超级方体—深圳湾超级城市设计国际竞赛方案
2018-07-13朱文一
朱文一
CBD是“中央商务区”(Central Business District)的英语缩写。其形象一般为扎堆在一起的摩天楼群及其垂直向上的城市天际线。2014年,深圳城市设计促进中心举办了深圳湾超级城市设计国际竞赛。竞赛选址深圳湾CBD核心区,要求在110公顷的土地上,修建500万m2的建筑。容积率为4.27。这是典型的CBD指标。地段地处深圳湾中部,交通发达,风景秀丽,滨水宜人。这为探索CBD设计的新类型和新形象提供了难得的机遇和平台。
朱文一工作室提交的“超级方体”(Super Cube)设计方案以其巧妙的构思、匹配的设计和独特的形态获得三等奖(图1),从匹配地段、小街坊式、滨水空间、扁平形象等方面来展示方案的特点。
首先是匹配地段现状及其上位规划要求(图2)。超级方体方案在遵循CBD地块规划的基础上,将设计范围扩展至深圳湾海上,以此体现地段的滨海特征(图3)。另一方面,方案特别尊重现状,统筹考虑地段北面已经建成的楼盘住区以及周边现状建筑。在延续现状和规划格网前提下,方案加密格网,增加海上格网;同时叠加45度方向干道,以突显CBD核心区的边界和识别性(图4)。即使在普通的地图模式图中,超级方体方案依然具有显著的识别性(图5)。
其次是探索CBD核心区小街坊空间模式。超级方体方案摒弃通常的大马路轴线对称布局,采用均布30m宽度小道路的方式,形成去中心化的街区空间网格,以激活整体街区的活力。由此形成的小街坊南北长约70m,东西宽约50m,高约50m,符合CBD市场经济对应的空间特征,所谓小街坊、大价值。小街坊可以满足金融、媒体、科技等多种功能的办公需求(图6、图7)。同时,通过骑楼等方式实现人车分层(图8);通过屋顶公共化设计形成既具活力又绿色的小街坊屋顶(图9)。
再次是探索CBD滨海空间新景观。超级方体方案将寸土寸金的滨海空间设计为公共空间,设想展示中国广大地域丰富多彩的戏曲文化(图10)。斜向升起的V型广场一方面创造了鸟瞰城市的奇妙观景平台,同时也展示了海滨大道上的独特景象(图11)。从蛇口北望深圳湾,可以看到独一无二的滨海城市轮廓线(图12)。
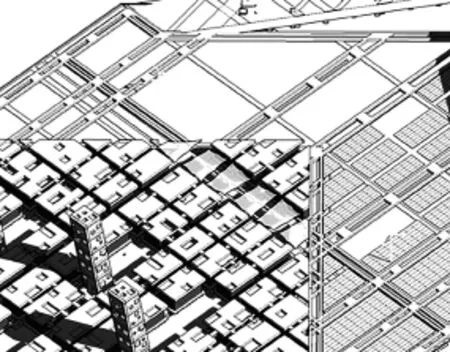
图1 / Figure 1超级方体整体形象 / The Image of the Super Cube
最后是尝试万能视角下的扁平化设计。在数字化生存时代,万能视角下的建筑体验已经不可回避。笔者提出的万能视角建筑学,即万能视角优先的建筑学,阐述了数字时代建筑设计理念[1-2]。超级方体方案充分体现了万能视角建筑学所表述的理念和方法,不仅创造了凡人视角的城市地标,同时也探索了在万能视角下具有强烈识别性的城市地标形象(图13)。后者为数字化生存时代智能手机小屏上体验城市地标提供了实验性的样本(图14)。
此外,未来的CBD应该体现新能源的可能性。超级方体方案结合大面积太阳能光伏板设计,探索了城市与基础设施相结合的空间模式。
Super Cube: A Proposal for the Shenzhen Bay Super City International Competition, Shenzhen, China
ZHU Wenyi
Facts
Location: Shenzhen, China
Time: January-May, 2014
Host: Urban Planning and Land and Resources
Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
Organizer: Shenzhen Center for Design
Program: Shenzhen Bay Super City International Competition Aera: 5,300,000 m2
Design Team
Chief Architect: ZHU Wenyi
Team Member: FU Junsheng, XIA Ji, LIANG Yingya,LIU Zhiqiang, LI Jintai, HAO Tian CBD is the abbreviation of the Central Business District. Its image is generally a group of skyscrapers and the vertical and upward skyline of the city. In 2014, the Urban Planning and Land and
Resources Commission of Shenzhen Municipality hosted the Shenzhen Bay Super City International Competition. The future super city will be in the core area of Shenzhen Bay CBD and requires the construction of 5 million m2of buildings on 110 hectares of land. The FAR is 4.27. This is a typical CBD. The site is located in the central part of Shenzhen Bay, with developed traffic, beautiful scenery and pleasant waterfront. This provides a rare opportunity and platform for exploring the new typology and new image of CBD design.
