univariate dimension-reduction method for multi-dimensional integration in stochastic mechanics[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 19(4): 393−408.
[19] YOUN B D, XI Zhimin, WANG Pingfeng. Eigenvector dimension reduction (EDR) method for sensitivity-free probability analysis[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2008, 37(1): 13−28.
[20] LI Gang, ZHANG Kai. A combined reliability analysis approach with dimension reduction method and maximum entropy method[J] Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2011, 43(1): 121−143.
[21] ZHANG Xufang, PANDEY M D, ZHANG Yimin. A numerical method for structural uncertainty response computation[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2011, 54(12): 3347−3357.
(编辑 伍锦花)
Hybrid structural reliability analysis method based on dimension reduction algorithm
MENG Guangwei, FENG Xinyu, ZHOU Liming, LI Feng
(School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130025, China)
A new hybrid reliability analysis method based on dimension reduction algorithm was proposed, aiming at solving the hybrid uncertain problems of structures with both fuzzy variables and random variables in engineering practice. Firstly, fuzzy variables were transformed into corresponding interval variables within the level set using the concept of−cut set in fuzzy mathematics. Taking advantage of dimension reduction method, structural performance functionwithrandom variables was expanded tofunctions, each with one random variable. This dimension reduction formula is then expanded by Taylor method to get the expression of the upper and lower limits of the performance function. By using the variable transformation method, the random variables could be changed to mutual independent normal variables, with mean value zero and the variance 0.5. Combining the binomial theorem, Gauss-Hermite integration method and variable transformation method, the statistical moments of the upper and lower limits of the structural performance function were computed. After substituting the moment information into the Edgeworth series expansion formula, the intervals of structural failure probability corresponding to the λ−cut set were obtained. Therefore, the membership function of the failure probability was calculated. The results show that the proposed method has high precision with low computational cost.
structural reliability; hybrid reliability; dimension reduction method; fuzzy variable; Edgeworth series
TB114.3
A
1672−7207(2018)08−1944−06
10.11817/j.issn.1672−7207.2018.08.015
2017−08−26;
2017−10−26
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51305157);吉林省科技厅基金资助项目(20160520064JH)(Project(51305157) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(20160520064JH) supported by the Science and Technology Department Fund of Jilin Province)
李锋,博士,副教授,从事结构可靠性研究:E-mail:fengli@jlu.edu.cn