The “Super Cube” design proposal submitted by Zhu Wenyi Atelier won the third prize for its clever idea, matching design, and unique form (Figure 1). The proposal can be demonstrated in terms of matching locations, small blocks, waterfront spaces, and fl at image.
The first is matching the status quo of the lot and its planning requirements (Figure 2). Taking consideration of the CBD plan guidelines, the Super Cube scheme extends the design area to the Shenzhen Bay Sea to re fl ect the coastal features of the site (Figure 3). On the other hand, the scheme particularly respects the status quo and considers
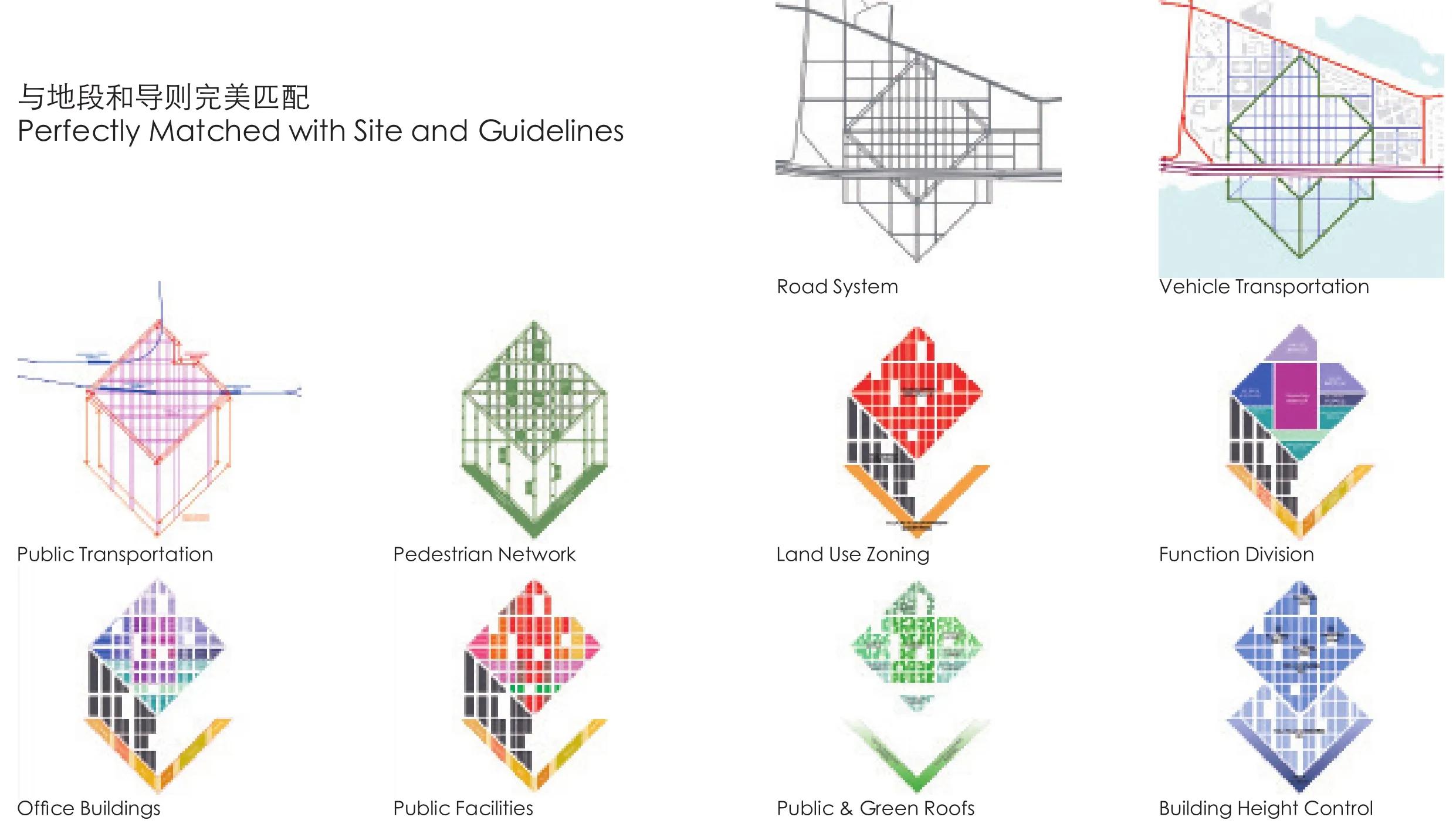
图2 / Figure 2方案匹配地段及其上位规划 / Matching the Planning Guidelines
the existing real estate residential districts and the surrounding existing buildings on the north side of the site. Based on the status quo and planning grid, the scheme doubled the grid and increases the maritime grid; at the same time it superimposes the 45-degree direction main road to highlight the boundary and the recognition of the core area of the CBD (Figure 4). Even in the map with normal mode, the Super Cube scheme still has been recognized by its signi fi cant image (Figure 5).
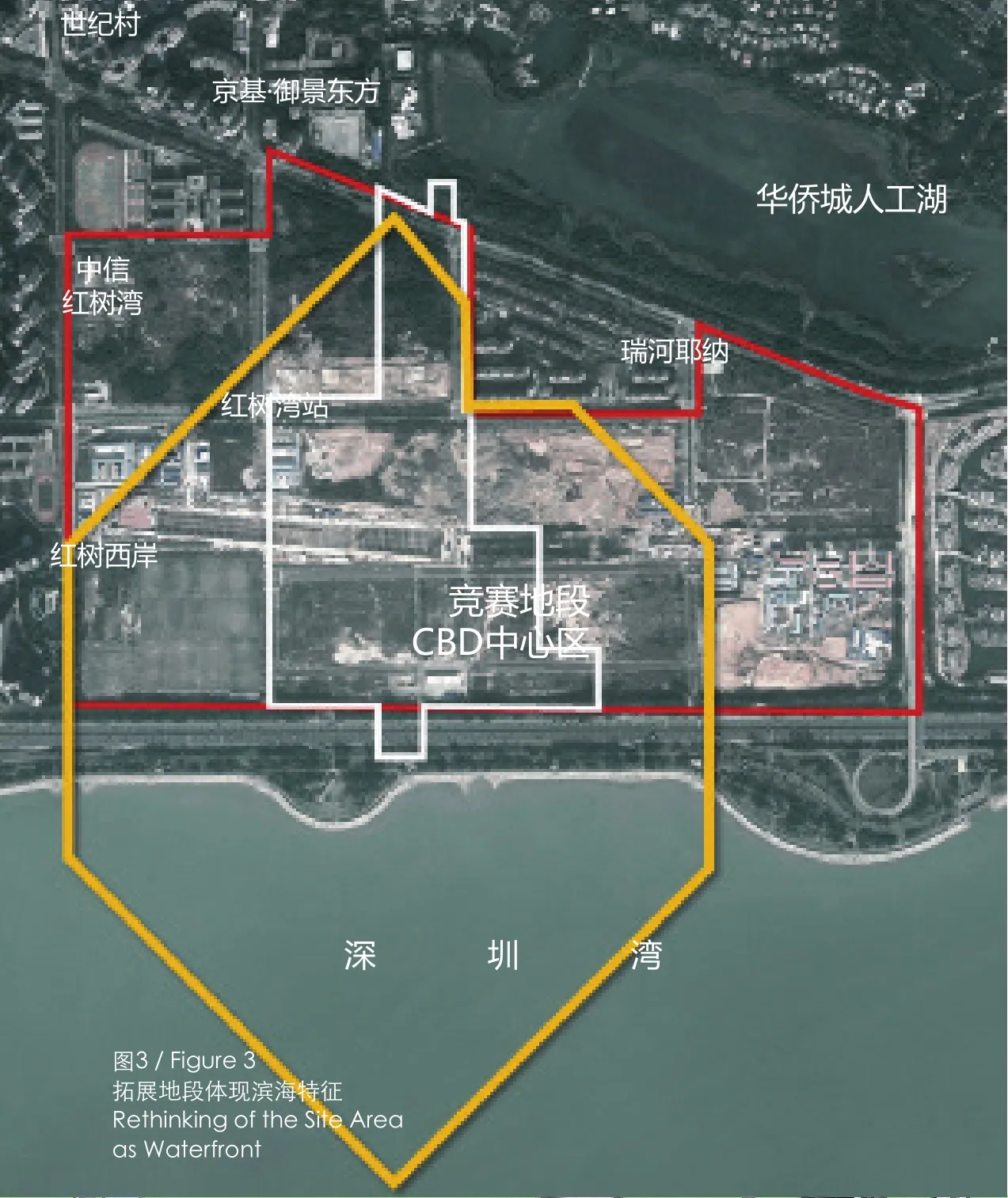
图3 / Figure 3拓展地段体现滨海特征Rethinking of the Site Area as Waterfront
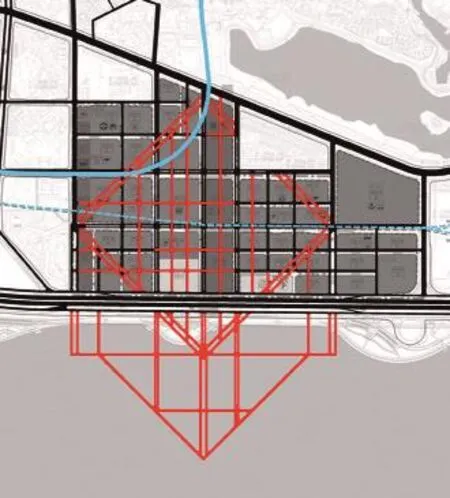
图4 / Figure 4CBD核心区新边界及其识别性New Eage for CBD Core Area and Its Recognition
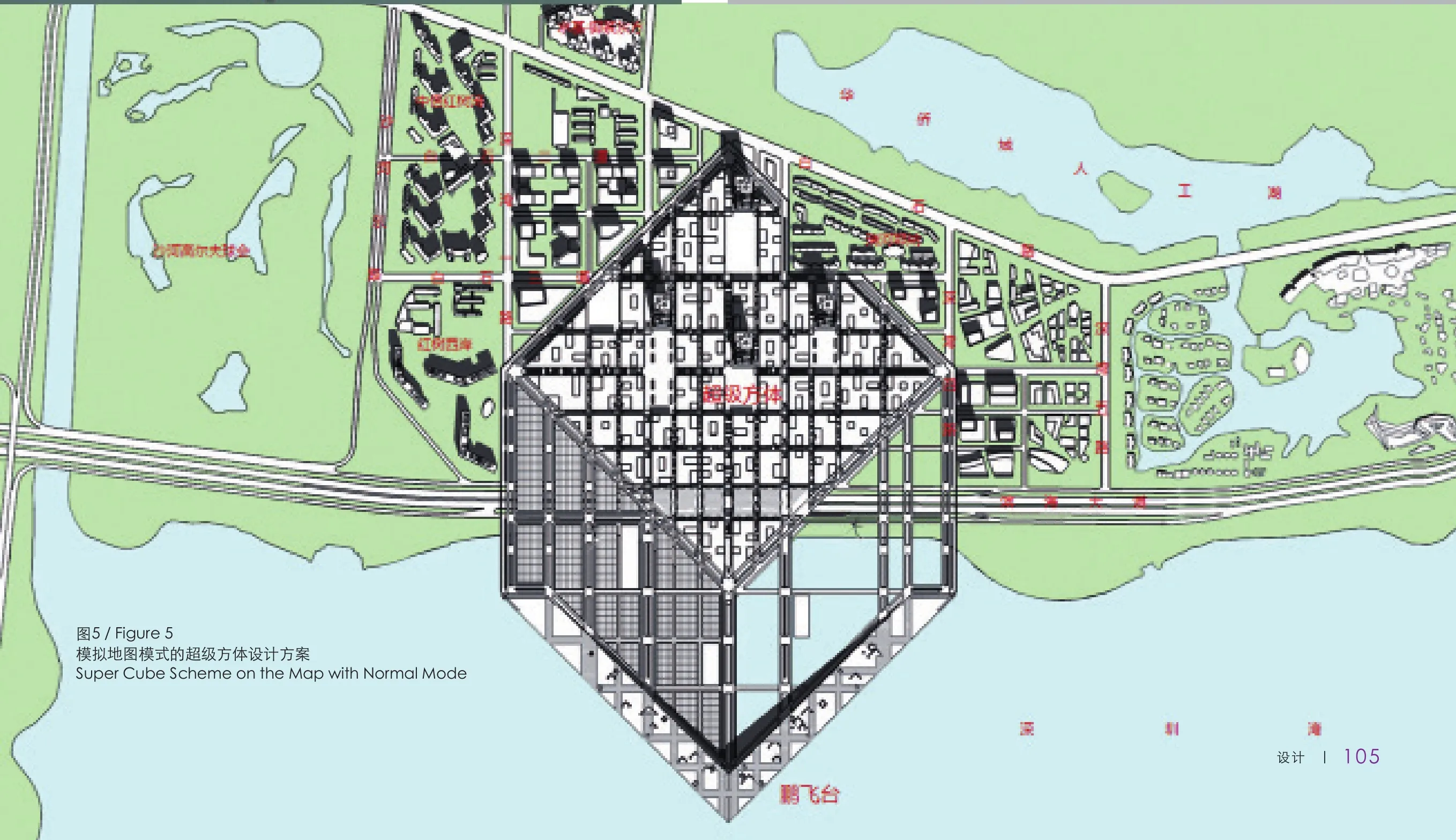
图5 / Figure 5模拟地图模式的超级方体设计方案Super Cube Scheme on the Map with Normal Mode
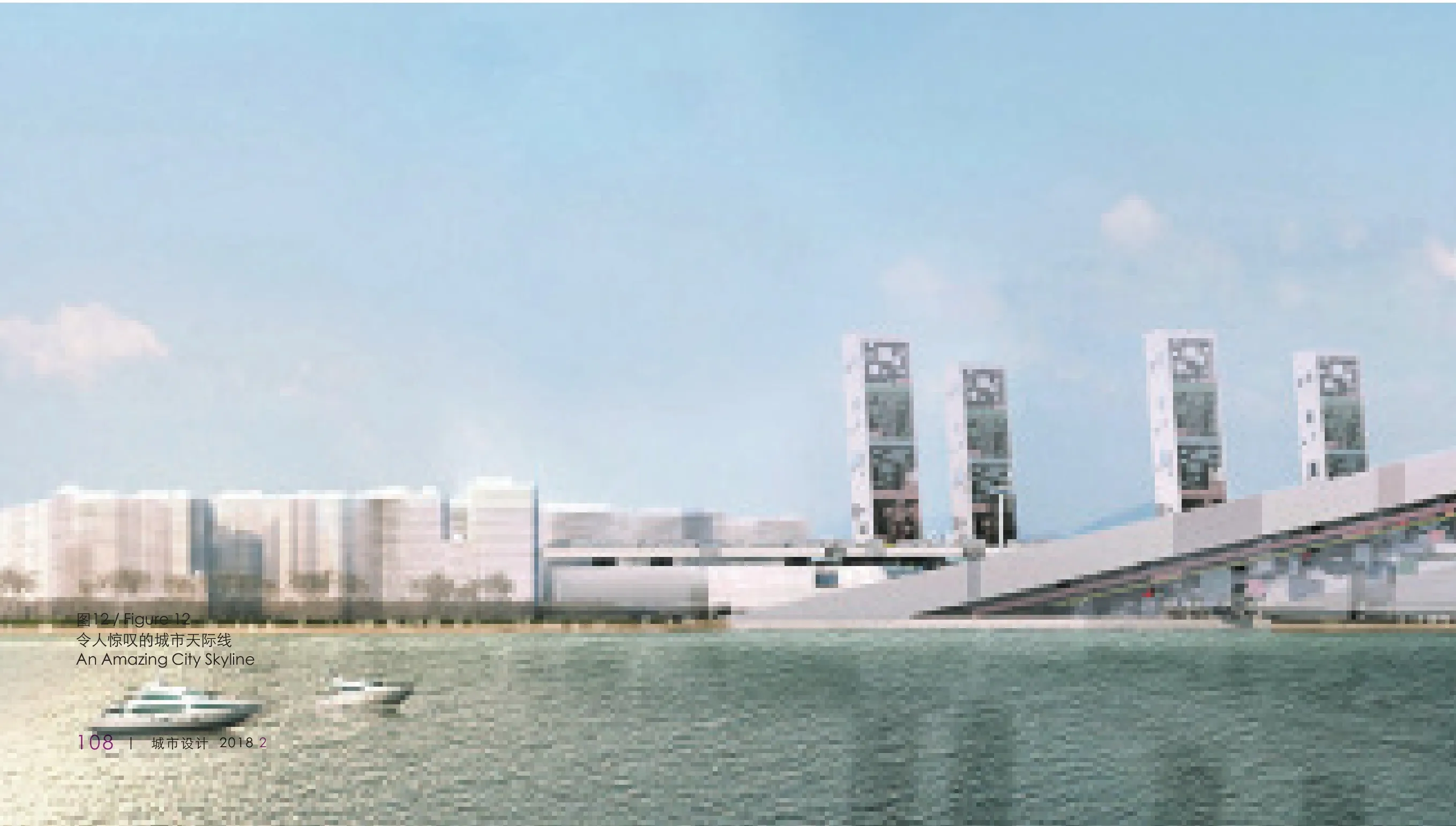

图12 / Figure 12令人惊叹的城市天际线An Amazing City Skyline
Followed by exploring the small blocks model of the CBD core area. Instead of symmetrical layout of the axis of the Wide Road, the Super Cube scheme chooses a 30 m wide “Narrow” road for creating a decentralized street space grid and activating the vitality of the overall block. The size of each small block is approximately 70m long from north to south, 50 m wide from east to west, and approximately 50 m high, conforming to the land use of the CBD’s market, and the so-called small blocks and large values. Small blocks can meet the office spaces of financial, media, technology and other functions (Figure 6, Figure 7). At the same time, people and vehicles are stratified by means such as Qilou Buildings, a modern building with opened-colonnaded fi rst fl oor in south China cities(Figure 8); through designing the public roof, a vibrant and green roof on the small block is formed(Figure 9).
The third is to explore the new landscape of the coastal space of the CBD. The Super Cube Scheme designed the coastal space with high cost of land as a public space, envisaging the display of a variety of traditional Chinese opera cultures (Figure 10). The diagonally raised V-shaped plaza on the one hand creates an amazing view of the city from a bird’s-eye view and also shows a unique scenery on the seafront boulevard (Figure 11). Looking northward at Shenzhen Bay from Shekou District, you can see the unique coastal city skyline (Figure 12).
The fourth is to try a flat design from God’s eye view. In the Being Digital Era, a new way of building experience God’s Eye View Architecture proposed by ZHU Wenyi[1-2]. The Super Cube Scheme fully embodies the ideas and methods expressed by God’s Eye View Architecture, not only creating a Man’s Eye View city landmark, but also exploring the city landmark that are strongly discernible from God’s eye view (Figure 13). The latter provides an experience of urban landmarks on the smartphone’s small screen in the Being Digital Era (Figure 14).In addition, the future of CBD should have the possibility of new energy. A large-area solar photovoltaic panel is designed as one of the most important part of the Super Cube Scheme. It explores an urbanism with infrastructural facilities.
